Stop-task Scheduler
Stop 스케줄러는 매우 심플하다. 어떠한 스케줄러보다 우선 순위가 더 높아 preemption되지 않으며 다른 cpu로 migration도 허용하지 않는다. 따라서 모든 요청에 대해 대부분 거절하거나 아무런 일도 하지 않는다. 오직 stop 태스크 수 및 런타임 계산만 허용한다.
용도
- active 로드 밸런싱
- 로드 밸런싱을 수행 시 특정 cpu의 태스크를 pull 마이그레이션 해오는데 특정 cpu에서 동작 중인 current 태스크는 pull 마이그레이션을 할 수 없다. 이러한 경우 IPI를 통해 stop 스케줄러를 사용하는 cpu stopper 스레드를 깨워 동작 중이었던 태스크를 push 마이그레이션하게 할 수 있다.
- cpu offline
- cpu를 off하기 위해 런큐에서 동작 중인 태스크를 migration하기 위해서도 사용되고 있다.
select_task_rq_stop()
kernel/sched/stop_task.c
static int
select_task_rq_stop(struct task_struct *p, int cpu, int sd_flag, int flags)
{
return task_cpu(p); /* stop tasks as never migrate */
}
migration을 허용하지 않는다.
check_preempt_curr_stop()
kernel/sched/stop_task.c
static void
check_preempt_curr_stop(struct rq *rq, struct task_struct *p, int flags)
{
/* we're never preempted */
}
수행 중인 stop 태스크의 preemption을 허용하지 않으므로 preemption 체크를 할 필요없다.
yield_task_stop()
kernel/sched/stop_task.c
static void yield_task_stop(struct rq *rq)
{
BUG(); /* the stop task should never yield, its pointless. */
}
수행 중인 stop 태스크의 preemption을 허용하지 않는다.
enqueue_task_stop()
kernel/sched/stop_task.c
static void
enqueue_task_stop(struct rq *rq, struct task_struct *p, int flags)
{
add_nr_running(rq, 1);
}
런큐에 동작중인 엔티티의 수를 증가시킨다.
dequeue_task_stop()
static void
dequeue_task_stop(struct rq *rq, struct task_struct *p, int flags)
{
sub_nr_running(rq, 1);
}
런큐에 동작중인 엔티티의 수를 감소시킨다.
task_tick_stop()
kernel/sched/stop_task.c
static void task_tick_stop(struct rq *rq, struct task_struct *curr, int queued)
{
}
task 틱마다 아무런 동작도 하지 않는다.
update_curr_stop()
kernel/sched/stop_task.c
static void update_curr_stop(struct rq *rq)
{
}
아무런 동작도 하지 않는다.
switched_to_stop()
kernel/sched/stop_task.c
static void switched_to_stop(struct rq *rq, struct task_struct *p)
{
BUG(); /* its impossible to change to this class */
}
설계상 이 stop 태스크로의 스위칭은 불가능하다.
prio_changed_stop()
kernel/sched/stop_task.c
static void
prio_changed_stop(struct rq *rq, struct task_struct *p, int oldprio)
{
BUG(); /* how!?, what priority? */
}
stop 태스크 자체가 최고 높은 우선 순위의 태스크로 별도로 수치를 변경할 수 없다.
get_rr_interval_stop()
kernel/sched/stop_task.c
static unsigned int
get_rr_interval_stop(struct rq *rq, struct task_struct *task)
{
return 0;
}
stop 태스크가 스스로 yield하기 전까지 계속 수행되어야 하므로 stop 스케줄러는 인터벌을 사용하지 않는다.
put_prev_task_stop()
kernel/sched/stop_task.c
static void put_prev_task_stop(struct rq *rq, struct task_struct *prev)
{
struct task_struct *curr = rq->curr;
u64 delta_exec;
delta_exec = rq_clock_task(rq) - curr->se.exec_start;
if (unlikely((s64)delta_exec < 0))
delta_exec = 0;
schedstat_set(curr->se.statistics.exec_max,
max(curr->se.statistics.exec_max, delta_exec));
curr->se.sum_exec_runtime += delta_exec;
account_group_exec_runtime(curr, delta_exec);
curr->se.exec_start = rq_clock_task(rq);
cpuacct_charge(curr, delta_exec);
}
이전 stop 태스크의 사용이 완료되었으므로 관련 실행 시각을 갱신한다.
- 코드 라인 6~8에서 stop 태스크가 실행한 delta 시간을 얻어온다.
- 코드 라인 13에서 stop 태스크의 총 실행 시간을 갱신한다.
- 코드 라인 14에서 스레드그룹의 총 실행시간을 갱신한다.
- 코드 라인 16에서 stop 태스크의 시작 실행 시각을 다시 현재 시각으로 설정한다.
- 코드 라인 17에서 stop 태스크의 cpu accounting 그룹용 총 실행 시간을 갱신한다.
Stop-task 스케줄러 OPS
kernel/sched/stop_task.c
/*
* Simple, special scheduling class for the per-CPU stop tasks:
*/
const struct sched_class stop_sched_class = {
.next = &dl_sched_class,
.enqueue_task = enqueue_task_stop,
.dequeue_task = dequeue_task_stop,
.yield_task = yield_task_stop,
.check_preempt_curr = check_preempt_curr_stop,
.pick_next_task = pick_next_task_stop,
.put_prev_task = put_prev_task_stop,
#ifdef CONFIG_SMP
.select_task_rq = select_task_rq_stop,
#endif
.set_curr_task = set_curr_task_stop,
.task_tick = task_tick_stop,
.get_rr_interval = get_rr_interval_stop,
.prio_changed = prio_changed_stop,
.switched_to = switched_to_stop,
.update_curr = update_curr_stop,
};
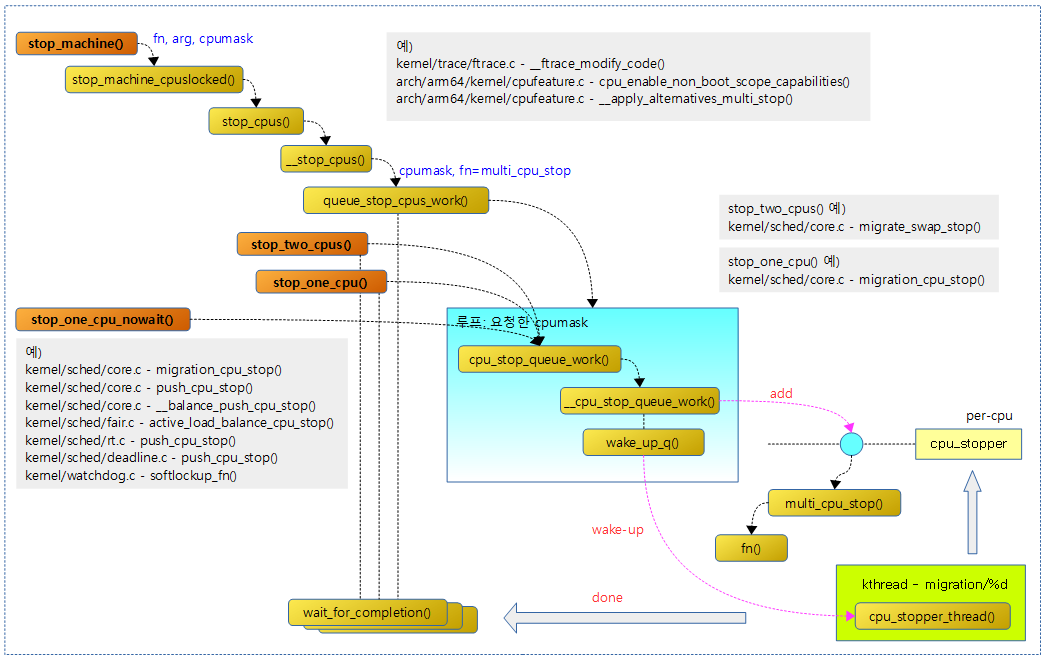
Stop-Machine의 Stopper
stop-machine 함수는 리눅스 커널에서 제공하는 API 중 하나로, 멀티코어 시스템에서 모든 프로세서를 중지시키고 특정 함수를 하나의 프로세서에서 실행할 수 있게 한다. 이 함수는 전체 cpu의 정지 또는 일부 cpu의 정지가 필요한 작업에 사용한다.
stop-machine 함수의 사용은 신중히 고려되어야 하며, 잘못 사용하면 시스템 성능에 큰 영향을 미칠 수 있으며 시스템 불안정성을 초래할 수 있다. 일반적으로 시스템이 정상적으로 작동할 때 수행할 수 없는 중요한 시스템 작업에만 사용한다.
리눅스 스케줄러에서 다음과 같은 경우에 현재 cpu의 런큐에서 동작하는 current 태스크를 옮겨야 하는 경우가 발생한다. 이 때 가장 우선 순위가 높은 stop 스케줄러에 stopper 스레드를 동작시켜 action을 취할 함수들을 호출한다.
- cpu를 offline으로 변경함에 따른 task들의 migration
- 로드 밸런스에 의해 현재 동작 중인 current 태스크를 다른 cpu의 런큐로 옮겨야 하는 경우
다음 그림은 stop-machine 주요 함수들의 처리 과정을 보여준다.
참고
- Scheduler -1- (Basic) | 문c
- Scheduler -2- (Global Cpu Load) | 문c
- Scheduler -3- (PELT) | 문c
- Scheduler -4- (Group Scheduling) | 문c
- Scheduler -5- (Scheduler Core) | 문c
- Scheduler -6- (CFS Scheduler) | 문c
- Scheduler -7- (Preemption & Context Switch) | 문c
- Scheduler -8- (CFS Bandwidth) | 문c
- Scheduler -9- (RT Scheduler) | 문c
- Scheduler -10- (Deadline Scheduler) | 문c
- Scheduler -11- (Stop Scheduler) | 문c – 현재 글
- Scheduler -12- (Idle Scheduler) | 문c
- Scheduler -13- (Scheduling Domain 1) | 문c
- Scheduler -14- (Scheduling Domain 2) | 문c
- Scheduler -15- (Load Balance 1) | 문c
- Scheduler -16- (Load Balance 2) | 문c
- Scheduler -17- (Load Balance 3 NUMA) | 문c
- Scheduler -18- (Load Balance 4 EAS) | 문c
- Scheduler -19- (초기화) | 문c
- PID 관리 | 문c
- do_fork() | 문c
- cpu_startup_entry() | 문c
- 런큐 로드 평균(cpu_load[]) – v4.0 | 문c
- PELT(Per-Entity Load Tracking) – v4.0 | 문c