<kernel v5.0>
Migration
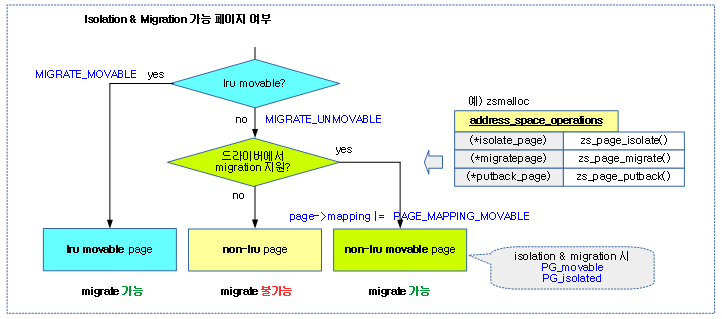
non-movable 페이지의 migration 지원
커널은 전통적으로 movable LRU 페이지에 대해서만 migration을 지원해왔다. 최근 임베디드 시스템인 WbOS, android 등에서 많은 수의 non-movable 페이지들을 사용하여 왔다. 이러한 non-movable 페이지들이 많이 사용되면서 high order 할당에 문제가 생기는 리포트들이 보고되어왔다. 따라서 이러한 문제점들을 제거하기 위해 몇개의 노력을 해왔었지만 (예를 들면 압축 알고리즘 개선, slub fallback 시 0 order 할당, reserved 메모리, vmalloc, …) 여전히 non-movable 페이지들이 많이 사용되면 장기적으로는 효과가 없었다.
이 번에는 non-movable 페이지들을 movable이 가능하도록 지원하기 위해 아래 패치를 통해 드라이버(zram, GPU memory, …)들에 (*isolate_page), (*migratepage) 등의 후크 함수를 구현할 수 있도록 하였다. 이러한 후크 함수가 지원되는 드라이버의 경우 커널이 non-movable로 분류할지라도 이러한 드라이버를 통해서 migration 할 수 있게 하였다.
다음 그림은 페이지 유형별 isolation 및 migration 지원 여부를 보여준다.
migrate_pages()
mm/migrate.c
/* * migrate_pages - migrate the pages specified in a list, to the free pages * supplied as the target for the page migration * * @from: The list of pages to be migrated. * @get_new_page: The function used to allocate free pages to be used * as the target of the page migration. * @put_new_page: The function used to free target pages if migration * fails, or NULL if no special handling is necessary. * @private: Private data to be passed on to get_new_page() * @mode: The migration mode that specifies the constraints for * page migration, if any. * @reason: The reason for page migration. * * The function returns after 10 attempts or if no pages are movable any more * because the list has become empty or no retryable pages exist any more. * The caller should call putback_movable_pages() to return pages to the LRU * or free list only if ret != 0. * * Returns the number of pages that were not migrated, or an error code. */
int migrate_pages(struct list_head *from, new_page_t get_new_page,
free_page_t put_new_page, unsigned long private,
enum migrate_mode mode, int reason)
{
int retry = 1;
int nr_failed = 0;
int nr_succeeded = 0;
int pass = 0;
struct page *page;
struct page *page2;
int swapwrite = current->flags & PF_SWAPWRITE;
int rc;
if (!swapwrite)
current->flags |= PF_SWAPWRITE;
for(pass = 0; pass < 10 && retry; pass++) {
retry = 0;
list_for_each_entry_safe(page, page2, from, lru) {
retry:
cond_resched();
if (PageHuge(page))
rc = unmap_and_move_huge_page(get_new_page,
put_new_page, private, page,
pass > 2, mode, reason);
else
rc = unmap_and_move(get_new_page, put_new_page,
private, page, pass > 2, mode,
reason);
switch(rc) {
case -ENOMEM:
/*
* THP migration might be unsupported or the
* allocation could've failed so we should
* retry on the same page with the THP split
* to base pages.
*
* Head page is retried immediately and tail
* pages are added to the tail of the list so
* we encounter them after the rest of the list
* is processed.
*/
if (PageTransHuge(page) && !PageHuge(page)) {
lock_page(page);
rc = split_huge_page_to_list(page, from);
unlock_page(page);
if (!rc) {
list_safe_reset_next(page, page2, lru);
goto retry;
}
}
nr_failed++;
goto out;
case -EAGAIN:
retry++;
break;
case MIGRATEPAGE_SUCCESS:
nr_succeeded++;
break;
default:
/*
* Permanent failure (-EBUSY, -ENOSYS, etc.):
* unlike -EAGAIN case, the failed page is
* removed from migration page list and not
* retried in the next outer loop.
*/
nr_failed++;
break;
}
}
}
nr_failed += retry;
rc = nr_failed;
out:
if (nr_succeeded)
count_vm_events(PGMIGRATE_SUCCESS, nr_succeeded);
if (nr_failed)
count_vm_events(PGMIGRATE_FAIL, nr_failed);
trace_mm_migrate_pages(nr_succeeded, nr_failed, mode, reason);
if (!swapwrite)
current->flags &= ~PF_SWAPWRITE;
return rc;
}
최대 10번을 시도하여 migrate 스캐너가 isolation한 페이지를 unmap 한 후 free 스캐너가 isolation한 free 페이지로 migration한다.
- 코드 라인 11~15에서 현재 태스크가 swap write를 지원하지 않는 경우 migration을 하는 동안만 swap write를 지원하도록 플래그를 추가한다.
- 코드 라인 17~18에서 최대 반복 횟수를 10번으로 제한을 한다.
- 코드 라인 20에서 인수로 전달받은 @from 리스트의 페이지들 만큼 루프를 돈다.
- 코드 라인 24~31에서 huge 페이지 또는 일반 페이지의 unmap과 move를 수행한다. 10번 시도 중 4번째 시도 부터는 force 값을 1로 하여 full sync 모드에서 writeback 페이지들도 강제로 writeback이 끝날 때까지 대기하도록 강제한다.
- 코드 라인 33~56에서 migration 결과가 메모리 부족인 경우 처리를 중단한다. 만일 TransHuge 페이지인 경우에 한해 페이지를 split 한 후 retry한다.
- 코드 라인 57~59에서 migration을 다시 시도해야 하는 경우이다.
- 코드 라인 60~62에서 migration 결과가 성공한 경우이다.
- 코드 라인 63~72에서 migration 결과가 실패한 경우이다.
- 코드 라인 77에서 10번을 시도하고 완료하였거나 메모리 부족으로 처리를 완료하고자 도달하는 out 레이블이다.
- 코드 라인 84~85에서 현재 태스크에 설정해둔 swap writing 을 원래 상태로 돌려놓는다.
일반 페이지의 Migration
unmap_and_move()
mm/migrate.c -1/2-
/* * Obtain the lock on page, remove all ptes and migrate the page * to the newly allocated page in newpage. */
static ICE_noinline int unmap_and_move(new_page_t get_new_page,
free_page_t put_new_page,
unsigned long private, struct page *page,
int force, enum migrate_mode mode,
enum migrate_reason reason)
{
int rc = MIGRATEPAGE_SUCCESS;
struct page *newpage;
if (!thp_migration_supported() && PageTransHuge(page))
return -ENOMEM;
newpage = get_new_page(page, private);
if (!newpage)
return -ENOMEM;
if (page_count(page) == 1) {
/* page was freed from under us. So we are done. */
ClearPageActive(page);
ClearPageUnevictable(page);
if (unlikely(__PageMovable(page))) {
lock_page(page);
if (!PageMovable(page))
__ClearPageIsolated(page);
unlock_page(page);
}
if (put_new_page)
put_new_page(newpage, private);
else
put_page(newpage);
goto out;
}
rc = __unmap_and_move(page, newpage, force, mode);
if (rc == MIGRATEPAGE_SUCCESS)
set_page_owner_migrate_reason(newpage, reason);
migrate 스캐너가 isolation한 페이지를 unmap한 후 free 스캐너가 isolation한 free 페이지로 migration한다.
- 코드 라인 10~11에서 thp(Transparent Huge Page) migration이 지원하지 않을 때 thp 에 대해 -ENOMEM을 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 13~15에서 @get_new_page 함수를 통해 free 페이지를 가져온다.
- compaction 시에는 @get_new_page에 compaction_alloc() 함수를 사용하여 free 스캐너가 관리하는 리스트에서 선두의 free 페이지를 가져온다.
- 코드 라인 17~32에서 page가 이미 free 된 경우 페이지의 active 및 unevictable 플래그를 클리어한다.
- 코드 라인 21~26에서 낮은 확률로 non-lru movable 페이지이지만 드라이버에 (*isolate_page) 후크 함수의 구현이 없는 경우 isolated 플래그를 클리어한다.
- 코드 라인 27~31에서 @put_new_page 함수가 주어진 경우 이 함수를 통해 free 페이지를 다시 되돌려 놓고, 지정되지 않은 경우 페이지 를 버디 시스템으로 돌려 놓는다.
- compaction 시에는 @put_new_page에 compaction_free() 함수를 사용하여 free 스캐너가 관리하는 리스트로 되돌려 놓는다.
- 코드 라인 34~36에서 매핑을 푼 후 page를 newpage로 migration 한다. migration이 성공한 경우 디버그를 위해 페이지 owner에 reason을 기록해둔다.
mm/migrate.c -2/2-
out:
if (rc != -EAGAIN) {
/*
* A page that has been migrated has all references
* removed and will be freed. A page that has not been
* migrated will have kepts its references and be
* restored.
*/
list_del(&page->lru);
/*
* Compaction can migrate also non-LRU pages which are
* not accounted to NR_ISOLATED_*. They can be recognized
* as __PageMovable
*/
if (likely(!__PageMovable(page)))
mod_node_page_state(page_pgdat(page), NR_ISOLATED_ANON +
page_is_file_cache(page), -hpage_nr_pages(page));
}
/*
* If migration is successful, releases reference grabbed during
* isolation. Otherwise, restore the page to right list unless
* we want to retry.
*/
if (rc == MIGRATEPAGE_SUCCESS) {
put_page(page);
if (reason == MR_MEMORY_FAILURE) {
/*
* Set PG_HWPoison on just freed page
* intentionally. Although it's rather weird,
* it's how HWPoison flag works at the moment.
*/
if (set_hwpoison_free_buddy_page(page))
num_poisoned_pages_inc();
}
} else {
if (rc != -EAGAIN) {
if (likely(!__PageMovable(page))) {
putback_lru_page(page);
goto put_new;
}
lock_page(page);
if (PageMovable(page))
putback_movable_page(page);
else
__ClearPageIsolated(page);
unlock_page(page);
put_page(page);
}
put_new:
if (put_new_page)
put_new_page(newpage, private);
else
put_page(newpage);
}
return rc;
}
- 코드 라인 1~19에서 out: 레이블이다. migration 결과가 -EAGAIN이 아닌 경우 페이지를 LRU 리스트에서 분리한다. 그리고 높은 확률로 non-lru movable 페이지가 아닌 경우 nr_isolated_anon 또는 nr_isolated_file 카운터를 감소시킨다.
- 코드 라인 26~36에서 migrate가 성공한 경우 페이지의 참조 카운터를 감소시켜 버디 시스템에 돌려보낸다.
- 코드 라인 37~42에서 migrate 결과가 -EAGAIN인 경우 movable 매핑된 페이지가 아니면 LRU 리스트에 되돌려 놓는다.
- 코드 라인 44~50에서 migrate 실패한 경우의 처리이다. non-lru movable free 페이지에 대해서는 파일 시스템의 (*putback_page) 후크 함수를 통해 원 위치로 돌려놓고, lru movable인 경우 원래 있었던 위치인 LRU 리스트로 되돌린다.
- 코드 라인 52~56에서 put_new: 레이블이다. @put_new_page가 주어진 경우 해당 함수를 통해 free 페이지를 다시 되돌려 놓는다. 그렇지 않은 경우 버디 시스템으로 되돌려 놓는다.
__unmap_and_move()
mm/migrate.c -1/3-
static int __unmap_and_move(struct page *page, struct page *newpage,
int force, enum migrate_mode mode)
{
int rc = -EAGAIN;
int page_was_mapped = 0;
struct anon_vma *anon_vma = NULL;
bool is_lru = !__PageMovable(page);
if (!trylock_page(page)) {
if (!force || mode == MIGRATE_ASYNC)
goto out;
/*
* It's not safe for direct compaction to call lock_page.
* For example, during page readahead pages are added locked
* to the LRU. Later, when the IO completes the pages are
* marked uptodate and unlocked. However, the queueing
* could be merging multiple pages for one bio (e.g.
* mpage_readpages). If an allocation happens for the
* second or third page, the process can end up locking
* the same page twice and deadlocking. Rather than
* trying to be clever about what pages can be locked,
* avoid the use of lock_page for direct compaction
* altogether.
*/
if (current->flags & PF_MEMALLOC)
goto out;
lock_page(page);
}
if (PageWriteback(page)) {
/*
* Only in the case of a full synchronous migration is it
* necessary to wait for PageWriteback. In the async case,
* the retry loop is too short and in the sync-light case,
* the overhead of stalling is too much
*/
switch (mode) {
case MIGRATE_SYNC:
case MIGRATE_SYNC_NO_COPY:
break;
default:
rc = -EBUSY;
goto out_unlock;
}
if (!force)
goto out_unlock;
wait_on_page_writeback(page);
}
page를 unmapping 하고 newpage에 migration한다.
- 코드 라인 7에서 lru movable 페이지 여부를 is_lru에 담는다.
- true=lru movable페이지
- false=non-lru movable 페이지
- 코드 라인 9~30에서 에서 page에 대한 lock을 획득한다. 만일 락 획득 시도가 실패한 경우 @force가 0이거나 async migrate 모드인 경우 -EAGAIN 에러로 함수를 종료한다. 그리고 pfmemalloc상황에서 호출된 경우 migration이 이중으로 동작할 필요 없다.
- 코드 라인 32~50에서 page가 파일시스템에 writeback 중인 경우 sync 또는 sync_no_copy인 경우 -EAGAIN 에러를 반환한다. 단 @force가 강제된 경우 writeback이 완료될 때까지 대기한다. 그 외의 async 및 sync_light 모드의 경우 -EBUSY 에러를 반환한다.
mm/migrate.c -2/3-
. /*
* By try_to_unmap(), page->mapcount goes down to 0 here. In this case,
* we cannot notice that anon_vma is freed while we migrates a page.
* This get_anon_vma() delays freeing anon_vma pointer until the end
* of migration. File cache pages are no problem because of page_lock()
* File Caches may use write_page() or lock_page() in migration, then,
* just care Anon page here.
*
* Only page_get_anon_vma() understands the subtleties of
* getting a hold on an anon_vma from outside one of its mms.
* But if we cannot get anon_vma, then we won't need it anyway,
* because that implies that the anon page is no longer mapped
* (and cannot be remapped so long as we hold the page lock).
*/
if (PageAnon(page) && !PageKsm(page))
anon_vma = page_get_anon_vma(page);
/*
* Block others from accessing the new page when we get around to
* establishing additional references. We are usually the only one
* holding a reference to newpage at this point. We used to have a BUG
* here if trylock_page(newpage) fails, but would like to allow for
* cases where there might be a race with the previous use of newpage.
* This is much like races on refcount of oldpage: just don't BUG().
*/
if (unlikely(!trylock_page(newpage)))
goto out_unlock;
if (unlikely(!is_lru)) {
rc = move_to_new_page(newpage, page, mode);
goto out_unlock_both;
}
/*
* Corner case handling:
* 1. When a new swap-cache page is read into, it is added to the LRU
* and treated as swapcache but it has no rmap yet.
* Calling try_to_unmap() against a page->mapping==NULL page will
* trigger a BUG. So handle it here.
* 2. An orphaned page (see truncate_complete_page) might have
* fs-private metadata. The page can be picked up due to memory
* offlining. Everywhere else except page reclaim, the page is
* invisible to the vm, so the page can not be migrated. So try to
* free the metadata, so the page can be freed.
*/
if (!page->mapping) {
VM_BUG_ON_PAGE(PageAnon(page), page);
if (page_has_private(page)) {
try_to_free_buffers(page);
goto out_unlock_both;
}
} else if (page_mapped(page)) {
/* Establish migration ptes */
VM_BUG_ON_PAGE(PageAnon(page) && !PageKsm(page) && !anon_vma,
page);
try_to_unmap(page,
TTU_MIGRATION|TTU_IGNORE_MLOCK|TTU_IGNORE_ACCESS);
page_was_mapped = 1;
}
if (!page_mapped(page))
rc = move_to_new_page(newpage, page, mode);
if (page_was_mapped)
remove_migration_ptes(page,
rc == MIGRATEPAGE_SUCCESS ? newpage : page, false);
- 코드 라인 15~16에서 KSM(Kernel Shared Memory)을 제외한 anon 페이지인 경우anon_vma를구해온다.
- 코드 라인 29~32에서 낮은 확률로 non-lru movable 페이지인 경우 페이지를 new 페이지로 옮기고 매핑 제거 루틴을 수행할 필요가 없으므로 곧장 out_unlock_both: 레이블로 이동한다.
- 코드 라인 46~59에서 다음은 일반적이지 않은 코너 케이스에 해당하는 처리이다. 만일 anon 페이지이면서 별도의 버퍼를 사용하는(예: ksm) 경우 free 버퍼를 제거하고 함수를 빠져나간다. 그 외의 경우 이 페이지로 매핑된 모든 페이지 테이블에서 매핑을 해제하게 한다.
- 코드 라인 61~62에서 페이지 테이블에 매핑되지 않은 페이지인 경우 페이지를 new 페이지로 옮긴 후 매핑 제거 루틴을 수행할 필요 없이 곧바로 out_unlock_both 레이블로 이동한다.
- 코드 라인 64~66에서 페이지가 매핑되었었던 경우 기존 페이지에 연결된 모든 매핑을 새 페이지로 옮긴다.
mm/migrate.c -3/3-
out_unlock_both:
unlock_page(newpage);
out_unlock:
/* Drop an anon_vma reference if we took one */
if (anon_vma)
put_anon_vma(anon_vma);
unlock_page(page);
out:
/*
* If migration is successful, decrease refcount of the newpage
* which will not free the page because new page owner increased
* refcounter. As well, if it is LRU page, add the page to LRU
* list in here. Use the old state of the isolated source page to
* determine if we migrated a LRU page. newpage was already unlocked
* and possibly modified by its owner - don't rely on the page
* state.
*/
if (rc == MIGRATEPAGE_SUCCESS) {
if (unlikely(!is_lru))
put_page(newpage);
else
putback_lru_page(newpage);
}
return rc;
}
- 코드 라인 1~2에서 out_unlock_both: 레이블에서는 새 페이지에 대한 lock을 먼저 release 한다.
- 코드 라인 3~7에서 out_unlock: 레이블에서는 기존 페이지에 대해 lock을 release 한다. 만일 anon 페이지인 경우 anon_vma에 대한 사용이 완료되었으므로 참조카운터를 감소시킨다.
- 코드 라인 8~23에서 migration이 성공한 경우 사용 중으로 바뀐 newpage의 사용을 완료시킨다. lru movable 페이지인 경우에는 LRU 리스트로 되돌린다.
Non-lru movable 페이지 여부 확인
PageMovable()
mm/compaction.c
int PageMovable(struct page *page)
{
struct address_space *mapping;
VM_BUG_ON_PAGE(!PageLocked(page), page);
if (!__PageMovable(page))
return 0;
mapping = page_mapping(page);
if (mapping && mapping->a_ops && mapping->a_ops->isolate_page)
return 1;
return 0;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(PageMovable);
non-lru movable 페이지 여부를 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 6~7에서 non-lru movable 페이지가 아닌 경우 0을 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 9~13에서 매핑된 페이지의 드라이버에 (*isolate_page) 후크 함수가 지원되는 경우 1을 반환하고, 그렇지 않은 경우 0을 반환한다.
__PageMovable()
static __always_inline int __PageMovable(struct page *page)
{
return ((unsigned long)page->mapping & PAGE_MAPPING_FLAGS) ==
PAGE_MAPPING_MOVABLE;
}
non-lru movable 페이지 여부를 반환한다.
writeback 완료까지 대기
wait_on_page_writeback()
include/linux/pagemap.h
/*
* Wait for a page to complete writeback
*/
static inline void wait_on_page_writeback(struct page *page)
{
if (PageWriteback(page))
wait_on_page_bit(page, PG_writeback);
}
page가 writeback이 완료될 때까지 기다린다.
새 페이지로 이동
move_to_new_page()
mm/migrate.c
/* * Move a page to a newly allocated page * The page is locked and all ptes have been successfully removed. * * The new page will have replaced the old page if this function * is successful. * * Return value: * < 0 - error code * MIGRATEPAGE_SUCCESS - success */
static int move_to_new_page(struct page *newpage, struct page *page,
enum migrate_mode mode)
{
struct address_space *mapping;
int rc = -EAGAIN;
bool is_lru = !__PageMovable(page);
VM_BUG_ON_PAGE(!PageLocked(page), page);
VM_BUG_ON_PAGE(!PageLocked(newpage), newpage);
mapping = page_mapping(page);
if (likely(is_lru)) {
if (!mapping)
rc = migrate_page(mapping, newpage, page, mode);
else if (mapping->a_ops->migratepage)
/*
* Most pages have a mapping and most filesystems
* provide a migratepage callback. Anonymous pages
* are part of swap space which also has its own
* migratepage callback. This is the most common path
* for page migration.
*/
rc = mapping->a_ops->migratepage(mapping, newpage,
page, mode);
else
rc = fallback_migrate_page(mapping, newpage,
page, mode);
} else {
/*
* In case of non-lru page, it could be released after
* isolation step. In that case, we shouldn't try migration.
*/
VM_BUG_ON_PAGE(!PageIsolated(page), page);
if (!PageMovable(page)) {
rc = MIGRATEPAGE_SUCCESS;
__ClearPageIsolated(page);
goto out;
}
rc = mapping->a_ops->migratepage(mapping, newpage,
page, mode);
WARN_ON_ONCE(rc == MIGRATEPAGE_SUCCESS &&
!PageIsolated(page));
}
/*
* When successful, old pagecache page->mapping must be cleared before
* page is freed; but stats require that PageAnon be left as PageAnon.
*/
if (rc == MIGRATEPAGE_SUCCESS) {
if (__PageMovable(page)) {
VM_BUG_ON_PAGE(!PageIsolated(page), page);
/*
* We clear PG_movable under page_lock so any compactor
* cannot try to migrate this page.
*/
__ClearPageIsolated(page);
}
/*
* Anonymous and movable page->mapping will be cleard by
* free_pages_prepare so don't reset it here for keeping
* the type to work PageAnon, for example.
*/
if (!PageMappingFlags(page))
page->mapping = NULL;
}
out:
return rc;
}
페이지를 새로 할당 받은 페이지로 migration 한다.
- 코드 라인 6에서 movable 페이지가 lru 리스트에서 관리되는 페이지인지 여부를 알아온다.
- 코드 라인 11~28에서 lru movable 페이지의 migration을 수행한다. 처리 유형은 다음 3가지이다.
- A) anon 페이지의 migration
- B) swap 캐시 및 파일 캐시 페이지의 (*migratepage)를 사용한 migration
- C) swap 캐시 및 파일 캐시 페이지의 (*migratepage)가 없을 때 사용한 fallback migration
- 코드 라인 29~45에서 non-lru movable 페이지의 migration을 수행한다. 처리 유형은 1 가지이다.
- D) non-lru 페이지 migration을 수행한다. 단 파일 시스템에 (*migratepages) 후크가 구현되지 않은 경우 isolated 플래그를 제거하고 성공을 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 51~69에서 migration이 성공한 경우 기존 페이지는 이제 free 페이지가 된 경우이다. non-lru 페이지였던 경우 isolated 플래그를 제거한다. 그리고 매핑되었던 경우 매핑을 제거한다.
A) lru movable – anon 페이지의 migration
migrate_page()
mm/migrate.c
/* * Common logic to directly migrate a single LRU page suitable for * pages that do not use PagePrivate/PagePrivate2. * * Pages are locked upon entry and exit. */
int migrate_page(struct address_space *mapping,
struct page *newpage, struct page *page,
enum migrate_mode mode)
{
int rc;
BUG_ON(PageWriteback(page)); /* Writeback must be complete */
rc = migrate_page_move_mapping(mapping, newpage, page, mode, 0);
if (rc != MIGRATEPAGE_SUCCESS)
return rc;
if (mode != MIGRATE_SYNC_NO_COPY)
migrate_page_copy(newpage, page);
else
migrate_page_states(newpage, page);
return MIGRATEPAGE_SUCCESS;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(migrate_page);
lru movable 페이지를 새로 할당 받은 페이지로 매핑을 migration하고 copy 한다.
- 코드 라인 9~12에서 페이지를 migrate 한다.
- 코드 라인 14~17에서 MIGRATE_SYNC_NO_COPY 모드에서는 페이지 디스크립터 정보만 옮기지만, 그 외의 모드에서는 cpu에서 페이지 프레임 복사도 추가하여 수행한다.
B) swap 캐시 및 파일 캐시 페이지의 (*migratepage)를 사용한 migration
다음 루틴에서 지원한다.
- mm/shmem.c – migrate_page()
- mm/swap_state.c – migrate_page()
- fs/block_dev.c – buffer_migrate_page_norefs()
- fs/ubifs/file.c – ubifs_migrate_page()
- fs/ext2/inode.c – buffer_migrate_page()
- fs/btrfs/disk-io.c – btree_migratepage()
- fs/f2fs/checkpoint.c – f2fs_migrate_page()
- fs/xfs/xfs_aops.c – iomap_migrate_page()
- fs/hugetlbfs/inode.c – hugetlbfs_migrate_page()
- fs/nfs/file.c – nfs_migrate_page()
- …
C) fallback migrate
fallback_migrate_page()
mm/migrate.c
/* * Default handling if a filesystem does not provide a migration function. */
static int fallback_migrate_page(struct address_space *mapping,
struct page *newpage, struct page *page, enum migrate_mode mode)
{
if (PageDirty(page)) {
/* Only writeback pages in full synchronous migration */
switch (mode) {
case MIGRATE_SYNC:
case MIGRATE_SYNC_NO_COPY:
break;
default:
return -EBUSY;
}
return writeout(mapping, page);
}
/*
* Buffers may be managed in a filesystem specific way.
* We must have no buffers or drop them.
*/
if (page_has_private(page) &&
!try_to_release_page(page, GFP_KERNEL))
return -EAGAIN;
return migrate_page(mapping, newpage, page, mode);
}
파일 시스템이 migration 기능을 지원하지 못할 때 default 호출되어 페이지를 migration 한다.
- 코드 라인 4~14에서 ditty 페이지이면서 MIGRATE_SYNC 또는 MIGRATE_SYNC_NO_COPY 모드로 동작하는 경우에는 페이지를 기록하여 dirty 상태를 클리어한 후 리턴한다. 그 외의 모드의 경우 -EBUSY를 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 20~22에서 private 페이지인 경우 파일 시스템 등이 생성한 해당 페이지에 대한 메타 데이터를 제거한다.
- 코드 라인 24에서 page를 새 페이지로 migration한다.
D) non-lru 페이지 migration
다음 루틴에서 지원한다.
- mm/zsmalloc.c – zs_page_migrate()
- mm/balloon_compaction.c – balloon_page_migrate()
- drivers/virtio/virtio_balloon.c – virtballoon_migratepage()
매핑 이동
migrate_page_move_mapping()
이 함수는 다음 루틴에서 호출되어 사용된다.
- mm/migrate.c – migrate_page()
- mm/migrate.c – __buffer_migrate_page()
- fs/iomap.c – iomap_migrate_page()
- fs/ubifs/file.c – ubifs_migrate_page()
- fs/f2fs/data.c – f2fs_migrate_page()
- fs/aio.c – aio_migratepage()
mm/migrate.c -1/2-
/* * Replace the page in the mapping. * * The number of remaining references must be: * 1 for anonymous pages without a mapping * 2 for pages with a mapping * 3 for pages with a mapping and PagePrivate/PagePrivate2 set. */
int migrate_page_move_mapping(struct address_space *mapping,
struct page *newpage, struct page *page, enum migrate_mode mode,
int extra_count)
{
XA_STATE(xas, &mapping->i_pages, page_index(page));
struct zone *oldzone, *newzone;
int dirty;
int expected_count = expected_page_refs(page) + extra_count;
if (!mapping) {
/* Anonymous page without mapping */
if (page_count(page) != expected_count)
return -EAGAIN;
/* No turning back from here */
newpage->index = page->index;
newpage->mapping = page->mapping;
if (PageSwapBacked(page))
__SetPageSwapBacked(newpage);
return MIGRATEPAGE_SUCCESS;
}
oldzone = page_zone(page);
newzone = page_zone(newpage);
xas_lock_irq(&xas);
if (page_count(page) != expected_count || xas_load(&xas) != page) {
xas_unlock_irq(&xas);
return -EAGAIN;
}
if (!page_ref_freeze(page, expected_count)) {
xas_unlock_irq(&xas);
return -EAGAIN;
}
/*
* Now we know that no one else is looking at the page:
* no turning back from here.
*/
newpage->index = page->index;
newpage->mapping = page->mapping;
page_ref_add(newpage, hpage_nr_pages(page)); /* add cache reference */
if (PageSwapBacked(page)) {
__SetPageSwapBacked(newpage);
if (PageSwapCache(page)) {
SetPageSwapCache(newpage);
set_page_private(newpage, page_private(page));
}
} else {
VM_BUG_ON_PAGE(PageSwapCache(page), page);
}
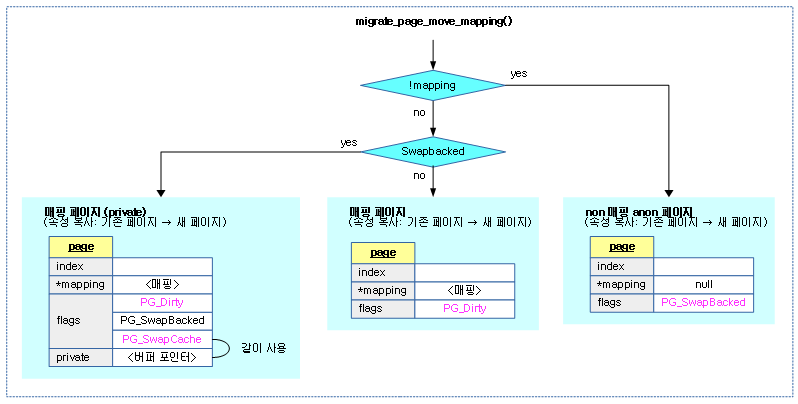
페이지의 매핑을 newpage로 migration 한다.
- 코드 라인 10~22에서 매핑되지 않은 anon 페이지의 경우 새 페이지에 인덱스와 매핑 정보를 옮긴다. 그리고 SwapBacked 플래그가 설정된 경우 제거한다. 만일 참조 카운터가 expected_count와 다른 경우 -EAGAIN을 반환하고 그렇지 않은 경우 success를 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 27에서 xas array 락을 획득한다.
- 코드 라인 28~31에서 참조 카운터가 expected_count가 아니면 -EAGAIN을 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 33~36에서 참조 카운터를 0으로 리셋한다. 리셋 전 값이 expected_count가 아닌 경우 -EAGAIN을 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 42~44에서 매핑된 페이지의 새 페이지에 인덱스, 매핑, 참조카운터를 옮긴다.
- 코드 라인 45~53에서 SwapBacked 플래그를 옮긴다. 그리고 SwapCache 플래그도 옮기고 private 데이터에 저장된 값도 옮긴다.
mm/migrate.c -2/2-
/* Move dirty while page refs frozen and newpage not yet exposed */
dirty = PageDirty(page);
if (dirty) {
ClearPageDirty(page);
SetPageDirty(newpage);
}
xas_store(&xas, newpage);
if (PageTransHuge(page)) {
int i;
for (i = 1; i < HPAGE_PMD_NR; i++) {
xas_next(&xas);
xas_store(&xas, newpage + i);
}
}
/*
* Drop cache reference from old page by unfreezing
* to one less reference.
* We know this isn't the last reference.
*/
page_ref_unfreeze(page, expected_count - hpage_nr_pages(page));
xas_unlock(&xas);
/* Leave irq disabled to prevent preemption while updating stats */
/*
* If moved to a different zone then also account
* the page for that zone. Other VM counters will be
* taken care of when we establish references to the
* new page and drop references to the old page.
*
* Note that anonymous pages are accounted for
* via NR_FILE_PAGES and NR_ANON_MAPPED if they
* are mapped to swap space.
*/
if (newzone != oldzone) {
__dec_node_state(oldzone->zone_pgdat, NR_FILE_PAGES);
__inc_node_state(newzone->zone_pgdat, NR_FILE_PAGES);
if (PageSwapBacked(page) && !PageSwapCache(page)) {
__dec_node_state(oldzone->zone_pgdat, NR_SHMEM);
__inc_node_state(newzone->zone_pgdat, NR_SHMEM);
}
if (dirty && mapping_cap_account_dirty(mapping)) {
__dec_node_state(oldzone->zone_pgdat, NR_FILE_DIRTY);
__dec_zone_state(oldzone, NR_ZONE_WRITE_PENDING);
__inc_node_state(newzone->zone_pgdat, NR_FILE_DIRTY);
__inc_zone_state(newzone, NR_ZONE_WRITE_PENDING);
}
}
local_irq_enable();
return MIGRATEPAGE_SUCCESS;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(migrate_page_move_mapping);
- 코드 라인 2~6에서 Dirty 플래그가 있는 경우 새 페이지에 옮기고, 기존 페이지는 제거한다.
- 코드 라인8에서 xas xarray에 새페이지를 저장한다. 기존에는 radix tree를 사용했었는데 xarray 데이터 구조로 변경하였다.
- 코드 라인 9~16에서 thp인 경우 소속된 각 페이지를 xas xarray에 저장한다.
- 코드 라인 23에서 페이지의 참조 카운터를 페이지 수 만큼 지정한다.
- 코드 라인 25에서 xas array 락을 release 한다.
- 코드 라인 38~51 존이 변경된 경우 관련 카운터들 값을 증감한다.
다음 그림은 페이지 유형에 따라 기존 페이지에서 새 페이지로 관련 속성들을 복사하는 모습을 보여준다.
Rmap walk를 통한 페이지 migration
remove_migration_ptes()
mm/migrate.c
/* * Get rid of all migration entries and replace them by * references to the indicated page. */
static void remove_migration_ptes(struct page *old, struct page *new)
{
struct rmap_walk_control rwc = {
.rmap_one = remove_migration_pte,
.arg = old,
};
if (locked)
rmap_walk_locked(new, &rwc);
else
rmap_walk(new, &rwc);
}
@old 페이지에 연결된 모든 매핑을 @new 페이지로 옮긴다.
- 코드 라인 3~6에서 기존 페이지를 참고하는 모든 vma를 찾기위해 rmap walk를 사용하도록 준비한다.
- 코드 라인 8~11에서 rmap walk를 통해 관련 vma에 연결된 기존 매핑을 제거하고 새 페이지에 매핑을 옮긴다.
remove_migration_pte()
mm/migrate.c
/* * Restore a potential migration pte to a working pte entry */
static bool remove_migration_pte(struct page *page, struct vm_area_struct *vma,
unsigned long addr, void *old)
{
struct page_vma_mapped_walk pvmw = {
.page = old,
.vma = vma,
.address = addr,
.flags = PVMW_SYNC | PVMW_MIGRATION,
};
struct page *new;
pte_t pte;
swp_entry_t entry;
VM_BUG_ON_PAGE(PageTail(page), page);
while (page_vma_mapped_walk(&pvmw)) {
if (PageKsm(page))
new = page;
else
new = page - pvmw.page->index +
linear_page_index(vma, pvmw.address);
#ifdef CONFIG_ARCH_ENABLE_THP_MIGRATION
/* PMD-mapped THP migration entry */
if (!pvmw.pte) {
VM_BUG_ON_PAGE(PageHuge(page) || !PageTransCompound(page), page);
remove_migration_pmd(&pvmw, new);
continue;
}
#endif
get_page(new);
pte = pte_mkold(mk_pte(new, READ_ONCE(vma->vm_page_prot)));
if (pte_swp_soft_dirty(*pvmw.pte))
pte = pte_mksoft_dirty(pte);
/*
* Recheck VMA as permissions can change since migration started
*/
entry = pte_to_swp_entry(*pvmw.pte);
if (is_write_migration_entry(entry))
pte = maybe_mkwrite(pte, vma);
if (unlikely(is_zone_device_page(new))) {
if (is_device_private_page(new)) {
entry = make_device_private_entry(new, pte_write(pte));
pte = swp_entry_to_pte(entry);
} else if (is_device_public_page(new)) {
pte = pte_mkdevmap(pte);
flush_dcache_page(new);
}
} else
flush_dcache_page(new);
#ifdef CONFIG_HUGETLB_PAGE
if (PageHuge(new)) {
pte = pte_mkhuge(pte);
pte = arch_make_huge_pte(pte, vma, new, 0);
set_huge_pte_at(vma->vm_mm, pvmw.address, pvmw.pte, pte);
if (PageAnon(new))
hugepage_add_anon_rmap(new, vma, pvmw.address);
else
page_dup_rmap(new, true);
} else
#endif
{
set_pte_at(vma->vm_mm, pvmw.address, pvmw.pte, pte);
if (PageAnon(new))
page_add_anon_rmap(new, vma, pvmw.address, false);
else
page_add_file_rmap(new, false);
}
if (vma->vm_flags & VM_LOCKED && !PageTransCompound(new))
mlock_vma_page(new);
if (PageTransHuge(page) && PageMlocked(page))
clear_page_mlock(page);
/* No need to invalidate - it was non-present before */
update_mmu_cache(vma, pvmw.address, pvmw.pte);
}
return true;
}
@old 페이지에 연결된 모든 매핑을 @new 페이지로 옮긴다.
- 코드 라인 4~15에서 old 페이지에 대한 매핑이 모두 제거될 때까지 반복한다.
- Rmap -3- (PVMW) | 문c
- 코드 라인 16~20에서 migration될 새 페이지를 구한다.
- 코드 라인 24~28에서 pmd에 매핑된 thp 엔트리인 경우 pmd 엔트리로의 migration을 수행한 후 계속한다.
- 코드 라인 31~34에서 새 페이지를 사용하기로 참조 카운터를 증가시킨다. 그런 후 이 페이지에 대한 pte 엔트리를 준비한다. 기존 pte 엔트리의 soft dirty 상태도 옮긴다.
- 코드 라인 39~41에서 swap 엔트리가 migration 가능한 swap 엔트리에서 write 속성의 vma를 사용하면 pte 속성에 write 속성을 부가한다.
- migration이 시작한 이후로 permission이 변경될 수 있는데 VMA를 다시 write 속성을 조사하여 변경된 경우 추가한다.
- 코드 라인 43~52에서 새 페이지에 대한 데이터 캐시를 flush 한다.
- private 페이지를 운영하는 존 디바이스인 경우 새 페이지에 대한 pte 엔트리를 가져온다.
- private 페이지가 아닌 존 디바이스인 경우는 새 페이지에 대한 pte 엔트리를 가져오고 추가로 새 페이지에 대한 데이터 캐시를 flush한다.
- 코드 라인 55~62에서 새 페이지가 huge 페이지인 경우 정규 매핑을 추가하고, rmap에도 추가한다.
- 코드 라인 63~72에서 huge 페이지가 아닌 경우 정규 매핑을 추가하고, rmap에도 추가한다.
- 코드 라인 73~74에서 VM_LOCKED 플래그를 가진 vma에 thp 및 hugetlbfs 페이지가 아닌 경우에만 새 페이지에 mlock 플래그 설정을 한다.
- 코드 라인 76~77에서 만일 새 thp에 mlocked 플래그가 설정된 경우 클리어한다.
- 참고로 thp는 mlock 설정을 할 수 없다.
- 코드 라인 80에서 캐시 flush가 필요한 아키텍처에서 flush를 수행한다.
- ARMv6 이상에서는 아무런 동작도 수행하지 않고, ARMv6 미만에서 cache coherent를 위한 flush 루틴들이 동작한다.
페이지 프레임 복사
migrate_page_copy()
mm/migrate.c
void migrate_page_copy(struct page *newpage, struct page *page)
{
if (PageHuge(page) || PageTransHuge(page))
copy_huge_page(newpage, page);
else
copy_highpage(newpage, page);
migrate_page_states(newpage, page);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(migrate_page_copy);
기존 페이지 프레임을 새 페이지 프레임으로 복사한다. 또한 관련 페이지 디스크립터도 복사한다.
- 코드 라인 3~4에서 huge 페이지 또는 thp인 경우의 복사 루틴을 수행한다.
- 코드 라인 5~6에서 그렇지 않은 일반 페이지의 경우의 복사 루틴을 수행한다.
- 코드 라인 8에서 페이지 디스크립터도 복사한다.
copy_huge_page()
mm/migrate.c
static void copy_huge_page(struct page *dst, struct page *src)
{
int i;
int nr_pages;
if (PageHuge(src)) {
/* hugetlbfs page */
struct hstate *h = page_hstate(src);
nr_pages = pages_per_huge_page(h);
if (unlikely(nr_pages > MAX_ORDER_NR_PAGES)) {
__copy_gigantic_page(dst, src, nr_pages);
return;
}
} else {
/* thp page */
BUG_ON(!PageTransHuge(src));
nr_pages = hpage_nr_pages(src);
}
for (i = 0; i < nr_pages; i++) {
cond_resched();
copy_highpage(dst + i, src + i);
}
}
@src huge 페이지 프레임을 @dst로 복사한다.
- 코드 라인 6~14에서 hugetlbfs 페이지이면서 최대 order 페이지 수보다 큰 페이지인 경우 단순히 페이지 구조체 포인터를 증가시키는 것으로 정확히 동작하는 것을 보장하지 못한다. 따라서 페이지 디스크립터의 포인터를 정확히 처리하기 위해 별도의 함수에서 처리한다.
- 코드 라인 15~19에서 thp에 대한 페이지 수를 알아온다.
- 코드 라인 21~24에서 페이지 수만큼 순회하며 @src+i의 페이지 프레임을 @dst+i로 복사한다.
__copy_gigantic_page()
mm/migrate.c
/* * Gigantic pages are so large that we do not guarantee that page++ pointer * arithmetic will work across the entire page. We need something more * specialized. */
static void __copy_gigantic_page(struct page *dst, struct page *src,
int nr_pages)
{
int i;
struct page *dst_base = dst;
struct page *src_base = src;
for (i = 0; i < nr_pages; ) {
cond_resched();
copy_highpage(dst, src);
i++;
dst = mem_map_next(dst, dst_base, i);
src = mem_map_next(src, src_base, i);
}
}
최대 order 페이지 수 보다 큰 @src 페이지 프레임을 @dst로 복사한다.
mem_map_next()
mm/internal.h
/* * Iterator over all subpages within the maximally aligned gigantic * page 'base'. Handle any discontiguity in the mem_map. */
static inline struct page *mem_map_next(struct page *iter,
struct page *base, int offset)
{
if (unlikely((offset & (MAX_ORDER_NR_PAGES - 1)) == 0)) {
unsigned long pfn = page_to_pfn(base) + offset;
if (!pfn_valid(pfn))
return NULL;
return pfn_to_page(pfn);
}
return iter + 1;
}
@iter 페이지의 다음 페이지를 구해 반환한다. 최대 order 페이지 수를 초과하는 페이지의 경우 섹션별로 관리되는 mem_map의 경계를 초과할 수 있어 잘못된 주소가 나올 가능성이 있으므로 그럴 때마다 페이지 디스크립터의 주소를 정확히 재산출한다.
- 코드 라인 4~9에서 낮은 확률로 offset이 최대 order 페이지 수(default: 1024 = 4M(4K 페이지)) 단위로 정렬된 경우에는 page 디스크립터 포인터를 증가시키면 mem_map의 경계를 초과할 수 있으므로 pfn 값을 먼저 구한 후 pfn_to_page() 함수를 사용하여 page 디스크립터를 다시 구한다.
- 코드 라인 10에서 다음 페이지 디스크립터를 반환한다.
copy_highpage()
include/linux/highmem.h
static inline void copy_highpage(struct page *to, struct page *from)
{
char *vfrom, *vto;
vfrom = kmap_atomic(from);
vto = kmap_atomic(to);
copy_page(vto, vfrom);
kunmap_atomic(vto);
kunmap_atomic(vfrom);
}
@from 페이지 프레임을 @to로 복사한다.
- 코드 라인 5~6에서 32비트 시스템에서 highmem 페이지인 경우 fixmap을 사용하여 임시로 매핑하도록 한다.
- 코드 라인 7에서 아키텍처가 지원하는 가장 빠른 방법으로 페이지 프레임을 복사한다.
- 코드 라인 8~9에서 fixmap에 임시 매핑한 페이지의 매핑을 해제한다.
페이지 디스크립터 정보 복사
migrate_page_states()
mm/migrate.c
/* * Copy the page to its new location */
void migrate_page_states(struct page *newpage, struct page *page)
{
int cpupid;
if (PageError(page))
SetPageError(newpage);
if (PageReferenced(page))
SetPageReferenced(newpage);
if (PageUptodate(page))
SetPageUptodate(newpage);
if (TestClearPageActive(page)) {
VM_BUG_ON_PAGE(PageUnevictable(page), page);
SetPageActive(newpage);
} else if (TestClearPageUnevictable(page))
SetPageUnevictable(newpage);
if (PageWorkingset(page))
SetPageWorkingset(newpage);
if (PageChecked(page))
SetPageChecked(newpage);
if (PageMappedToDisk(page))
SetPageMappedToDisk(newpage);
/* Move dirty on pages not done by migrate_page_move_mapping() */
if (PageDirty(page))
SetPageDirty(newpage);
if (page_is_young(page))
set_page_young(newpage);
if (page_is_idle(page))
set_page_idle(newpage);
/*
* Copy NUMA information to the new page, to prevent over-eager
* future migrations of this same page.
*/
cpupid = page_cpupid_xchg_last(page, -1);
page_cpupid_xchg_last(newpage, cpupid);
ksm_migrate_page(newpage, page);
/*
* Please do not reorder this without considering how mm/ksm.c's
* get_ksm_page() depends upon ksm_migrate_page() and PageSwapCache().
*/
if (PageSwapCache(page))
ClearPageSwapCache(page);
ClearPagePrivate(page);
set_page_private(page, 0);
/*
* If any waiters have accumulated on the new page then
* wake them up.
*/
if (PageWriteback(newpage))
end_page_writeback(newpage);
copy_page_owner(page, newpage);
mem_cgroup_migrate(page, newpage);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(migrate_page_states);
기존 페이지 디스크립터 내용을 새 페이지의 디스크립터로 옮긴다.
- 코드 라인 5~6에서 PG_error 플래그를 옮긴다.
- 코드 라인 7~8에서 PG_referenced 플래그를 옮긴다.
- 코드 라인 9~10에서 PG_uptodate 플래그를 옮긴다.
- 코드 라인 11~15에서 PG_active 플래그 또는 PG_unevictable 플래그를 옮기고, 기존 페이지에서는 제거한다.
- 코드 라인 16~17에서 PG_workingset 플래그를 옮긴다.
- 코드 라인 18~19에서 PG_checked 플래그를 옮긴다.
- 코드 라인 20~21에서 PG_mappedtodist 플래그를 옮긴다.
- 코드 라인 24~25에서 PG_dirty 플래그를 옮긴다.
- 코드 라인 27~28에서 Young 플래그를 옮긴다.
- 32bit 시스템의 경우 page 구조체가 아닌 page_ext 구조체에 존재한다.
- 코드 라인 29~30에서 Idle 플래그를 옮긴다.
- 32bit 시스템의 경우 page 구조체가 아닌 page_ext 구조체에 존재한다.
- 코드 라인 36~37에서 cpupid 정보를 옮기고, 기존 페이지에는 -1을 대입한다.
- 코드 라인 39에서 ksm 페이지이면서, 복사할 대상이 statble 노드 매핑된 경우 stable 노드 매핑 정보를 제거한다.
- KSM(Kernel Same page Merging)이 application이 주소 공간에서 같은 내용을 가진 페이지를 스캔하여 한 페이지로 merge 시킬 수 있도록 하는 기능이다.
- 참고: How to use the Kernel Samepage Merging feature | kernel.org
- 코드 라인 44~45에서 기존 페이지의 SwapCache 정보를 제거한다.
- 코드 라인 46~47에서 기존 페이지의 Private 플래그를 제거하고, p->private에 0을 대입한다.
- 코드 라인 53~54에서 새 페이지에 Writeback 플래그가 설정된 경우 lru의 tail로 rotate하고, 관련 태스크를 깨워 즉각 회수가 가능하도록 한다.
- 코드 라인 56에서 page owner 정보를 옮긴다.
- 코드 라인 58에서 memcg 정보를 옮긴다.
참고
- Zoned Allocator -1- (물리 페이지 할당-Fastpath) | 문c
- Zoned Allocator -2- (물리 페이지 할당-Slowpath) | 문c
- Zoned Allocator -3- (Buddy 페이지 할당) | 문c
- Zoned Allocator -4- (Buddy 페이지 해지) | 문c
- Zoned Allocator -5- (Per-CPU Page Frame Cache) | 문c
- Zoned Allocator -6- (Watermark) | 문c
- Zoned Allocator -7- (Direct Compact) | 문c
- Zoned Allocator -8- (Direct Compact-Isolation) | 문c
- Zoned Allocator -9- (Direct Compact-Migration) | 문c – 현재 글
- Zoned Allocator -10- (LRU & pagevec) | 문c
- Zoned Allocator -11- (Direct Reclaim) | 문c
- Zoned Allocator -12- (Direct Reclaim-Shrink-1) | 문c
- Zoned Allocator -13- (Direct Reclaim-Shrink-2) | 문c
- Zoned Allocator -14- (Kswapd) | 문c