<kernel v5.0>
Per-CPU Page Frame Cache
- 커널에서 메모리 할당은 주로 큰 페이지보다 single 페이지(0-order page) 프레임을 요청하는 경우가 대부분이다.
- single 페이지 요청인 경우에만 할당 처리 성능을 높이기 위해 각각의 zone에 per-cpu page frame cache를 준비하고 미리 여러 개의 페이지를 준비한 후 요청한 single 페이지에 대해 buddy를 사용하지 않고 곧바로 캐시된 페이지를 요청자에게 전달한다.
- 버디를 사용할 경우에는 존에 대한 락이 필요한데, per-cpu를 사용하여 lock-less로 구현하여 성능을 올렸다.
- 기존 커널에서 각 zone에는 hot 캐시와 cold 캐시를 사용해왔었는데 그 용도가 하나로 통합되었고 hot 요청인 경우 준비된 캐시 페이지 중 앞쪽을 사용하게 하고 cold 요청인 경우 뒷 쪽 페이지를 사용하게 한다.
- 커널 2.6.25-rc1 이후 부터 각 zone 마다 3개의 migratetype 수 만큼 캐시 배열로 관리한다.
- 커널 모니터가 캐시 페이지가 low 워터마크 수 이하로 떨어지는 것을 커널 모니터가 detect하면 미리 batch 수 만큼 페이지를 캐시에 할당해 놓는다.
- single 페이지 요청 시 캐시된 페이지가 없는 경우에는 batch 수 만큼 페이지를 캐시에 할당 받은 후 그 중 한 페이지를 요청자에게 전달한다.
- single 페이지 해제 시 캐시된 페이지가 high 이상인 경우 batch 수 만큼 버디 시스템에 되돌린다.
pcp에서 order 0 페이지 할당/해제
order 0 페이지 할당
rmqueue_pcplist()
mm/page_alloc.c
/* Lock and remove page from the per-cpu list */
static struct page *rmqueue_pcplist(struct zone *preferred_zone,
struct zone *zone, unsigned int order,
gfp_t gfp_flags, int migratetype,
unsigned int alloc_flags)
{
struct per_cpu_pages *pcp;
struct list_head *list;
struct page *page;
unsigned long flags;
local_irq_save(flags);
pcp = &this_cpu_ptr(zone->pageset)->pcp;
list = &pcp->lists[migratetype];
page = __rmqueue_pcplist(zone, migratetype, alloc_flags, pcp, list);
if (page) {
__count_zid_vm_events(PGALLOC, page_zonenum(page), 1 << order);
zone_statistics(preferred_zone, zone);
}
local_irq_restore(flags);
return page;
}
@migratetype의 order 0 페이지를 pcp에서 할당하고 페이지 디스크립터를 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 12~15에서 per-cpu로 구현된 버디 시스템 캐시인 pcp는 cost가 많이 소모되는 lock을 사용하지 않고 로컬 인터럽트만 disable한 상태로 @migratetype의 order 0 페이지를 pcp에서 할당한다.
- 코드 라인 16~19에서 PGALLOC 카운터를 페이지 수 만큼 증가시킨다.
- 코드 라인 21에서 할당한 페이지를 반환한다.
__rmqueue_pcplist()
mm/page_alloc.c
/* Remove page from the per-cpu list, caller must protect the list */
static struct page *__rmqueue_pcplist(struct zone *zone, int migratetype,
unsigned int alloc_flags,
struct per_cpu_pages *pcp,
struct list_head *list)
{
struct page *page;
do {
if (list_empty(list)) {
pcp->count += rmqueue_bulk(zone, 0,
pcp->batch, list,
migratetype, alloc_flags);
if (unlikely(list_empty(list)))
return NULL;
}
page = list_first_entry(list, struct page, lru);
list_del(&page->lru);
pcp->count--;
} while (check_new_pcp(page));
return page;
}
@migratetype의 order 0 페이지를 pcp로부터 할당하고 페이지 디스크립터를 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 9~16에서 pcp의 @list가 비어있는 경우 버디 시스템에서 pcp->batch 수 만큼 이주시킨다.
- 코드 라인 18~20에서 pcp의 @list에서 첫 엔트리를 가져온다.
- 코드 라인 21에서 할당할 엔트리에 문제가 없는지 체크한다.
- 코드 라인 23에서 할당할 order 0 페이지를 반환한다.
order 0 페이지 회수
free_unref_page()
mm/page_alloc.c
/* * Free a 0-order page */
void free_unref_page(struct page *page)
{
unsigned long flags;
unsigned long pfn = page_to_pfn(page);
if (!free_unref_page_prepare(page, pfn))
return;
local_irq_save(flags);
free_unref_page_commit(page, pfn);
local_irq_restore(flags);
}
order 0 페이지를 pcp에 회수한다.
- 코드 라인 6~7에서 free할 페이지를 준비한다. 만일 페이지 상태가 bad 판정된 경우 함수를 빠져나간다.
- 코드 라인 9~11에서 로컬 irq를 disable한 상태로 order 0 페이지를 pcp에 회수한다.
free_unref_page_prepare()
mm/page_alloc.c
static bool free_unref_page_prepare(struct page *page, unsigned long pfn)
{
int migratetype;
if (!free_pcp_prepare(page))
return false;
migratetype = get_pfnblock_migratetype(page, pfn);
set_pcppage_migratetype(page, migratetype);
return true;
}
free할 페이지를 준비한다. (정상=true, bad=false)
- 코드 라인 5~6에서 free할 페이지의 상태를 체크하여 bad 판정된 경우 false 결과를 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 8~10에서 페이지가 속한 페이지 블럭의 migrate 타입을 페이지에 저장하고 true를 반환한다.
free_unref_page_commit()
mm/page_alloc.c
static void free_unref_page_commit(struct page *page, unsigned long pfn)
{
struct zone *zone = page_zone(page);
struct per_cpu_pages *pcp;
int migratetype;
migratetype = get_pcppage_migratetype(page);
__count_vm_event(PGFREE);
/*
* We only track unmovable, reclaimable and movable on pcp lists.
* Free ISOLATE pages back to the allocator because they are being
* offlined but treat HIGHATOMIC as movable pages so we can get those
* areas back if necessary. Otherwise, we may have to free
* excessively into the page allocator
*/
if (migratetype >= MIGRATE_PCPTYPES) {
if (unlikely(is_migrate_isolate(migratetype))) {
free_one_page(zone, page, pfn, 0, migratetype);
return;
}
migratetype = MIGRATE_MOVABLE;
}
pcp = &this_cpu_ptr(zone->pageset)->pcp;
list_add(&page->lru, &pcp->lists[migratetype]);
pcp->count++;
if (pcp->count >= pcp->high) {
unsigned long batch = READ_ONCE(pcp->batch);
free_pcppages_bulk(zone, batch, pcp);
}
}
free할 0-order 페이지를 pcp로 회수한다.
- 코드 라인 8에서 PGFREE 카운터를 증가시킨다.
- 코드 라인 17~23에서 isolate 타입은 버디 시스템에 회수시키고, pcp에서 취급하지 않는 나머지 cma와 highatomic 타입은 movable 타입으로 변경한다.
- 코드 라인 25~27에서 migrate 타입의 pcp에 추가한다.
- 코드 라인 28~31에서 pcp 리스트의 엔트리 수가 pcp->high 이상인 경우이다. pcp에 일정 분량만을 관리하기 위해 pcp->batch 수 만큼 버디 시스템으로 이동시킨다.
get_pcppage_migratetype()
include/linux/mm.h
/* * A cached value of the page's pageblock's migratetype, used when the page is * put on a pcplist. Used to avoid the pageblock migratetype lookup when * freeing from pcplists in most cases, at the cost of possibly becoming stale. * Also the migratetype set in the page does not necessarily match the pcplist * index, e.g. page might have MIGRATE_CMA set but be on a pcplist with any * other index - this ensures that it will be put on the correct CMA freelist. */
static inline int get_pcppage_migratetype(struct page *page)
{
return page->index;
}
page->index에 저장된 migratetype을 알아온다.
pcp <-> 버디시스템 벌크 할당/회수
pcp <- 버디시스템 벌크 할당
rmqueue_bulk()
mm/page_alloc.c
/* * Obtain a specified number of elements from the buddy allocator, all under * a single hold of the lock, for efficiency. Add them to the supplied list. * Returns the number of new pages which were placed at *list. */
static int rmqueue_bulk(struct zone *zone, unsigned int order,
unsigned long count, struct list_head *list,
int migratetype, unsigned int alloc_flags)
{
int i, alloced = 0;
spin_lock(&zone->lock);
for (i = 0; i < count; ++i) {
struct page *page = __rmqueue(zone, order, migratetype,
alloc_flags);
if (unlikely(page == NULL))
break;
if (unlikely(check_pcp_refill(page)))
continue;
/*
* Split buddy pages returned by expand() are received here in
* physical page order. The page is added to the tail of
* caller's list. From the callers perspective, the linked list
* is ordered by page number under some conditions. This is
* useful for IO devices that can forward direction from the
* head, thus also in the physical page order. This is useful
* for IO devices that can merge IO requests if the physical
* pages are ordered properly.
*/
list_add_tail(&page->lru, list);
alloced++;
if (is_migrate_cma(get_pcppage_migratetype(page)))
__mod_zone_page_state(zone, NR_FREE_CMA_PAGES,
-(1 << order));
}
/*
* i pages were removed from the buddy list even if some leak due
* to check_pcp_refill failing so adjust NR_FREE_PAGES based
* on i. Do not confuse with 'alloced' which is the number of
* pages added to the pcp list.
*/
__mod_zone_page_state(zone, NR_FREE_PAGES, -(i << order));
spin_unlock(&zone->lock);
return alloced;
}
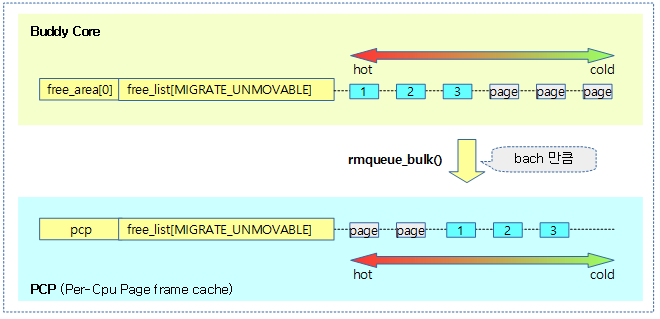
버디 시스템의 @order slot에서 @count 만큼 free 페이지를 가져와서 @list에 이동시킨다. 그런 후 실제 이동시킨 수를 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 8~15에서 count 수 만큼 루프를 돌며 버디 시스템으로 부터 @order 페이지를 가져온다.
- 코드 라인 27~28에서 가져온 페이지를 @list에 추가한다.
- 코드 라인 29~31에서 cma 페이지인 경우 NR_FREE_CMA_PAGES 카운터를 페이지 수 만큼 감소시킨다.
- 코드 라인 40에서 NR_FREE_PAGES를 루프를 돌며 이동시킨 페이지 수 만큼 감소시킨다.
- 코드 라인 42에서 이동시킨 수를 반환한다.
다음 그림은 버디시스템에 있는 free 페이지들이 batch 수 만큼 pcp로 벌크 이동하는 모습을 보여준다.
pcp -> 버디시스템 벌크 회수
free_pcppages_bulk()
/* * Frees a number of pages from the PCP lists * Assumes all pages on list are in same zone, and of same order. * count is the number of pages to free. * * If the zone was previously in an "all pages pinned" state then look to * see if this freeing clears that state. * * And clear the zone's pages_scanned counter, to hold off the "all pages are * pinned" detection logic. */
static void free_pcppages_bulk(struct zone *zone, int count,
struct per_cpu_pages *pcp)
{
int migratetype = 0;
int batch_free = 0;
int prefetch_nr = 0;
bool isolated_pageblocks;
struct page *page, *tmp;
LIST_HEAD(head);
while (count) {
struct list_head *list;
/*
* Remove pages from lists in a round-robin fashion. A
* batch_free count is maintained that is incremented when an
* empty list is encountered. This is so more pages are freed
* off fuller lists instead of spinning excessively around empty
* lists
*/
do {
batch_free++;
if (++migratetype == MIGRATE_PCPTYPES)
migratetype = 0;
list = &pcp->lists[migratetype];
} while (list_empty(list));
/* This is the only non-empty list. Free them all. */
if (batch_free == MIGRATE_PCPTYPES)
batch_free = count;
do {
page = list_last_entry(list, struct page, lru);
/* must delete to avoid corrupting pcp list */
list_del(&page->lru);
pcp->count--;
if (bulkfree_pcp_prepare(page))
continue;
list_add_tail(&page->lru, &head);
/*
* We are going to put the page back to the global
* pool, prefetch its buddy to speed up later access
* under zone->lock. It is believed the overhead of
* an additional test and calculating buddy_pfn here
* can be offset by reduced memory latency later. To
* avoid excessive prefetching due to large count, only
* prefetch buddy for the first pcp->batch nr of pages.
*/
if (prefetch_nr++ < pcp->batch)
prefetch_buddy(page);
} while (--count && --batch_free && !list_empty(list));
}
spin_lock(&zone->lock);
isolated_pageblocks = has_isolate_pageblock(zone);
/*
* Use safe version since after __free_one_page(),
* page->lru.next will not point to original list.
*/
list_for_each_entry_safe(page, tmp, &head, lru) {
int mt = get_pcppage_migratetype(page);
/* MIGRATE_ISOLATE page should not go to pcplists */
VM_BUG_ON_PAGE(is_migrate_isolate(mt), page);
/* Pageblock could have been isolated meanwhile */
if (unlikely(isolated_pageblocks))
mt = get_pageblock_migratetype(page);
__free_one_page(page, page_to_pfn(page), zone, 0, mt);
trace_mm_page_pcpu_drain(page, 0, mt);
}
spin_unlock(&zone->lock);
}
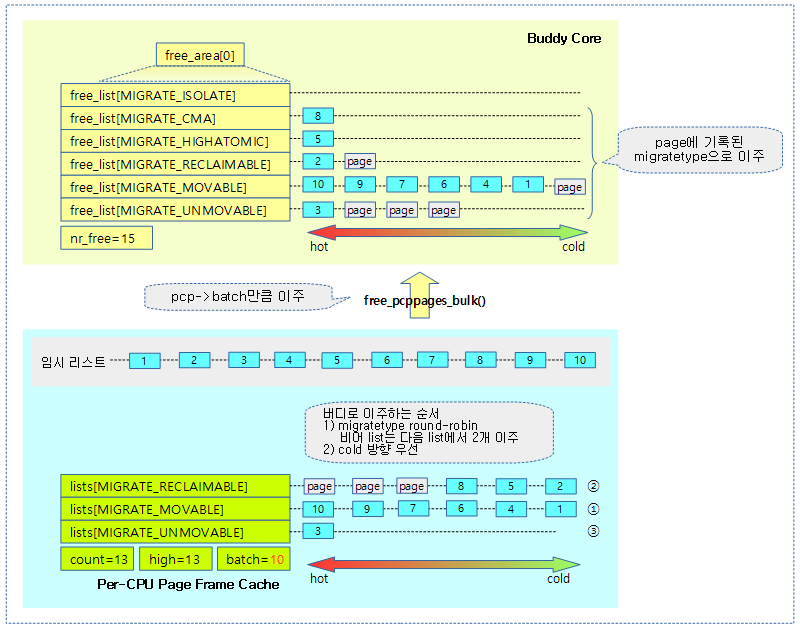
요청 zone의 pcp를 @count 만큼 버디시스템으로 회수한다.
- 코드 라인 11에서 @count 수 만큼 순회한다.
- 코드 라인 21~30에서 3가지 migrate 타입의 pcp 리스트를 순회하도록 migratetype을 정한다. 단 빈 pcp 리스트는 skip 한다.
- 처음 시작 시 movable(1), reclaimable(2), unmovable(0) migrate 타입으로 진행한다.
- batch_free 수 만큼씩 로드밸런싱하는데, 리스트가 비게 되면 너무 spin 되는 것을 억제하게 하기 위해 batch_free를 추가 증가시킨다.
- empty된 리스트 없이, 세 리스트에서 작업 시 1개씩 돌아가며 처리한다.
- 한 리스트가 empty 되고, 남은 두 리스트에서 작업 시 2개씩 처리한다.
- 두 리스트가 empty 되고, 마지막 리스트만 남게되면 한꺼번에 처리하기 위해 @count를 대입한다.
- 코드 라인 32~41에서 지정된 migratetype의 pcp 리스트에서 tail 방향 엔트리를 가져와서 임시 리스트의 head 방향에 추가한다.
- 코드 라인 52~53에서 pcp->batch 까지는 페이지에 대한 buddy 페이지를 prefetch 한다.이렇게 하면 버디 시스템에서 조금 더 빠른 성능으로 처리하기 위함이다.
- 코드 라인 54에서 한 개의 pcp 리스트에서 batch_free 수 만큼만 반복처리한다. 단 empty 되거나, @count가 0이되어 모두 처리한 경우 완료된다.
- 코드 라인 64~74에서 임시 리스트를 순회하며 해당 페이지가 속한 migrate 타입을 사용하여 버디 시스템의 해당 migrate 타입을 사용한 리스트로 회수시킨다. 단 회수 시킬 때 존에 isolate 타입 페이지가 존재하는 경우 페이지가 속한 페이지블럭의 migrate 타입을 사용한다.
아래 그림은 pcp가 overflow되어 batch 수 만큼 buddy로 이주하는 과정과 순서를 보여준다.
- free_list[0] 슬롯으로 페이지가 이주될 때 free_list[0]에 buddy 페이지가 존재하는 경우 buddy 페이지를 제거하고 다음 order인 free_list[1]으로 합쳐서 추가한다. 동일하게 free_list[1]에서도 buddy 페이지가 발견되면 다음 order로 통합하면서 buddy 페이지가 발견되지 않을 때까지 통합한다.
다음 그림은 pcp에서 버디로 옮겨지는 페이지의 순서를 보여준다.
다음과 같이 zone별 pagesets에 대한 카운터 정보를 확인할 수 있다.
pi@pi /proc $ cat zoneinfo
Node 0, zone Normal
pages free 190861
min 2048
low 2560
high 3072
scanned 0
spanned 241664
present 241664
managed 233403
nr_free_pages 190861
(...생략...)
nr_free_cma 935
protection: (0, 0)
pagesets
cpu: 0
count: 50
high: 186
batch: 31
vm stats threshold: 24
cpu: 1
count: 106
high: 186
batch: 31
vm stats threshold: 24
cpu: 2
count: 153
high: 186
batch: 31
vm stats threshold: 24
cpu: 3
count: 156
high: 186
batch: 31
vm stats threshold: 24
all_unreclaimable: 0
start_pfn: 0
inactive_ratio: 1
PCP(Per-Cpu Page frame cache) Drain
drain_all_pages()
/* * Spill all the per-cpu pages from all CPUs back into the buddy allocator. * * When zone parameter is non-NULL, spill just the single zone's pages. * * Note that this can be extremely slow as the draining happens in a workqueue. */
void drain_all_pages(struct zone *zone)
{
int cpu;
/*
* Allocate in the BSS so we wont require allocation in
* direct reclaim path for CONFIG_CPUMASK_OFFSTACK=y
*/
static cpumask_t cpus_with_pcps;
/*
* Make sure nobody triggers this path before mm_percpu_wq is fully
* initialized.
*/
if (WARN_ON_ONCE(!mm_percpu_wq))
return;
/*
* Do not drain if one is already in progress unless it's specific to
* a zone. Such callers are primarily CMA and memory hotplug and need
* the drain to be complete when the call returns.
*/
if (unlikely(!mutex_trylock(&pcpu_drain_mutex))) {
if (!zone)
return;
mutex_lock(&pcpu_drain_mutex);
}
/*
* We don't care about racing with CPU hotplug event
* as offline notification will cause the notified
* cpu to drain that CPU pcps and on_each_cpu_mask
* disables preemption as part of its processing
*/
for_each_online_cpu(cpu) {
struct per_cpu_pageset *pcp;
struct zone *z;
bool has_pcps = false;
if (zone) {
pcp = per_cpu_ptr(zone->pageset, cpu);
if (pcp->pcp.count)
has_pcps = true;
} else {
for_each_populated_zone(z) {
pcp = per_cpu_ptr(z->pageset, cpu);
if (pcp->pcp.count) {
has_pcps = true;
break;
}
}
}
if (has_pcps)
cpumask_set_cpu(cpu, &cpus_with_pcps);
else
cpumask_clear_cpu(cpu, &cpus_with_pcps);
}
for_each_cpu(cpu, &cpus_with_pcps) {
struct pcpu_drain *drain = per_cpu_ptr(&pcpu_drain, cpu);
drain->zone = zone;
INIT_WORK(&drain->work, drain_local_pages_wq);
queue_work_on(cpu, mm_percpu_wq, &drain->work);
}
for_each_cpu(cpu, &cpus_with_pcps)
flush_work(&per_cpu_ptr(&pcpu_drain, cpu)->work);
mutex_unlock(&pcpu_drain_mutex);
}
지정된 zone의 모든 online cpu에 있는 Per-CPU Page Frame Cache를 버디 메모리 할당자로 옮긴다. zone을 지정하지 않은 경우는 모든 populated zone에 대해 수행한다.
drain_local_pages()
mm/page_alloc.c
/* * Spill all of this CPU's per-cpu pages back into the buddy allocator. * * The CPU has to be pinned. When zone parameter is non-NULL, spill just * the single zone's pages. */
void drain_local_pages(struct zone *zone)
{
int cpu = smp_processor_id();
if (zone)
drain_pages_zone(cpu, zone);
else
drain_pages(cpu);
}
drain_pages()
mm/page_alloc.c
/* * Drain pcplists of all zones on the indicated processor. * * The processor must either be the current processor and the * thread pinned to the current processor or a processor that * is not online. */
static void drain_pages(unsigned int cpu)
{
struct zone *zone;
for_each_populated_zone(zone) {
drain_pages_zone(cpu, zone);
}
}
활성화된 zone 모두에 대해 Per-Cpu Page Fram Cache를 비운다.
drain_pages_zone()
mm/page_alloc.c
/* * Drain pcplists of the indicated processor and zone. * * The processor must either be the current processor and the * thread pinned to the current processor or a processor that * is not online. */
static void drain_pages_zone(unsigned int cpu, struct zone *zone)
{
unsigned long flags;
struct per_cpu_pageset *pset;
struct per_cpu_pages *pcp;
local_irq_save(flags);
pset = per_cpu_ptr(zone->pageset, cpu);
pcp = &pset->pcp;
if (pcp->count)
free_pcppages_bulk(zone, pcp->count, pcp);
local_irq_restore(flags);
}
요청 zone에 대한 Per-Cpu Page Fram Cache에 등록된 페이지들 모두 buddy 시스템으로 이주시킨다.
참고
- Zoned Allocator -1- (물리 페이지 할당-Fastpath) | 문c
- Zoned Allocator -2- (물리 페이지 할당-Slowpath) | 문c
- Zoned Allocator -3- (Buddy 페이지 할당) | 문c
- Zoned Allocator -4- (Buddy 페이지 해지) | 문c
- Zoned Allocator -5- (Per-CPU Page Frame Cache) | 문c – 현재 글
- Zoned Allocator -6- (Watermark) | 문c
- Zoned Allocator -7- (Direct Compact) | 문c
- Zoned Allocator -8- (Direct Compact-Isolation) | 문c
- Zoned Allocator -9- (Direct Compact-Migration) | 문c
- Zoned Allocator -10- (LRU & pagevec) | 문c
- Zoned Allocator -11- (Direct Reclaim) | 문c
- Zoned Allocator -12- (Direct Reclaim-Shrink-1) | 문c
- Zoned Allocator -13- (Direct Reclaim-Shrink-2) | 문c
- Zoned Allocator -14- (Kswapd) | 문c
- setup_per_cpu_pageset() | 문c
- page_alloc_init() | 문c
- CPU 비트맵 (API) | 문c