<kernel v5.0>
Zoned Allocator -7- (Direct Compact)
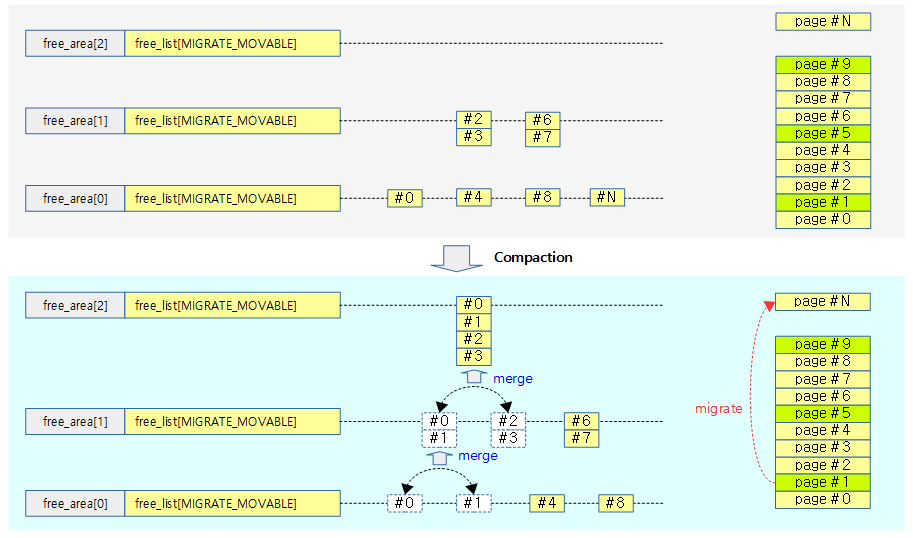
Compaction
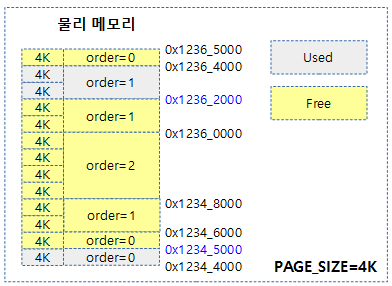
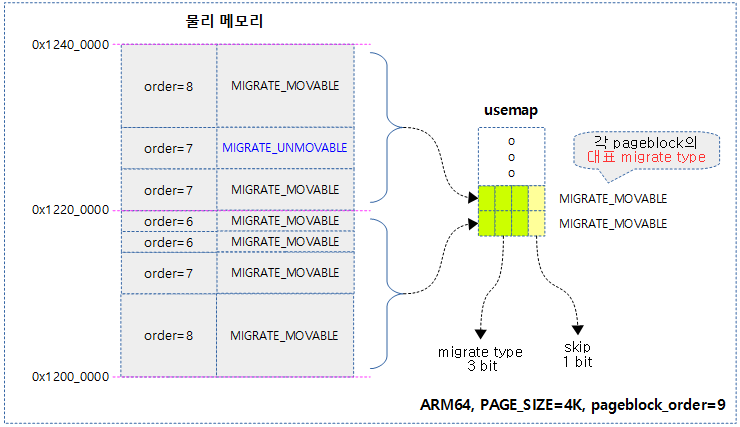
요청한 order 페이지에 대해 그 보다 많은 free 페이지가 있지만 그 페이지들이 파편화되어 높은 order 페이지 할당 요청에 대응하지 못하는 경우가 발생할 수 있다. 이러한 경우 사용중인 movable 페이지를 다른 곳으로 migration하여 연속된 free 페이지를 확보하는 방법을 compaction이라 한다.
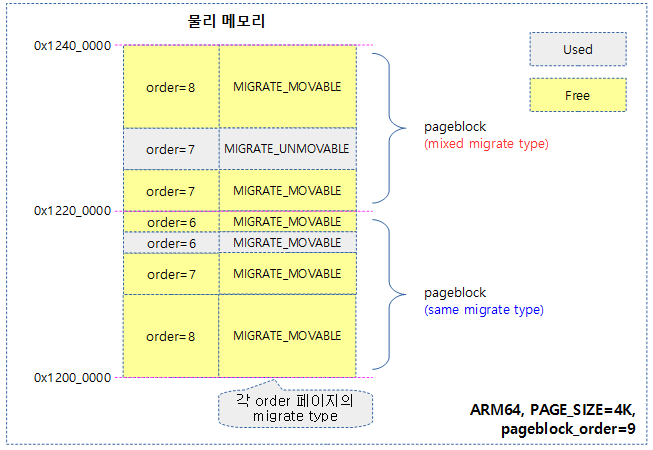
- movable 페이지들은 사용자 영역에서 할당한 메모리나 file에 해당한다. 커널이 할당한 unmovable 페이지들은 compaction할 수 없다.
다음 그림은 order 2 페이지 할당 요청에 대해 compaction이 수행되는 모습을 보여준다.
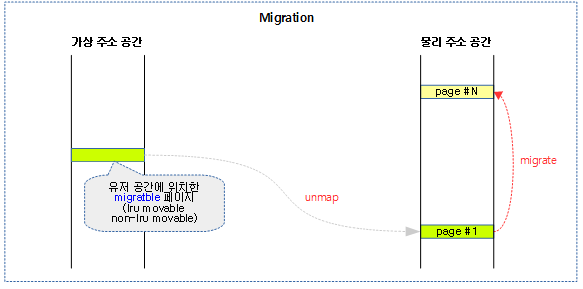
migration
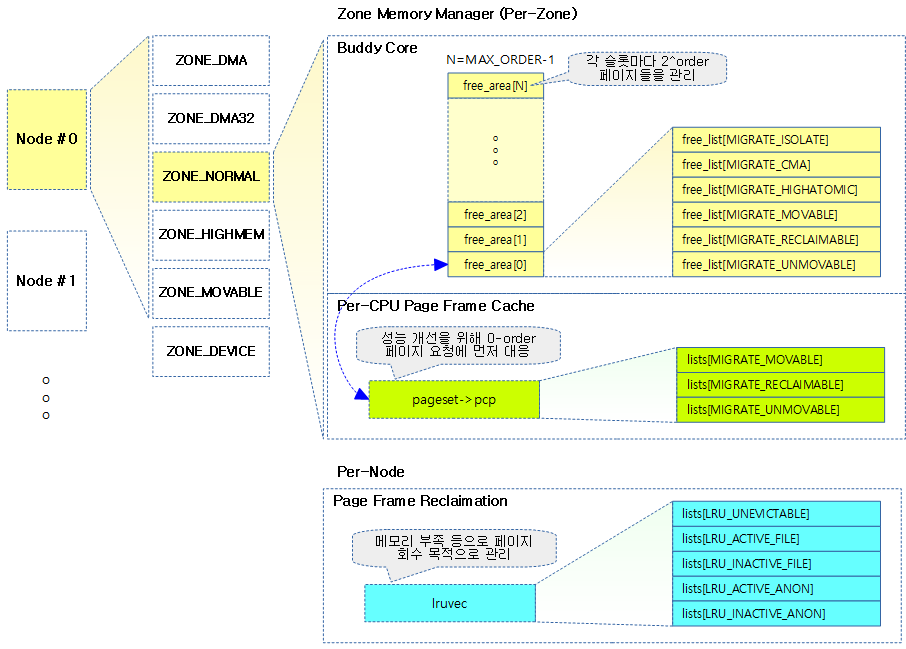
다음 그림과 같이 유저 공간에서 사용되는 migratble 페이지를 다른 물리 주소로 migrate(copy)하는 방법을 보여준다.
- migration 시 cpu가 페이지의 복사를 수행하지 않고 cpu cost를 낮추기 위해 DMA에 의해 복사를 수행하는 경우도 있다.
- migrate가 완료된 후 곧바로 가상 주소 공간에 매핑하지는 않는다. 추후 migrate된 페이지에 접근하는 경우 그 때 가상 주소는 변경 없이 물리 주소만 변경된 새로운 매핑이 맺어진다.
migratable 페이지
사용 중인 물리 페이지를 다른 물리 페이지로 옮길 수 있는 페이지이다. 다음과 같은 종류가 가능한다.
- lru movable 페이지
- LRU로 관리되는 movable 페이지는 커널 페이지 관리자가 직접 migration 가능한 페이지이다.
- non-lru movable 페이지
- LRU에서 관리되지 않는 페이지들은 기본적으로 migration이 불가능하다. 그러나 migration이 구현된 드라이버의 페이지들은 migration이 가능하고 이를 non-lru movable 페이지라고 한다.
- 예) zsram, balloon 메모리 드라이버
- LRU에서 관리되지 않는 페이지들은 기본적으로 migration이 불가능하다. 그러나 migration이 구현된 드라이버의 페이지들은 migration이 가능하고 이를 non-lru movable 페이지라고 한다.
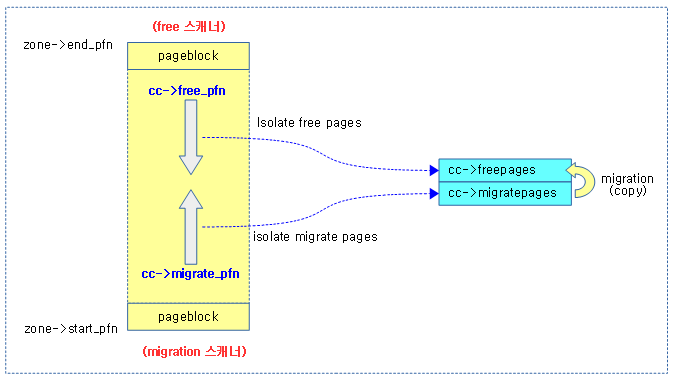
free 스캐너 & migrate 스캐너
compaction이 진행되면 존 내에서 다음 두 개의 스캐너가 각 페이지 블럭을 스캐닝하기 시작한다.
- free 스캐너
- 최상위 페이지 블럭부터 아래 방향으로 free 페이지를 찾는다.
- migrate 스캐너
- 최하위 페이지 블럭부터 윗 방향으로 사용 중인 migratable 페이지를 찾는다.
다음 그림과 같이 migrate 스캐너가 찾은 사용 중인 migratable 페이지를 free 스캐너가 찾은 free 페이지로 migration 하는 과정을 볼 수 있다.
compact_priority
include/linux/compaction.h
/* * Determines how hard direct compaction should try to succeed. * Lower value means higher priority, analogically to reclaim priority. */
enum compact_priority {
COMPACT_PRIO_SYNC_FULL,
MIN_COMPACT_PRIORITY = COMPACT_PRIO_SYNC_FULL,
COMPACT_PRIO_SYNC_LIGHT,
MIN_COMPACT_COSTLY_PRIORITY = COMPACT_PRIO_SYNC_LIGHT,
DEF_COMPACT_PRIORITY = COMPACT_PRIO_SYNC_LIGHT,
COMPACT_PRIO_ASYNC,
INIT_COMPACT_PRIORITY = COMPACT_PRIO_ASYNC
};
compactin 시도 시 성공을 위한 3 단계 우선 순위이다.
- COMPACT_PRIO_SYNC_FULL(0) & MIN_COMPACT_PRIORITY
- 가장 높은 우선 순위로 compaction 및 migration이 full sync로 동작한다.
- COMPACT_PRIO_SYNC_LIGHT(1) & MIN_COMPACT_COSTLY_PRIORITY & DEF_COMPACT_PRIORITY
- 디폴트 및 중간 우선 순위로 compaction이 sync로 동작하지만 migration은 async로 동작한다.
- COMPACT_PRIO_ASYNC(2) & INIT_COMPACT_PRIORITY
- 초기 및 가장 낮은 우선 순위로 compaction 및 migration이 async로 동작한다.
migrate_mode
include/linux/migrate_mode.h
/* * MIGRATE_ASYNC means never block * MIGRATE_SYNC_LIGHT in the current implementation means to allow blocking * on most operations but not ->writepage as the potential stall time * is too significant * MIGRATE_SYNC will block when migrating pages */
enum migrate_mode {
MIGRATE_ASYNC,
MIGRATE_SYNC_LIGHT,
MIGRATE_SYNC,
MIGRATE_SYNC_NO_COPY
};
페이지를 migration할 때 사용하는 모드이다.
- MIGRATE_ASYNC
- 비동기 migration 모드로 동작하여 블러킹되지 않는다.
- async compaction 동작 시 사용된다.
- MIGRATE_SYNC_LIGHT
- writepage를 제외한 대부분을 동기 모드로 동작한다.
- kcompactd 에서 사용
- sync compaction 동작 시 사용된다.
- MIGRATE_SYNC
- 동기 migration 모드로 동작하여 블러킹된다.
- MIGRATE_SYNC_NO_COPY
- 동기 migration 모드로 동작하여 블러킹되지만, migration 페이지에 대해 cpu가 복사를 하지 않고 DMA를 활용하여 복사하게 한다.
Compaction 동작 모드
compaction은 다음과 같이 3가지 방법이 있다.
- direct-compaction
- order 만큼의 free 페이지 할당 요청 시 메모리 부족으로 인하여 해당 order의 할당이 어려울 때 compaction이 수행될 때 이를 페이지 할당 API 내부에서 직접 호출하는 방식이다.
- manual-compaction
- order와 관계없이 다음 명령을 통해 매뉴얼하게 요청한다.
- “echo 1 > /proc/sys/vm/compact_memory”
- order와 관계없이 다음 명령을 통해 매뉴얼하게 요청한다.
- kcompactd
- 메모리 부족 시 자동으로 wake되어 백그라운드에서 compaction을 수행한다.
Manual Compaction
다음과 같이 order별 페이지 상태를 확인해본다.
# cat /proc/pagetypeinfo Page block order: 10 Pages per block: 1024 Free pages count per migrate type at order 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Node 0, zone DMA, type Unmovable 485 196 50044 12 5 0 0 1 1 1 0 Node 0, zone DMA, type Movable 22 69 66 51 46 30 21 11 8 1 386 Node 0, zone DMA, type Reclaimable 50 25 11 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 Node 0, zone DMA, type HighAtomic 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Node 0, zone DMA, type CMA 1284 886 567 319 149 81 46 31 11 10 61 Node 0, zone DMA, type Isolate 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Number of blocks type Unmovable Movable Reclaimable HighAtomic CMA Isolate Node 0, zone DMA 403 417 6 0 124 0
movable 페이지를 compaction 하기 위해 다음 명령을 통해 매뉴얼 compaction을 진행해본다.
echo 1 > /proc/sys/vm/compact_memory
다음과 같이 movable 페이지의 일부가 compaction이 된 결과를 확인할 수 있다. 다만 커널이 사용했었던 unmovable 페이지들은 compaction이 안되는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
# cat /proc/pagetypeinfo Page block order: 10 Pages per block: 1024 Free pages count per migrate type at order 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Node 0, zone DMA, type Unmovable 489 196 50044 11 5 0 0 1 1 1 0 Node 0, zone DMA, type Movable 22 43 36 32 27 24 18 14 9 1 386 Node 0, zone DMA, type Reclaimable 69 26 11 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 Node 0, zone DMA, type HighAtomic 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Node 0, zone DMA, type CMA 1189 814 521 292 134 75 42 30 12 9 63 Node 0, zone DMA, type Isolate 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Number of blocks type Unmovable Movable Reclaimable HighAtomic CMA Isolate Node 0, zone DMA 403 417 6 0 124 0
kcomactd
메모리 부족 시 자동으로 wake되어 백그라운드에서 compaction을 수행하며 kernel v4.6-rc1에서 소개되었다.
- 참고
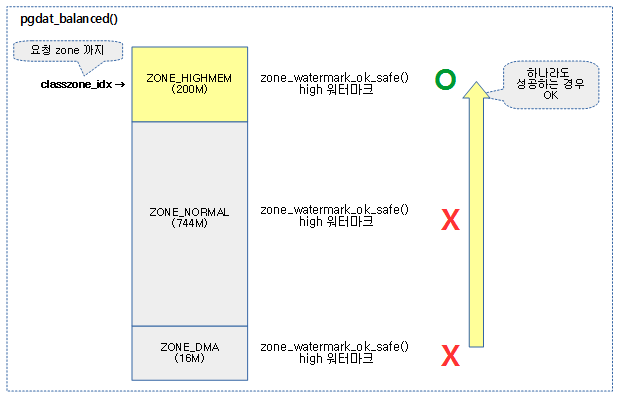
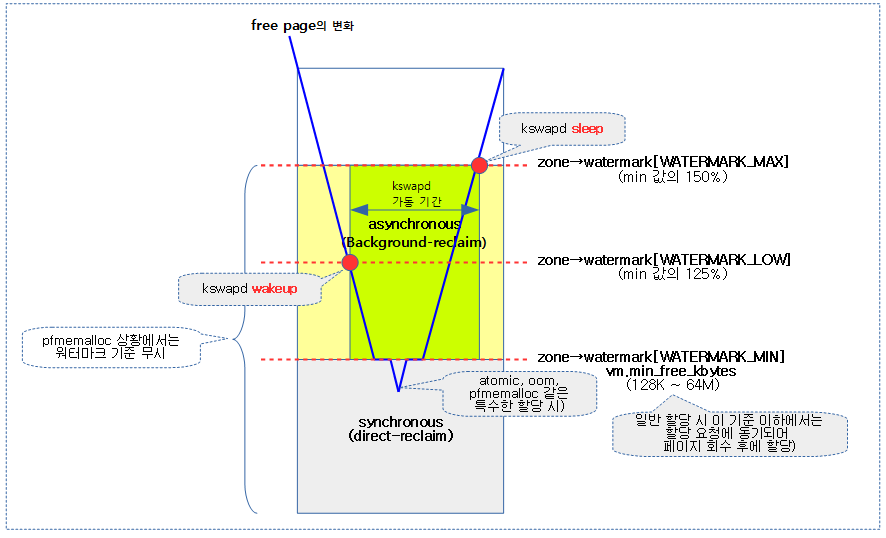
밸런싱 판단
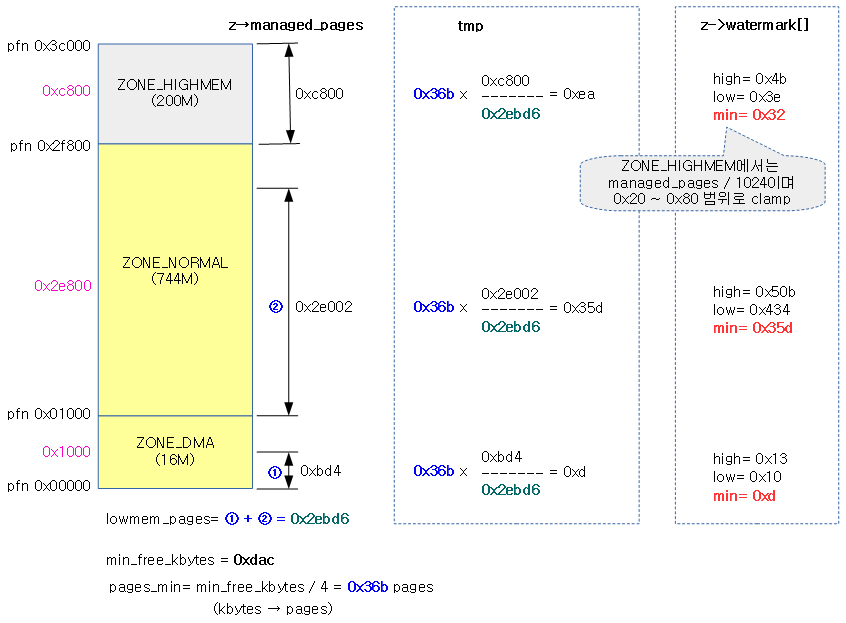
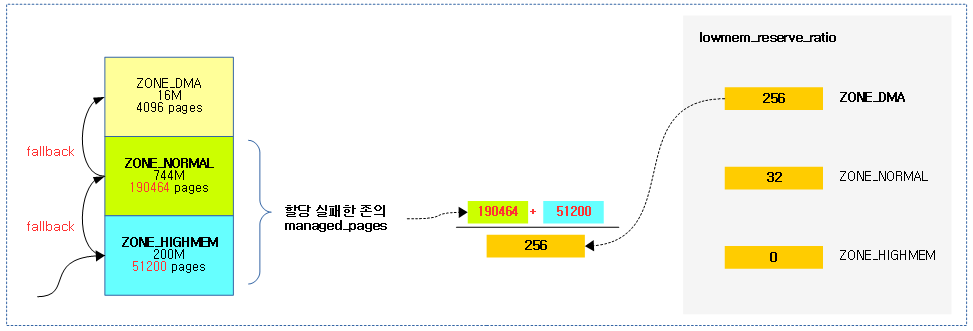
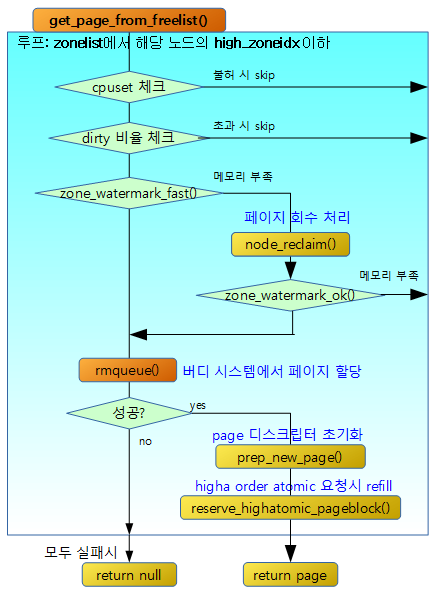
high 워터마크 이상에서 요청한 2^order 페이지의 할당이 가능한 상태인지 여부를 체크한다.
pgdat_balanced()
mm/vmscan.c
/* * Returns true if there is an eligible zone balanced for the request order * and classzone_idx */
static bool pgdat_balanced(pg_data_t *pgdat, int order, int classzone_idx)
{
int i;
unsigned long mark = -1;
struct zone *zone;
/*
* Check watermarks bottom-up as lower zones are more likely to
* meet watermarks.
*/
for (i = 0; i <= classzone_idx; i++) {
zone = pgdat->node_zones + i;
if (!managed_zone(zone))
continue;
mark = high_wmark_pages(zone);
if (zone_watermark_ok_safe(zone, order, mark, classzone_idx))
return true;
}
/*
* If a node has no populated zone within classzone_idx, it does not
* need balancing by definition. This can happen if a zone-restricted
* allocation tries to wake a remote kswapd.
*/
if (mark == -1)
return true;
return false;
}
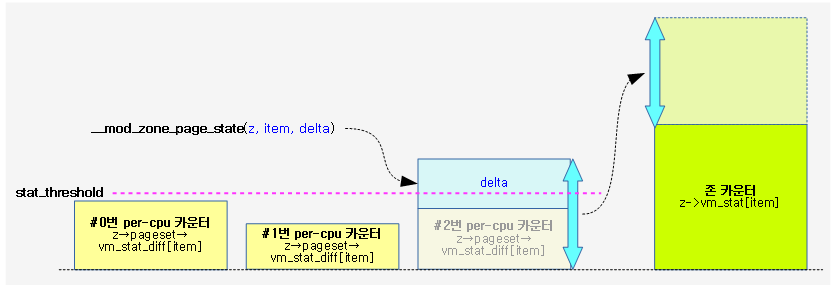
노드의 @classzone_idx 이하의 존에 대해 밸런스 유무를 반환한다. free page가 high 워터마크 초과 여부를 판단하여 밸런스가 잡혀있는지 유무를 판단한다.
- 코드 라인 11~20에서 0번 존에서 @classzone_idx 존까지 순회하며 high 워터마크 이상에서 order 페이지를 확보가능하면 tuue를 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 27~28에서 managed 페이지가 하나도 없는 경우 밸런싱 작업이 필요 없으므로 true를 반환한다.
다음 그림과 같이 요청한 노드의 classzone_idx 존까지 밸런스가 잡힌 경우 true를 반환한다.
compaction 수행 조건
compaction 지속 여부 확인
compaction_suitable()
mm/compaction.c
enum compact_result compaction_suitable(struct zone *zone, int order,
unsigned int alloc_flags,
int classzone_idx)
{
enum compact_result ret;
int fragindex;
ret = __compaction_suitable(zone, order, alloc_flags, classzone_idx,
zone_page_state(zone, NR_FREE_PAGES));
/*
* fragmentation index determines if allocation failures are due to
* low memory or external fragmentation
*
* index of -1000 would imply allocations might succeed depending on
* watermarks, but we already failed the high-order watermark check
* index towards 0 implies failure is due to lack of memory
* index towards 1000 implies failure is due to fragmentation
*
* Only compact if a failure would be due to fragmentation. Also
* ignore fragindex for non-costly orders where the alternative to
* a successful reclaim/compaction is OOM. Fragindex and the
* vm.extfrag_threshold sysctl is meant as a heuristic to prevent
* excessive compaction for costly orders, but it should not be at the
* expense of system stability.
*/
if (ret == COMPACT_CONTINUE && (order > PAGE_ALLOC_COSTLY_ORDER)) {
fragindex = fragmentation_index(zone, order);
if (fragindex >= 0 && fragindex <= sysctl_extfrag_threshold)
ret = COMPACT_NOT_SUITABLE_ZONE;
}
trace_mm_compaction_suitable(zone, order, ret);
if (ret == COMPACT_NOT_SUITABLE_ZONE)
ret = COMPACT_SKIPPED;
return ret;
}
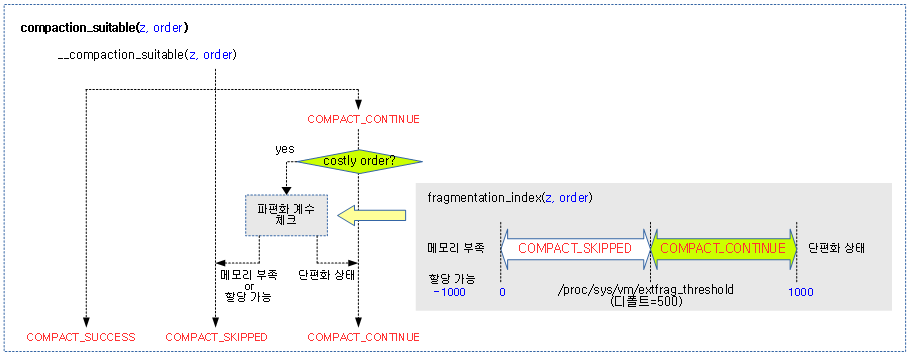
요청 zone에서 2^order 페이지의 할당을 위해 compaction 수행 적합 결과를 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 8~9에서 compaction 지속 여부에 대한 결과를 알아온다.
- 코드 라인 26~34에서 costly order 페이지 요청이 continue 결과 판정인 경우 파편화 계수 값을 확인하여 compaction이 힘들다 판단하면 COMPACT_SKIPPED를 리턴 값으로 변경한다.
- 단편화 계수가 [0, sysctl_extfrag_threshold] 범위이면 compaction을 하지 않을 목적이다.
- sysctl_extfrag_threshold
- 디폴트 값은 500이다.
- “proc/sys/vm/extfrag_threshold” 파일을 사용하여 값을 변경할 수 있다.
다음 그림은 compaction 지속 여부의 결과가 반환되는 모습을 보여주는데, costly order 요청이 continue 결과 판정일 때 정말 continue해도 되는지 단편화 계수를 추가로 확인하는 과정을 보여준다.
compact_result
include/linux/compaction.h
/* Return values for compact_zone() and try_to_compact_pages() */
/* When adding new states, please adjust include/trace/events/compaction.h */
enum compact_result {
/* For more detailed tracepoint output - internal to compaction */
COMPACT_NOT_SUITABLE_ZONE,
/*
* compaction didn't start as it was not possible or direct reclaim
* was more suitable
*/
COMPACT_SKIPPED,
/* compaction didn't start as it was deferred due to past failures */
COMPACT_DEFERRED,
/* compaction not active last round */
COMPACT_INACTIVE = COMPACT_DEFERRED,
/* For more detailed tracepoint output - internal to compaction */
COMPACT_NO_SUITABLE_PAGE,
/* compaction should continue to another pageblock */
COMPACT_CONTINUE,
/*
* The full zone was compacted scanned but wasn't successfull to compact
* suitable pages.
*/
COMPACT_COMPLETE,
/*
* direct compaction has scanned part of the zone but wasn't successfull
* to compact suitable pages.
*/
COMPACT_PARTIAL_SKIPPED,
/* compaction terminated prematurely due to lock contentions */
COMPACT_CONTENDED,
/*
* direct compaction terminated after concluding that the allocation
* should now succeed
*/
COMPACT_SUCCESS,
};
compaction 시도 전 확인 결과 또는 compaction 수행 후 결과 값이다.
- COMPACT_NOT_SUITABLE_ZONE
- trace 디버그 출력 또는 내부용으로 사용된다.
- COMPACT_SKIPPED
- compaction을 수행할 수 없는 상태이거나 direct-reclaim이 더 적합한 경우라서 compaction을 skip 한다.
- COMPACT_DEFERRED & COMPACT_INACTIVE
- 지난 compaction 수행 시 실패하였기 때문에 이 번에는 유예시키기 위해 compaction을 skip 한다.
- COMPACT_NO_SUITABLE_PAGE
- trace 디버그 출력 또는 내부용으로 사용된다.
- COMPACT_CONTINUE
- 다른 페이지 블럭을 계속 compaction 진행되어야 한다.
- manual compaction의 경우 관련 영역의 모든 블럭이 완료될 때까지 진행한다.
- COMPACT_COMPLETE
- 모든 존에 대해 compaction이 완료하였지만, compaction을 통해 할당 가능한 페이지를 확보하지 못한 상태이다.
- COMPACT_PARTIAL_SKIPPED
- 존의 일부에 대해서 direct compaction을 수행하였으나 아직 할당 가능한 페이지의 확보는 성공하지 못한 상태이다.
- COMPACT_CONTENDED
- lock 경합으로 인해 compaction이 조기에 종료되었다.
- COMPACT_SUCCESS
- 할당 가능한 페이지를 확보한 후에 direct compaction이 종료되었다.
__compaction_suitable()
mm/compaction.c
/* * compaction_suitable: Is this suitable to run compaction on this zone now? * Returns * COMPACT_SKIPPED - If there are too few free pages for compaction * COMPACT_PARTIAL - If the allocation would succeed without compaction * COMPACT_CONTINUE - If compaction should run now */
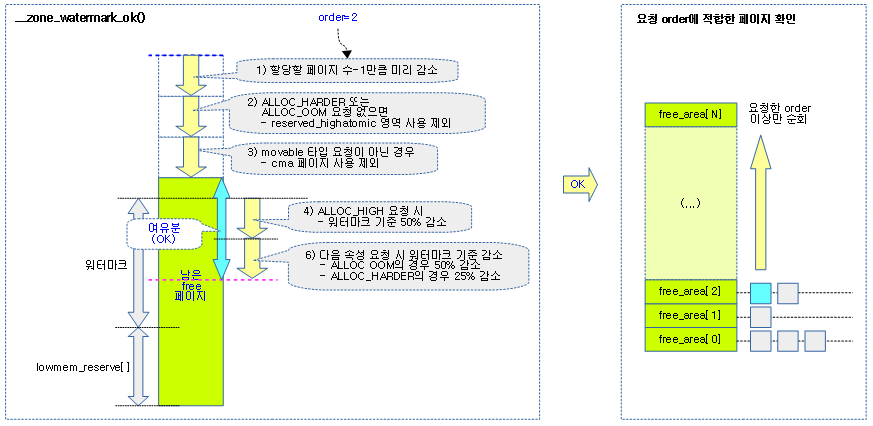
static enum compact_result __compaction_suitable(struct zone *zone, int order,
unsigned int alloc_flags,
int classzone_idx,
unsigned long wmark_target)
{
unsigned long watermark;
if (is_via_compact_memory(order))
return COMPACT_CONTINUE;
watermark = wmark_pages(zone, alloc_flags & ALLOC_WMARK_MASK);
/*
* If watermarks for high-order allocation are already met, there
* should be no need for compaction at all.
*/
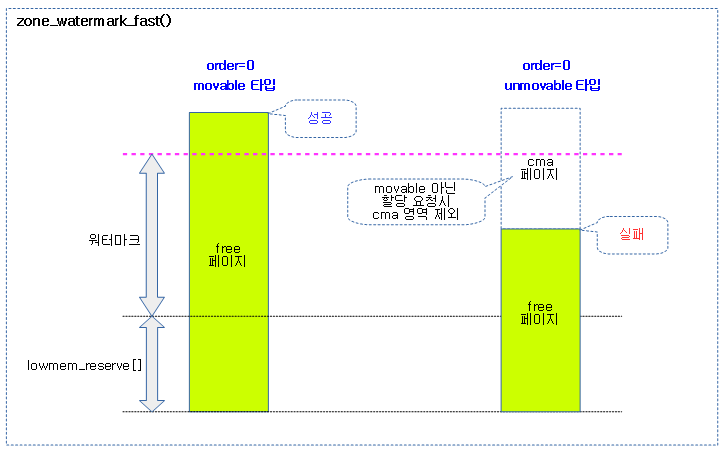
if (zone_watermark_ok(zone, order, watermark, classzone_idx,
alloc_flags))
return COMPACT_SUCCESS;
/*
* Watermarks for order-0 must be met for compaction to be able to
* isolate free pages for migration targets. This means that the
* watermark and alloc_flags have to match, or be more pessimistic than
* the check in __isolate_free_page(). We don't use the direct
* compactor's alloc_flags, as they are not relevant for freepage
* isolation. We however do use the direct compactor's classzone_idx to
* skip over zones where lowmem reserves would prevent allocation even
* if compaction succeeds.
* For costly orders, we require low watermark instead of min for
* compaction to proceed to increase its chances.
* ALLOC_CMA is used, as pages in CMA pageblocks are considered
* suitable migration targets
*/
watermark = (order > PAGE_ALLOC_COSTLY_ORDER) ?
low_wmark_pages(zone) : min_wmark_pages(zone);
watermark += compact_gap(order);
if (!__zone_watermark_ok(zone, 0, watermark, classzone_idx,
ALLOC_CMA, wmark_target))
return COMPACT_SKIPPED;
return COMPACT_CONTINUE;
}
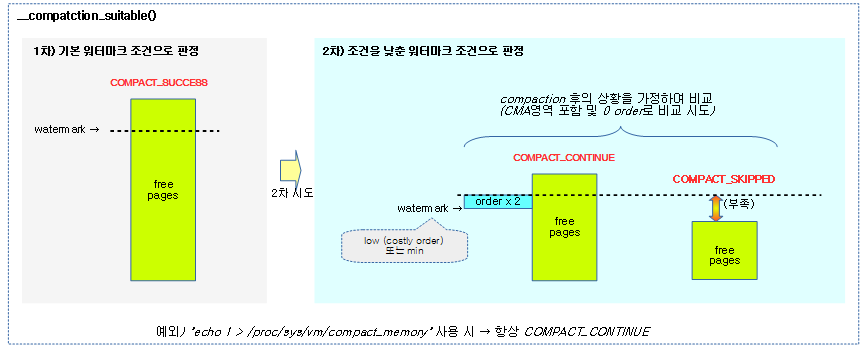
요청 zone과 order를 사용하여 compaction을 진행 여부에 결과를 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 8~9에서 유저가 compaction을 요청한 경우 무조건 진행하게 하기 위해 COMPACT_CONTINUE를 반환한다.
- “echo 1 > /proc/sys/vm/compact_memory”로 compaction을 요청할 수 있다.
- 코드 라인 11에서 요청 존의 워터마크를 알아온다.
- 코드 라인 16~18에서 1차로 워터마크 이상의 free 페이지가 확보된 경우 compaction이 더 이상 필요 없는 상황으로 COMPACT_SUCCESS를 반환한다.
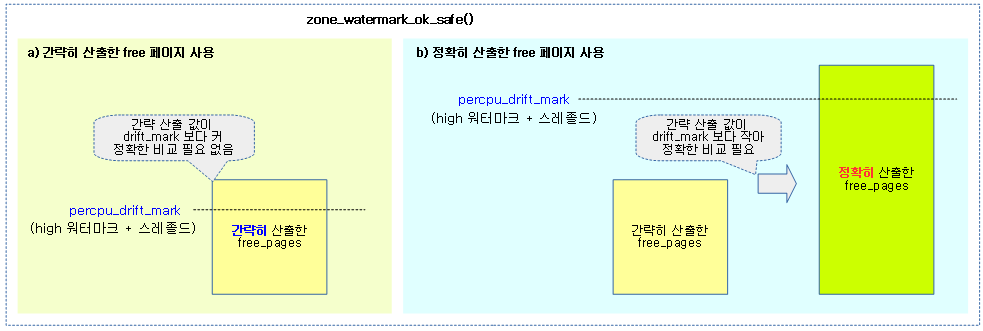
- 코드 라인 34~41에서 2차로 compaction이 완료된 상황을 가정한 상황으로 비교하여 그 결과 여전히 메모리가 부족한 경우라 판단하면 COMPACT_SKIPPED를 반환하고, 페이지 확보 가능성이 있는 경우 COMPACT_CONTINUE를 반환한다.
- costly high order 요청인 경우 low 워터마크 기준으로, 그리고 낮은 order 요청인 경우 min 워터마크 기준을 사용한다.
- compaction을 진행하는 잠시 동안 페이지들을 복사하여 할당을 하므로, 요청 order 페이지 수의 두 배를 워터마크 값에 더한 값으로 cma 영역을 포함하여 0 order 페이지 기준으로 낮춰 비교할 때 할당 가능 여부를 판단한다.
다음 그림은 compaction을 계속 수행해도 되는지알아보는 과정을 보여준다.
- 2차 조건에서는 compaction 상황 후를 가정하여 0 order로 기준을 변경한 워터마크와 비교한다.
단편화 계수 산출
fragmentation_index()
mm/vmstat.c
/* Same as __fragmentation index but allocs contig_page_info on stack */
int fragmentation_index(struct zone *zone, unsigned int order)
{
struct contig_page_info info;
fill_contig_page_info(zone, order, &info);
return __fragmentation_index(order, &info);
}
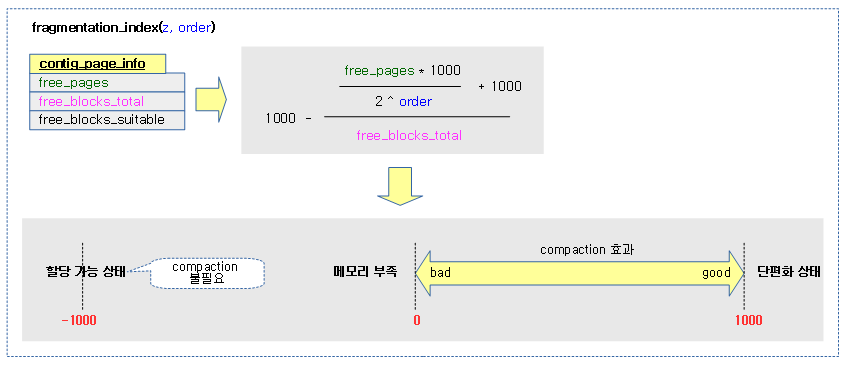
compaction을 해야할지 여부를 판단하기 위해 요청 zone과 order에 대한 단편화 계수를 알아온다. 단편화 계수 값은 -1000을 반환하면 할당할 페이지가 있으므로 compaction이 필요 없는 상태이다. 그 외의 경우는 0 ~ 1000 범위 이내의 값으로 sysctl_extfrag_threshold 이하인 경우 compaction을 하지 않을 목적이다.
- 코드 라인 6에서 지정된 zone의 버디 시스템에서 전체 free 블럭, 전체 free page 및 order 페이지의 할당 가능한 free 블럭 수 정보를 info에 담아온다.
- 코드 라인 7에서 요청 order와 contig_page 정보를 사용하여 단편화 계수를 계산해온다.
다음 그림은 단편화 계수의 값을 산출하는 과정을 보여준다.
fill_contig_page_info()
mm/vmstat.c
/* * Calculate the number of free pages in a zone, how many contiguous * pages are free and how many are large enough to satisfy an allocation of * the target size. Note that this function makes no attempt to estimate * how many suitable free blocks there *might* be if MOVABLE pages were * migrated. Calculating that is possible, but expensive and can be * figured out from userspace */
static void fill_contig_page_info(struct zone *zone,
unsigned int suitable_order,
struct contig_page_info *info)
{
unsigned int order;
info->free_pages = 0;
info->free_blocks_total = 0;
info->free_blocks_suitable = 0;
for (order = 0; order < MAX_ORDER; order++) {
unsigned long blocks;
/* Count number of free blocks */
blocks = zone->free_area[order].nr_free;
info->free_blocks_total += blocks;
/* Count free base pages */
info->free_pages += blocks << order;
/* Count the suitable free blocks */
if (order >= suitable_order)
info->free_blocks_suitable += blocks <<
(order - suitable_order);
}
}
지정된 zone의 버디 시스템에서 전체 free 블럭, 전체 free page 및 suitable_order의 할당 가능한 free 블럭 수 정보를 info에 contig_page_info 구조체로 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 11~16에서 zone이 관리하는 버디 시스템의 order별 리스트를 순회하며 전체 free 블럭 수를 합산한다.
- 코드 라인 19에서 free 페이지 수를 합산한다.
- 코드 라인 22~24에서 요청 order 이상의 free 블럭 수를 합산한다.
contig_page_info 구조체
mm/vmstat.c
#ifdef CONFIG_COMPACTION
struct contig_page_info {
unsigned long free_pages;
unsigned long free_blocks_total;
unsigned long free_blocks_suitable;
};
#endif
요청한 order에 대한 단편화 계수를 산출하기 위한 정보이다.
- free_pages
- 버디 시스템에서 관리되고 있는 모든 free 페이지 수
- 예) order 3 페이지 2 개 있는 경우
- 16(2^3 * 2)페이지
- free_blocks_total
- 버디 시스템에서 관리되고 있는 모든 free 블럭(대표 페이지) 수
- 예) order 3 페이지 2 개 있는 경우
- 2
- free_blocks_suitable
- 요청한 order를 만족시키는 free 블럭(대표 페이지) 수
__fragmentation_index()
mm/vmstat.c
/* * A fragmentation index only makes sense if an allocation of a requested * size would fail. If that is true, the fragmentation index indicates * whether external fragmentation or a lack of memory was the problem. * The value can be used to determine if page reclaim or compaction * should be used */
static int __fragmentation_index(unsigned int order, struct contig_page_info *info)
{
unsigned long requested = 1UL << order;
if (WARN_ON_ONCE(order >= MAX_ORDER))
return 0;
if (!info->free_blocks_total)
return 0;
/* Fragmentation index only makes sense when a request would fail */
if (info->free_blocks_suitable)
return -1000;
/*
* Index is between 0 and 1 so return within 3 decimal places
*
* 0 => allocation would fail due to lack of memory
* 1 => allocation would fail due to fragmentation
*/
return 1000 - div_u64( (1000+(div_u64(info->free_pages * 1000ULL, requested))), info->free_blocks_total);
}
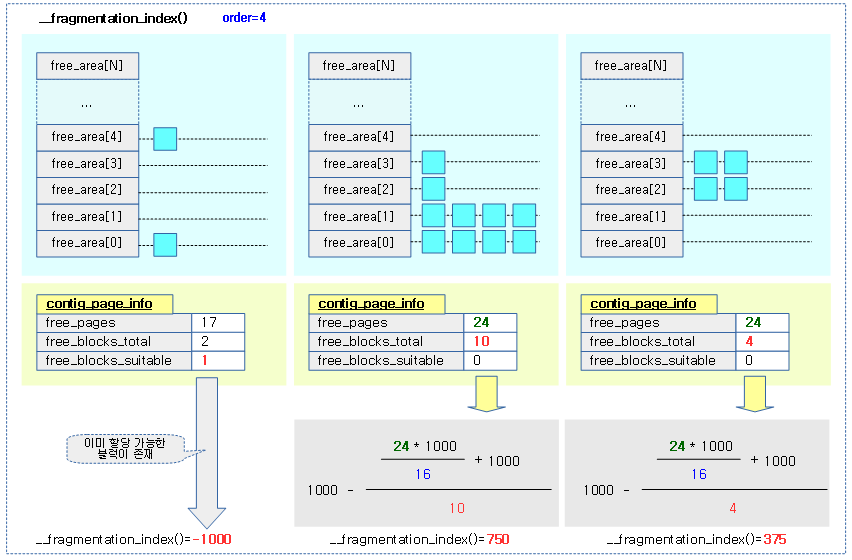
요청 order와 free 페이지 및 free 블럭 정보를 사용하여 단편화 계수를 반환한다.
- 0에 가까운 값 (낮은 단편화 계수)
- 은 메모리 부족으로 인해 할당이 실패될 상황이다.
- 이후에 compaction 해도 할당 실패될 가능성 높은 상태
- 1000에 가까운 값 (높은 단편화 계수)
- 단편화로 인해 할당이 실패될 상황이다.
- compaction 하면 할당 성공할 가능성 높은 상태
- -1000 (할당 가능한 상태)
- 요청 order 블럭이 존재하여 할당이 가능한 상태이다.
- compaction이 필요하지 않다
- 코드 라인 5~6에서 최대 버디 order를 초과하는 order를 페이지를 요청하는 경우 0을 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 8~9에서 전체 free block 수가 0인 경우 compaction을 할 수 없어 0을 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 12~13에서 요청 order 페이지를 처리할 수 있는 free block이 있는 경우 compaction이 필요 없으므로 -1000을 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 21에서 1000 – (전체 free page x 1000 / 필요 page 수 + 1000) / 전체 free block 수
- 0에 가까울 수록 메모리 부족으로 compaction을 허용하지 않는것이 좋다.
- 1000에 가까울 수록 파편화된 페이지에 대해 compaction하는 것이 좋다.
다음 그림은 단편화 계수의 값을 산출하는 과정을 보여준다.
Compaction 수행
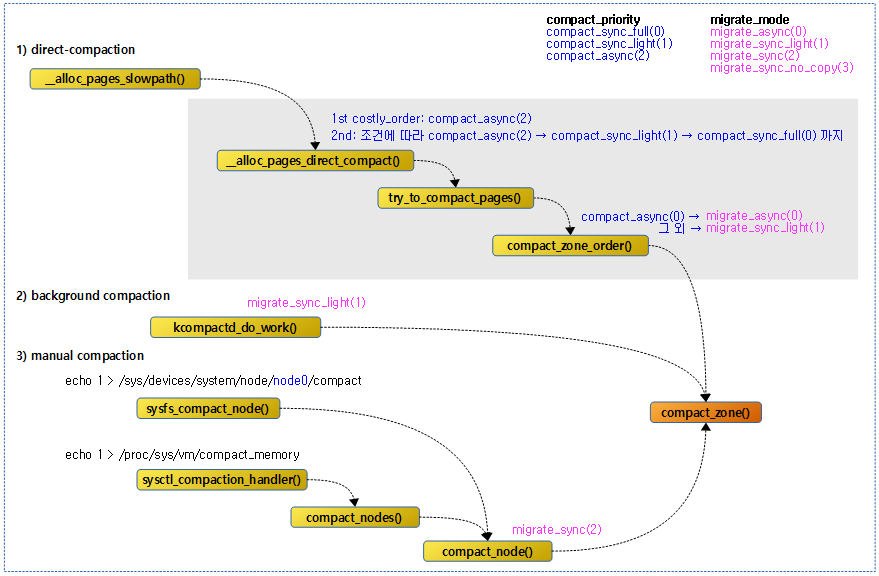
다음 그림은 compaction이 수행되는 여러 경로를 보여준다.
- compact 우선순위와 migrate 모드도 같이 확인해본다.
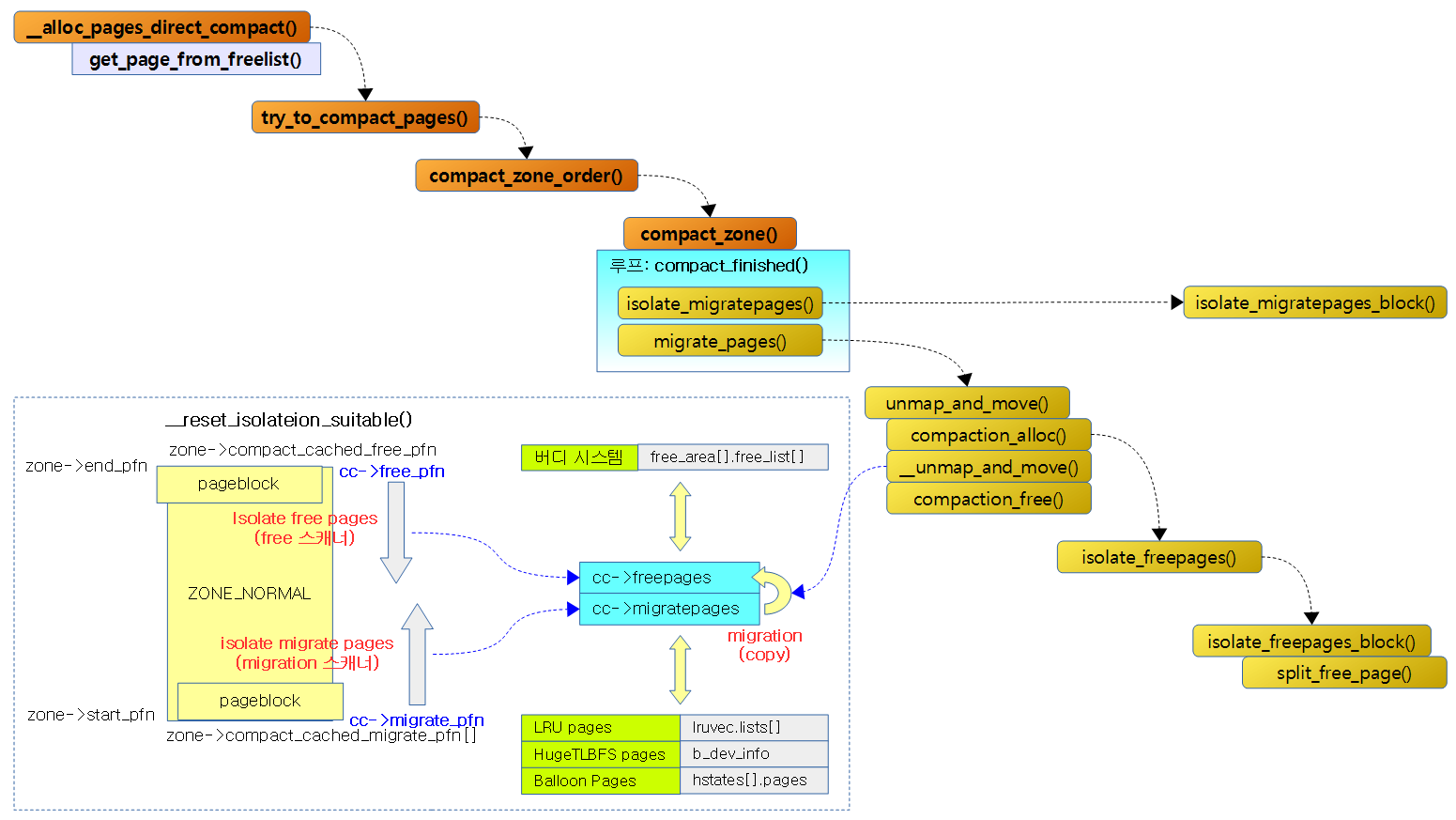
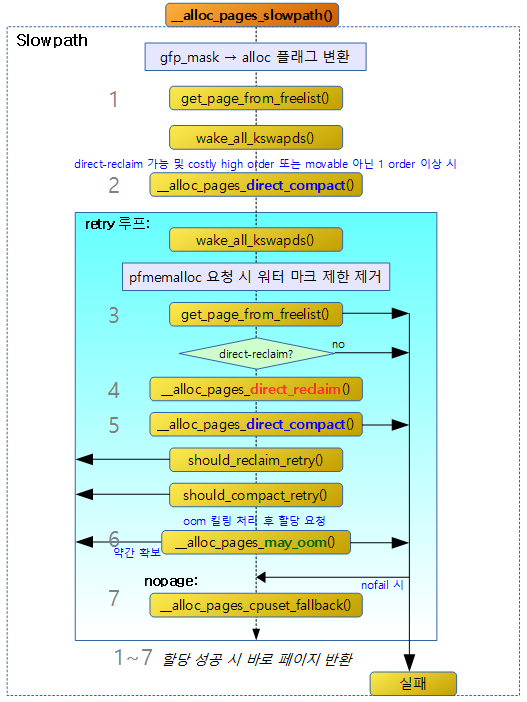
다음 그림은 direct compaction이 수행될 때의 함수 흐름을 보여준다.
Direct-compaction을 사용한 페이지 할당
__alloc_pages_direct_compact()
mm/page_alloc.c
/* Try memory compaction for high-order allocations before reclaim */
static struct page *
__alloc_pages_direct_compact(gfp_t gfp_mask, unsigned int order,
unsigned int alloc_flags, const struct alloc_context *ac,
enum compact_priority prio, enum compact_result *compact_result)
{
struct page *page;
unsigned long pflags;
unsigned int noreclaim_flag;
if (!order)
return NULL;
psi_memstall_enter(&pflags);
noreclaim_flag = memalloc_noreclaim_save();
*compact_result = try_to_compact_pages(gfp_mask, order, alloc_flags, ac,
prio);
memalloc_noreclaim_restore(noreclaim_flag);
psi_memstall_leave(&pflags);
if (*compact_result <= COMPACT_INACTIVE)
return NULL;
/*
* At least in one zone compaction wasn't deferred or skipped, so let's
* count a compaction stall
*/
count_vm_event(COMPACTSTALL);
page = get_page_from_freelist(gfp_mask, order, alloc_flags, ac);
if (page) {
struct zone *zone = page_zone(page);
zone->compact_blockskip_flush = false;
compaction_defer_reset(zone, order, true);
count_vm_event(COMPACTSUCCESS);
return page;
}
/*
* It's bad if compaction run occurs and fails. The most likely reason
* is that pages exist, but not enough to satisfy watermarks.
*/
count_vm_event(COMPACTFAIL);
cond_resched();
return NULL;
}
direct-compaction을 수행한 후 페이지 할당을 시도한다.
- 코드 라인 11~12에서 order가 0인 경우 compaction으로 해결될 수 없으므로 처리하지 않는다.
- 코드 라인 14에서 메모리 부족으로 인한 현재 태스크의 psi 산출을 시작하는 지점이다.
- psi는 2018년 커널 v4.20-rc1에서 소개되었다.
- 참고
- 코드 라인 15에서 direct-compaction을 수행하기 위해 요청한 order 메모리의 2배 만큼의 메모리를 할당해야하는데 현재 메모리 부족 상황이므로 현재 태스크에 pfmemalloc 플래그를 사용하여 워터마크 제한 없이 메모리를 할당할 수 있도록 설정한다.
- 코드 라인 17~18에서 요청 order 페이지를 위해 direct-compaction을 시도하고 compact 진행 상태를 결과로 알아온다.
- 코드 라인 20에서 psi 산출을 종료하는 지점이다.
- 코드 라인 21에서 현재 태스크에서 pfmemalloc 플래그의 사용을 원위치한다.
- 코드 라인 23~24에서 compaction 수행 결과로 inactive 이하이면 더 이상 페이지 확보가 힘든 상황이므로 null을 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 30에서 COMPACTSTALL 카운터를 증가시킨다.
- 코드 라인 32~41에서 페이지 확보를 시도한다. 페이지가 확보된 경우 COMPACTSUCCESS 카운터를 증가시키고, zone의 compact_blockskip_flush에 false를 대입하고 compaction에 대한 트래킹 카운터들을 리셋한 후 페이지를 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 47~51에서 페이지 할당이 실패한 경우 COMPACTFAIL stat을 증가시키고 리스케쥴 필요한 경우 sleep하고 함수를 빠져나간다.
다음 그림은 direct compaction의 함수별 진행 흐름을 보여준다.
try_to_compact_pages()
mm/compaction.c
/** * try_to_compact_pages - Direct compact to satisfy a high-order allocation * @gfp_mask: The GFP mask of the current allocation * @order: The order of the current allocation * @alloc_flags: The allocation flags of the current allocation * @ac: The context of current allocation * @prio: Determines how hard direct compaction should try to succeed * * This is the main entry point for direct page compaction. */
enum compact_result try_to_compact_pages(gfp_t gfp_mask, unsigned int order,
unsigned int alloc_flags, const struct alloc_context *ac,
enum compact_priority prio)
{
int may_perform_io = gfp_mask & __GFP_IO;
struct zoneref *z;
struct zone *zone;
enum compact_result rc = COMPACT_SKIPPED;
/*
* Check if the GFP flags allow compaction - GFP_NOIO is really
* tricky context because the migration might require IO
*/
if (!may_perform_io)
return COMPACT_SKIPPED;
trace_mm_compaction_try_to_compact_pages(order, gfp_mask, prio);
/* Compact each zone in the list */
for_each_zone_zonelist_nodemask(zone, z, ac->zonelist, ac->high_zoneidx,
ac->nodemask) {
enum compact_result status;
if (prio > MIN_COMPACT_PRIORITY
&& compaction_deferred(zone, order)) {
rc = max_t(enum compact_result, COMPACT_DEFERRED, rc);
continue;
}
status = compact_zone_order(zone, order, gfp_mask, prio,
alloc_flags, ac_classzone_idx(ac));
rc = max(status, rc);
/* The allocation should succeed, stop compacting */
if (status == COMPACT_SUCCESS) {
/*
* We think the allocation will succeed in this zone,
* but it is not certain, hence the false. The caller
* will repeat this with true if allocation indeed
* succeeds in this zone.
*/
compaction_defer_reset(zone, order, false);
break;
}
if (prio != COMPACT_PRIO_ASYNC && (status == COMPACT_COMPLETE ||
status == COMPACT_PARTIAL_SKIPPED))
/*
* We think that allocation won't succeed in this zone
* so we defer compaction there. If it ends up
* succeeding after all, it will be reset.
*/
defer_compaction(zone, order);
/*
* We might have stopped compacting due to need_resched() in
* async compaction, or due to a fatal signal detected. In that
* case do not try further zones
*/
if ((prio == COMPACT_PRIO_ASYNC && need_resched())
|| fatal_signal_pending(current))
break;
}
return rc;
}
요청 order를 위해 compaction을 시도하고 compact 진행 상태를 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 14~15에서 compaction을 하는 과정에 migration이 io를 유발한다. 따라서 io 허용 요청이 없는 경우에는 compaction을 진행할 수 없으므로 COMPACT_SKIPPED를 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 20~28 zonelist에서 지정된 nodemask와 high_zoneidx 이하의 zone에 대해 순회하며 compaction 우선 순위가 가장 높은 단계가 아닌 경우 해당 zone에서 지난 compaction 수행 시 실패한 경우 곧바로 compaction을 수행해도 성공하지 못할 가능성이 크므로 이번 시도에서는 유예시키기 위해 skip한다.
- 코드 라인 30~45에서 순회 중인 존에서 comaction 결과가 성공인 경우 유예 플래그를 리셋하고 결과를 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 47~54에서 compaction이 비동기가 아닌 모드로 동작하는 경우이면서 compaction 결과가 complete 또는 partial skipped 인 경우 순회 중인 존을 유예 표식한다.
- 코드 라인 61~63에서 비동기로 compaction이 진행 중인 경우 다른 태스크로 부터 선점 요청이 있거나 현재 태스크에 fatal 시그널이 인입된 경우 현재 결과로 함수를 빠져나간다.
order를 위한 존 compaction
compact_zone_order()
mm/compaction.c
static enum compact_result compact_zone_order(struct zone *zone, int order,
gfp_t gfp_mask, enum compact_priority prio,
unsigned int alloc_flags, int classzone_idx)
{
enum compact_result ret;
struct compact_control cc = {
.nr_freepages = 0,
.nr_migratepages = 0,
.total_migrate_scanned = 0,
.total_free_scanned = 0,
.order = order,
.gfp_mask = gfp_mask,
.zone = zone,
.mode = (prio == COMPACT_PRIO_ASYNC) ?
MIGRATE_ASYNC : MIGRATE_SYNC_LIGHT,
.alloc_flags = alloc_flags,
.classzone_idx = classzone_idx,
.direct_compaction = true,
.whole_zone = (prio == MIN_COMPACT_PRIORITY),
.ignore_skip_hint = (prio == MIN_COMPACT_PRIORITY),
.ignore_block_suitable = (prio == MIN_COMPACT_PRIORITY)
};
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&cc.freepages);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&cc.migratepages);
ret = compact_zone(zone, &cc);
VM_BUG_ON(!list_empty(&cc.freepages));
VM_BUG_ON(!list_empty(&cc.migratepages));
return ret;
}
compact_control_cc 구조체를 준비한 후 요청한 zone과 order 및 migrate 모드로 compact를 수행하고 결과를 반환한다.
존 compaction
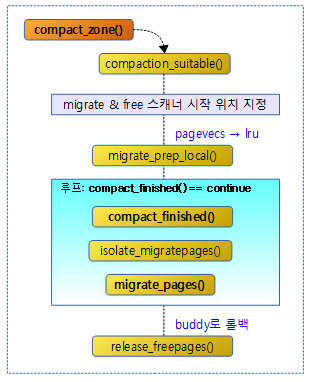
다음 그림과 같이 compact_zone() 함수의 처리 과정을 보여준다.
compact_zone()
mm/compaction.c -1/3-
static enum compact_result compact_zone(struct zone *zone, struct compact_control *cc)
{
enum compact_result ret;
unsigned long start_pfn = zone->zone_start_pfn;
unsigned long end_pfn = zone_end_pfn(zone);
const bool sync = cc->mode != MIGRATE_ASYNC;
cc->migratetype = gfpflags_to_migratetype(cc->gfp_mask);
ret = compaction_suitable(zone, cc->order, cc->alloc_flags,
cc->classzone_idx);
/* Compaction is likely to fail */
if (ret == COMPACT_SUCCESS || ret == COMPACT_SKIPPED)
return ret;
/* huh, compaction_suitable is returning something unexpected */
VM_BUG_ON(ret != COMPACT_CONTINUE);
/*
* Clear pageblock skip if there were failures recently and compaction
* is about to be retried after being deferred.
*/
if (compaction_restarting(zone, cc->order))
__reset_isolation_suitable(zone);
/*
* Setup to move all movable pages to the end of the zone. Used cached
* information on where the scanners should start (unless we explicitly
* want to compact the whole zone), but check that it is initialised
* by ensuring the values are within zone boundaries.
*/
if (cc->whole_zone) {
cc->migrate_pfn = start_pfn;
cc->free_pfn = pageblock_start_pfn(end_pfn - 1);
} else {
cc->migrate_pfn = zone->compact_cached_migrate_pfn[sync];
cc->free_pfn = zone->compact_cached_free_pfn;
if (cc->free_pfn < start_pfn || cc->free_pfn >= end_pfn) {
cc->free_pfn = pageblock_start_pfn(end_pfn - 1);
zone->compact_cached_free_pfn = cc->free_pfn;
}
if (cc->migrate_pfn < start_pfn || cc->migrate_pfn >= end_pfn) {
cc->migrate_pfn = start_pfn;
zone->compact_cached_migrate_pfn[0] = cc->migrate_pfn;
zone->compact_cached_migrate_pfn[1] = cc->migrate_pfn;
}
if (cc->migrate_pfn == start_pfn)
cc->whole_zone = true;
}
cc->last_migrated_pfn = 0;
trace_mm_compaction_begin(start_pfn, cc->migrate_pfn,
cc->free_pfn, end_pfn, sync);
migrate_prep_local();
요청 order를 위해 compaction을 시도하고 compact 진행 상태를 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 4~5에서 compaction은 존의 시작 pfn 부터 끝 pfn까지가 대상이다.
- 코드 라인 6에서 migraton 싱크 여부를 알아온다.
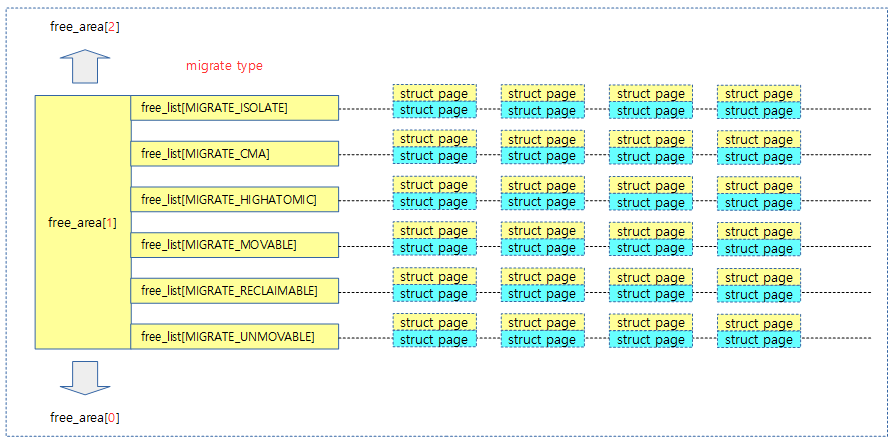
- 코드 라인 8에서 gfp 플래그를 사용하여 migrate 타입을 구한다.
- unmovable(0), movable(1), reclaimable(2)
- 코드 라인 9~13에서 compaction을 진행 여부에 대한 결과를 알아와서 이미 할당할 페이지가 있거나 skipped 결과인 경우 compaction을 하지 않고 함수를 빠져나간다.
- 코드 라인 22~23에서 compaction 유예가 최대 횟수(63)까지 도달한 경우 compaction을 다시 처음부터 하기 위해 zone의 usemap(pageblock_flags)에서 모든 PB_migrate_skip 비트를 clear한다.
- 코드 라인 31~33에서 처음 시작 시 migrate 스캐너의 시작은 존의 시작 pfn 으로 설정하고, free 스캐너의 시작은 존의 끝 pfn으로 설정한다.
- 코드 라인 34~36에서 지난 compactin에 연이어 동작해야 하는 경우 migrate 스캐너와 free 스캐너가 마지막 처리한 pfn 위치에서 계속하도록 한다.
- 코드 라인 37~40에서 free 스캐너의 pfn이 존의 범위를 벗어나는 경우 다시 존의 끝 블럭에 해당하는 페이지로 이동시킨다.
- 코드 라인 41~45에서 migrate 스캐너의 pfn이 존의 범위를 벗어나는 경우 다시 존의 시작 블럭에 해당하는 페이지로 이동시킨다.
- migrate pfn 위치를 기억시키는 캐시는 async(0) 및 sync(1)를 구분하여 2 개를 사용한다.
- 코드 라인 47~48에서 migrate 스캐너의 pfn이 시작 위치에 있는 경우 whole_zone을 true로 한다.
- 코드 라인 51에서 마지막 migrated pfn을 0으로 리셋한다.
- 코드 라인 52에서 migrate를 시작하기 전에 로컬 cpu가 할 일을 수행한다.
- lru 캐시인 pagevec으로부터 페이지들을 lru로 drain 한다.
mm/compaction.c -2/3-
. while ((ret = compact_finished(zone, cc)) == COMPACT_CONTINUE) {
int err;
switch (isolate_migratepages(zone, cc)) {
case ISOLATE_ABORT:
ret = COMPACT_CONTENDED;
putback_movable_pages(&cc->migratepages);
cc->nr_migratepages = 0;
goto out;
case ISOLATE_NONE:
/*
* We haven't isolated and migrated anything, but
* there might still be unflushed migrations from
* previous cc->order aligned block.
*/
goto check_drain;
case ISOLATE_SUCCESS:
;
}
err = migrate_pages(&cc->migratepages, compaction_alloc,
compaction_free, (unsigned long)cc, cc->mode,
MR_COMPACTION);
trace_mm_compaction_migratepages(cc->nr_migratepages, err,
&cc->migratepages);
/* All pages were either migrated or will be released */
cc->nr_migratepages = 0;
if (err) {
putback_movable_pages(&cc->migratepages);
/*
* migrate_pages() may return -ENOMEM when scanners meet
* and we want compact_finished() to detect it
*/
if (err == -ENOMEM && !compact_scanners_met(cc)) {
ret = COMPACT_CONTENDED;
goto out;
}
/*
* We failed to migrate at least one page in the current
* order-aligned block, so skip the rest of it.
*/
if (cc->direct_compaction &&
(cc->mode == MIGRATE_ASYNC)) {
cc->migrate_pfn = block_end_pfn(
cc->migrate_pfn - 1, cc->order);
/* Draining pcplists is useless in this case */
cc->last_migrated_pfn = 0;
}
}
- 코드 라인 1에서 compact를 수행한 결과가 COMPACT_CONTINUE인 동안 루프를 돈다.
- 코드 라인 4~9에서 페이지를 isoaltion한 결과가 ISOLATE_ABORT일 때 compaction 결과를 COMPACT_CONTENDED로 변경하고 migrate 페이지들을 원위치 시킨 후 migrate 페이지 수를 0으로 클리어한 다음 out 레이블을 통해 함수를 빠져나간다.
- 코드 라인 10~16에서 isolation 결과가 ISOLATE_NONE인 경우 아무 페이지도 isolation하지 않은 경우이고, 이 때에 cpu 캐시를 drain하기 위해 check_drain 레이블로 이동한 후 계속 루프를 진행하게 한다.
- 코드 라인 17~19에서 결과가 ISOLATE_SUCCESS인 경우 migration을 위해 다음 루틴을 계속 진행한다.
- 코드 라인 21~23에서 migrate 스캐너가 가리키는 페이지를 free 스캐너가 가리키는 페이지로 migration한다.
- 코드 라인 30~31에서 migration에 실패한 경우이다. migrate하려고 하는 페이지들을 다시 원래 위치로 돌려 놓는다.
- 코드 라인 36~39에서 스캐닝이 완료되지 않은 채로 메모리 부족이면 compaction 결과로 COMPACT_CONTENDED를 담고 out 레이블로 이동하여 함수를 빠져나간다.
- 코드 라인 44~51에서 async로 direct-compaction을 요청한 경우 지금 처리 중인 migrate 블럭을 skip 하게 한다.
mm/compaction.c -3/3-
check_drain:
/*
* Has the migration scanner moved away from the previous
* cc->order aligned block where we migrated from? If yes,
* flush the pages that were freed, so that they can merge and
* compact_finished() can detect immediately if allocation
* would succeed.
*/
if (cc->order > 0 && cc->last_migrated_pfn) {
int cpu;
unsigned long current_block_start =
block_start_pfn(cc->migrate_pfn, cc->order);
if (cc->last_migrated_pfn < current_block_start) {
cpu = get_cpu();
lru_add_drain_cpu(cpu);
drain_local_pages(zone);
put_cpu();
/* No more flushing until we migrate again */
cc->last_migrated_pfn = 0;
}
}
}
out:
/*
* Release free pages and update where the free scanner should restart,
* so we don't leave any returned pages behind in the next attempt.
*/
if (cc->nr_freepages > 0) {
unsigned long free_pfn = release_freepages(&cc->freepages);
cc->nr_freepages = 0;
VM_BUG_ON(free_pfn == 0);
/* The cached pfn is always the first in a pageblock */
free_pfn = pageblock_start_pfn(free_pfn);
/*
* Only go back, not forward. The cached pfn might have been
* already reset to zone end in compact_finished()
*/
if (free_pfn > zone->compact_cached_free_pfn)
zone->compact_cached_free_pfn = free_pfn;
}
count_compact_events(COMPACTMIGRATE_SCANNED, cc->total_migrate_scanned);
count_compact_events(COMPACTFREE_SCANNED, cc->total_free_scanned);
trace_mm_compaction_end(start_pfn, cc->migrate_pfn,
cc->free_pfn, end_pfn, sync, ret);
return ret;
}
- 코드 라인 1에서 check_drain: 레이블에서는 lru 캐시인 pagevec들을 비울지 여부를 판단한다.
- 코드 라인 9~22에서 만일 요청 order가 0이 아니고 마지막 migrate pfn이 현재 진행되는 블럭 밑에 존재하는 경우 lru 캐시인 pagevec들을 비우면 병합할 가능성이 커지고 compact_finished() 에서 할당 성공 여부를 즉시 감지할 수 있게된다.
- 코드 라인 26~44에서 out: 레이블이다. free 스캐너용 free 페이지들을 다시 되돌리고, 캐시에 위치를 기억시켜둔다.
- 코드 라인 46~47에서 COMPACTMIGRATE_SCANNED 및 COMPACTFREE_SCANNED 카운터를 갱신한다.
release_freepages()
mm/compaction.c
static unsigned long release_freepages(struct list_head *freelist)
{
struct page *page, *next;
unsigned long high_pfn = 0;
list_for_each_entry_safe(page, next, freelist, lru) {
unsigned long pfn = page_to_pfn(page);
list_del(&page->lru);
__free_page(page);
if (pfn > high_pfn)
high_pfn = pfn;
}
return high_pfn;
}
freelist에 있는 페이지들을 제거하고 모두 해제하고 가장 큰 pfn 값을 반환한다.
compaction 유예
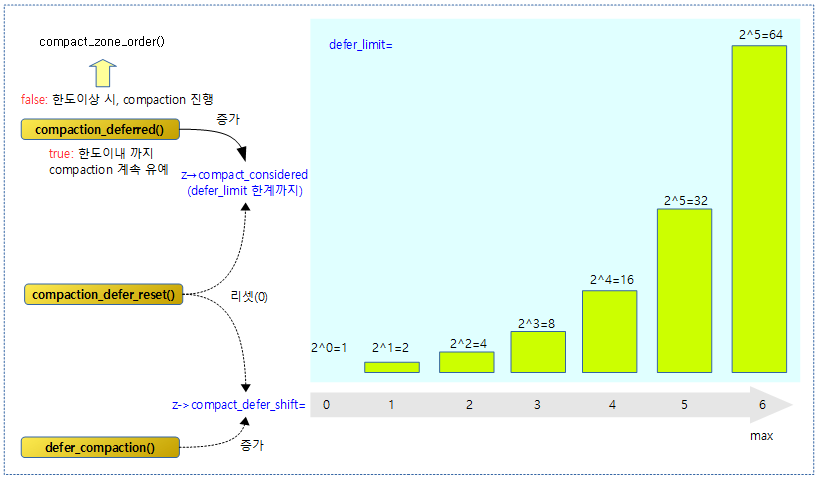
존에 대해 compaction을 유예할지 여부를 알아오는데, 유예 카운터를 증가시키며 한계에 도달하기 직전까지 compaction을 유예시킬 목적이다. 유예 카운터(compact_considered)는 compact_defer_shift 단계마다 높아져 최대 64까지 증가될 수 있다.
다음 그림은 유예 카운터 및 유예 shift 카운터에 대해 증가시키거나 리셋하는 3개의 함수 용도를 보여준다.
- compaction_deferred() 함수의 결과가 true일때 곧바로 compaction이 진행되지 않도록 유예시킨다.
compaction_deferred()
mm/compaction.c
/* Returns true if compaction should be skipped this time */
bool compaction_deferred(struct zone *zone, int order)
{
unsigned long defer_limit = 1UL << zone->compact_defer_shift;
if (order < zone->compact_order_failed)
return false;
/* Avoid possible overflow */
if (++zone->compact_considered > defer_limit)
zone->compact_considered = defer_limit;
if (zone->compact_considered >= defer_limit)
return false;
trace_mm_compaction_deferred(zone, order);
return true;
}
이번 타임에 compaction이 유예 처리되어 skip해야 하는지 여부를 반환한다. (true=compaction 유예, false=compaction 진행)
- 코드 라인 6~7에서 지난 compaction에서 사용한 fail된 오더 값보다 더 작은 order 요청인 경우 다시 compaction을 시도해봐야 하므로 false를 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 10~18 존의 유예 카운터(compact_considered)를 증가시킨다. 최대 유예 한계(1 << compact_defer_shift) 미만에서는 true를 반환하여 compactin을 유예 시킨다. 최대 유예 한계 이상인 경우 false를 반환하여 compaction을 시도하도록 한다.
defer_compaction()
mm/compaction.c
/*
* Compaction is deferred when compaction fails to result in a page
* allocation success. 1 << compact_defer_limit compactions are skipped up
* to a limit of 1 << COMPACT_MAX_DEFER_SHIFT
*/
void defer_compaction(struct zone *zone, int order)
{
zone->compact_considered = 0;
zone->compact_defer_shift++;
if (order < zone->compact_order_failed)
zone->compact_order_failed = order;
if (zone->compact_defer_shift > COMPACT_MAX_DEFER_SHIFT)
zone->compact_defer_shift = COMPACT_MAX_DEFER_SHIFT;
trace_mm_compaction_defer_compaction(zone, order);
}
요청한 존에서 order 페이지의 할당을 못한 채로 compaction이 완료될 때마다 유예 카운터는 0으로 리셋하고, 유예 한계 카운터는 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64까지 증가한다.
compaction_defer_reset()
mm/compaction.c
/* * Update defer tracking counters after successful compaction of given order, * which means an allocation either succeeded (alloc_success == true) or is * expected to succeed. */
void compaction_defer_reset(struct zone *zone, int order,
bool alloc_success)
{
if (alloc_success) {
zone->compact_considered = 0;
zone->compact_defer_shift = 0;
}
if (order >= zone->compact_order_failed)
zone->compact_order_failed = order + 1;
trace_mm_compaction_defer_reset(zone, order);
}
요청한 존에서 compaction 수행 후 order 페이지에 대한 성공이 기대될 때 호출되는 함수이다. 실제 페이지 할당 성공 시 호출되는 경우에는 유예 카운터 및 유예 한계 카운터를 0으로 리셋한다.
- 코드 라인 4~7에서 요청한 존에서 compaction 수행 후 order 페이지의 할당이 성공한 경우 유예 카운터 및 유예 한계 카운터를 0으로 리셋한다.
- 코드 라인 8~9에서 fail 오더 값으로는 요청한 order + 1 값으로 설정한다.
compaction_restarting()
mm/compaction.c
/* Returns true if restarting compaction after many failures */
bool compaction_restarting(struct zone *zone, int order)
{
if (order < zone->compact_order_failed)
return false;
return zone->compact_defer_shift == COMPACT_MAX_DEFER_SHIFT &&
zone->compact_considered >= 1UL << zone->compact_defer_shift;
}
compaction 최대 유예 횟수(64)에 도달한 경우 true를 반환한다.
- 요청 order가 compact_order_failed 보다 작은 경우 false를 반환
- compact_defer_shift가 마지막(6)이면서 compact_considered값이 64이상인 경우 true를 반환
compact 종료 체크
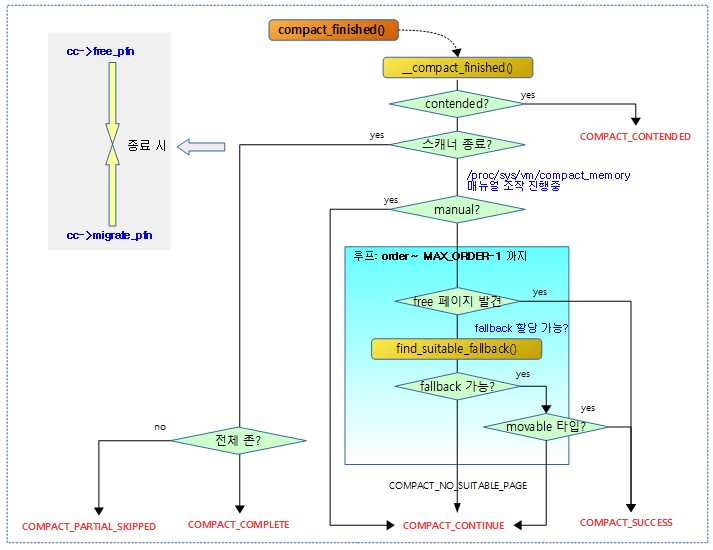
compact_finished()
mm/compaction.c
static enum compact_result compact_finished(struct zone *zone,
struct compact_control *cc)
{
int ret;
ret = __compact_finished(zone, cc);
trace_mm_compaction_finished(zone, cc->order, ret);
if (ret == COMPACT_NO_SUITABLE_PAGE)
ret = COMPACT_CONTINUE;
return ret;
}
compact 완료 여부를 판단하기 위해 진행 상태를 반환한다.
다음 그림은 compact 완료 여부를 판단하기 위해 진행 상태를 알아오는 모습을 보여준다.
__compact_finished()
mm/compaction.c -1/2-
static enum compact_result __compact_finished(struct zone *zone,
struct compact_control *cc)
{
unsigned int order;
const int migratetype = cc->migratetype;
if (cc->contended || fatal_signal_pending(current))
return COMPACT_CONTENDED;
/* Compaction run completes if the migrate and free scanner meet */
if (compact_scanners_met(cc)) {
/* Let the next compaction start anew. */
reset_cached_positions(zone);
/*
* Mark that the PG_migrate_skip information should be cleared
* by kswapd when it goes to sleep. kcompactd does not set the
* flag itself as the decision to be clear should be directly
* based on an allocation request.
*/
if (cc->direct_compaction)
zone->compact_blockskip_flush = true;
if (cc->whole_zone)
return COMPACT_COMPLETE;
else
return COMPACT_PARTIAL_SKIPPED;
}
if (is_via_compact_memory(cc->order))
return COMPACT_CONTINUE;
if (cc->finishing_block) {
/*
* We have finished the pageblock, but better check again that
* we really succeeded.
*/
if (IS_ALIGNED(cc->migrate_pfn, pageblock_nr_pages))
cc->finishing_block = false;
else
return COMPACT_CONTINUE;
}
- 코드 라인 7~8에서 compaction 수행 중 현재 태스크에 급하게 처리할 preemption 요청 또는 fatal 시그널이 있는 경우 COMPACT_CONTENDED를 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 11~28에서 free 스캐너와 migrate 스캐너 둘이 만난 경우 compaction이 완료된 경우이다. 다음 스캐닝을 위해 스캔 시작 위치를 리셋한다. 전체 zone을 스캔한 경우라면 COMPACT_COMPLETE를 반환하고, 일부 존만 수행한 경우라면 COMPACT_PARTIAL_SKIPPED를 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 30~31에서 유저가 개입하여 compaction을 수행한 경우에 전체 블럭에 대해 무조건(force) compaction을 하기 위해 COMPACT_CONTINUE를 반환한다.
- “echo 1 > /proc/sys/vm/compact_memory”
- 코드 라인 33~42에서 페이지 블럭 하나를 완료한 경우이다. 정말 migrate 스캐너가 페이지 블럭 하나를 끝낸 경우인지 다시 확인하여 중간에 종료된 경우라면 COMPACT_CONTINUE를 반환하여 계속하도록 하게 한다.
mm/compaction.c -2/2-
/* Direct compactor: Is a suitable page free? */
for (order = cc->order; order < MAX_ORDER; order++) {
struct free_area *area = &zone->free_area[order];
bool can_steal;
/* Job done if page is free of the right migratetype */
if (!list_empty(&area->free_list[migratetype]))
return COMPACT_SUCCESS;
#ifdef CONFIG_CMA
/* MIGRATE_MOVABLE can fallback on MIGRATE_CMA */
if (migratetype == MIGRATE_MOVABLE &&
!list_empty(&area->free_list[MIGRATE_CMA]))
return COMPACT_SUCCESS;
#endif
/*
* Job done if allocation would steal freepages from
* other migratetype buddy lists.
*/
if (find_suitable_fallback(area, order, migratetype,
true, &can_steal) != -1) {
/* movable pages are OK in any pageblock */
if (migratetype == MIGRATE_MOVABLE)
return COMPACT_SUCCESS;
/*
* We are stealing for a non-movable allocation. Make
* sure we finish compacting the current pageblock
* first so it is as free as possible and we won't
* have to steal another one soon. This only applies
* to sync compaction, as async compaction operates
* on pageblocks of the same migratetype.
*/
if (cc->mode == MIGRATE_ASYNC ||
IS_ALIGNED(cc->migrate_pfn,
pageblock_nr_pages)) {
return COMPACT_SUCCESS;
}
cc->finishing_block = true;
return COMPACT_CONTINUE;
}
}
return COMPACT_NO_SUITABLE_PAGE;
}
필요로 하는 free 페이지가 확보될 수 있는지 확인한다.
- 코드 라인 2~8에서 @order부터 마지막 order까지 순회하며 해당 order의 free 리스트에 free 페이지가 발견된 경우 COMPACT_SUCCESS를 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 12~14에서 movable 페이지 요청인 경우 cma 타입 리스트에서 free 페이지가 발견된 경우 COMPACT_SUCCESS를 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 20~25에서 다른 타입에서 가져올 free 페이지가 있는 경우 movable 타입이면 COMPACT_SUCCESS를 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 35~39에서 compaction이 aync 수행 중이거나 migrate 스캐너가 한 페이지 블럭을 완료한 상태라면 COMPACT_SUCCESS를 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 41~42에서 COMPACT_CONTINUE를 반환한다. 그리고 finishing_block을 true로 변경하여 다음 compaction에서 중단하지 않고 페이지 블럭이 완료될 때 까지 계속 compaction을 할지 여부를 조사하게 한다.
- 코드 라인 46에서 페이지 확보가 실패하였으므로 COMPACT_NO_SUITABLE_PAGE를 반환한다.
참고
- Zoned Allocator -1- (물리 페이지 할당-Fastpath) | 문c
- Zoned Allocator -2- (물리 페이지 할당-Slowpath) | 문c
- Zoned Allocator -3- (Buddy 페이지 할당) | 문c
- Zoned Allocator -4- (Buddy 페이지 해지) | 문c
- Zoned Allocator -5- (Per-CPU Page Frame Cache) | 문c
- Zoned Allocator -6- (Watermark) | 문c
- Zoned Allocator -7- (Direct Compact) | 문c – 현재 글
- Zoned Allocator -8- (Direct Compact-Isolation) | 문c
- Zoned Allocator -9- (Direct Compact-Migration) | 문c
- Zoned Allocator -10- (LRU & pagevec) | 문c
- Zoned Allocator -11- (Direct Reclaim) | 문c
- Zoned Allocator -12- (Direct Reclaim-Shrink-1) | 문c
- Zoned Allocator -13- (Direct Reclaim-Shrink-2) | 문c
- Zoned Allocator -14- (Kswapd) | 문c
- Memory compaction (2010) | LWN.net
- Linux: Memory fragmentation and compaction | uninformativ.de