<kernel v5.4>
RCU(Read Copy Update) -7- (Preemptible RCU)
rcu read-side critical section 에서 preemption이 가능한 모델을 사용하려면 CONFIG_PREEMPT_RCU 커널 옵션이 설정되어야 하는데, preemptible 커널이 선택되는 경우 함께 디폴트로 설정된다.
QS 체크, 기록 및 보고
preemptible rcu를 사용하여 read-side critical section 내에서 preemption 되어 블럭된 태스크가 있을 때와 없을 때의 qs 체크 후 qs 기록 및 qs 보고가 어떻게 다른지 알아본다.
- qs 체크
- qs 상태인지 확인하는 과정
- qs 기록
- qs 상태가 인지되어 qs를 해당 cpu의 rcu_data에 기록
- qs 보고
- 해당 cpu의 rcu_data에 기록된 qs를 노드(rcu_node) 및 글로벌(rcu_state)에 보고
블럭드 태스크 비존재 시
gp 시작 이후 스케줄 틱마다 qs 체크를 시도하는데 rcu read-side critical section 내부 및 외부에서 qs 체크 변화는 다음과 같다.
- 내부: 증가된 t->rcu_read_lock_nesting 카운터로 인해 qs 기록하지 않는다.
- 외부: t->rcu_read_lock_nesting이 0이므로 qs 기록한다.
기록된 qs는 이후 rdp(rcu_data) -> rnp((rcu_node) -> rsp(rcu_state) 단계에 걸쳐 qs를 보고하는 과정을 거치는데 보통 콜백을 처리하는 rcu core에서 rcu_check_quiescent_state() 함수를 통해 qs 보고가 이루어진다.
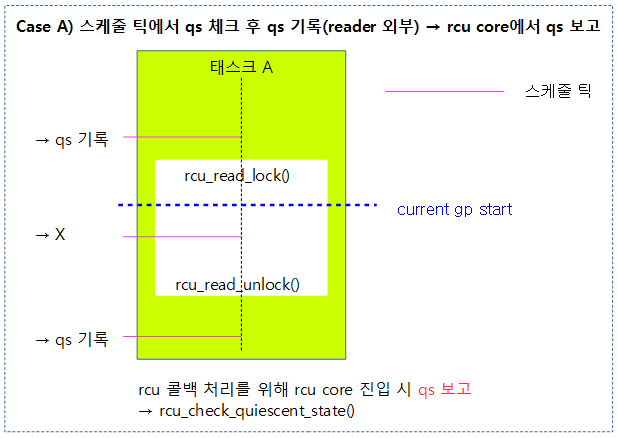
다음 그림은 스케줄 틱에서 qs를 체크하는데, 블럭된 태스크가 없는 rcu read-side critical section 외부인 경우 qs를 기록한 후, 나중에 기록된 qs의 보고가 이루어지는 과정을 보여준다.
- gp가 새롭게 시작하면 기존의 qs는 모두 무시되므로, current gp start 이후의 스케줄 틱을 관찰한다.
블럭드 태스크 존재 시
gp 시작 이후 rcu read-side critical section 내부에서 preemption이 발생하면 해당 태스크는 qs가 체크가 되지만, 블럭드 태스크가 된다. 다시 resume하고, rcu_read_unlock()을 수행하는 순간 block된 태스크로 인해 rcu read unblock special 케이스가 적용되는데 이 때 irq/bh/preempt가 모두 enable된 상태인 경우 블럭된 태스크의 unblock을 수행하고 qs를 보고한다.
또 하나, 블럭드 태스크가 되고 irq/bh/preempt disable이 수행된 이후 rcu_read_unlock()을 수행하는 순간부터 preemption으로 인해 block된 태스크를 가진 이유로 rcu read unlock special 케이스가 적용된다. 이 때 irq/bh/preempt가 disable 되어 있는 경우 해당 cpu는 deferred qs가 되어 qs 보고를 유예하게 된다. 추후 다시 deferred qs가 해제되는 순간 deferred qs가 제거되며 블럭된 태스크의 unblock을 수행하고 qs를 보고한다.
- deferred qs의 해제
- 스케줄 틱에서 nest되지 않고 irq/bh/preempt enable 상황인 경우
- rcu read unlock에서 nest를 빠져나갈 때 irq/bh/preempt enable 상황인 경우
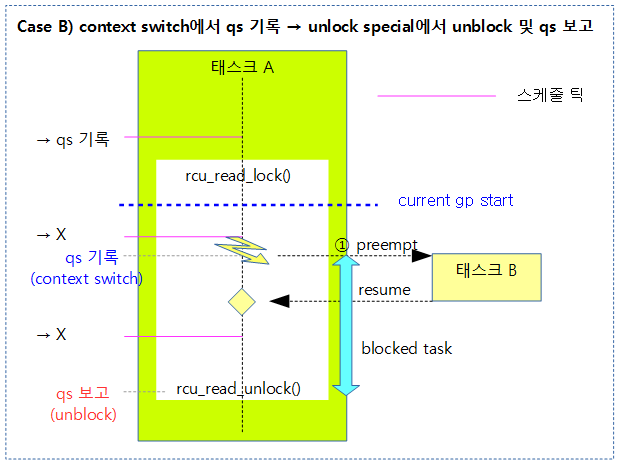
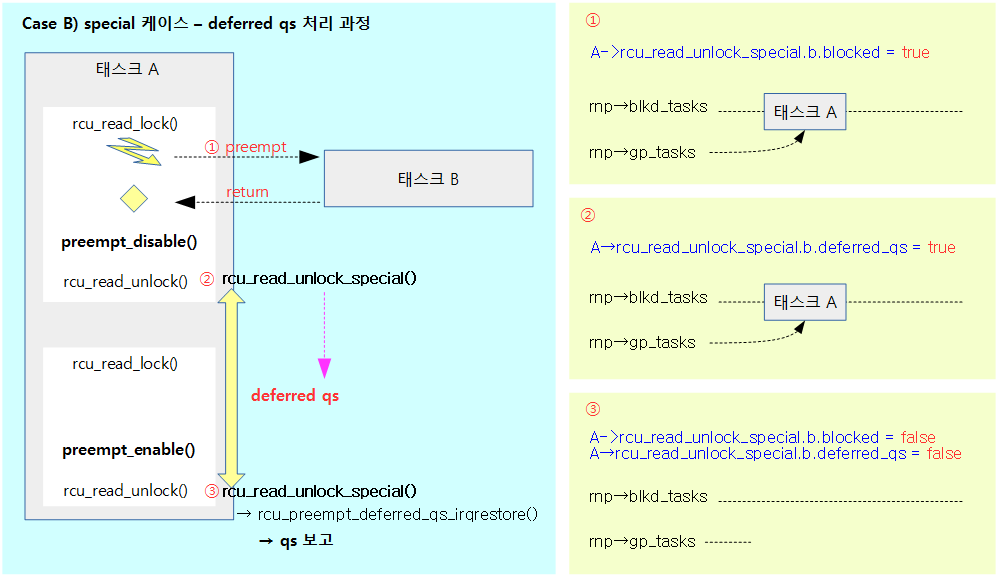
다음 그림은 블럭된 태스크가 존재하는 상황에서 context switch로 qs가 기록된 이후 unlock special 상황에서 unblock 태스크 처리 및 qs를 보고하는 과정을 보여준다.
다음 그림은 블럭된 태스크가 존재하는 상황에서 context switch로 qs가 기록된 이후 deferred qs 가 해제되는 순간 unblock 태스크 처리 및 qs를 보고하는 과정을 보여준다.
preemptible RCU Read-side Critical Section
다음 그림은 preemptible RCU를 사용할 때 rcu read-side critical section 내에서 preempt되는 태스크를 관리하기 위해 다음 3 곳에서 호출되는 함수들의 관계를 보여준다.
- rcu_read_unlock()의 special 케이스를 호출하는 rcu_read_unlock_special()
- 스케줄 틱에서 호출되는 rcu_sched_clock_irq()
- preemption이 발생하여 context-switch 될 때 호출되는 rcu_note_context_switch()
rcu_read_lock()
include/linux/rcupdate.h
/** * rcu_read_lock() - mark the beginning of an RCU read-side critical section * * When synchronize_rcu() is invoked on one CPU while other CPUs * are within RCU read-side critical sections, then the * synchronize_rcu() is guaranteed to block until after all the other * CPUs exit their critical sections. Similarly, if call_rcu() is invoked * on one CPU while other CPUs are within RCU read-side critical * sections, invocation of the corresponding RCU callback is deferred * until after the all the other CPUs exit their critical sections. * * Note, however, that RCU callbacks are permitted to run concurrently * with new RCU read-side critical sections. One way that this can happen * is via the following sequence of events: (1) CPU 0 enters an RCU * read-side critical section, (2) CPU 1 invokes call_rcu() to register * an RCU callback, (3) CPU 0 exits the RCU read-side critical section, * (4) CPU 2 enters a RCU read-side critical section, (5) the RCU * callback is invoked. This is legal, because the RCU read-side critical * section that was running concurrently with the call_rcu() (and which * therefore might be referencing something that the corresponding RCU * callback would free up) has completed before the corresponding * RCU callback is invoked. * * RCU read-side critical sections may be nested. Any deferred actions * will be deferred until the outermost RCU read-side critical section * completes. * * You can avoid reading and understanding the next paragraph by * following this rule: don't put anything in an rcu_read_lock() RCU * read-side critical section that would block in a !PREEMPT kernel. * But if you want the full story, read on! * * In non-preemptible RCU implementations (TREE_RCU and TINY_RCU), * it is illegal to block while in an RCU read-side critical section. * In preemptible RCU implementations (PREEMPT_RCU) in CONFIG_PREEMPTION * kernel builds, RCU read-side critical sections may be preempted, * but explicit blocking is illegal. Finally, in preemptible RCU * implementations in real-time (with -rt patchset) kernel builds, RCU * read-side critical sections may be preempted and they may also block, but * only when acquiring spinlocks that are subject to priority inheritance. */
static __always_inline void rcu_read_lock(void)
{
__rcu_read_lock();
__acquire(RCU);
rcu_lock_acquire(&rcu_lock_map);
RCU_LOCKDEP_WARN(!rcu_is_watching(),
"rcu_read_lock() used illegally while idle");
}
rcu read-side critical section의 시작을 알린다.
__rcu_read_lock()
kernel/rcu/tree_plugin.h
/* * Preemptible RCU implementation for rcu_read_lock(). * Just increment ->rcu_read_lock_nesting, shared state will be updated * if we block. */
void __rcu_read_lock(void)
{
current->rcu_read_lock_nesting++;
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_PROVE_LOCKING))
WARN_ON_ONCE(current->rcu_read_lock_nesting > RCU_NEST_PMAX);
barrier(); /* critical section after entry code. */
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(__rcu_read_lock);
premptible rcu를 사용 시 사용되며 rcu read-side critical section의 시작을 알린다.
- 코드 라인 3에서 현재 태스크의 rcu_read_lock_nesting 카운터를 1 증가시킨다.
- 코드 라인 4~5에서 lock 디버깅을 위해 사용되며 증가 시킨 카운터가 오버 플로우(0x3fff_ffff)되면 경고 메시지를 출력한다.
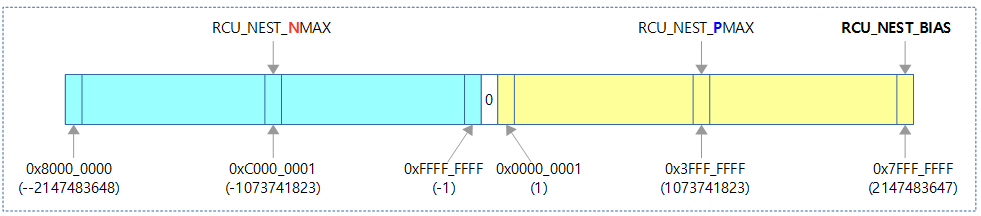
RCU_NEST_* 상수
kernel/rcu/tree_plugin.h
/* Bias and limit values for ->rcu_read_lock_nesting. */ #define RCU_NEST_BIAS INT_MAX #define RCU_NEST_NMAX (-INT_MAX / 2) #define RCU_NEST_PMAX (INT_MAX / 2)
다음 그림에서 RCU_NEST_* 관련 상수 값을 보여준다.
rcu_read_unlock()
include/linux/rcupdate.h
/** * rcu_read_unlock() - marks the end of an RCU read-side critical section. * * In most situations, rcu_read_unlock() is immune from deadlock. * However, in kernels built with CONFIG_RCU_BOOST, rcu_read_unlock() * is responsible for deboosting, which it does via rt_mutex_unlock(). * Unfortunately, this function acquires the scheduler's runqueue and * priority-inheritance spinlocks. This means that deadlock could result * if the caller of rcu_read_unlock() already holds one of these locks or * any lock that is ever acquired while holding them. * * That said, RCU readers are never priority boosted unless they were * preempted. Therefore, one way to avoid deadlock is to make sure * that preemption never happens within any RCU read-side critical * section whose outermost rcu_read_unlock() is called with one of * rt_mutex_unlock()'s locks held. Such preemption can be avoided in * a number of ways, for example, by invoking preempt_disable() before * critical section's outermost rcu_read_lock(). * * Given that the set of locks acquired by rt_mutex_unlock() might change * at any time, a somewhat more future-proofed approach is to make sure * that that preemption never happens within any RCU read-side critical * section whose outermost rcu_read_unlock() is called with irqs disabled. * This approach relies on the fact that rt_mutex_unlock() currently only * acquires irq-disabled locks. * * The second of these two approaches is best in most situations, * however, the first approach can also be useful, at least to those * developers willing to keep abreast of the set of locks acquired by * rt_mutex_unlock(). * * See rcu_read_lock() for more information. */
static inline void rcu_read_unlock(void)
{
RCU_LOCKDEP_WARN(!rcu_is_watching(),
"rcu_read_unlock() used illegally while idle");
__release(RCU);
__rcu_read_unlock();
rcu_lock_release(&rcu_lock_map); /* Keep acq info for rls diags. */
}
rcu read-side critical section의 끝을 알린다.
__rcu_read_unlock()
kernel/rcu/tree_plugin.h
/* * Preemptible RCU implementation for rcu_read_unlock(). * Decrement ->rcu_read_lock_nesting. If the result is zero (outermost * rcu_read_unlock()) and ->rcu_read_unlock_special is non-zero, then * invoke rcu_read_unlock_special() to clean up after a context switch * in an RCU read-side critical section and other special cases. */
void __rcu_read_unlock(void)
{
struct task_struct *t = current;
if (t->rcu_read_lock_nesting != 1) {
--t->rcu_read_lock_nesting;
} else {
barrier(); /* critical section before exit code. */
t->rcu_read_lock_nesting = -RCU_NEST_BIAS;
barrier(); /* assign before ->rcu_read_unlock_special load */
if (unlikely(READ_ONCE(t->rcu_read_unlock_special.s)))
rcu_read_unlock_special(t);
barrier(); /* ->rcu_read_unlock_special load before assign */
t->rcu_read_lock_nesting = 0;
}
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_PROVE_LOCKING)) {
int rrln = t->rcu_read_lock_nesting;
WARN_ON_ONCE(rrln < 0 && rrln > RCU_NEST_NMAX);
}
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(__rcu_read_unlock);
premptible rcu를 사용 시 사용되며 rcu read-side critical section의 끝을 알린다.
- 코드 라인 3~6에서 현재 태스크의 rcu_read_lock_nesting 카운터가 1이 아닌 경우 1 만큼 감소시킨다.
- 이 전에 이미 rcu_read_lock()가 호출되었었고, 그 후 중첩된 경우이다.
- 코드 라인 7~15에서 현재 태스크의 rcu_read_lock_nesting 카운터가 1일 때 일시적으로 RCU_NEST_BIAS(0x7fff_ffff) 만큼 뺀 후 unlock special 케이스가 감지되면 이를 수행하고 추후 카운터를 0으로 변경한다. 이 때 카운터 값은 일시적으로 음수로 변경된다.
- 1 – 0x7fff_ffff = 0x8000_0002 (-2,147,483,646)
- special 케이스의 감지는 nest 없이 마지막 rcu_read_unlock()에서 t->rcu_read_unlock_special.s 값을 관찰하여 판단한다.
- special 값은 blocked, need_qs, exp_hint 및 deferred_qs와 같이 총 4가지가 운영된다.
- 코드 라인 16~20에서 lock 디버깅을 위해 사용되며 감소 시킨 카운터가 언더 플로우(-1073741823 ~ -1)되면 경고 메시지를 출력한다.
rcu_read_unlock()의 special 케이스
rcu_read_unlock()을 통해 rcu read-side critical 섹션을 빠져나가는 순간에 irq/bh/preempt가 disable인 경우 곧바로 gp가 완료되면 안되므로 해당 cpu의 qs를 보고하지 않고 지연(deferred qs)시킨다. 이렇게 특별한 조건을 처리하기 위해 unlock special 케이스를 두었고 다음과 같이 동작한다.
- 먼저 preemption이 발생하는 경우 해당 cpu에 대해 qs가 기록된다. 그런데 rcu read-side critical 섹션 내에서 preemption이 발생하는 경우엔 이 태스크를 blocked 태스크에 추가하고, 나중에 rcu_read_unlock() 함수의 special 케이스에서 이를 인지하기 위해 rcu_read_unlock_special.b.blocked 비트를 1로 설정해둔다.
- rcu_read_unlock() 호출 시 위의 blocked 등의 이유로 unlock special 케이스를 만나게 되면 interrupt, bh(softirq) 및 preemption의 disable/enable 여부에 따라 다음과 같이 동작한다.
- disable된 상태인 경우 deferred qs로 만든다.
- enable 상태인 경우 deferred qs 상태를 해제한다. 그리고 blocked 상태인 경우 해제하고 qs 또한 보고한다.
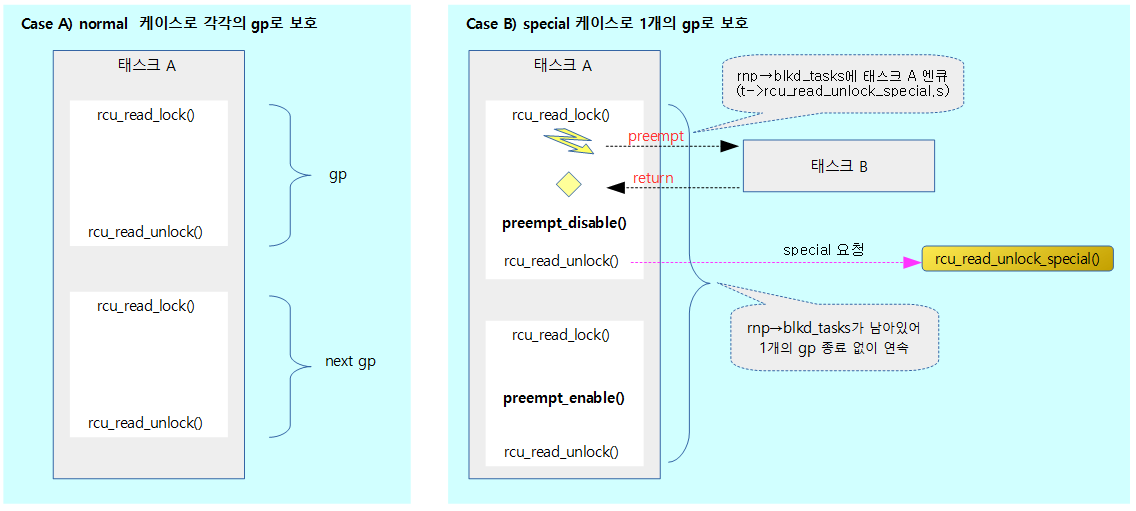
다음 그림은 rcu_read_unlock() 함수 호출 시 special 케이스를 통해 gp가 종료되지 않고 연속될 수 있도록 하는 모습을 보여준다.
rcu_read_unlock_special()
kernel/rcu/tree_plugin.h
/* * Handle special cases during rcu_read_unlock(), such as needing to * notify RCU core processing or task having blocked during the RCU * read-side critical section. */
static void rcu_read_unlock_special(struct task_struct *t)
{
unsigned long flags;
bool preempt_bh_were_disabled =
!!(preempt_count() & (PREEMPT_MASK | SOFTIRQ_MASK));
bool irqs_were_disabled;
/* NMI handlers cannot block and cannot safely manipulate state. */
if (in_nmi())
return;
local_irq_save(flags);
irqs_were_disabled = irqs_disabled_flags(flags);
if (preempt_bh_were_disabled || irqs_were_disabled) {
bool exp;
struct rcu_data *rdp = this_cpu_ptr(&rcu_data);
struct rcu_node *rnp = rdp->mynode;
t->rcu_read_unlock_special.b.exp_hint = false;
exp = (t->rcu_blocked_node && t->rcu_blocked_node->exp_tasks) ||
(rdp->grpmask & rnp->expmask) ||
tick_nohz_full_cpu(rdp->cpu);
// Need to defer quiescent state until everything is enabled.
if (irqs_were_disabled && use_softirq &&
(in_interrupt() ||
(exp && !t->rcu_read_unlock_special.b.deferred_qs))) {
// Using softirq, safe to awaken, and we get
// no help from enabling irqs, unlike bh/preempt.
raise_softirq_irqoff(RCU_SOFTIRQ);
} else {
// Enabling BH or preempt does reschedule, so...
// Also if no expediting or NO_HZ_FULL, slow is OK.
set_tsk_need_resched(current);
set_preempt_need_resched();
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_IRQ_WORK) && irqs_were_disabled &&
!rdp->defer_qs_iw_pending && exp) {
// Get scheduler to re-evaluate and call hooks.
// If !IRQ_WORK, FQS scan will eventually IPI.
init_irq_work(&rdp->defer_qs_iw,
rcu_preempt_deferred_qs_handler);
rdp->defer_qs_iw_pending = true;
irq_work_queue_on(&rdp->defer_qs_iw, rdp->cpu);
}
}
t->rcu_read_unlock_special.b.deferred_qs = true;
local_irq_restore(flags);
return;
}
WRITE_ONCE(t->rcu_read_unlock_special.b.exp_hint, false);
rcu_preempt_deferred_qs_irqrestore(t, flags);
}
premptible rcu를 사용 시 rcu_read_unlock() 함수에서 special 케이스가 감지된 경우 호출된다. 블럭된 태스크가 있을 때 irq/bh/preempt 중 하나라도 disable된 경우 deferred qs 처리하고, 그렇지 않고 enable된 경우 deferred qs를 해제하고, 블럭드 상태인 경우 해제하고 qs도 보고한다.
- 코드 라인 4~5에서 preempt와 softirq가 disable된 상태인지 여부를 preempt_bh_were_disabled 변수에 대입한다.
- 코드 라인 9~10에서 NMI 인터럽트가 진행 중인 경우 처리를 하지 않고 함수를 빠져나간다.
- 코드 라인 12~13에서 local irq가 disable되어 있는 상태인지 여부를 irqs_were_disabled 변수에 대입하고, local irq를 disable한다.
- 코드 라인 14~19에서 special 케이스를 만족시키는 경우 태스크에서 rcu_read_unlock_special의 exp_hint 비트를 클리어한다.
- rcu_read_unlock()에서 가장 바깥쪽 rcu read-side critical section이고 special 비트들 중 하나라도 존재하는 경우 special 케이스가 적용된다.
- 코드 라인 20~22에서 softirq를 호출하는 급행(exp) 처리는 다음 세 조건 중 하나라도 만족하면 시도한다.
- 태스크가 read-side critical section에서 preempt되어 블럭된 상태이고 노드에도 블럭된 태스크가 존재하는 경우
- 아직도 현재 cpu가 급행 qs를 보고하지 못한 상태인 경우
- 현재 cpu가 nohz full 상태라 qs를 보고하지 못한 상태인 경우
- 코드 라인 24~29에서 irq가 disable 상태였었고 rcu 콜백에 softirq 호출을 사용하고 다음 두 조건 중 하나를 만족하는 경우이다. 인터럽트 context에서 급행 gp를 빠르게 처리하기 위해 rcu용 softirq를 호출한다.
- 인터럽트 처리중인 경우
- 급행(exp == true) 가능하고, 유예 qs 요청되지 않은 상태인(태스크에 rcu_read_unlock_special의 deferred_qs 비트가 false) 경우
- 코드 라인 30~44에서 그 외의 경우 약간 느리더라도 유예 qs 체크를 위해 리스케줄 요청을 한다. 만일 인터럽트도 disable되어있고, softirq도 사용하지 않고, nohz full 상태로 진입한 경우 qs 보고가 무한정 처리되지 못할 수 있다. 따라서 이를 빠르게 처리하기 위해 irq 워크큐를 사용하여 rcu_preempt_deferred_qs_handler() 함수를 호출하게 한다.
- 빠르게 처리하기 위해 강제로 irq를 발생시킨다.
- irq 워크(IPI call)를 통해 rdp->defer_qs_iw_pending 변수에 false를 대입한다.
- 코드 라인 45~47에서 irq/bh/preempt가 하나라도 disable 된 상태에서는 특정 시점까지 qs 보고를 지연시킬 목적으로 deferred qs 상태로 설정하다. 태스크에서 rcu_read_unlock_special의 deferred_qs 비트를 true로 변경하고 로컬 irq를 복구한 후 함수를 빠져나간다.
- 코드 라인 49에서 special 케이스를 만족시키지 못한 경우이다. 태스크에서 rcu_read_unlock_speciald의 exp_hint 비트를 클리어한다.
- 코드 라인 50에서 deferred qs를 해제한다. 또한 block 상태인 경우 block 태스크를 해제하고 qs를 보고한다.
다음 그림은 rcu_read_unlock() 함수내에서 special 케이스를 진행할 때 블럭되었던 태스크 A가 해제된 후 qs를 보고하는 과정을 보여준다.
다음 그림은 rcu_read_unlock() 함수내에서 special 케이스를 진행할 때 블럭되었던 태스크 A가 해제된 후 곧바로 qs를 보고하지 않고 deferred qs로 전환된 나중에 qs로 체크하는 과정을 보여준다.
RCU preempt 될 때 스케줄 처리
rcu_note_context_switch()
kernel/rcu/tree_plugin.h
/* * We have entered the scheduler, and the current task might soon be * context-switched away from. If this task is in an RCU read-side * critical section, we will no longer be able to rely on the CPU to * record that fact, so we enqueue the task on the blkd_tasks list. * The task will dequeue itself when it exits the outermost enclosing * RCU read-side critical section. Therefore, the current grace period * cannot be permitted to complete until the blkd_tasks list entries * predating the current grace period drain, in other words, until * rnp->gp_tasks becomes NULL. * * Caller must disable interrupts. */
void rcu_note_context_switch(bool preempt)
{
struct task_struct *t = current;
struct rcu_data *rdp = this_cpu_ptr(&rcu_data);
struct rcu_node *rnp;
trace_rcu_utilization(TPS("Start context switch"));
lockdep_assert_irqs_disabled();
WARN_ON_ONCE(!preempt && t->rcu_read_lock_nesting > 0);
if (t->rcu_read_lock_nesting > 0 &&
!t->rcu_read_unlock_special.b.blocked) {
/* Possibly blocking in an RCU read-side critical section. */
rnp = rdp->mynode;
raw_spin_lock_rcu_node(rnp);
t->rcu_read_unlock_special.b.blocked = true;
t->rcu_blocked_node = rnp;
/*
* Verify the CPU's sanity, trace the preemption, and
* then queue the task as required based on the states
* of any ongoing and expedited grace periods.
*/
WARN_ON_ONCE((rdp->grpmask & rcu_rnp_online_cpus(rnp)) == 0);
WARN_ON_ONCE(!list_empty(&t->rcu_node_entry));
trace_rcu_preempt_task(rcu_state.name,
t->pid,
(rnp->qsmask & rdp->grpmask)
? rnp->gp_seq
: rcu_seq_snap(&rnp->gp_seq));
rcu_preempt_ctxt_queue(rnp, rdp);
} else {
rcu_preempt_deferred_qs(t);
}
/*
* Either we were not in an RCU read-side critical section to
* begin with, or we have now recorded that critical section
* globally. Either way, we can now note a quiescent state
* for this CPU. Again, if we were in an RCU read-side critical
* section, and if that critical section was blocking the current
* grace period, then the fact that the task has been enqueued
* means that we continue to block the current grace period.
*/
rcu_qs();
if (rdp->exp_deferred_qs)
rcu_report_exp_rdp(rdp);
trace_rcu_utilization(TPS("End context switch"));
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(rcu_note_context_switch);
context-switching을 수행하기 전에 rcu에 관련된 처리를 수행한다. context switch가 진행될 때 해당 cpu에 대해 qs를 기록한다. 현재 태스크가 rcu read-side critical section에서 처음 preempt된 경우 현재 태스크를 해당 rcu 노드의 블럭드 태스크 리스트에 추가한다. 그 외 이미 deferred qs 상태인 경우 deferred qs를 해제하고, 블럭드 상태인 경우 이를 제거하고 qs도 보고한다.
- 코드 라인 9에서 rcu_read_lock() 호출한 상태는 반드시 preempt된 경우에만 호출되어야 한다. 그렇지 않은 경우 경고 메시지를 출력한다.
- rcu_read_lock() 호출 후 강제로 schedule() 같은 API를 사용하여 블럭시키면 안된다.
- 코드 라인 10~31에서 rcu read-side critical section에 진입 후 preemption되어 처음 블럭된 태스크가 없는 상태인 경우 노드락을 잡은 후 태스크를 blocked 표기 및 이 노드를 가리키게 한다. 그 후 태스크를 블럭드 리스트에 추가한다.
- 코드 라인 32~34에서 deferred qs 상태인 경우 deferred qs를 해제한다. 또한 block 해제 가능한 상태인 경우 block 태스크를 해제한 후 qs를 보고한다.
- 코드 라인 45에서 현재 cpu의 qs를 기록한다.
- 코드 라인 46~47에서 현재 cpu에서 급행 qs가 유예된 경우 유예 상태를 제거하고 상위 노드로 qs를 보고하게 한다.
블럭드 리스트에 태스크 추가
rcu_preempt_ctxt_queue()
kernel/rcu/tree_plugin.h -1/2-
/* * Queues a task preempted within an RCU-preempt read-side critical * section into the appropriate location within the ->blkd_tasks list, * depending on the states of any ongoing normal and expedited grace * periods. The ->gp_tasks pointer indicates which element the normal * grace period is waiting on (NULL if none), and the ->exp_tasks pointer * indicates which element the expedited grace period is waiting on (again, * NULL if none). If a grace period is waiting on a given element in the * ->blkd_tasks list, it also waits on all subsequent elements. Thus, * adding a task to the tail of the list blocks any grace period that is * already waiting on one of the elements. In contrast, adding a task * to the head of the list won't block any grace period that is already * waiting on one of the elements. * * This queuing is imprecise, and can sometimes make an ongoing grace * period wait for a task that is not strictly speaking blocking it. * Given the choice, we needlessly block a normal grace period rather than * blocking an expedited grace period. * * Note that an endless sequence of expedited grace periods still cannot * indefinitely postpone a normal grace period. Eventually, all of the * fixed number of preempted tasks blocking the normal grace period that are * not also blocking the expedited grace period will resume and complete * their RCU read-side critical sections. At that point, the ->gp_tasks * pointer will equal the ->exp_tasks pointer, at which point the end of * the corresponding expedited grace period will also be the end of the * normal grace period. */
static void rcu_preempt_ctxt_queue(struct rcu_node *rnp, struct rcu_data *rdp)
__releases(rnp->lock) /* But leaves rrupts disabled. */
{
int blkd_state = (rnp->gp_tasks ? RCU_GP_TASKS : 0) +
(rnp->exp_tasks ? RCU_EXP_TASKS : 0) +
(rnp->qsmask & rdp->grpmask ? RCU_GP_BLKD : 0) +
(rnp->expmask & rdp->grpmask ? RCU_EXP_BLKD : 0);
struct task_struct *t = current;
raw_lockdep_assert_held_rcu_node(rnp);
WARN_ON_ONCE(rdp->mynode != rnp);
WARN_ON_ONCE(!rcu_is_leaf_node(rnp));
/* RCU better not be waiting on newly onlined CPUs! */
WARN_ON_ONCE(rnp->qsmaskinitnext & ~rnp->qsmaskinit & rnp->qsmask &
rdp->grpmask);
/*
* Decide where to queue the newly blocked task. In theory,
* this could be an if-statement. In practice, when I tried
* that, it was quite messy.
*/
switch (blkd_state) {
case 0:
case RCU_EXP_TASKS:
case RCU_EXP_TASKS + RCU_GP_BLKD:
case RCU_GP_TASKS:
case RCU_GP_TASKS + RCU_EXP_TASKS:
/*
* Blocking neither GP, or first task blocking the normal
* GP but not blocking the already-waiting expedited GP.
* Queue at the head of the list to avoid unnecessarily
* blocking the already-waiting GPs.
*/
list_add(&t->rcu_node_entry, &rnp->blkd_tasks);
break;
case RCU_EXP_BLKD:
case RCU_GP_BLKD:
case RCU_GP_BLKD + RCU_EXP_BLKD:
case RCU_GP_TASKS + RCU_EXP_BLKD:
case RCU_GP_TASKS + RCU_GP_BLKD + RCU_EXP_BLKD:
case RCU_GP_TASKS + RCU_EXP_TASKS + RCU_GP_BLKD + RCU_EXP_BLKD:
/*
* First task arriving that blocks either GP, or first task
* arriving that blocks the expedited GP (with the normal
* GP already waiting), or a task arriving that blocks
* both GPs with both GPs already waiting. Queue at the
* tail of the list to avoid any GP waiting on any of the
* already queued tasks that are not blocking it.
*/
list_add_tail(&t->rcu_node_entry, &rnp->blkd_tasks);
break;
case RCU_EXP_TASKS + RCU_EXP_BLKD:
case RCU_EXP_TASKS + RCU_GP_BLKD + RCU_EXP_BLKD:
case RCU_GP_TASKS + RCU_EXP_TASKS + RCU_EXP_BLKD:
/*
* Second or subsequent task blocking the expedited GP.
* The task either does not block the normal GP, or is the
* first task blocking the normal GP. Queue just after
* the first task blocking the expedited GP.
*/
list_add(&t->rcu_node_entry, rnp->exp_tasks);
break;
case RCU_GP_TASKS + RCU_GP_BLKD:
case RCU_GP_TASKS + RCU_EXP_TASKS + RCU_GP_BLKD:
/*
* Second or subsequent task blocking the normal GP.
* The task does not block the expedited GP. Queue just
* after the first task blocking the normal GP.
*/
list_add(&t->rcu_node_entry, rnp->gp_tasks);
break;
default:
/* Yet another exercise in excessive paranoia. */
WARN_ON_ONCE(1);
break;
}
rcu read-side critical section에 진입 후 preemption되어 처음 블럭된 태스크를 블럭드 리스트에 추가한다.
- 코드 라인 4~7에서 노드에서 4가지 조합으로 블럭드 상태를 알아온다.
- 현재 일반 gp에서 일반 gp 태스크를 가리키고 있는지 여부
- 현재 급행 gp에서 급행 gp 태스크를 가리키고 있는지 여부
- 미완료된 일반 qs가 있어 추가할 일반 gp 태스크인지 여부
- 미완료된 급행 qs가 있어 추가할 급행 gp 태스크인지 여부
- 코드 라인 8에서 현재 태스크가 preemption될 예정이다.
- Task A (current) -> Task B 인 경우 태스크 A에 해당한다.
- 코드 라인 22~36에서 블럭드 태스크 리스트에 현재 태스크를 추가한다.
- 코드 라인 38~54에서 블럭드 태스크 리스트의 뒤쪽에 현재 태스크를 추가한다.
- 코드 라인 56~67에서 급행 gp 태스크 리스트에 현재 태스크를 추가한다.
- 코드 라인 69~78에서 일반 gp 태스크 리스트에 현재 태스크를 추가한다.
kernel/rcu/tree_plugin.h -2/2-
/*
* We have now queued the task. If it was the first one to
* block either grace period, update the ->gp_tasks and/or
* ->exp_tasks pointers, respectively, to reference the newly
* blocked tasks.
*/
if (!rnp->gp_tasks && (blkd_state & RCU_GP_BLKD)) {
rnp->gp_tasks = &t->rcu_node_entry;
WARN_ON_ONCE(rnp->completedqs == rnp->gp_seq);
}
if (!rnp->exp_tasks && (blkd_state & RCU_EXP_BLKD))
rnp->exp_tasks = &t->rcu_node_entry;
WARN_ON_ONCE(!(blkd_state & RCU_GP_BLKD) !=
!(rnp->qsmask & rdp->grpmask));
WARN_ON_ONCE(!(blkd_state & RCU_EXP_BLKD) !=
!(rnp->expmask & rdp->grpmask));
raw_spin_unlock_rcu_node(rnp); /* interrupts remain disabled. */
/*
* Report the quiescent state for the expedited GP. This expedited
* GP should not be able to end until we report, so there should be
* no need to check for a subsequent expedited GP. (Though we are
* still in a quiescent state in any case.)
*/
if (blkd_state & RCU_EXP_BLKD && rdp->exp_deferred_qs)
rcu_report_exp_rdp(rdp);
else
WARN_ON_ONCE(rdp->exp_deferred_qs);
}
- 코드 라인 7~10에서 첫 일반 gp 태스크가 추가된 경우이다.
- 일반 gp 태스크 리스트 포인터가 비어있고, 일반 gp 태스크가 추가될 때 gp 태스크 리스트 포인터가 현재 태스크를 가리키게 한다.
- 코드 라인 11~12에서 첫 급행 gp 태스크가 추가된 경우이다.
- 급행 gp 태스크 리스트 포인터가 비어있고, 급행 gp 태스크가 추가될 때 급행 gp 태스크 리스트 포인터가 현재 태스크를 가리키게 한다.
- 코드 라인 25~26에서 급행 gp 태스크가 추가되었고 현재 cpu가 급행 qs 유예 상태인 경우 유예 상태를 제거하고 노드에 급행 qs를 보고한다.
kernel/rcu/tree_plugin.h
/* Flags for rcu_preempt_ctxt_queue() decision table. */ #define RCU_GP_TASKS 0x8 #define RCU_EXP_TASKS 0x4 #define RCU_GP_BLKD 0x2 #define RCU_EXP_BLKD 0x1
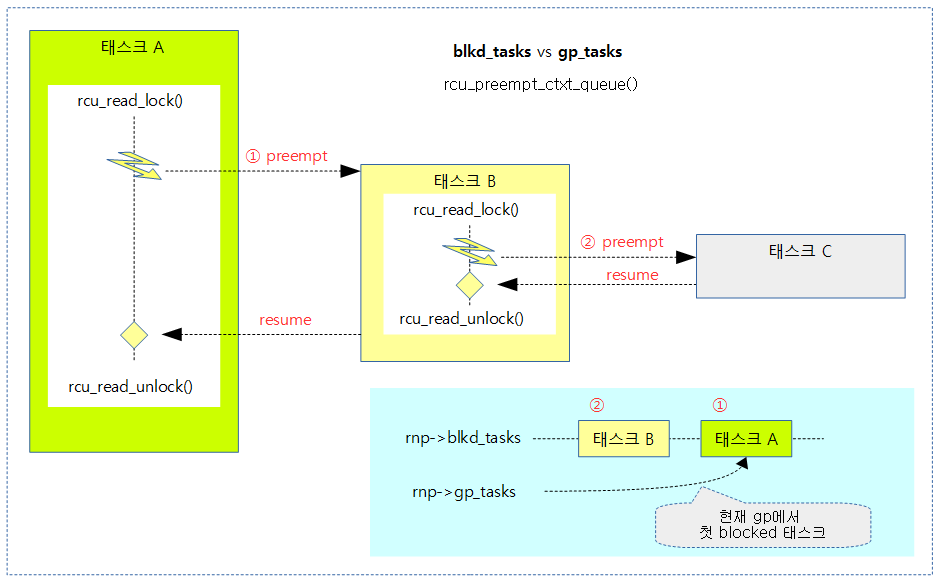
다음 그림은 rcu read-side critical secition 내에서 preempt되어 rcu_preempt_ctxt_queue() 함수가 블럭드 태스크를 추가하는 모습을 보여준다.
- gp가 계속 유효한 태스크는 A이다.
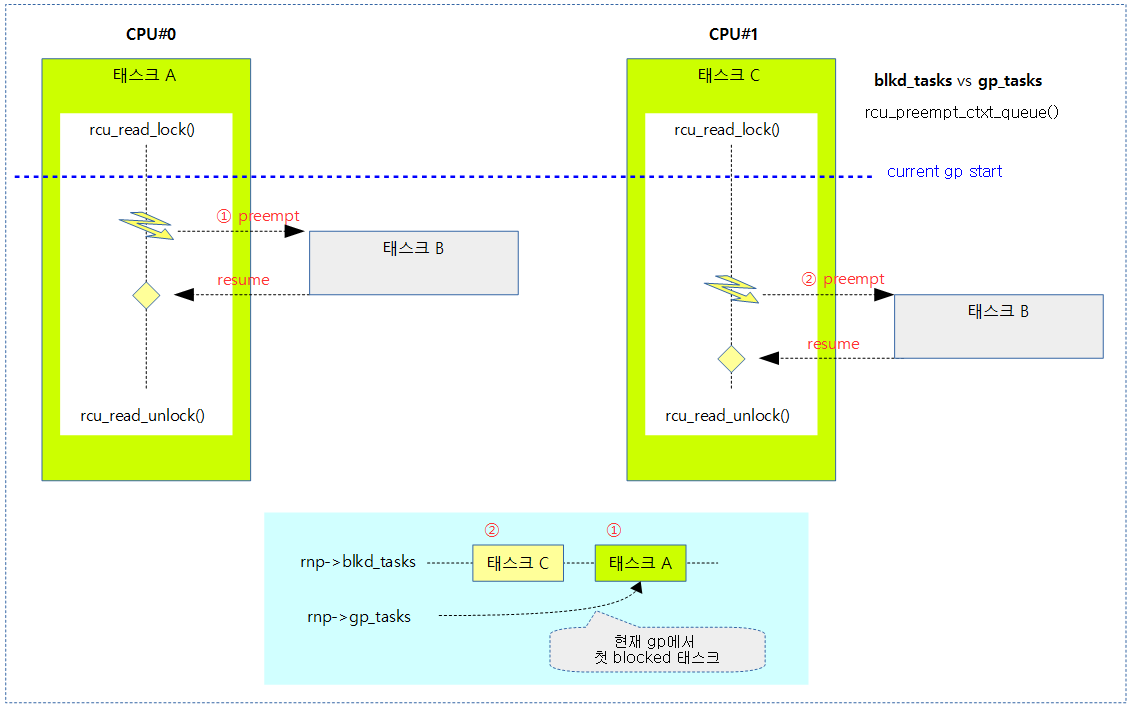
다음 그림은 rcu_read_unlock() 함수내에서 여러 개의 cpu에서 동시에 special 케이스를 진행할 때 현재 gp 시작 이후 가장 처음 블럭된 블럭되었던 태스크 A가 gp_tasks에 지정된 모습을 보여준다.
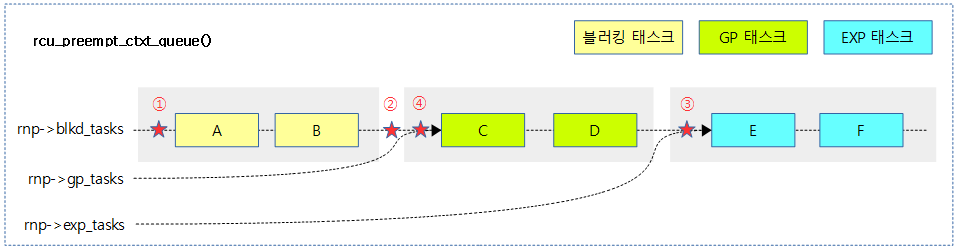
다음 그림은 태스크들이 blkd_tasks에 추가될 때 gp_tasks와 exp_tasks는 리스트 포인터를 이용하여 3가지 리스트로 관리를 하는 모습을 보여준다.
- 코드 라인 아래 붉은 색 원에 있는 숫자는 코드에서 각 case 문 순서에 해당한다.
- (2)번의 경우 blkd_tasks 리스트의 뒤에 추가하는데 case 문 뒤에 이어지는 조건에서 추가된 태스크가 어떤 영역에 들어갈지 결정된다.
스케줄틱에서 qs 처리
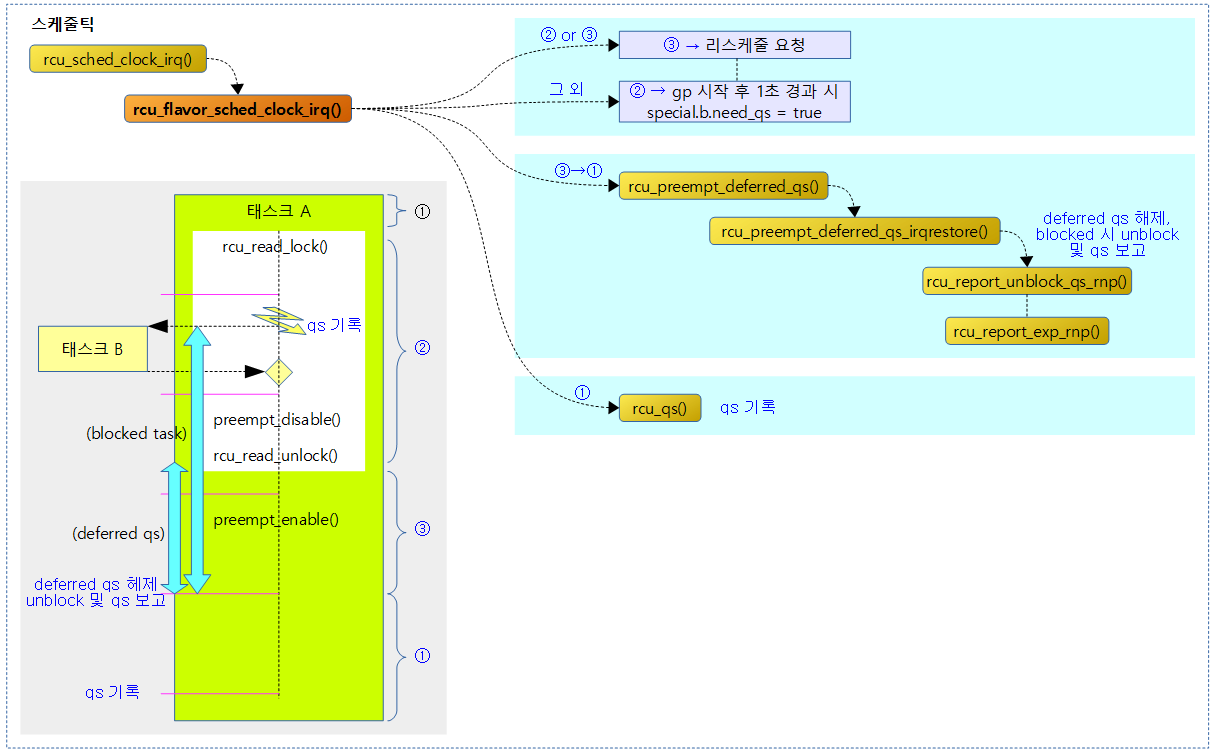
rcu_sched_clock_irq()
kernel/rcu/tree.c
/* * This function is invoked from each scheduling-clock interrupt, * and checks to see if this CPU is in a non-context-switch quiescent * state, for example, user mode or idle loop. It also schedules RCU * core processing. If the current grace period has gone on too long, * it will ask the scheduler to manufacture a context switch for the sole * purpose of providing a providing the needed quiescent state. */
void rcu_sched_clock_irq(int user)
{
trace_rcu_utilization(TPS("Start scheduler-tick"));
raw_cpu_inc(rcu_data.ticks_this_gp);
/* The load-acquire pairs with the store-release setting to true. */
if (smp_load_acquire(this_cpu_ptr(&rcu_data.rcu_urgent_qs))) {
/* Idle and userspace execution already are quiescent states. */
if (!rcu_is_cpu_rrupt_from_idle() && !user) {
set_tsk_need_resched(current);
set_preempt_need_resched();
}
__this_cpu_write(rcu_data.rcu_urgent_qs, false);
}
rcu_flavor_sched_clock_irq(user);
if (rcu_pending())
invoke_rcu_core();
trace_rcu_utilization(TPS("End scheduler-tick"));
}
매 스케줄 틱마다 호출되어 rcu 관련하여 현재 cpu의 qs를 체크하고, gp 완료되어 처리를 기다리는 콜백들을 처리하기 위해 동작한다.
- 코드 라인 4에서 이 함수가 호출될 때 마다 현재 cpu의 ticks_this_gp를 1 증가시킨다.
- 이 정보는 gp 시작 시 초기화되며, print_cpu_stall_info() 함수내에서 cpu의 rcu stall 정보를 출력할 때에만 사용된다.
- 코드 라인 6~13에서 현재 cpu에서 rcu_urgent_qs가 검출되는 경우 이를 제거하고, 만일 커널에서 실행 중에 인터럽트가 들어온 경우 리스케줄 요청한다.
- 코드 라인 14에서 스케줄 틱마다 qs를 체크한다.
- 코드 라인 15~16에서 rcu 콜백이 아직 처리되지 않고 남아있는 경우 콜백 처리를 시작한다.
rcu_flavor_sched_clock_irq()
kernel/rcu/tree_plugin.h
/* * Check for a quiescent state from the current CPU, including voluntary * context switches for Tasks RCU. When a task blocks, the task is * recorded in the corresponding CPU's rcu_node structure, which is checked * elsewhere, hence this function need only check for quiescent states * related to the current CPU, not to those related to tasks. */
static void rcu_flavor_sched_clock_irq(int user)
{
struct task_struct *t = current;
if (user || rcu_is_cpu_rrupt_from_idle()) {
rcu_note_voluntary_context_switch(current);
}
if (t->rcu_read_lock_nesting > 0 ||
(preempt_count() & (PREEMPT_MASK | SOFTIRQ_MASK))) {
/* No QS, force context switch if deferred. */
if (rcu_preempt_need_deferred_qs(t)) {
set_tsk_need_resched(t);
set_preempt_need_resched();
}
} else if (rcu_preempt_need_deferred_qs(t)) {
rcu_preempt_deferred_qs(t); /* Report deferred QS. */
return;
} else if (!t->rcu_read_lock_nesting) {
rcu_qs(); /* Report immediate QS. */
return;
}
/* If GP is oldish, ask for help from rcu_read_unlock_special(). */
if (t->rcu_read_lock_nesting > 0 &&
__this_cpu_read(rcu_data.core_needs_qs) &&
__this_cpu_read(rcu_data.cpu_no_qs.b.norm) &&
!t->rcu_read_unlock_special.b.need_qs &&
time_after(jiffies, rcu_state.gp_start + HZ))
t->rcu_read_unlock_special.b.need_qs = true;
}
스케줄 틱마다 현재 cpu의 qs를 체크하고 조건에 따라 qs를 기록 또는 deferred qs를 처리하고 qs를 보고한다.
- 코드 라인 5~7에서 유저 태스크 또는 커널 태스크의 idle 중에 스케줄 틱으로 진입한 경우 태스크의 holdout 상태의 태스크를 클리어한다.
- 코드 라인 8~21에서 스케줄 틱마다 현재 cpu의 qs 체크 관련하여 다음 4가지 조건 중 하나를 수행한다.
- rcu reader가 내부에 있거나 bh/preempt disable 상태인 경우
- rcu reader 내부가 아닌 경우에만 리스케줄 요청 후 계속 진행한다.
- deferred qs 상태인 경우
- deferred qs 상태인 경우 deferred qs를 해제한다. 또한 block 해제 가능한 상태인 경우 block 태스크를 해제하고 qs 보고하고 함수를 빠져나간다.
- rcu reader 외부에 있는 경우
- 현재 cpu의 qs를 기록하고 함수를 빠져나간다.
- 그 외 다음을 계속 진행한다.
- rcu reader가 내부에 있거나 bh/preempt disable 상태인 경우
- 코드 라인 24~29에서 rcu read-side critical section이 진행 중이고, 현재 cpu의 qs가 아직 체크되지 않았고, unlock special의 need_qs가 없으며, gp 시작 후 1초가 경과한 경우 unlock special을 동작시키기 위해 need_qs를 true로 변경한다.
다음 그림은 스케줄 틱마다 현재 cpu의 qs를 체크하고 조건에 따라 qs를 기록 또는 보고하는 과정을 보여준다.
deferred qs 처리 및 block 태스크 해제 시 qs 보고
rcu_preempt_deferred_qs()
kernel/rcu/tree_plugin.h
/* * Report a deferred quiescent state if needed and safe to do so. * As with rcu_preempt_need_deferred_qs(), "safe" involves only * not being in an RCU read-side critical section. The caller must * evaluate safety in terms of interrupt, softirq, and preemption * disabling. */
static void rcu_preempt_deferred_qs(struct task_struct *t)
{
unsigned long flags;
bool couldrecurse = t->rcu_read_lock_nesting >= 0;
if (!rcu_preempt_need_deferred_qs(t))
return;
if (couldrecurse)
t->rcu_read_lock_nesting -= RCU_NEST_BIAS;
local_irq_save(flags);
rcu_preempt_deferred_qs_irqrestore(t, flags);
if (couldrecurse)
t->rcu_read_lock_nesting += RCU_NEST_BIAS;
}
deferred qs 상태인 경우 deferred qs를 해제한다. 또한 block 해제 가능한 상태인 경우 block 태스크를 해제하고 qs 보고한다.
- 코드 라인 4에서 현재 태스크에 RCU_NEST_BIAS가 진행중이지 않은지 여부를 couldrecurse에 알아온다.
- RCU_NEST_BIAS 진행 중인 경우 음수가 되어 이 값은 false가 된다.
- 코드 라인 6~7에서 이미 qs 유예 처리가 진행 중인 경우 함수를 빠져나간다.
- 코드 라인 8~9에서 couldrecurse가 true인 경우에만 t->rcu_read_lock_nesting 값에서 임시로 RCU_NEST_BIAS을 뺀다.
- 코드 라인 10~11에서 스핀락을 획득한 후 deferred qs 상태인 경우 deferred qs를 해제한다. 또한 block 해제 가능한 상태인 경우 block 태스크를 해제하고 qs를 보고한다.
- 코드 라인 12~13에서 t->rcu_read_lock_nesting 값을 원래 값으로 원복한다.
rcu_preempt_need_deferred_qs()
kernel/rcu/tree_plugin.h
/* * Is a deferred quiescent-state pending, and are we also not in * an RCU read-side critical section? It is the caller's responsibility * to ensure it is otherwise safe to report any deferred quiescent * states. The reason for this is that it is safe to report a * quiescent state during context switch even though preemption * is disabled. This function cannot be expected to understand these * nuances, so the caller must handle them. */
static bool rcu_preempt_need_deferred_qs(struct task_struct *t)
{
return (__this_cpu_read(rcu_data.exp_deferred_qs) ||
READ_ONCE(t->rcu_read_unlock_special.s)) &&
t->rcu_read_lock_nesting <= 0;
}
deferred qs 처리가 펜딩중인지 또는 급행 deferred qs가 이미 진행중인지 여부를 반환한다.
- 이미 급행 qs 유예(exp_deferred_qs)가 설정된 경우이거나
- 태스크에 rcu_read_unlock_special.s 가 설정되었고 다른 곳에서 deferred qs가 펜딩중인 경우(RCU_NEST_BIAS 처리)
IRQ 워크 – qs 유예 핸들러
rcu_preempt_deferred_qs_handler()
kernel/rcu/tree_plugin.h
/* * Minimal handler to give the scheduler a chance to re-evaluate. */
static void rcu_preempt_deferred_qs_handler(struct irq_work *iwp)
{
struct rcu_data *rdp;
rdp = container_of(iwp, struct rcu_data, defer_qs_iw);
rdp->defer_qs_iw_pending = false;
}
irq 워크로 부터 호출되는 핸들러이다. 현재 cpu에 해당하는 rdp->defer_qs_iw_pending에 false를 대입한다.
irq 복구하면서 deferred qs 해제 및 블럭 태스크 해제
rcu_preempt_deferred_qs_irqrestore()
kernel/rcu/tree_plugin.h -1/2-
/* * Report deferred quiescent states. The deferral time can * be quite short, for example, in the case of the call from * rcu_read_unlock_special(). */
static void
rcu_preempt_deferred_qs_irqrestore(struct task_struct *t, unsigned long flags)
{
bool empty_exp;
bool empty_norm;
bool empty_exp_now;
struct list_head *np;
bool drop_boost_mutex = false;
struct rcu_data *rdp;
struct rcu_node *rnp;
union rcu_special special;
/*
* If RCU core is waiting for this CPU to exit its critical section,
* report the fact that it has exited. Because irqs are disabled,
* t->rcu_read_unlock_special cannot change.
*/
special = t->rcu_read_unlock_special;
rdp = this_cpu_ptr(&rcu_data);
if (!special.s && !rdp->exp_deferred_qs) {
local_irq_restore(flags);
return;
}
t->rcu_read_unlock_special.b.deferred_qs = false;
if (special.b.need_qs) {
rcu_qs();
t->rcu_read_unlock_special.b.need_qs = false;
if (!t->rcu_read_unlock_special.s && !rdp->exp_deferred_qs) {
local_irq_restore(flags);
return;
}
}
/*
* Respond to a request by an expedited grace period for a
* quiescent state from this CPU. Note that requests from
* tasks are handled when removing the task from the
* blocked-tasks list below.
*/
if (rdp->exp_deferred_qs) {
rcu_report_exp_rdp(rdp);
if (!t->rcu_read_unlock_special.s) {
local_irq_restore(flags);
return;
}
}
preemptible rcu에서 irq를 해제하면서 deferred qs가 설정된 경우 해제하고, 블럭 태스크도 해제한 후 qs를 보고한다.
- 코드 라인 18~23에서 태스크에 unlock special이 설정되지 않았고 급행 qs의 유예도 없는 경우 로컬 irq를 원복한 후 함수를 빠져나간다.
- 코드 라인 24에서 태스크에서 unlock spcial의 deferred qs를 해제한다.
- 코드 라인 25~32에서 태스크에서 unlock special의 need_qs가 설정된 경우 이를 클리어하고, 현재 cpu의 qs를 즉각 보고한다. 다시 한 번 태스크에 unlock special이 설정되지 않았고 급행 qs의 유예도 없는 경우 로컬 irq를 원복한 후 함수를 빠져나간다.
- rcu reader nesting 후 deferred qs 설정된 경우도 아닌데 gp 시작 후 1초가 지나면 need_qs를 설정하여 unlock special 케이스에서 qs를 보고하게 한다.
- 코드 라인 40~46에서 급행 qs 유예가 설정된 경우 이를 보고한다. 만일 태스크에 unlock special이 설정되지 않은 경우 로컬 irq를 원복한 후 함수를 빠져나간다.
kernel/rcu/tree_plugin.h -2/2-
/* Clean up if blocked during RCU read-side critical section. */
if (special.b.blocked) {
t->rcu_read_unlock_special.b.blocked = false;
/*
* Remove this task from the list it blocked on. The task
* now remains queued on the rcu_node corresponding to the
* CPU it first blocked on, so there is no longer any need
* to loop. Retain a WARN_ON_ONCE() out of sheer paranoia.
*/
rnp = t->rcu_blocked_node;
raw_spin_lock_rcu_node(rnp); /* irqs already disabled. */
WARN_ON_ONCE(rnp != t->rcu_blocked_node);
WARN_ON_ONCE(!rcu_is_leaf_node(rnp));
empty_norm = !rcu_preempt_blocked_readers_cgp(rnp);
WARN_ON_ONCE(rnp->completedqs == rnp->gp_seq &&
(!empty_norm || rnp->qsmask));
empty_exp = sync_rcu_preempt_exp_done(rnp);
smp_mb(); /* ensure expedited fastpath sees end of RCU c-s. */
np = rcu_next_node_entry(t, rnp);
list_del_init(&t->rcu_node_entry);
t->rcu_blocked_node = NULL;
trace_rcu_unlock_preempted_task(TPS("rcu_preempt"),
rnp->gp_seq, t->pid);
if (&t->rcu_node_entry == rnp->gp_tasks)
rnp->gp_tasks = np;
if (&t->rcu_node_entry == rnp->exp_tasks)
rnp->exp_tasks = np;
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_RCU_BOOST)) {
/* Snapshot ->boost_mtx ownership w/rnp->lock held. */
drop_boost_mutex = rt_mutex_owner(&rnp->boost_mtx) == t;
if (&t->rcu_node_entry == rnp->boost_tasks)
rnp->boost_tasks = np;
}
/*
* If this was the last task on the current list, and if
* we aren't waiting on any CPUs, report the quiescent state.
* Note that rcu_report_unblock_qs_rnp() releases rnp->lock,
* so we must take a snapshot of the expedited state.
*/
empty_exp_now = sync_rcu_preempt_exp_done(rnp);
if (!empty_norm && !rcu_preempt_blocked_readers_cgp(rnp)) {
trace_rcu_quiescent_state_report(TPS("preempt_rcu"),
rnp->gp_seq,
0, rnp->qsmask,
rnp->level,
rnp->grplo,
rnp->grphi,
!!rnp->gp_tasks);
rcu_report_unblock_qs_rnp(rnp, flags);
} else {
raw_spin_unlock_irqrestore_rcu_node(rnp, flags);
}
/* Unboost if we were boosted. */
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_RCU_BOOST) && drop_boost_mutex)
rt_mutex_futex_unlock(&rnp->boost_mtx);
/*
* If this was the last task on the expedited lists,
* then we need to report up the rcu_node hierarchy.
*/
if (!empty_exp && empty_exp_now)
rcu_report_exp_rnp(rnp, true);
} else {
local_irq_restore(flags);
}
}
- 코드 라인 2~3에서 preemptible rcu에서 태스크가 rcu critical seciont에 진입 후 preemption되어 태스크에 unlock special의 blocked 비트가 설정된 경우 이를 클리어한다.
- 코드 라인 11~12에서 태스크가 블럭된 노드에 대해 스핀락을 얻어온다.
- 코드 라인 15에서 현재 gp에서 해당 노드의 preemptible rcu의 블럭드 태스크들이 없는지 여부를 empty_norm에 담는다. (다시 읽어 비교할 예정)
- 코드 라인 18에서 현재 gp에서 해당 노드에 preemptible rcu의 블럭드 태스크들이 없고 급행 qs 보고도 모두 완료된 여부를 empty_exp에 담는다. (다시 읽어 비교할 예정)
- 코드 라인 20~34에서 노드의 블럭드 태스크 리스트에서 첫 블럭드 태스크를 리스트에서 제거한다. 그 후 다음 3가지 포인터도 다음 블럭드 태스크를 가리키게 한다.
- gp_tasks가 제거한 블럭드 태스크를 가리키고 있었던 경우
- exp_tasks가 제거한 블럭드 태스크를 가리키고 있었던 경우
- boost_tasks가 제거한 블럭드 태스크를 가리키고 있었던 경우
- 코드 라인 42에서 해당 노드에 preemptible rcu의 블럭드 태스크들이 없고 급행 qs 보고도 모두 완료된 경우 여부를 empty_exp_now에 담는다.
- 코드 라인 43~54에서 해당 노드의 preemptible rcu의 블럭드 태스크들이 있었지만(empty_norm == false) 다시 읽었을 때 없어진 경우unblock 되었으므로 qs를 보고한다. 그 외의 경우 스핀 락과 로컬 irq 원복하고 preempt도 enable 한다.
- 코드 라인 57~58에서 이미 bootst된 경우 boost unlock 한다.
- 코드 라인 64~65에서 블럭드 상태였지만 급행 qs가 모두 완료된 경우 급행 qs를 보고한다.
- 코드 라인 66~68에서 preemptible rcu에서 태스크가 rcu critical seciont에 진입 후 preemption되지 않아 블럭된적이 없으면 그냥 로컬 irq를 원복한다.
blocked 태스크 체크 에러 시 덤프
rcu_preempt_check_blocked_tasks()
kernel/rcu/tree_plugin.h
/* * Check that the list of blocked tasks for the newly completed grace * period is in fact empty. It is a serious bug to complete a grace * period that still has RCU readers blocked! This function must be * invoked -before- updating this rnp's ->gp_seq, and the rnp's ->lock * must be held by the caller. * * Also, if there are blocked tasks on the list, they automatically * block the newly created grace period, so set up ->gp_tasks accordingly. */
static void rcu_preempt_check_blocked_tasks(struct rcu_node *rnp)
{
struct task_struct *t;
RCU_LOCKDEP_WARN(preemptible(), "rcu_preempt_check_blocked_tasks() invoked with preemption enabled!!!\n");
if (WARN_ON_ONCE(rcu_preempt_blocked_readers_cgp(rnp)))
dump_blkd_tasks(rnp, 10);
if (rcu_preempt_has_tasks(rnp) &&
(rnp->qsmaskinit || rnp->wait_blkd_tasks)) {
rnp->gp_tasks = rnp->blkd_tasks.next;
t = container_of(rnp->gp_tasks, struct task_struct,
rcu_node_entry);
trace_rcu_unlock_preempted_task(TPS("rcu_preempt-GPS"),
rnp->gp_seq, t->pid);
}
WARN_ON_ONCE(rnp->qsmask);
}
gp 시작할 때 이 함수가 호출되어 블럭된 태스크들이 있는지 체크한다. 만일 해당 노드에 블럭된 태스크들이 있으면 dump 출력을 한다.
dump_blkd_tasks()
kernel/rcu/tree_plugin.h
/* * Dump the blocked-tasks state, but limit the list dump to the * specified number of elements. */
static void
dump_blkd_tasks(struct rcu_node *rnp, int ncheck)
{
int cpu;
int i;
struct list_head *lhp;
bool onl;
struct rcu_data *rdp;
struct rcu_node *rnp1;
raw_lockdep_assert_held_rcu_node(rnp);
pr_info("%s: grp: %d-%d level: %d ->gp_seq %ld ->completedqs %ld\n",
__func__, rnp->grplo, rnp->grphi, rnp->level,
(long)rnp->gp_seq, (long)rnp->completedqs);
for (rnp1 = rnp; rnp1; rnp1 = rnp1->parent)
pr_info("%s: %d:%d ->qsmask %#lx ->qsmaskinit %#lx ->qsmaskinitnext %#lx\n",
__func__, rnp1->grplo, rnp1->grphi, rnp1->qsmask, rnp1->qsmaskinit, rnp1->qsmaskinitnext);
pr_info("%s: ->gp_tasks %p ->boost_tasks %p ->exp_tasks %p\n",
__func__, rnp->gp_tasks, rnp->boost_tasks, rnp->exp_tasks);
pr_info("%s: ->blkd_tasks", __func__);
i = 0;
list_for_each(lhp, &rnp->blkd_tasks) {
pr_cont(" %p", lhp);
if (++i >= ncheck)
break;
}
pr_cont("\n");
for (cpu = rnp->grplo; cpu <= rnp->grphi; cpu++) {
rdp = per_cpu_ptr(&rcu_data, cpu);
onl = !!(rdp->grpmask & rcu_rnp_online_cpus(rnp));
pr_info("\t%d: %c online: %ld(%d) offline: %ld(%d)\n",
cpu, ".o"[onl],
(long)rdp->rcu_onl_gp_seq, rdp->rcu_onl_gp_flags,
(long)rdp->rcu_ofl_gp_seq, rdp->rcu_ofl_gp_flags);
}
}
노드에 블럭된 태스크들이 있을 때 호출되며, 관련 정보를 덤프한다.
no-hz idle 진입전에 rcu 콜백들 호출
rcu_prepare_for_idle()
kernel/rcu/tree_plugin.h
/* * Prepare a CPU for idle from an RCU perspective. The first major task * is to sense whether nohz mode has been enabled or disabled via sysfs. * The second major task is to check to see if a non-lazy callback has * arrived at a CPU that previously had only lazy callbacks. The third * major task is to accelerate (that is, assign grace-period numbers to) * any recently arrived callbacks. * * The caller must have disabled interrupts. */
static void rcu_prepare_for_idle(void)
{
bool needwake;
struct rcu_data *rdp = this_cpu_ptr(&rcu_data);
struct rcu_node *rnp;
int tne;
lockdep_assert_irqs_disabled();
if (rcu_segcblist_is_offloaded(&rdp->cblist))
return;
/* Handle nohz enablement switches conservatively. */
tne = READ_ONCE(tick_nohz_active);
if (tne != rdp->tick_nohz_enabled_snap) {
if (!rcu_segcblist_empty(&rdp->cblist))
invoke_rcu_core(); /* force nohz to see update. */
rdp->tick_nohz_enabled_snap = tne;
return;
}
if (!tne)
return;
/*
* If a non-lazy callback arrived at a CPU having only lazy
* callbacks, invoke RCU core for the side-effect of recalculating
* idle duration on re-entry to idle.
*/
if (rdp->all_lazy && rcu_segcblist_n_nonlazy_cbs(&rdp->cblist)) {
rdp->all_lazy = false;
invoke_rcu_core();
return;
}
/*
* If we have not yet accelerated this jiffy, accelerate all
* callbacks on this CPU.
*/
if (rdp->last_accelerate == jiffies)
return;
rdp->last_accelerate = jiffies;
if (rcu_segcblist_pend_cbs(&rdp->cblist)) {
rnp = rdp->mynode;
raw_spin_lock_rcu_node(rnp); /* irqs already disabled. */
needwake = rcu_accelerate_cbs(rnp, rdp);
raw_spin_unlock_rcu_node(rnp); /* irqs remain disabled. */
if (needwake)
rcu_gp_kthread_wake();
}
}
cpu가 idle 진입 전에 남은 non-lazy rcu 콜백들을 호출하여 처리한다.
- 코드 라인 9~10에서 콜백 offloaded 상태인 경우 함수를 빠져나간다.
- 코드 라인 13~21에서 nohz_active에 변경이 있는 경우 남은 콜백이 있으면 콜백을 처리하기 위해 rcu core를 호출하고 함수를 빠져나간다. 만일 nohz가 active되어 있지 않은 경우 함수를 빠져나간다.
- nohz는 절전이 필요한 모바일 시스템에서 사용되는 옵션이다.
- 코드 라인 28~32에서 non-lazy 콜백이 도착했는데 기존에 모든 콜백이 lazy인 경우 rdp->all_lazy를 false로 변경 후 콜백을 처리하기 위해 rcu core를 호출하고 함수를 빠져나간다.
- non lazy 콜백들은 idle 진입할 때 모두 호출한다.
- 코드 라인 38~40에서 현재 jiffies 틱에 이미 accelerate 처리한 경우 함수를 빠져나간다.
- 코드 라인 41~48에서 펜딩 콜백들이 있는 경우 acceleration 처리한다.
rcu_special 유니언
include/linux/sched.h
union rcu_special {
struct {
u8 blocked;
u8 need_qs;
u8 exp_hint; /* Hint for performance. */
u8 deferred_qs;
} b; /* Bits. */
u32 s; /* Set of bits. */
};
태스크에서 rcu read-side critical section 수행 중 unlock special 케이스로 동작해야 하는데 이를 관리하기 위한 유니언 값이다.
- b.blocked
- rcu read-side critical section 수행 중 태스크가 preempt 되어 블럭된 적이 있는지 여부를 나태낸다.
- __schedule() -> rcu_note_context_switch() 함수 호출 경로를 통해 수행된다.
- b.need_qs
- rcu reader nesting 상태에서 deferred qs 설정된 경우도 아닌데 gp 시작 후 1초가 지났는지 매 스케줄 틱마다 체크한 후 발생 시 need_qs를 설정한다. 그 후 이렇게 설정된 비트는 unlock special 케이스에서 qs를 보고하게 한다.
- 스케줄 틱 -> update_process_times() -> rcu_sched_clock_irq() -> rcu_flavor_sched_clock_irq() 함수 호출 경로를 통해 수행된다.
- b.exp_hint
- 급행 qs를 처리하도록 IPI call로 호출된 rcu_exp_handler() 함수내에서 태스크가 rcu read-side critical section내에서 수행 중이고 급행 qs가 보고되지 않은 경우 이 비트를 true로 설정한다. 이 때 rdp->exp_deferred_qs도 true로 설정된다.
- b.deferred_qs
- preempt 되었었던 rcu reader에서 irq/bh/preempt 들 중 하나라도 disable된 상태에서 rcu_read_unlock 하는 경우 rcu_read_unlock_special의 deferred_qs 비트를 설정한다.
- 추후 qs 완료는 rcu_preempt_deferred_qs_irqrestore() 함수가 호출될 때 블럭된 태스크를 제거하면서 qs가 보고된다.
- rcu_read_unlock() -> rcu_read_unlock_special() 함수 호출 경로를 통해 수행된다.
- preempt 되었었던 rcu reader에서 irq/bh/preempt 들 중 하나라도 disable된 상태에서 rcu_read_unlock 하는 경우 rcu_read_unlock_special의 deferred_qs 비트를 설정한다.
- s
- 위의 비트 모두를 합한 비트셋
rcu_noqs 유니언
kernel/rcu/tree.h
/* * Union to allow "aggregate OR" operation on the need for a quiescent * state by the normal and expedited grace periods. */
union rcu_noqs {
struct {
u8 norm;
u8 exp;
} b; /* Bits. */
u16 s; /* Set of bits, aggregate OR here. */
};
cpu에서 qs가 아직 체크되지 않은지 여부를 관리하는 유니온 값이다.
- b.norm
- normal gp를 사용할 때 이 값이 1인 경우 현재 cpu에서 qs가 체크되지 않은 상태이다. 체크되면 0으로 바뀐다.
- b.exp
- 급행 gp를 사용할 때 이 값이 1인 경우 현재 cpu에서 급행 qs가 체크되지 않은 상태이다. 체크되면 0으로 바뀐다.
- s
- 위의 비트 모두 합한 비트셋
참고
- RCU(Read Copy Update) -1- (Basic) | 문c
- RCU(Read Copy Update) -2- (Callback process) | 문c
- RCU(Read Copy Update) -3- (RCU threads) | 문c
- RCU(Read Copy Update) -4- (NOCB process) | 문c
- RCU(Read Copy Update) -5- (Callback list) | 문c
- RCU(Read Copy Update) -6- (Expedited GP) | 문c
- RCU(Read Copy Update) -7- (Preemptible RCU) | 문c – 현재글
- rcu_init() | 문c
- wait_for_completion() | 문c