<kernel v5.4>
RCU(Read Copy Update) -2- (Callback process)
RCU_BH 및 RCU_SCHED state 제거
커널 v4.20-rc1 부터 rcu_preempt, rcu_bh 및 rcu_sched와 같이 3 종류의 state를 사용하여 왔는데 rcu_preempt 하나로 통합되었다.
- call_rcu_bh() 및 call_rcu_sched() 함수는 제거되었고, 대신 call_rcu() 만을 사용한다.
다음은 커널 v4.19에서 사용하는 rcu 스레드를 보여준다.
$ ps -ef | grep rcu root 3 2 0 Jan15 ? 00:00:00 [rcu_gp] root 4 2 0 Jan15 ? 00:00:00 [rcu_par_gp] root 10 2 0 Jan15 ? 00:27:01 [rcu_preempt] root 11 2 0 Jan15 ? 00:00:10 [rcu_sched] root 12 2 0 Jan15 ? 00:00:00 [rcu_bh] root 32 2 0 Jan15 ? 00:00:00 [rcu_tasks_kthre]
다음은 커널 v5.4에서 사용하는 rcu 스레드를 보여준다.
- rcu_sched 및 rcu_bh가 없는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
$ ps -ef | grep rcu root 3 2 0 Mar10 ? 00:00:00 [rcu_gp] root 4 2 0 Mar10 ? 00:00:00 [rcu_par_gp] root 10 2 0 Mar10 ? 00:00:06 [rcu_preempt] root 20 2 0 Mar10 ? 00:00:00 [rcu_tasks_kthre]
RCU 동기 Update
synchronize_rcu()
kernel/rcu/tree.c
/** * synchronize_rcu - wait until a grace period has elapsed. * * Control will return to the caller some time after a full grace * period has elapsed, in other words after all currently executing RCU * read-side critical sections have completed. Note, however, that * upon return from synchronize_rcu(), the caller might well be executing * concurrently with new RCU read-side critical sections that began while * synchronize_rcu() was waiting. RCU read-side critical sections are * delimited by rcu_read_lock() and rcu_read_unlock(), and may be nested. * In addition, regions of code across which interrupts, preemption, or * softirqs have been disabled also serve as RCU read-side critical * sections. This includes hardware interrupt handlers, softirq handlers, * and NMI handlers. * * Note that this guarantee implies further memory-ordering guarantees. * On systems with more than one CPU, when synchronize_rcu() returns, * each CPU is guaranteed to have executed a full memory barrier since * the end of its last RCU read-side critical section whose beginning * preceded the call to synchronize_rcu(). In addition, each CPU having * an RCU read-side critical section that extends beyond the return from * synchronize_rcu() is guaranteed to have executed a full memory barrier * after the beginning of synchronize_rcu() and before the beginning of * that RCU read-side critical section. Note that these guarantees include * CPUs that are offline, idle, or executing in user mode, as well as CPUs * that are executing in the kernel. * * Furthermore, if CPU A invoked synchronize_rcu(), which returned * to its caller on CPU B, then both CPU A and CPU B are guaranteed * to have executed a full memory barrier during the execution of * synchronize_rcu() -- even if CPU A and CPU B are the same CPU (but * again only if the system has more than one CPU). */
void synchronize_rcu(void)
{
RCU_LOCKDEP_WARN(lock_is_held(&rcu_bh_lock_map) ||
lock_is_held(&rcu_lock_map) ||
lock_is_held(&rcu_sched_lock_map),
"Illegal synchronize_rcu() in RCU read-side critical section");
if (rcu_blocking_is_gp())
return;
if (rcu_gp_is_expedited())
synchronize_rcu_expedited();
else
wait_rcu_gp(call_rcu);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(synchronize_rcu);
grace period가 지날때까지 기다린다(sleep).
- 코드 라인 7~8에서 아직 rcu의 gp 사용이 블러킹상태인 경우엔 gp 대기 없이 곧바로 함수를 빠져나간다.
- preemptible 커널에서 아직 rcu 스케쥴러가 동작하지 않는 경우
- 부팅 중인 경우 또는 1개의 online cpu만을 사용하는 경우
- 코드 라인 9~12에서 gp를 대기할 때 조건에 따라 다음 두 가지중 하나를 선택하여 동작한다.
- 더 신속한 Brute-force RCU grace period 방법
- 일반 RCU grace period 방법
rcu_blocking_is_gp()
kernel/rcu/tree.c
/* * During early boot, any blocking grace-period wait automatically * implies a grace period. Later on, this is never the case for PREEMPT. * * Howevr, because a context switch is a grace period for !PREEMPT, any * blocking grace-period wait automatically implies a grace period if * there is only one CPU online at any point time during execution of * either synchronize_rcu() or synchronize_rcu_expedited(). It is OK to * occasionally incorrectly indicate that there are multiple CPUs online * when there was in fact only one the whole time, as this just adds some * overhead: RCU still operates correctly. */
static int rcu_blocking_is_gp(void)
{
int ret;
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_PREEMPTION))
return rcu_scheduler_active == RCU_SCHEDULER_INACTIVE;
might_sleep(); /* Check for RCU read-side critical section. */
preempt_disable();
ret = num_online_cpus() <= 1;
preempt_enable();
return ret;
}
rcu의 gp 사용이 블러킹된 상태인지 여부를 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 5~6에서 preemptible 커널인 경우 rcu 스케쥴러가 비활성화 여부에 따라 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 7~11에서 online cpu수를 카운트하여 1개 이하인 경우 blocking 상태로 반환한다. 1개의 cpu인 경우 might_sleep() 이후에 preempt_disable() 및 preempt_enable()을 반복하였으므로 필요한 GP는 완료된 것으로 간주한다.
다음 그림은 동기화 rcu 요청 함수인 synchronize_rcu() 및 비동기 rcu 요청 함수인 call_rcu() 함수 두 가지에 대해 각각 호출 경로를 보여준다.
wait_rcu_gp()
include/linux/rcupdate_wait.h
#define wait_rcu_gp(...) _wait_rcu_gp(false, __VA_ARGS__)
Grace Period가 완료될 때까지 대기한다. 인자로 gp 완료를 대기하는 다음 두 함수 중 하나가 주어진다.
- call_rcu()
- call_rcu_tasks()
_wait_rcu_gp()
include/linux/rcupdate_wait.h
#define _wait_rcu_gp(checktiny, ...) \
do { \
call_rcu_func_t __crcu_array[] = { __VA_ARGS__ }; \
struct rcu_synchronize __rs_array[ARRAY_SIZE(__crcu_array)]; \
__wait_rcu_gp(checktiny, ARRAY_SIZE(__crcu_array), \
__crcu_array, __rs_array); \
} while (0)
가변 인자를 받아 처리할 수 있게 하였으나, 현제 실제 커널 코드에서는 1 개의 인자만 받아 처리하고 있다.
__wait_rcu_gp()
kernel/rcu/update.c
void __wait_rcu_gp(bool checktiny, int n, call_rcu_func_t *crcu_array,
struct rcu_synchronize *rs_array)
{
int i;
int j;
/* Initialize and register callbacks for each crcu_array element. */
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (checktiny &&
(crcu_array[i] == call_rcu)) {
might_sleep();
continue;
}
init_rcu_head_on_stack(&rs_array[i].head);
init_completion(&rs_array[i].completion);
for (j = 0; j < i; j++)
if (crcu_array[j] == crcu_array[i])
break;
if (j == i)
(crcu_array[i])(&rs_array[i].head, wakeme_after_rcu);
}
/* Wait for all callbacks to be invoked. */
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (checktiny &&
(crcu_array[i] == call_rcu))
continue;
for (j = 0; j < i; j++)
if (crcu_array[j] == crcu_array[i])
break;
if (j == i)
wait_for_completion(&rs_array[i].completion);
destroy_rcu_head_on_stack(&rs_array[i].head);
}
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(__wait_rcu_gp);
Grace Period가 완료될 때까지 대기한다. (@checktiny는 tiny/true 모델을 구분한다. 두 번째 인자는 전달 되는 array 크기를 갖고, 세 번째 인자는 호출할 비동기 콜백 함수(call_rcu() 또는 call_rcu_tasks())가 주어지며 마지막으로 네 번째 인자에는 gp 대기를 위한 rcu_synchronize 구조체 배열이 전달된다)
- 코드 라인 8~13에서 인자 수 @n 만큼 순회하며 첫 번째 인자 @checktiny 가 설정되었고, 세 번째 인자로 call_rcu 함수가 지정된 경우 preemption pointer를 실행한 후 skip 한다.
- 현재 커널 코드들에서는 @checktiny=0으로 호출되고 있다.
- 코드 라인 14~15에서 마지막 인자로 제공된 @rs_array의 rcu head를 스택에서 초기화하고, 또한 completion도 초기화한다.
- @rs_array에는 gp 비동기 처리를 위한 다음 두 함수가 사용되고 있다.
- 코드 라인 16~20에서 중복된 함수 호출이 없으면 세 번째 인자로 전달 받은 다음의 gp 비동기 처리 함수 중 하나를 호출하고, 인자로 rcuhead와 wakeme_after_rcu() 콜백 함수를지정한다.
- call_rcu()
- call_rcu_tasks()
- 코드 라인 24~27에서 인자 수 @n 만큼 순회하며 인자로 call_rcu 함수가 지정된 경우 skip 한다.
- 코드 라인 28~32에서중복된 함수 호출이 없으면 순회 중인 인덱스에 해당하는 콜백 함수가 처리 완료될 때까지 대기한다.
- 코드 라인 33에서 스택에 위치한 rcu head를 제거한다.
wakeme_after_rcu()
kernel/rcu/update.c
/** * wakeme_after_rcu() - Callback function to awaken a task after grace period * @head: Pointer to rcu_head member within rcu_synchronize structure * * Awaken the corresponding task now that a grace period has elapsed. */
void wakeme_after_rcu(struct rcu_head *head)
{
struct rcu_synchronize *rcu;
rcu = container_of(head, struct rcu_synchronize, head);
complete(&rcu->completion);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(wakeme_after_rcu);
gp가 완료되었음을 알리도록 complete 처리를 한다. (콜백 함수)
RCU 비동기 Update
call_rcu()
/** * call_rcu() - Queue an RCU callback for invocation after a grace period. * @head: structure to be used for queueing the RCU updates. * @func: actual callback function to be invoked after the grace period * * The callback function will be invoked some time after a full grace * period elapses, in other words after all pre-existing RCU read-side * critical sections have completed. However, the callback function * might well execute concurrently with RCU read-side critical sections * that started after call_rcu() was invoked. RCU read-side critical * sections are delimited by rcu_read_lock() and rcu_read_unlock(), and * may be nested. In addition, regions of code across which interrupts, * preemption, or softirqs have been disabled also serve as RCU read-side * critical sections. This includes hardware interrupt handlers, softirq * handlers, and NMI handlers. * * Note that all CPUs must agree that the grace period extended beyond * all pre-existing RCU read-side critical section. On systems with more * than one CPU, this means that when "func()" is invoked, each CPU is * guaranteed to have executed a full memory barrier since the end of its * last RCU read-side critical section whose beginning preceded the call * to call_rcu(). It also means that each CPU executing an RCU read-side * critical section that continues beyond the start of "func()" must have * executed a memory barrier after the call_rcu() but before the beginning * of that RCU read-side critical section. Note that these guarantees * include CPUs that are offline, idle, or executing in user mode, as * well as CPUs that are executing in the kernel. * * Furthermore, if CPU A invoked call_rcu() and CPU B invoked the * resulting RCU callback function "func()", then both CPU A and CPU B are * guaranteed to execute a full memory barrier during the time interval * between the call to call_rcu() and the invocation of "func()" -- even * if CPU A and CPU B are the same CPU (but again only if the system has * more than one CPU). */
void call_rcu(struct rcu_head *head, rcu_callback_t func)
{
__call_rcu(head, func, 0);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(call_rcu);
rcu 콜백 함수 @func을 등록한다. 이 rcu 콜백 함수는 GP(Grace Period) 완료 후 호출된다.
__call_rcu()
kernel/rcu/tree.c
/* * Helper function for call_rcu() and friends. The cpu argument will * normally be -1, indicating "currently running CPU". It may specify * a CPU only if that CPU is a no-CBs CPU. Currently, only rcu_barrier() * is expected to specify a CPU. */
static void
__call_rcu(struct rcu_head *head, rcu_callback_t func, bool lazy)
{
unsigned long flags;
struct rcu_data *rdp;
bool was_alldone;
/* Misaligned rcu_head! */
WARN_ON_ONCE((unsigned long)head & (sizeof(void *) - 1));
if (debug_rcu_head_queue(head)) {
/*
* Probable double call_rcu(), so leak the callback.
* Use rcu:rcu_callback trace event to find the previous
* time callback was passed to __call_rcu().
*/
WARN_ONCE(1, "__call_rcu(): Double-freed CB %p->%pS()!!!\n",
head, head->func);
WRITE_ONCE(head->func, rcu_leak_callback);
return;
}
head->func = func;
head->next = NULL;
local_irq_save(flags);
rdp = this_cpu_ptr(&rcu_data);
/* Add the callback to our list. */
if (unlikely(!rcu_segcblist_is_enabled(&rdp->cblist))) {
// This can trigger due to call_rcu() from offline CPU:
WARN_ON_ONCE(rcu_scheduler_active != RCU_SCHEDULER_INACTIVE);
WARN_ON_ONCE(!rcu_is_watching());
// Very early boot, before rcu_init(). Initialize if needed
// and then drop through to queue the callback.
if (rcu_segcblist_empty(&rdp->cblist))
rcu_segcblist_init(&rdp->cblist);
}
if (rcu_nocb_try_bypass(rdp, head, &was_alldone, flags))
return; // Enqueued onto ->nocb_bypass, so just leave.
/* If we get here, rcu_nocb_try_bypass() acquired ->nocb_lock. */
rcu_segcblist_enqueue(&rdp->cblist, head, lazy);
if (__is_kfree_rcu_offset((unsigned long)func))
trace_rcu_kfree_callback(rcu_state.name, head,
(unsigned long)func,
rcu_segcblist_n_lazy_cbs(&rdp->cblist),
rcu_segcblist_n_cbs(&rdp->cblist));
else
trace_rcu_callback(rcu_state.name, head,
rcu_segcblist_n_lazy_cbs(&rdp->cblist),
rcu_segcblist_n_cbs(&rdp->cblist));
/* Go handle any RCU core processing required. */
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_RCU_NOCB_CPU) &&
unlikely(rcu_segcblist_is_offloaded(&rdp->cblist))) {
__call_rcu_nocb_wake(rdp, was_alldone, flags); /* unlocks */
} else {
__call_rcu_core(rdp, head, flags);
local_irq_restore(flags);
}
}
call_rcu의 헬퍼 함수로 grace period가 지난 후에 RCU 콜백을 호출할 수 있도록 큐에 추가한다. @lazy가 true인 경우 kfree_call_rcu() 함수에서 호출하는 경우이며 @func에는 콜백 함수 대신 offset이 담긴다.
- 코드 라인 11~21에서 CONFIG_DEBUG_OBJECTS_RCU_HEAD 커널 옵션을 사용하여 디버깅을 하는 동안 __call_rcu() 함수가 이중 호출되는 경우 경고 메시지를 출력하고 함수를 빠져나간다.
- 코드 라인 22~23에서 rcu 인스턴스에 인수로 전달받은 콜백 함수를 대입한다. rcu는 리스트로 연결되는데 가장 마지막에 추가되므로 마지막을 의미하는 null을 대입한다.
- 코드 라인 25에서 cpu별 rcu 데이터를 표현한 자료 구조에서 현재 cpu에 대한 rcu 데이터를 rdp에 알아온다.
- 코드 라인 28~36에서 낮은 확률로 early 부트 중이라 disable 되었고, rcu 콜백 리스트가 준비되지 않은 경우 콜백 리스트를 초기화하고 enable 한다.
- 코드 라인 37~38에서 낮은 확률로 no-cb용 커널 스레드에서 처리할 콜백이 인입된 경우를 위한 처리를 수행한다.
- 코드 라인 40에서 rcu 콜백 함수를 콜백 리스트에 엔큐한다.
- 코드 라인 41~49에서 kfree 타입 또는 일반 타입의 rcu 요청에 맞게 trace 로그를 출력한다.
- 코드 라인 52~58에서 no-callback 처리용 스레드를 깨우거나 __call_rcu_core() 함수를 호출하여 rcu 코어 처리를 수행한다.
다음 그림은 __call_rcu() 함수를 호출하여 콜백을 추가하는 과정과 이를 처리하는 과정 두 가지를 모두 보여준다.
__call_rcu_core()
kernel/rcu/tree.c
/* * Handle any core-RCU processing required by a call_rcu() invocation. */
static void __call_rcu_core(struct rcu_data *rdp, struct rcu_head *head,
unsigned long flags)
{
/*
* If called from an extended quiescent state, invoke the RCU
* core in order to force a re-evaluation of RCU's idleness.
*/
if (!rcu_is_watching())
invoke_rcu_core();
/* If interrupts were disabled or CPU offline, don't invoke RCU core. */
if (irqs_disabled_flags(flags) || cpu_is_offline(smp_processor_id()))
return;
/*
* Force the grace period if too many callbacks or too long waiting.
* Enforce hysteresis, and don't invoke rcu_force_quiescent_state()
* if some other CPU has recently done so. Also, don't bother
* invoking rcu_force_quiescent_state() if the newly enqueued callback
* is the only one waiting for a grace period to complete.
*/
if (unlikely(rcu_segcblist_n_cbs(&rdp->cblist) >
rdp->qlen_last_fqs_check + qhimark)) {
/* Are we ignoring a completed grace period? */
note_gp_changes(rdp);
/* Start a new grace period if one not already started. */
if (!rcu_gp_in_progress()) {
rcu_accelerate_cbs_unlocked(rdp->mynode, rdp);
} else {
/* Give the grace period a kick. */
rdp->blimit = DEFAULT_MAX_RCU_BLIMIT;
if (rcu_state.n_force_qs == rdp->n_force_qs_snap &&
rcu_segcblist_first_pend_cb(&rdp->cblist) != head)
rcu_force_quiescent_state();
rdp->n_force_qs_snap = rcu_state.n_force_qs;
rdp->qlen_last_fqs_check = rcu_segcblist_n_cbs(&rdp->cblist);
}
}
}
rcu 처리(새 콜백, qs, gp 등의 변화) 를 위해 rcu core를 호출한다.
- 코드 라인 8~9에서 현재 cpu가 extended-qs(idle 또는 idle 진입) 상태에서 호출된 경우 rcu core 처리를 위해 rcu softirq 또는 rcu core 스레드를 호출한다.
- 스케줄 틱에서도 rcu에 대한 softirq 호출을 하지만 더 빨리 처리하기 위함이다.
- 코드 라인 12~13에서 인터럽트가 disable된 상태인 경우이거나 offline 상태이면 함수를 빠져나간다.
- 코드 라인 22~26에서 낮은 확률로 rcu 콜백이 너무 많이 대기 중이면 force_qs 조건을 만족하는지 확인하기 전에 먼저 gp 상태 변경을 확인한다.
- 코드 라인 29~30에서 gp가 진행 중이 아니면 신규 콜백들을 묶어 가능한 경우 앞으로 accelerate 처리한다.
- 코드 라인 31~39에서 gp가 이미 진행 중이면 blimit 제한을 max(디폴트 10000개) 값으로 풀고 fqs(force quiescent state)를 진행한다.
- rcu_state.n_force_qs == rdp->n_force_qs_snap
- 현재 cpu가 force 처리한 qs 수가 글로벌에 저장한 수와 일치하면
- 다른 cpu가 force 하는 경우 글로벌 값이 변경되므로 이 경우에는 force qs 처리하지 않을 계획이다.
- rcu_state.n_force_qs == rdp->n_force_qs_snap
rcu_is_watching()
kernel/rcu/tree.c
/** * rcu_is_watching - see if RCU thinks that the current CPU is not idle * * Return true if RCU is watching the running CPU, which means that this * CPU can safely enter RCU read-side critical sections. In other words, * if the current CPU is not in its idle loop or is in an interrupt or * NMI handler, return true. */
bool notrace rcu_is_watching(void)
{
bool ret;
preempt_disable_notrace();
ret = !rcu_dynticks_curr_cpu_in_eqs();
preempt_enable_notrace();
return ret;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(rcu_is_watching);
rcu가 동작중인 cpu를 감시하는지 여부를 반환한다. (true=watching, nohz idle 상태가 아니거나 인터럽트 진행중일 때 안전하게 read-side 크리티컬 섹션에 진입 가능한 상태이다.)
invoke_rcu_core()
kernel/rcu/tree.c
/* * Wake up this CPU's rcuc kthread to do RCU core processing. */
static void invoke_rcu_core(void)
{
if (!cpu_online(smp_processor_id()))
return;
if (use_softirq)
raise_softirq(RCU_SOFTIRQ);
else
invoke_rcu_core_kthread();
}
rcu softirq가 enable(디폴트)된 경우 softirq를 호출하고, 그렇지 않은 경우 rcu core 스레드를 깨운다.
- use_softirq
- “module/rcutree/parameters/use_softirq” 파라미터 값에 의해 결정된다. (디폴트=1)
rcu의 3단계 자료 관리
3단계 구조
rcu의 상태 관리를 위해 접근 비용 별로 3 단계의 구조로 관리한다.
- rcu_state
- 글로벌에 하나만 존재하며 락을 사용하여 접근한다.
- rcu_node
- 노드별로 구성되며, 하이라키 구조(노드 관리는 64개씩, leaf 노드는 16개)로 관리한다. (NUMA의 노드가 아니라 관리목적의 cpu들의 집합이다)
- 노드 락을 사용하여 접근한다.
- rcu_data
- per-cpu 별로 구성된다.
- 로컬 cpu에 대한 접근 시에 사용하므로 락없이 사용된다.
약칭
- rsp
- rcu_state 구조체 포인터
- rnp
- rcu_node 구조체 포인터
- rdp
- rcu_data 구조체 포인터
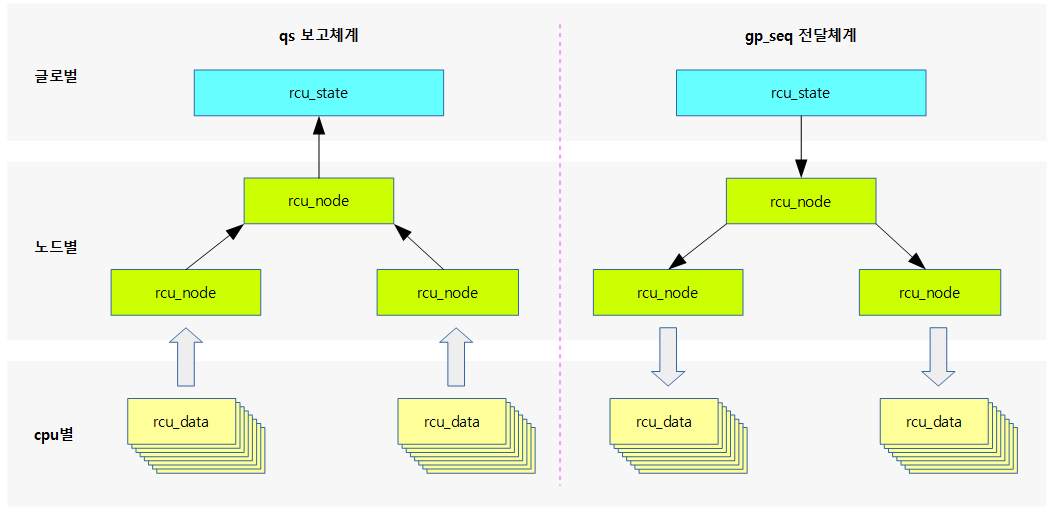
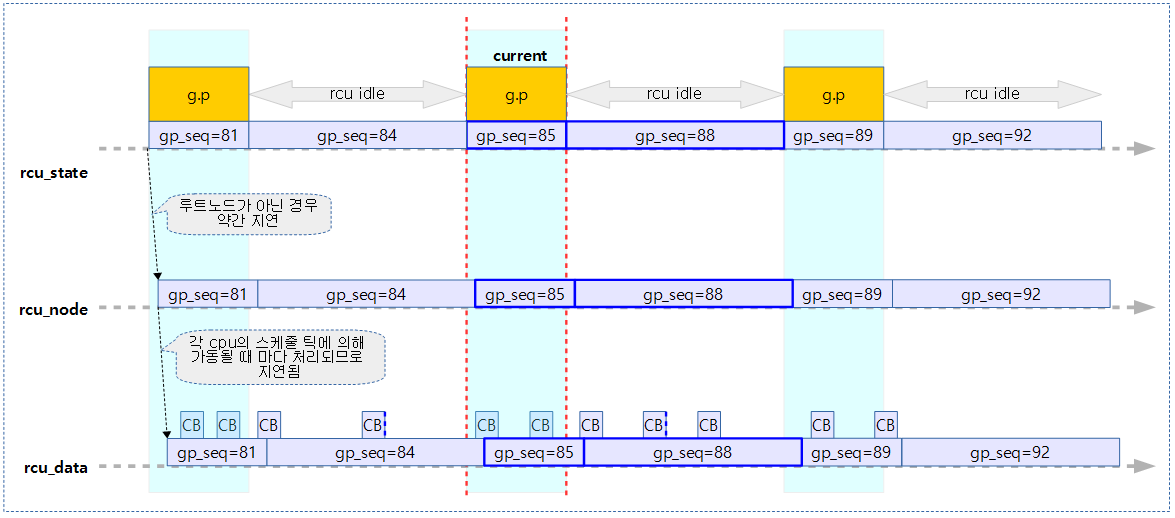
다음 그림과 같이 rcu 데이터 구조체들이 3 단계로 운영되고 있음을 보여준다.
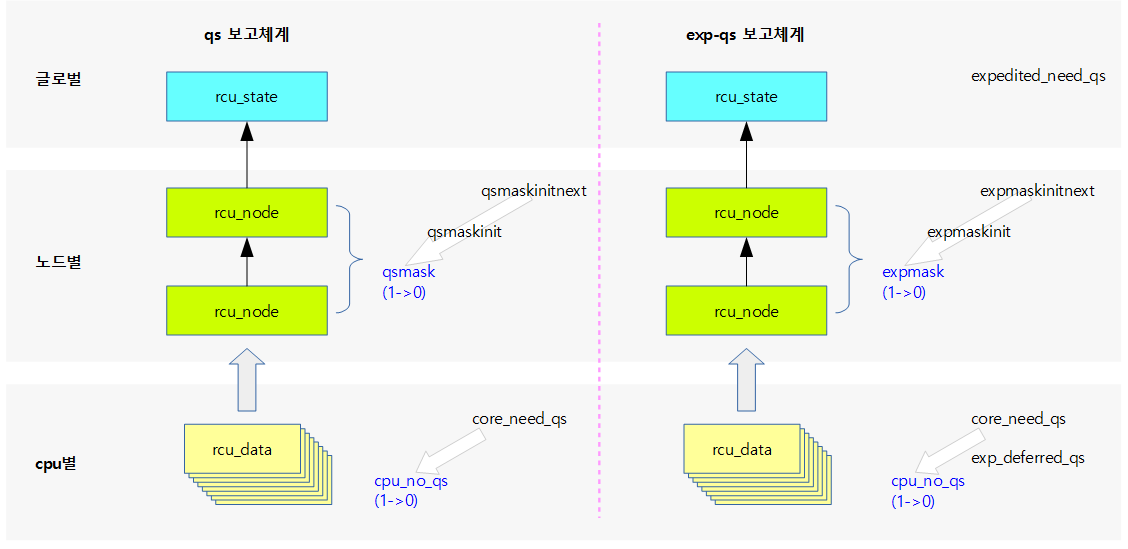
다음 그림은 qs와 급행 qs의 보고에 사용되는 각 멤버들을 보여준다.
- qs 보고 체계
- gp 시작 후
- qs 체크가 필요한 경우 core_need_qs 및 cpu_no_qs를 1로 클리어한다.
- qsmaskinitnext는 핫플러그 online cpu 상태가 변경될 때마다 이의 변화를 수용하고, qsmakinit에 이를 복사하여 사용한다. 그리고 이를 qsmaskinit에 복사한 후 매 gp가 시작될 때마다 qsmaskinit -> qsmask로 복사하여 qs를 체크할 준비를 한다.
- qs 보고
- cpu에서 qs가 체크된 경우 core_need_qs와 cpu_no_qs를 모두 클리어한다.
- 노드에 보고하여 해당 cpu에 대한 qsmask를 클리어한다. 하위 노드들의 qs가 모두 체크되면 상위 노드도 동일하게 전달하여 처리한다.
- gp 시작 후
- 급행 qs 보고 체계
- gp 시작 후
- 급행 qs 체크가 필요한 경우 core_need_qs 및 cpu_no_qs를 1로 클리어한다.
- expmaskinitnext는 핫플러그 online cpu 상태가 변경될 때마다 이의 변화를 수용하고, expmakinit에 이를 복사하여 사용한다. 그리고 이를 매 gp가 시작될 때마다 expmaskinit -> expmask로 복사하여 급행 qs를 체크할 준비를 한다.
- 급행 qs 보고
- cpu에서 급행 qs가 체크된 경우 core_need_qs와 cpu_no_qs를 모두 클리어한다.
- 노드에 보고하여 해당 cpu에 대한 expmask를 클리어한다. 하위 노드들의 급행 qs가 모두 체크되면 상위 노드도 동일하게 전달하여 처리한다.
- exp_deferred_qs의 경우는 disable(irq, bh, preemption) 상태에서 rcu_read_unlock()이 수행될 때에도 qs를 완료 시키면 안된다. 이 때 qs의 완료를 지연시키기 위해 사용된다.
- gp 시작 후
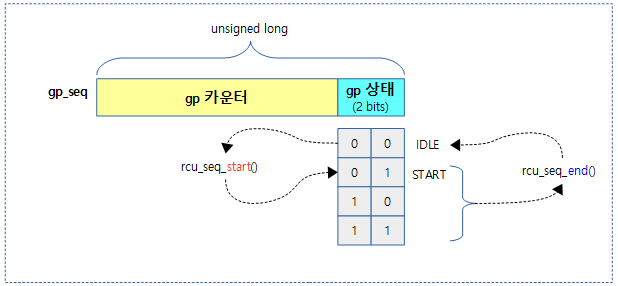
gp 시퀀스 관리
기존 gpnum이 삭제되고, 새로운 gp 시퀀스 번호(gp_seq)가 커널 v4.19-rc1에서 소개되었다.
gp 시퀀스는 다음과 같이 두 개의 파트로 나누어 관리한다.
- gp 카운터
- 새로운 gp가 시작될 때마다 gp 카운터가 증가된다.
- overflow에 대한 빠른 버그를 찾기위해 jiffies가 -300초에 해당하는 틱부터 시작하였다시피 gp 카운터도 -300부터 시작한다.
- gp 상태
- idle(0)
- gp가 동작하지 않는 idle 상태이다.
- start(1)
- gp가 시작되어 동작하는 상태이다.
- 그 외의 번호는 srcu에서만 사용되므로 생략한다.
- idle(0)
다음 그림과 같이 gp 시퀀스는 두 개의 파트로 나누어 관리한다.
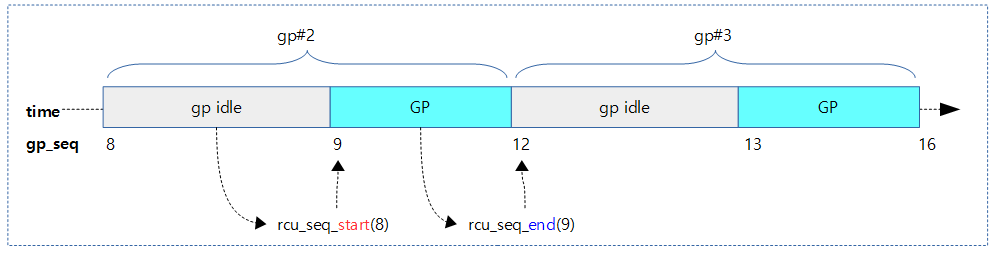
다음 그림과 같이 새로운 gp가 시작하고 끝날때 마다 gp 시퀀스가 증가되는 모습을 보여준다.
위 3가지 구조체에 공통적으로 gp_seq가 담겨 있다. rcu 관리에서 최대한 락 사용을 억제하기 위해 per-cpu를 사용한 rcu_data는 로컬 cpu 데이터를 취급한다. 로컬 데이터는 해당 cpu가 필요한 시점에서만 갱신한다. 따라서 이로 인해 로컬 gp_seq는 글로벌 gp_seq 번호에 비해 최대 1 만큼 늦어질 수도 있다. 루트 노드의 값은 항상 rcu_state의 값들과 동시에 변경되지만 그 외의 노드들 값은 노드 락을 거는 시간이 필요하므로 약간씩 지연된다. (모든 값의 차이는 최대 1을 초과할 수 없다.)
gp 시퀀스 번호 관련 함수들
/* * Grace-period counter management. */
#define RCU_SEQ_CTR_SHIFT 2 #define RCU_SEQ_STATE_MASK ((1 << RCU_SEQ_CTR_SHIFT) - 1)
rcu_seq_ctr()
kernel/rcu/rcu.h
/* * Return the counter portion of a sequence number previously returned * by rcu_seq_snap() or rcu_seq_current(). */
static inline unsigned long rcu_seq_ctr(unsigned long s)
{
return s >> RCU_SEQ_CTR_SHIFT;
}
gp 시퀀스의 카운터 부분만을 반환한다.
rcu_seq_state()
kernel/rcu/rcu.h
/* * Return the state portion of a sequence number previously returned * by rcu_seq_snap() or rcu_seq_current(). */
static inline int rcu_seq_state(unsigned long s)
{
return s & RCU_SEQ_STATE_MASK;
}
gp 시퀀스의 상태 값만을 반환한다. (0~3)
rcu_seq_set_state()
kernel/rcu/rcu.h
/* * Set the state portion of the pointed-to sequence number. * The caller is responsible for preventing conflicting updates. */
static inline void rcu_seq_set_state(unsigned long *sp, int newstate)
{
WARN_ON_ONCE(newstate & ~RCU_SEQ_STATE_MASK);
WRITE_ONCE(*sp, (*sp & ~RCU_SEQ_STATE_MASK) + newstate);
}
gp 시퀀스의 상태 부분을 @newstate로 갱신한다.
rcu_seq_start()
kernel/rcu/rcu.h
/* Adjust sequence number for start of update-side operation. */
static inline void rcu_seq_start(unsigned long *sp)
{
WRITE_ONCE(*sp, *sp + 1);
smp_mb(); /* Ensure update-side operation after counter increment. */
WARN_ON_ONCE(rcu_seq_state(*sp) != 1);
}
gp 시작을 위해 gp 시퀀스를 1 증가시킨다. (rcu_seq_end() 함수가 호출된 후 gp idle 상태인대 이후에 gp 시작을 처리한다)
rcu_seq_endval()
kernel/rcu/rcu.h
/* Compute the end-of-grace-period value for the specified sequence number. */
static inline unsigned long rcu_seq_endval(unsigned long *sp)
{
return (*sp | RCU_SEQ_STATE_MASK) + 1;
}
gp 종료를 위해 gp 시퀀스 @sp의 카운터 부분을 1 증가시키고, 상태 부분은 0(gp idle)인 값을 반환한다.
rcu_seq_end()
kernel/rcu/rcu.h
/* Adjust sequence number for end of update-side operation. */
static inline void rcu_seq_end(unsigned long *sp)
{
smp_mb(); /* Ensure update-side operation before counter increment. */
WARN_ON_ONCE(!rcu_seq_state(*sp));
WRITE_ONCE(*sp, rcu_seq_endval(sp));
}
gp 종료를 위해 gp 시퀀스 @sp의 카운터 부분을 1 증가시키고, 상태 부분은 0(gp idle)으로 변경한다.
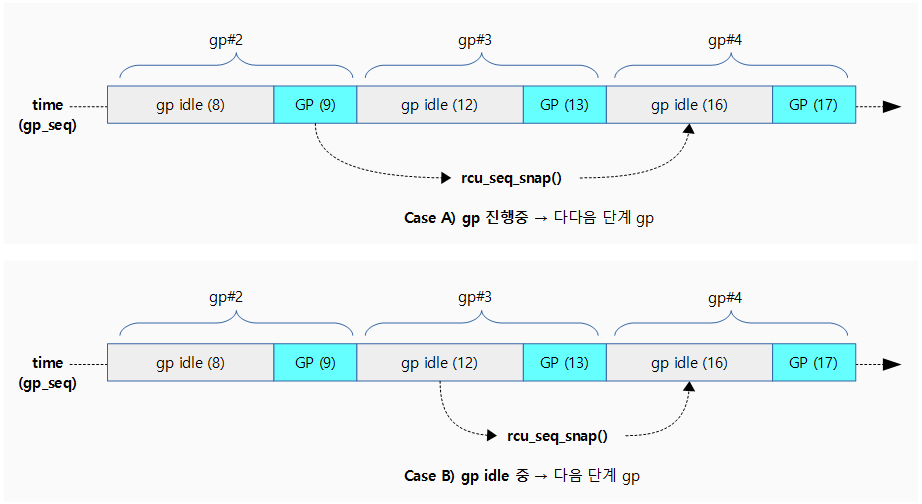
rcu_seq_snap()
kernel/rcu/rcu.h
/* * rcu_seq_snap - Take a snapshot of the update side's sequence number. * * This function returns the earliest value of the grace-period sequence number * that will indicate that a full grace period has elapsed since the current * time. Once the grace-period sequence number has reached this value, it will * be safe to invoke all callbacks that have been registered prior to the * current time. This value is the current grace-period number plus two to the * power of the number of low-order bits reserved for state, then rounded up to * the next value in which the state bits are all zero. */
static inline unsigned long rcu_seq_snap(unsigned long *sp)
{
unsigned long s;
s = (READ_ONCE(*sp) + 2 * RCU_SEQ_STATE_MASK + 1) & ~RCU_SEQ_STATE_MASK;
smp_mb(); /* Above access must not bleed into critical section. */
return s;
}
현재까지 등록된 콜백이 안전하게 처리될 수 있는 가장 빠른 update side의 gp 시퀀스 번호를 알아온다. (gp가 진행 중인 경우 안전하게 두 단계 뒤의 gp 시퀀스를 반환하고, gp가 idle 상태인 경우 다음 단계 뒤의 시퀀스 번호를 반환한다. 반환 되는 gp 시퀀스의 상태는 idle 이다.)
- 예) sp=12 (gp idle)
- 16
- 예) sp=9 (gp start)
- 16
다음 그림은 gp 시퀀스의 스냅샷 값을 알아오는 모습을 보여준다.
rcu_seq_current()
kernel/rcu/rcu.h
/* Return the current value the update side's sequence number, no ordering. */
static inline unsigned long rcu_seq_current(unsigned long *sp)
{
return READ_ONCE(*sp);
}
update side의 현재 gp 시퀀스 값을 반환한다.
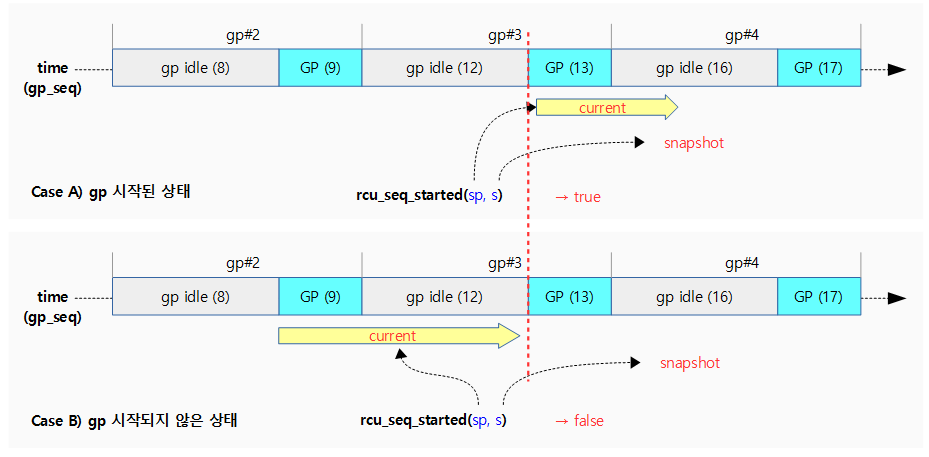
rcu_seq_started()
kernel/rcu/rcu.h
/* * Given a snapshot from rcu_seq_snap(), determine whether or not the * corresponding update-side operation has started. */
static inline bool rcu_seq_started(unsigned long *sp, unsigned long s)
{
return ULONG_CMP_LT((s - 1) & ~RCU_SEQ_STATE_MASK, READ_ONCE(*sp));
}
스냅샷 @s를 통해 gp가 시작되었는지 여부를 반환한다.
- 참고로 스냅샷 @s의 하위 2비트는 0으로 항상 gp_idle 상태 값을 반환한다.
- rounddown(@s-1, 4) < @sp
다음 그림은 rcu_seq_started() 함수를 통해 스냅샷 기준으로 gp가 이미 시작되었는지 여부를 알아온다.
- gp 시퀀스가 9 또는 12에 있을 때 스냅샷을 발급하면 16이다. 이후 gp 시퀀스가 13이 되는 순간 gp가 시작되어 이 함수가 true를 반환한다.
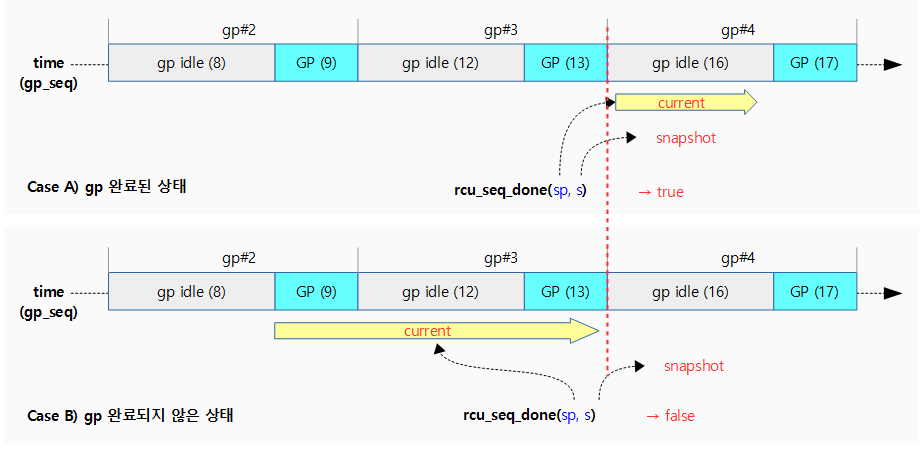
rcu_seq_done()
kernel/rcu/rcu.h
/* * Given a snapshot from rcu_seq_snap(), determine whether or not a * full update-side operation has occurred. */
static inline bool rcu_seq_done(unsigned long *sp, unsigned long s)
{
return ULONG_CMP_GE(READ_ONCE(*sp), s);
}
스냅샷 @s를 통해 gp가 완료되었는지 여부를 반환한다.
- 이 함수는 nocb 운용 시 rcu_segcblist_nextgp() 함수에서 반환된 wait 구간의 gp 시퀀스 값을 스냅샷 @s 값으로 사용하며, gp 시퀀스가 이 값에 도달하는 순간 true를 반환한다.
- 참고로 세그먼트 콜백리스트 각 구간의 gp 시퀀스 값은 스냅샷 값을 사용하므로 항상 gp idle 상태이다.
- @sp >= @s
다음 그림은 rcu_seq_done() 함수를 통해 스냅샷 기준으로 gp가 완료되었는지 여부를 알아온다.
- gp 시퀀스가 9 또는 12에 있을 때 스냅샷을 발급하면 16이다. 이후 gp 시퀀스가 13이 되는 순간 gp가 시작되어 이 함수가 true를 반환한다.
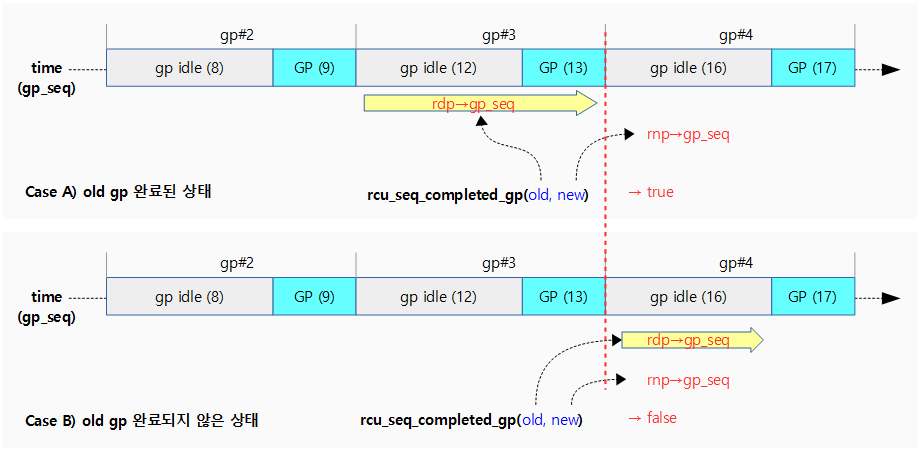
rcu_seq_completed_gp()
kernel/rcu/rcu.h
/* * Has a grace period completed since the time the old gp_seq was collected? */
static inline bool rcu_seq_completed_gp(unsigned long old, unsigned long new)
{
return ULONG_CMP_LT(old, new & ~RCU_SEQ_STATE_MASK);
}
노드의 gp 시퀀스 @new가 기존 cpu가 진행하던 gp 시퀀스 @old를 초과하는 것으로 gp를 완료하면 true를 반환한다.
- @old < rounddown(@new, 4)
- 예) old=5, new=9
- 5 < 8 = true
다음 그림은 rcu_seq_completed_gp() 함수를 통해 new gp 기준으로 old gp가 완료되었는지 여부를 알아온다.
- 노드의 gp 시퀀스가 기존 cpu가 진행하던 gp를 완료하면 true를 반환한다.
- 현재 cpu의 gp 시퀀스가 #3 구간의 gp를 진행하고 있을 때(12, 13), 노드의 gp 시퀀스가 기존 #3 구간을 끝내고 새 구간으로 진입하면 이 함수가 true를 반환한다.
rcu_seq_new_gp()
kernel/rcu/rcu.h
/* * Has a grace period started since the time the old gp_seq was collected? */
static inline bool rcu_seq_new_gp(unsigned long old, unsigned long new)
{
return ULONG_CMP_LT((old + RCU_SEQ_STATE_MASK) & ~RCU_SEQ_STATE_MASK,
new);
}
gp 시퀀스 old 이후로 새로운 gp가 시작되었는지 여부를 반환한다.
- roundup(@old, 4) < @new
- 예) old=5, new=9
- 8 < 9 = true
다음 그림은 rcu_seq_new_gp() 함수를 통해 old gp 이후로 new gp가 시작되었는지 여부를 알아온다.
- 현재 cpu의 gp 시퀀스 구간보다 노드의 gp 시퀀스가 새로운 gp를 시작하게되면 true를 반환한다.
- 현재 cpu의 gp 시퀀스가 #2 구간의 gp를 진행하고 있거나(9) #3 구간에서 gp가 idle 중일 때, 노드의 gp 시퀀스가 새 구간 #3의 gp를 시작(13)하면 이 함수가 true를 반환한다.
rcu_seq_diff()
kernel/rcu/rcu.h
/* * Roughly how many full grace periods have elapsed between the collection * of the two specified grace periods? */
static inline unsigned long rcu_seq_diff(unsigned long new, unsigned long old)
{
unsigned long rnd_diff;
if (old == new)
return 0;
/*
* Compute the number of grace periods (still shifted up), plus
* one if either of new and old is not an exact grace period.
*/
rnd_diff = (new & ~RCU_SEQ_STATE_MASK) -
((old + RCU_SEQ_STATE_MASK) & ~RCU_SEQ_STATE_MASK) +
((new & RCU_SEQ_STATE_MASK) || (old & RCU_SEQ_STATE_MASK));
if (ULONG_CMP_GE(RCU_SEQ_STATE_MASK, rnd_diff))
return 1; /* Definitely no grace period has elapsed. */
return ((rnd_diff - RCU_SEQ_STATE_MASK - 1) >> RCU_SEQ_CTR_SHIFT) + 2;
}
두 개의 gp 시퀀스 간에 소요된 gp 수를 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 5~6에서 두 값이 동일한 경우 0을 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 11~13에서 rnd_diff 값을 다음과 같이 구한다.
- = 내림 @new – 올림 @old + @new 상태 || @old 상태
- 코드 라인 14~15에서 rnd_diff 값이 3 미만인 경우 1을 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 16에서 다음 값을 반환한다.
- (rnd_diff – 4) >> 2 + 2
RCU CB 처리 (softirq)
rcu_core_si()
kernel/rcu/tree.c
static void rcu_core_si(struct softirq_action *h)
{
rcu_core();
}
완료된 rcu 콜백들을 호출하여 처리한다.
rcu_core()
kernel/rcu/tree.c
/* Perform RCU core processing work for the current CPU. */
static __latent_entropy void rcu_core(void)
{
unsigned long flags;
struct rcu_data *rdp = raw_cpu_ptr(&rcu_data);
struct rcu_node *rnp = rdp->mynode;
const bool offloaded = IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_RCU_NOCB_CPU) &&
rcu_segcblist_is_offloaded(&rdp->cblist);
if (cpu_is_offline(smp_processor_id()))
return;
trace_rcu_utilization(TPS("Start RCU core"));
WARN_ON_ONCE(!rdp->beenonline);
/* Report any deferred quiescent states if preemption enabled. */
if (!(preempt_count() & PREEMPT_MASK)) {
rcu_preempt_deferred_qs(current);
} else if (rcu_preempt_need_deferred_qs(current)) {
set_tsk_need_resched(current);
set_preempt_need_resched();
}
/* Update RCU state based on any recent quiescent states. */
rcu_check_quiescent_state(rdp);
/* No grace period and unregistered callbacks? */
if (!rcu_gp_in_progress() &&
rcu_segcblist_is_enabled(&rdp->cblist) && !offloaded) {
local_irq_save(flags);
if (!rcu_segcblist_restempty(&rdp->cblist, RCU_NEXT_READY_TAIL))
rcu_accelerate_cbs_unlocked(rnp, rdp);
local_irq_restore(flags);
}
rcu_check_gp_start_stall(rnp, rdp, rcu_jiffies_till_stall_check());
/* If there are callbacks ready, invoke them. */
if (!offloaded && rcu_segcblist_ready_cbs(&rdp->cblist) &&
likely(READ_ONCE(rcu_scheduler_fully_active)))
rcu_do_batch(rdp);
/* Do any needed deferred wakeups of rcuo kthreads. */
do_nocb_deferred_wakeup(rdp);
trace_rcu_utilization(TPS("End RCU core"));
}
완료된 rcu 콜백들을 호출하여 처리한다.
- 코드 라인 9~10에서 cpu가 offline 상태인 경우 함수를 빠져나간다.
- 코드 라인 15~20에서 preempt 가능한 상태인 경우(preempt 카운터=0)인 경우 deferred qs를 처리한다. 그렇지 않고 deferred qs가 pending 상태인 경우 리스케줄 요청을 수행한다.
- deferred qs 상태인 경우 deferred qs를 해제하고, blocked 상태인 경우 blocked 해제 후 qs를 보고한다.
- 코드 라인 23에서 현재 cpu에 대해 새 gp가 시작되었는지 체크한다. 또한 qs 상태를 체크하고 패스된 경우 rdp에 기록하여 상위 노드로 보고하게 한다.
- 코드 라인 26~32에서 gp가 idle 상태이면서 새로운 콜백이 존재하고, 필요 시 acceleration을 수행한다.
- 코드 라인 34에서 gp 요청을 체크한다.
- 코드 라인 37~39에서 완료된 콜백이 있는 경우 rcu 콜백들을 호출한다.
- 코드 라인 42에서 rcu no-callback을 위한 처리를 한다
rcu_do_batch()
kernel/rcu/tree.c -1/2-
/* * Invoke any RCU callbacks that have made it to the end of their grace * period. Thottle as specified by rdp->blimit. */
static void rcu_do_batch(struct rcu_data *rdp)
{
unsigned long flags;
const bool offloaded = IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_RCU_NOCB_CPU) &&
rcu_segcblist_is_offloaded(&rdp->cblist);
struct rcu_head *rhp;
struct rcu_cblist rcl = RCU_CBLIST_INITIALIZER(rcl);
long bl, count;
long pending, tlimit = 0;
/* If no callbacks are ready, just return. */
if (!rcu_segcblist_ready_cbs(&rdp->cblist)) {
trace_rcu_batch_start(rcu_state.name,
rcu_segcblist_n_lazy_cbs(&rdp->cblist),
rcu_segcblist_n_cbs(&rdp->cblist), 0);
trace_rcu_batch_end(rcu_state.name, 0,
!rcu_segcblist_empty(&rdp->cblist),
need_resched(), is_idle_task(current),
rcu_is_callbacks_kthread());
return;
}
/*
* Extract the list of ready callbacks, disabling to prevent
* races with call_rcu() from interrupt handlers. Leave the
* callback counts, as rcu_barrier() needs to be conservative.
*/
local_irq_save(flags);
rcu_nocb_lock(rdp);
WARN_ON_ONCE(cpu_is_offline(smp_processor_id()));
pending = rcu_segcblist_n_cbs(&rdp->cblist);
bl = max(rdp->blimit, pending >> rcu_divisor);
if (unlikely(bl > 100))
tlimit = local_clock() + rcu_resched_ns;
trace_rcu_batch_start(rcu_state.name,
rcu_segcblist_n_lazy_cbs(&rdp->cblist),
rcu_segcblist_n_cbs(&rdp->cblist), bl);
rcu_segcblist_extract_done_cbs(&rdp->cblist, &rcl);
if (offloaded)
rdp->qlen_last_fqs_check = rcu_segcblist_n_cbs(&rdp->cblist);
rcu_nocb_unlock_irqrestore(rdp, flags);
seg 콜백리스트의 완료 구간에서 대기중인 rcu 콜백들을 호출한다.
- 코드 라인 4~5에서 set 콜백리스트를 no-cb offload 처리하는지 여부를 알아온다.
- softirq에서 콜백을 처리하지 않고, no-cb 스레드에 떠넘겨 처리하는 경우인지를 알아온다.
- 코드 라인 12~21에서 seg 콜백 리스트의 완료 구간에서 대기중인 rcu 콜백들이 하나도 없는 경우 그냥 함수를 빠져나간다.
- 코드 라인 31~34에서 blimit 값을 구하고, 이 값이 100을 초과하는 경우 현재 시각보다 3ms 후로 tlimit 제한 시각을 구한다.
- 코드 라인 38에서 rcu seg 콜백리스트의 done 구간의 콜백들을 extract하여 rcl 리스트로 옮긴다.
- 코드 라인 39~40에서 콜백을 no-cb 스레드에서 처리해야 하는 경우 rdp->qlen_last_fqs_check에 콜백 수를 대입한다.
kernel/rcu/tree.c -2/2-
/* Invoke callbacks. */
rhp = rcu_cblist_dequeue(&rcl);
for (; rhp; rhp = rcu_cblist_dequeue(&rcl)) {
debug_rcu_head_unqueue(rhp);
if (__rcu_reclaim(rcu_state.name, rhp))
rcu_cblist_dequeued_lazy(&rcl);
/*
* Stop only if limit reached and CPU has something to do.
* Note: The rcl structure counts down from zero.
*/
if (-rcl.len >= bl && !offloaded &&
(need_resched() ||
(!is_idle_task(current) && !rcu_is_callbacks_kthread())))
break;
if (unlikely(tlimit)) {
/* only call local_clock() every 32 callbacks */
if (likely((-rcl.len & 31) || local_clock() < tlimit))
continue;
/* Exceeded the time limit, so leave. */
break;
}
if (offloaded) {
WARN_ON_ONCE(in_serving_softirq());
local_bh_enable();
lockdep_assert_irqs_enabled();
cond_resched_tasks_rcu_qs();
lockdep_assert_irqs_enabled();
local_bh_disable();
}
}
local_irq_save(flags);
rcu_nocb_lock(rdp);
count = -rcl.len;
trace_rcu_batch_end(rcu_state.name, count, !!rcl.head, need_resched(),
is_idle_task(current), rcu_is_callbacks_kthread());
/* Update counts and requeue any remaining callbacks. */
rcu_segcblist_insert_done_cbs(&rdp->cblist, &rcl);
smp_mb(); /* List handling before counting for rcu_barrier(). */
rcu_segcblist_insert_count(&rdp->cblist, &rcl);
/* Reinstate batch limit if we have worked down the excess. */
count = rcu_segcblist_n_cbs(&rdp->cblist);
if (rdp->blimit >= DEFAULT_MAX_RCU_BLIMIT && count <= qlowmark)
rdp->blimit = blimit;
/* Reset ->qlen_last_fqs_check trigger if enough CBs have drained. */
if (count == 0 && rdp->qlen_last_fqs_check != 0) {
rdp->qlen_last_fqs_check = 0;
rdp->n_force_qs_snap = rcu_state.n_force_qs;
} else if (count < rdp->qlen_last_fqs_check - qhimark)
rdp->qlen_last_fqs_check = count;
/*
* The following usually indicates a double call_rcu(). To track
* this down, try building with CONFIG_DEBUG_OBJECTS_RCU_HEAD=y.
*/
WARN_ON_ONCE(count == 0 && !rcu_segcblist_empty(&rdp->cblist));
WARN_ON_ONCE(!IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_RCU_NOCB_CPU) &&
count != 0 && rcu_segcblist_empty(&rdp->cblist));
rcu_nocb_unlock_irqrestore(rdp, flags);
/* Re-invoke RCU core processing if there are callbacks remaining. */
if (!offloaded && rcu_segcblist_ready_cbs(&rdp->cblist))
invoke_rcu_core();
}
- 코드 라인 2~3에서 seg 콜백 리스트를 순회하며 콜백을 하나씩 디큐해온다.
- 코드 라인 5~6에서 rcu 콜백을 recliaim 호출하여 처리하고, kfree용 콜백인 경우 lazy 카운터를 감소시킨다.
- 코드 라인 11~14에서 호출된 콜백 수가 blimit 이상이면서 offload되지 않으며 다음 조건 중 하나라도 만족하는 경우 콜백을 그만 처리하기 위해 루프를 벗어난다.
- 조건
- 리스케줄 요청이 있는 경우
- 현재 태스크가 idle 태스크도 아니고 no-cb 커널 스레드도 아닌 경우
- 임시로 사용되는 로컬 콜백리스트의 len 멤버는 0부터 시작하여 디큐되어 호출될때마다 1씩 감소한다. 따라서 이 값에는 콜백 호출된 수가 음수 값으로 담겨 있게 된다.
- 조건
- 코드 라인 15~21에서 낮은 확률로 tlimit 제한 시각(3ms)이 설정된 경우 매 32개의 콜백을 처리할 때 마다 제한 시간을 초과한 경우 그만 처리하기 위해 루프를 벗어난다.
- 코드 라인 22~29에서 no-cb 커널 스레드에서 콜백들을 처리하도록 offload된 경우 현재 태스크의 rcu_tasks_holdout 멤버를 false로 변경한다.
- 코드 라인 34에서 호출한 콜백 수를 count 변수로 알아온다.
- 코드 라인 39~41에서 처리하지 않고 남은 콜백들을 다음에 처리하기 위해 다시 seg 콜백 리스트의 done 구간에 추가하고, 콜백 수도 추가한다.
- 코드 라인 44~46에서 rdp->blimit가 10000개 이상이고, seg 콜백 리스트에 있는 콜백 수가 qlowmark(디폴트=100) 이하인 경우 rdp->blimit을 blimit 값으로 재설정한다.
- 코드 라인 49~53에서 로컬 콜백 리스트의 콜백들을 모두 처리하여 count가 0이고, rdp->qlen_last_fqs_check가 0이 아닌 경우 이 값을 0으로 리셋한다. 만일 다 처리하지 않고 남은 수가 rdp->qlen_last_fqs_check – qhimark 보다 작은 경우 rdp->qlen_last_fqs_check 값을 남은 count 값으로 대입한다.
- 코드 라인 66~67에서 offloaded되지 않고 done 구간에 남은 콜백들이 여전히 남아 있는 경우 softirq를 호출하여 계속 처리하게 한다.
__rcu_reclaim()
kernel/rcu/rcu.h
/* * Reclaim the specified callback, either by invoking it (non-lazy case) * or freeing it directly (lazy case). Return true if lazy, false otherwise. */
static inline bool __rcu_reclaim(const char *rn, struct rcu_head *head)
{
rcu_callback_t f;
unsigned long offset = (unsigned long)head->func;
rcu_lock_acquire(&rcu_callback_map);
if (__is_kfree_rcu_offset(offset)) {
trace_rcu_invoke_kfree_callback(rn, head, offset);
kfree((void *)head - offset);
rcu_lock_release(&rcu_callback_map);
return true;
} else {
trace_rcu_invoke_callback(rn, head);
f = head->func;
WRITE_ONCE(head->func, (rcu_callback_t)0L);
f(head);
rcu_lock_release(&rcu_callback_map);
return false;
}
}
rcu 콜백을 recliaim 처리한다. (kfree용 콜백인 경우 kfree 후 true를 반환하고, 그 외의 경우 해당 콜백을 호출한 후 false를 반환한다.)
- 코드 라인 7~11에서 rcu 콜백에 함수가 아닌 kfree용 rcu offset이 담긴 경우 이를 통해 kfree를 수행하고 true를 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 12~19에서 rcu 콜백에 함수가 담긴 경우 이를 호출하고 false를 반환한다.
구조체
rcu_state 구조체
kernel/rcu/tree.h
/* * RCU global state, including node hierarchy. This hierarchy is * represented in "heap" form in a dense array. The root (first level) * of the hierarchy is in ->node[0] (referenced by ->level[0]), the second * level in ->node[1] through ->node[m] (->node[1] referenced by ->level[1]), * and the third level in ->node[m+1] and following (->node[m+1] referenced * by ->level[2]). The number of levels is determined by the number of * CPUs and by CONFIG_RCU_FANOUT. Small systems will have a "hierarchy" * consisting of a single rcu_node. */
struct rcu_state {
struct rcu_node node[NUM_RCU_NODES]; /* Hierarchy. */
struct rcu_node *level[RCU_NUM_LVLS + 1];
/* Hierarchy levels (+1 to */
/* shut bogus gcc warning) */
int ncpus; /* # CPUs seen so far. */
/* The following fields are guarded by the root rcu_node's lock. */
u8 boost ____cacheline_internodealigned_in_smp;
/* Subject to priority boost. */
unsigned long gp_seq; /* Grace-period sequence #. */
struct task_struct *gp_kthread; /* Task for grace periods. */
struct swait_queue_head gp_wq; /* Where GP task waits. */
short gp_flags; /* Commands for GP task. */
short gp_state; /* GP kthread sleep state. */
unsigned long gp_wake_time; /* Last GP kthread wake. */
unsigned long gp_wake_seq; /* ->gp_seq at ^^^. */
/* End of fields guarded by root rcu_node's lock. */
struct mutex barrier_mutex; /* Guards barrier fields. */
atomic_t barrier_cpu_count; /* # CPUs waiting on. */
struct completion barrier_completion; /* Wake at barrier end. */
unsigned long barrier_sequence; /* ++ at start and end of */
/* rcu_barrier(). */
/* End of fields guarded by barrier_mutex. */
struct mutex exp_mutex; /* Serialize expedited GP. */
struct mutex exp_wake_mutex; /* Serialize wakeup. */
unsigned long expedited_sequence; /* Take a ticket. */
atomic_t expedited_need_qs; /* # CPUs left to check in. */
struct swait_queue_head expedited_wq; /* Wait for check-ins. */
int ncpus_snap; /* # CPUs seen last time. */
unsigned long jiffies_force_qs; /* Time at which to invoke */
/* force_quiescent_state(). */
unsigned long jiffies_kick_kthreads; /* Time at which to kick */
/* kthreads, if configured. */
unsigned long n_force_qs; /* Number of calls to */
/* force_quiescent_state(). */
unsigned long gp_start; /* Time at which GP started, */
/* but in jiffies. */
unsigned long gp_end; /* Time last GP ended, again */
/* in jiffies. */
unsigned long gp_activity; /* Time of last GP kthread */
/* activity in jiffies. */
unsigned long gp_req_activity; /* Time of last GP request */
/* in jiffies. */
unsigned long jiffies_stall; /* Time at which to check */
/* for CPU stalls. */
unsigned long jiffies_resched; /* Time at which to resched */
/* a reluctant CPU. */
unsigned long n_force_qs_gpstart; /* Snapshot of n_force_qs at */
/* GP start. */
unsigned long gp_max; /* Maximum GP duration in */
/* jiffies. */
const char *name; /* Name of structure. */
char abbr; /* Abbreviated name. */
raw_spinlock_t ofl_lock ____cacheline_internodealigned_in_smp;
/* Synchronize offline with */
/* GP pre-initialization. */
};
rcu 글로벌 상태를 관리하는 구조체이다.
- node[]
- 컴파일 타임에 산출된 NUM_RCU_NODES 수 만큼 rcu_node 들이 배열에 배치된다.
- *level[]
- 각 레벨의 (0(top) 레벨부터 최대 3레벨까지) 첫 rcu_node를 가리킨다.
- 최소 노드가 1개 이상 존재하므로 level[0]는 항상 node[0]를 가리킨다.
- 노드가 2개 이상되면 level[1]은 node[1]을 가리킨다.
- ncpus
- cpu 수
- gp_seq
- 현재 grace period 번호
- overflow에 관련된 에러가 발생하는 것에 대해 빠르게 감지하기 위해 -300UL부터 시작한다.
- *gp_kthread
- grace period를 관리하는 커널 스레드이다.
- “rcu_preempt” 라는 이름을 사용한다.
- gp_wq
- gp 커널 스레드가 대기하는 wait queue이다.
- gp_flags
- gp 커널 스레드에 대한 명령이다.
- 2개의 gp 플래그를 사용한다.
- RCU_GP_FLAG_INIT(0x1) -> gp 시작 필요
- RCU_GP_FLAG_FQS(0x2) -> fqs 필요
- gp_state
- gp 커널 스레드의 상태이다.
- RCU_GP_IDLE(0) – gp가 동작하지 않는 상태
- RCU_GP_WAIT_GPS(1) – gp 시작 대기
- RCU_GP_DONE_GPS(2) – gp 시작을 위해 완료 대기
- RCU_GP_ONOFF(3) – gp 초기화 핫플러그
- RCU_GP_INIT(4) – gp 초기화
- RCU_GP_WAIT_FQS(5) – fqs 시간 대기
- RCU_GP_DOING_FQS(6) – fqs 시간 완료 대기
- RCU_GP_CLEANUP(7) – gp 클린업 시작
- RCU_GP_CLEANED(8) – gp 클린업 완료
- gp 커널 스레드의 상태이다.
- gp_wake_time
- 마지막 gp kthread 깨어난 시각
- gp_wake_seq
- gp kthread 깨어났을 때의 gp_seq
- barrier_mutex
- rcu_barrier() 함수에서 사용하는 베리어 뮤텍스
- barrier_cpu_count
- 베리어 대기중인 cpu 수
- barrier_completion
- 베리어 완료를 기다리기 위해 사용되는 completion
- barrier_sequence
- rcu_barrier()에서 사용하는 베리어용 gp 시퀀스
- exp_mutex
- expedited gp를 순서대로 처리하기 위한 뮤텍스 락
- exp_wake_mutex
- 순서대로 wakeup하기 위한 뮤텍스 락
- expedited_sequence
- 급행 grace period 시퀀스 번호
- expedited_need_qs
- expedited qs를 위해 남은 cpu 수
- sexpedited_wq
- 체크인 대기 워크큐
- ncpus_snap
- 지난 스캔에서 사용했던 cpu 수가 담긴다.
- jiffies_force_qs
- force_quiescent_state() -> gp kthread -> rcu_gp_fqs() 함수를 호출하여 fqs를 해야 할 시각(jiffies)
- gp 커널 스레드에서 gp가 완료되지 않아 강제로 fqs를 해야할 때까지 기다릴 시각이 담긴다.
- jiffies_kick_kthreads
- 현재 gp에서 이 값으로 지정된 시간이 흘러 stall된 커널 스레드를 깨우기 위한 시각이 담긴다.
- 2 * jiffies_till_first_fqs 시간을 사용한다.
- n_force_qs
- force_quiescent_state() -> gp kthread -> rcu_gp_fqs() 함수를 호출하여 fqs를 수행한 횟수
- 각 cpu(rcu_data)에서 수행한 값이 글로벌(rcu_state)에 갱신되며, 해당 cpu에 fqs를 수행했던 이후로 변경된 적이 없는지 확인하기 위해 사용된다.
- gp_start
- gp 시작된 시각(틱)
- gp_activity
- gp kthread가 동작했던 마지막 시각(틱)
- gp_req_activity
- gp 시작 및 종료 요청 시각(틱)이 담기며, gp stall 경과 시각을 체크할 때 사용한다.
- jiffies_stall
- cpu stall을 체크할 시각(틱)
- jiffies_resched
- cpu stall을 체크하는 시간의 절반의 시각(jiffies)으로 설정되고 필요에 따라 5 틱씩 증가
- 이 시각이 되면 리스케줄한다.
- n_force_qs_gpstart
- gp가 시작될 때마다 fqs를 수행한 횟수(n_force_qs)로 복사(snapshot)된다.
- gp_max
- 최대 gp 기간(jiffies)
- *name
- rcu 명
- “rcu_sched”, “rcu_bh”, “rcu_preempt”
- abbr
- 축약된 1 자리 rcu 명
- ‘s’, ‘b’, ‘p’
rcu_node 구조체
kernel/rcu/tree.h – 1/2
/* * Definition for node within the RCU grace-period-detection hierarchy. */
struct rcu_node {
raw_spinlock_t __private lock; /* Root rcu_node's lock protects */
/* some rcu_state fields as well as */
/* following. */
unsigned long gp_seq; /* Track rsp->rcu_gp_seq. */
unsigned long gp_seq_needed; /* Track furthest future GP request. */
unsigned long completedqs; /* All QSes done for this node. */
unsigned long qsmask; /* CPUs or groups that need to switch in */
/* order for current grace period to proceed.*/
/* In leaf rcu_node, each bit corresponds to */
/* an rcu_data structure, otherwise, each */
/* bit corresponds to a child rcu_node */
/* structure. */
unsigned long rcu_gp_init_mask; /* Mask of offline CPUs at GP init. */
unsigned long qsmaskinit;
/* Per-GP initial value for qsmask. */
/* Initialized from ->qsmaskinitnext at the */
/* beginning of each grace period. */
unsigned long qsmaskinitnext;
/* Online CPUs for next grace period. */
unsigned long expmask; /* CPUs or groups that need to check in */
/* to allow the current expedited GP */
/* to complete. */
unsigned long expmaskinit;
/* Per-GP initial values for expmask. */
/* Initialized from ->expmaskinitnext at the */
/* beginning of each expedited GP. */
unsigned long expmaskinitnext;
/* Online CPUs for next expedited GP. */
/* Any CPU that has ever been online will */
/* have its bit set. */
unsigned long ffmask; /* Fully functional CPUs. */
unsigned long grpmask; /* Mask to apply to parent qsmask. */
/* Only one bit will be set in this mask. */
int grplo; /* lowest-numbered CPU or group here. */
int grphi; /* highest-numbered CPU or group here. */
u8 grpnum; /* CPU/group number for next level up. */
u8 level; /* root is at level 0. */
bool wait_blkd_tasks;/* Necessary to wait for blocked tasks to */
/* exit RCU read-side critical sections */
/* before propagating offline up the */
/* rcu_node tree? */
struct rcu_node *parent;
struct list_head blkd_tasks;
/* Tasks blocked in RCU read-side critical */
/* section. Tasks are placed at the head */
/* of this list and age towards the tail. */
struct list_head *gp_tasks;
/* Pointer to the first task blocking the */
/* current grace period, or NULL if there */
/* is no such task. */
struct list_head *exp_tasks;
/* Pointer to the first task blocking the */
/* current expedited grace period, or NULL */
/* if there is no such task. If there */
/* is no current expedited grace period, */
/* then there can cannot be any such task. */
gp 감지를 포함하는 rcu 노드 구조체이다.
- lock
- rcu 노드 락
- gp_seq
- 이 노드에 대한 gp 번호
- gp_seq_needed
- 이 노드에 요청한 새 gp 번호
- completedqs
- 이 노드가 qs 되었을때의 completed 번호
- qsmask
- leaf 노드의 경우 qs를 보고해야 할 rcu_data에 대응하는 비트가 1로 설정된다.
- leaf 노드가 아닌 경우 qs를 보고해야 할 child 노드에 대응하는 비트가 1로 설정된다.
- rcu_gp_init_mask
- gp 초기화시의 offline cpumask
- qsmaskinit
- gp가 시작할 때마다 적용되는 초기값
- qsmask & expmask
- qsmaskinitnext
- 다음 gp를 위한 online cpumask
- expmask
- preemptible-rcu에서만 사용되며, 빠른(expedited) grace period가 진행중인 경우 설정된다..
- leaf 노드가 아닌 노드들의 초기값은 qsmaskinit으로한다. (snapshot)
- expmaskinit
- expmask의 per-gp 초기 값
- expmaskinitnext
- 다음 pepedited gp를 위한 online cpumask
- ffmask
- fully functional cpus
- grpmask
- 이 노드가 부모 노드의 qsmask에 대응하는 비트 값이다.
- 예) 512개의 cpu를 위해 루트노드에 32개의 leaf 노드가 있을 때 각 leaf 노드의 grpmask 값은 각각 0x1, 0x2, … 0x8000_0000이다.
- grplo
- 이 노드가 관리하는 시작 cpu 번호
- 예) grplo=48, grphi=63
- grphi
- 이 노드가 관리하는 끝 cpu 번호
- 예) grplo=48, grphi=63
- grpnum
- 상위 노드에서 볼 때 이 노드에 해당하는 그룹번호(32bits: 0~31, 64bits: 0~63)
- grpmask에 설정된 비트 번호와 같다.
- 예) grpmask=0x8000_0000인 경우 bit31이 설정되어 있다. 이러한 경우 grpnum=31이다.
- level
- 이 노드에 해당하는 노드 레벨
- 루트 노드는 0이다.
- 최대 값은 3이다. (최대 4 단계의 레벨 구성이 가능하다)
- wait_blkd_tasks
- read side critcal section에서 preemption된 블럭드 태스크가 있는지 여부
- *parent
- 부모 노드를 가리킨다.
- blkd_tasks
- preemptible 커널의 read side critical section에서 preempt된 경우 해당 태스크를 이 리스트에 추가된다.
- *gp_tasks
- 현재 일반 gp에서 블럭된 첫 번째 태스크를 가리킨다.
- *exp_tasks
- 현재 급행 gp에서 블럭된 첫 번째 태스크를 가리킨다.
kernel/rcu/tree.h – 2/2
struct list_head *boost_tasks;
/* Pointer to first task that needs to be */
/* priority boosted, or NULL if no priority */
/* boosting is needed for this rcu_node */
/* structure. If there are no tasks */
/* queued on this rcu_node structure that */
/* are blocking the current grace period, */
/* there can be no such task. */
struct rt_mutex boost_mtx;
/* Used only for the priority-boosting */
/* side effect, not as a lock. */
unsigned long boost_time;
/* When to start boosting (jiffies). */
struct task_struct *boost_kthread_task;
/* kthread that takes care of priority */
/* boosting for this rcu_node structure. */
unsigned int boost_kthread_status;
/* State of boost_kthread_task for tracing. */
#ifdef CONFIG_RCU_NOCB_CPU
struct swait_queue_head nocb_gp_wq[2];
/* Place for rcu_nocb_kthread() to wait GP. */
#endif /* #ifdef CONFIG_RCU_NOCB_CPU */
raw_spinlock_t fqslock ____cacheline_internodealigned_in_smp;
spinlock_t exp_lock ____cacheline_internodealigned_in_smp;
unsigned long exp_seq_rq;
wait_queue_head_t exp_wq[4];
struct rcu_exp_work rew;
bool exp_need_flush; /* Need to flush workitem? */
} ____cacheline_internodealigned_in_smp;
- *boost_tasks
- priority 부스트가 필요한 첫 태스크
- boost_mtx
- priority 부스트에 사용되는 락
- *boost_kthread_task
- 이 노드에서 priority 부스트를 수행하는 boost 커널 스레드
- boost_kthread_status
- boost_kthread_task trace를 위한 상태
- nocb_gp_wq[]
- 2 개의 no-cb용 커널 스레드의 대기큐
- exp_seq_rq
- 급행 grace period 시퀀스 번호
- exp_wq[]
- synchronize_rcu_expedited() 호출한 태스크들이 급행 gp를 대기하게 되는데, 이 호출한 태스크들이 대기하는 곳이다.
- 4개의 해시 리스트 형태로 운영된다. (급행 gp 시퀀스 번호에서 하위 2비트를 우측 시프트하여 버린 후 하위 2비트로 해시 운영한다)
- rew
- rcu_exp_work 구조체가 임베드되며, 내부에선 wait_rcu_exp_gp() 함수를 호출하는 워크큐가 사용된다.
- exp_need_flush
- sync_rcu_exp_select_cpus() 함수내부에서 각 leaf 노드들에서 위의 워크큐가 사용되는 경우 여부를 관리할 때 사용된다.
rcu_data 구조체
kernel/rcu/tree.h – 1/2
/* Per-CPU data for read-copy update. */
struct rcu_data {
/* 1) quiescent-state and grace-period handling : */
unsigned long gp_seq; /* Track rsp->rcu_gp_seq counter. */
unsigned long gp_seq_needed; /* Track furthest future GP request. */
union rcu_noqs cpu_no_qs; /* No QSes yet for this CPU. */
bool core_needs_qs; /* Core waits for quiesc state. */
bool beenonline; /* CPU online at least once. */
bool gpwrap; /* Possible ->gp_seq wrap. */
bool exp_deferred_qs; /* This CPU awaiting a deferred QS? */
struct rcu_node *mynode; /* This CPU's leaf of hierarchy */
unsigned long grpmask; /* Mask to apply to leaf qsmask. */
unsigned long ticks_this_gp; /* The number of scheduling-clock */
/* ticks this CPU has handled */
/* during and after the last grace */
/* period it is aware of. */
struct irq_work defer_qs_iw; /* Obtain later scheduler attention. */
bool defer_qs_iw_pending; /* Scheduler attention pending? */
/* 2) batch handling */
struct rcu_segcblist cblist; /* Segmented callback list, with */
/* different callbacks waiting for */
/* different grace periods. */
long qlen_last_fqs_check;
/* qlen at last check for QS forcing */
unsigned long n_force_qs_snap;
/* did other CPU force QS recently? */
long blimit; /* Upper limit on a processed batch */
/* 3) dynticks interface. */
int dynticks_snap; /* Per-GP tracking for dynticks. */
long dynticks_nesting; /* Track process nesting level. */
long dynticks_nmi_nesting; /* Track irq/NMI nesting level. */
atomic_t dynticks; /* Even value for idle, else odd. */
bool rcu_need_heavy_qs; /* GP old, so heavy quiescent state! */
bool rcu_urgent_qs; /* GP old need light quiescent state. */
#ifdef CONFIG_RCU_FAST_NO_HZ
bool all_lazy; /* All CPU's CBs lazy at idle start? */
unsigned long last_accelerate; /* Last jiffy CBs were accelerated. */
unsigned long last_advance_all; /* Last jiffy CBs were all advanced. */
int tick_nohz_enabled_snap; /* Previously seen value from sysfs. */
#endif /* #ifdef CONFIG_RCU_FAST_NO_HZ */
/* 4) rcu_barrier(), OOM callbacks, and expediting. */
struct rcu_head barrier_head;
int exp_dynticks_snap; /* Double-check need for IPI. */
1) qs와 gp 핸들링 관련
- gp_seq
- gp 시퀀스 번호
- gp_seq_needed
- 요청한 gp 시퀀스 번호
- cpu_no_qs
- gp 시작 후 설정되며 cpu에서 qs가 체크되면 클리어된다.
- 그 후 해당 노드 및 최상위 노드까지 보고하며, 각 노드의 rnp->qsmask의 비트 중 하위 rnp 또는 rdp의 ->grpmask에 해당하는 비트를 클리어한다.
- core_need_qs
- cpu가 qs를 체크해야 하는지 여부
- beenonline
- 한 번이라도 online 되었었던 경우 1로 설정된다.
- gpwrap
- nohz 진입한 cpu는 스케줄 틱을 한동안 갱신하지 못하는데, 이로 인해 gp 시퀀스 역시 장시간 갱신 못할 수도 있다. cpu의 gp 시퀀스가 노드용 gp 시퀀스에 비해 ulong 값의 1/4을 초과하도록 갱신을 못한 경우 gp 시퀀스를 오버플로우로 판정하여 이 값을 true로 변경한다.
- exp_deferred_qs
- 현재 cpu가 deferred qs를 대기중인지 여부
- *mynode
- 이 cpu를 관리하는 노드
- grpmask
- 이 cpu가 해당 leaf 노드의 qsmask에 대응하는 비트 값으로 qs 패스되면 leaf 노드의 qsmask에 반영한다.
- 예) 노드 당 16개의 cpu가 사용될 수 있으며 각각의 cpu에 대해 0x1, 0x2, … 0x1_0000 값이 배치된다.
- ticks_this_gp
- 마지막 gp 이후 구동된 스케줄 틱 수
- CONFIG_RCU_CPU_STALL_INFO 커널 옵션을 사용한 경우 cpu stall 정보의 출력을 위해 사용된다.
- defer_qs_iw
- defer_qs_iw_pending
2) 배치 핸들링
- cblist
- 콜백들이 추가되는 segmented 콜백 리스트이다.
- qlen_last_fqs_check
- fqs를 위해 마지막 체크시 사용할 qlen 값
- n_force_qs_snap
- n_force_qs가 복사된 값으로 최근에 fqs가 수행되었는지 확인하기 위해 사용된다.
- blimit
- 배치 처리할 콜백 제한 수
- 빠른 인터럽트 latency를 보장하게 하기 위해 콜백들이 많은 경우 한 번에 blimit 이하의 콜백들만 처리하게 한다.
3) dynticks(nohz) 인터페이스
- dynticks_snap
- dynticks->dynticks 값을 복사해두고 카운터 값이 변동이 있는지 확인하기 위해 사용된다.
- dynticks_nesting
- 초기 값은 1로 시작되며, eqs 진입 시 1 감소 시키며, 퇴출 시 1 증가 시킨다.
- dynticks_nmi_nesting
- 초기 값은 DYNTICK_IRQ_NONIDLE(long_max / 2 + 1)로 시작되며, irq/nmi 진출시 1(eqs)~2 증가되고, 퇴출시 1(eqs)~2 감소된다.
- dynticks
- per-cpu로 구성된 전역 rcu_dynticks에 연결된다.
- no-hz에서 qs상태를 관리하기 위해 사용한다.
- rcu_need_heavy_qs
- 2 * jiffies_to_sched_qs 시간(틱)동안 gp 연장
- rcu_urgent_qs
- jiffies_to_sched_qs 시간(틱)동안 gp 연장
- all_lazy
- 대기 중인 모든 콜백이 lazy(kfree) 타입 콜백인 경우 true가 된다.
- last_accelerate
- 최근 accelerate 콜백 처리한 시각(틱)
- last_advance_all
- 최근 advance 콜백 처리한 시각(틱)
- tick_nozh_enabled_snap
- nohz active 여부를 snap 저장하여 변경 여부를 체크하기 위해 사용한다.
4) rcu 배리어, OOM 콜백과 expediting
- barrier_head
- 베리어 역할로 사용하는 콜백
- exp_dynticks_snap
- bit0 클리어된 rdp->dynticks 값을 snap 저장하여 사용한다.
kernel/rcu/tree.h – 2/2
/* 5) Callback offloading. */
#ifdef CONFIG_RCU_NOCB_CPU
struct swait_queue_head nocb_cb_wq; /* For nocb kthreads to sleep on. */
struct task_struct *nocb_gp_kthread;
raw_spinlock_t nocb_lock; /* Guard following pair of fields. */
atomic_t nocb_lock_contended; /* Contention experienced. */
int nocb_defer_wakeup; /* Defer wakeup of nocb_kthread. */
struct timer_list nocb_timer; /* Enforce finite deferral. */
unsigned long nocb_gp_adv_time; /* Last call_rcu() CB adv (jiffies). */
/* The following fields are used by call_rcu, hence own cacheline. */
raw_spinlock_t nocb_bypass_lock ____cacheline_internodealigned_in_smp;
struct rcu_cblist nocb_bypass; /* Lock-contention-bypass CB list. */
unsigned long nocb_bypass_first; /* Time (jiffies) of first enqueue. */
unsigned long nocb_nobypass_last; /* Last ->cblist enqueue (jiffies). */
int nocb_nobypass_count; /* # ->cblist enqueues at ^^^ time. */
/* The following fields are used by GP kthread, hence own cacheline. */
raw_spinlock_t nocb_gp_lock ____cacheline_internodealigned_in_smp;
struct timer_list nocb_bypass_timer; /* Force nocb_bypass flush. */
u8 nocb_gp_sleep; /* Is the nocb GP thread asleep? */
u8 nocb_gp_bypass; /* Found a bypass on last scan? */
u8 nocb_gp_gp; /* GP to wait for on last scan? */
unsigned long nocb_gp_seq; /* If so, ->gp_seq to wait for. */
unsigned long nocb_gp_loops; /* # passes through wait code. */
struct swait_queue_head nocb_gp_wq; /* For nocb kthreads to sleep on. */
bool nocb_cb_sleep; /* Is the nocb CB thread asleep? */
struct task_struct *nocb_cb_kthread;
struct rcu_data *nocb_next_cb_rdp;
/* Next rcu_data in wakeup chain. */
/* The following fields are used by CB kthread, hence new cacheline. */
struct rcu_data *nocb_gp_rdp ____cacheline_internodealigned_in_smp;
/* GP rdp takes GP-end wakeups. */
#endif /* #ifdef CONFIG_RCU_NOCB_CPU */
/* 6) RCU priority boosting. */
struct task_struct *rcu_cpu_kthread_task;
/* rcuc per-CPU kthread or NULL. */
unsigned int rcu_cpu_kthread_status;
char rcu_cpu_has_work;
/* 7) Diagnostic data, including RCU CPU stall warnings. */
unsigned int softirq_snap; /* Snapshot of softirq activity. */
/* ->rcu_iw* fields protected by leaf rcu_node ->lock. */
struct irq_work rcu_iw; /* Check for non-irq activity. */
bool rcu_iw_pending; /* Is ->rcu_iw pending? */
unsigned long rcu_iw_gp_seq; /* ->gp_seq associated with ->rcu_iw. */
unsigned long rcu_ofl_gp_seq; /* ->gp_seq at last offline. */
short rcu_ofl_gp_flags; /* ->gp_flags at last offline. */
unsigned long rcu_onl_gp_seq; /* ->gp_seq at last online. */
short rcu_onl_gp_flags; /* ->gp_flags at last online. */
unsigned long last_fqs_resched; /* Time of last rcu_resched(). */
int cpu;
};
5) callback offloading (no-cb)
- nocb_cb_wq
- nocb 커널 스레드가 잠들때 대기하는 리스트
- *nocb_gp_kthread
- no-cb용 gp 커널 스레드
- nocb_lock
- no-cb용 스핀락
- nocb_lock_contended
- no-cb용 lock contention 유무를 관리하기 위해 사용되는 카운터이다.
- nocb_defer_wakeup
- no-cb용 커널 스레드를 깨우는 것에 대한 유예 상태
- RCU_NOGP_WAKE_NOT(0)
- RCU_NOGP_WAKE(1)
- RCU_NOGP_WAKE_FORCE(2)
- no-cb용 커널 스레드를 깨우는 것에 대한 유예 상태
- nocb_timer
- no-cb용 타이머
- no-cb용 gp 커널 스레드를 1틱 deferred wakeup을 할 때 사용한다.
- nocb_gp_adv_time
- no-cb용 gp 커널 스레드에서 콜백들을 flush 처리하고 advance 처리를 하는데, 1 틱이내에 반복하지 않기 위해 사용한다.
- nocb_bypass_lock
- no-cb bypass 갱신 시 사용하는 스핀락
- nocb_bypass
- no-cb용 bypass 콜백 리스트
- nocb_bypass_first
- no-cb용 bypass 에 처음 콜백이 추가될 때의 시각을 기록한다.
- no-cb용 bypass 리스트에 있는 콜백들을 flush하여 처리한 경우에도 해당 시각을 기록한다.
- 1ms 이내에 진입하는 콜백들이 일정량(16개)을 초과하여 진입할 때에만 no-cb용 bypass에 콜백을 추가하고 nocb_nobypass_count 카운터를 증가시키는데 이 카운터(는 이 시각이 바뀔 때마다 리셋된다.
- nocb_nobypass_last
- no-cb용 bypass 리스트에 콜백을 추가 시도할 때 갱신되는 시각(틱)이다.
- nocb_nobypass_count
- no-cb용 bypass 리스트를 사용하여 콜백을 추가하기 위해 카운팅을 한다.
- 이 값이 매 틱마다 nocb_nobypass_lim_per_jiffy(디폴트 1ms 당 16개) 갯 수를 초과할 때에만 no-cb용 bypass 리스트에 콜백을 추가한다.
- nocb_gp_lock
- no-cb용 gp 커널스레드가 사용하는 락
- nocb_bypass_timer
- no-cb용 bypass 타이머로 새 gp 요청을 기다리기 위해 슬립 전에 no-cb용 콜백들을 모두 flush 처리하기 위해 2틱을 설정하여 사용한다.
- nocb_gp_sleep
- no-cb용 gp 커널 스레드가 슬립 상태인지 여부를 담는다. gp 변화를 위해 외부에서 이 값을 false로 바꾸고 깨워 사용한다.
- nocb_gp_bypass
- no-cb용 gp 커널 스레드가 지난 스캔에서 bypass 모드로 동작하였는지 여부를 담는다.
- nocb_gp_gp
- no-cb용 gp 커널 스레드가 지난 스캔에서 wait 중인지 여부를 담는다.
- nocb_gp_seq
- no-cb용 gp 커널 스레드에서 gp idle 상태일때 -1 값을 갖고, 진행 중일 때 ->gp_seq 값을 담고 있다.
- nocb_gp_loops
- no-cb용 gp 커널 스레드의 루프 횟수를 카운팅하기 위해 사용된다. (gp state 출력용)
- nocb_gp_wq
- no-cb용 gp 커널 스레드가 슬립하는 곳이다.
- nocb_cb_sleep
- no-cb용 cb 커널 스레드가 슬립 상태인지 여부를 담는다. 콜백 처리를 위해 이 값을 false로 바꾸고 깨워 사용한다.
- *nocb_cb_kthread
- no-cb용 cb 커널 스레드를 가리킨다.
- *nocb_next_cb_rdp
- wakeup 체인에서 다음에 처리할 rdp를 가리킨다.
- *nocb_gp_rdp
- no-cb용 gp 커널 스레드가 있는 rdp(cpu)를 가리킨다.
6) rcu priority boosting
- *rcu_cpu_kthread_task
- rcuc 커널 스레드
- rcu_cpu_kthread_status
- rcu 커널 스레드 상태
- RCU_KTHREAD_STOPPED 0
- RCU_KTHREAD_RUNNING 1
- RCU_KTHREAD_WAITING 2
- RCU_KTHREAD_OFFCPU 3
- RCU_KTHREAD_YIELDING 4
- rcu 커널 스레드 상태
- rcu_cpu_has_work
- cpu에 처리할 콜백이 있어 cb용 콜백 처리 커널 스레드를 깨워야 할 때 사용된다.
7) diagnostic data / rcu cpu stall warning
- softirq_snap
- cpu stall 정보를 출력할 때 사용하기 위해 rcu softirq 카운터 값 복사(snap-shot)
- CONFIG_RCU_CPU_STALL_INFO 커널 옵션 필요
- rcu_iw
- rcu_iw_handler() 함수가 담긴 rcu irq work
- rcu_iw_pending
- rcu irq work 호출 전에 true가 담긴다.
- rcu_iw_gp_seq
- rcu irq work 호출 전에 rnp->gp_seq가 담긴다.
- rcu_ofl_gp_seq
- cpu offline 변경 시 gp_seq가 담긴다.
- rcu_ofl_gp_flags
- cpu offline 변경 시 gp_flags가 담긴다.
- rcu_onl_gp_seq
- cpu online 변경 시 gp_seq가 담긴다.
- rcu_onl_gp_flags
- cpu online 변경 시 gp_flags가 담긴다.
- last_fqs_resched
- 최근 fqs 리스케줄 시각(틱)이 담긴다.
- fqs 진행될 때 3 * jiffies_to_sched_qs 시간이 지난 경우 리스케줄 요청을 한다.
- cpu
- cpu 번호
참고
- RCU(Read Copy Update) -1- (Basic) | 문c
- RCU(Read Copy Update) -2- (Callback process) | 문c – 현재글
- RCU(Read Copy Update) -3- (RCU threads) | 문c
- RCU(Read Copy Update) -4- (NOCB process) | 문c
- RCU(Read Copy Update) -5- (Callback list) | 문c
- RCU(Read Copy Update) -6- (Expedited GP) | 문c
- RCU(Read Copy Update) -7- (Preemptible RCU) | 문c
- rcu_init() | 문c
- wait_for_completion() | 문c



내용 잘읽었습니다.
예전 RCU tree 구조와 통합전 rcu flavor만( rcu_bh, rcu_sched) 정리해두고, 최근커널은 분석을 미루고있었는데,
덕분에 매우깔끔하고 쉽게 내용정리 됐습니다.
감사합니다.
내용 오류 보고드리면, rcu_seq_endval()의 api 설명이 rcu_seq_end()와 중복되어있습니다.
안녕하세요?
잘 아시겠지만 rcu_seq_end()는 rcu_seq_endval()을 호출하므로 내용을 동일하지만 반환 값의 유무만 다릅니다.
일단 혼선이 있을 수도 있어 내용을 수정하였습니다.
잘못된 부분 알려주셔서 감사합니다. 좋은 하루 되세요~