<kernel v5.4>
Timer -3- (Clock Sources Subsystem)
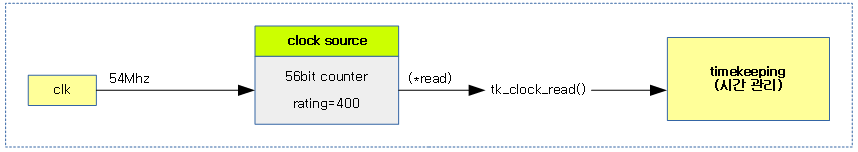
리눅스의 timekeeping subsystem에서 수행하는 시간 관리를 위해 clock sources subsystem에 등록된 클럭 소스들 중 가장 정확도가 높고 안정적인 클럭 소스를 찾아 제공하기 위한 framework를 제공한다.
- 주요 연관 관계
- clk(common clock foundation) -> clock sources subsystem -> timekeeping subsystem
다음 그림은 clock source의 연동 관계를 보여준다.
clocksource 등록
다음 그림은 19.2Mhz의 클럭 소스를 등록하는 과정을 보여준다.
clocksource_register_hz()
include/linux/clocksource.h
static inline int clocksource_register_hz(struct clocksource *cs, u32 hz)
{
return __clocksource_register_scale(cs, 1, hz);
}
요청한 hz의 클럭 소스를 등록한다.
clocksource_register_khz()
include/linux/clocksource.h
static inline int clocksource_register_khz(struct clocksource *cs, u32 khz)
{
return __clocksource_register_scale(cs, 1000, khz);
}
요청한 khz의 클럭 소스를 등록한다.
__clocksource_register_scale()
kernel/time/clocksource.c
/** * __clocksource_register_scale - Used to install new clocksources * @cs: clocksource to be registered * @scale: Scale factor multiplied against freq to get clocksource hz * @freq: clocksource frequency (cycles per second) divided by scale * * Returns -EBUSY if registration fails, zero otherwise. * * This *SHOULD NOT* be called directly! Please use the * clocksource_register_hz() or clocksource_register_khz helper functions. */
int __clocksource_register_scale(struct clocksource *cs, u32 scale, u32 freq)
{
unsigned long flags;
clocksource_arch_init(cs);
/* Initialize mult/shift and max_idle_ns */
__clocksource_update_freq_scale(cs, scale, freq);
/* Add clocksource to the clocksource list */
mutex_lock(&clocksource_mutex);
clocksource_watchdog_lock(&flags);
clocksource_enqueue(cs);
clocksource_enqueue_watchdog(cs);
clocksource_watchdog_unlock(&flags);
clocksource_select();
clocksource_select_watchdog(false);
__clocksource_suspend_select(cs);
mutex_unlock(&clocksource_mutex);
return 0;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(__clocksource_register_scale);
요청한 배율(scale) 및 주파수(freq)로 클럭소스를 등록한다.
- 코드 라인 5에서 아키텍처별 별도의 클럭 소스 초기화 루틴을 호출한다.
- 현재 x86 아키텍처만 사용하고 있다.
- 코드 라인 8에서 요청한 배율(scale) 및 주파수(freq)로 클럭의 mult, shift, maxadj, max_idle_ns 등을 산출한다.
- 코드 라인 14~15에서 클럭 소스 @cs를 클럭 소스 리스트에 등록하고, 필요 시 워치독 리스트에도 추가한다.
- 코드 라인 18에서 best 클럭 소스를 선택한다.
- 코드 라인 19에서 워치독할 클럭 소스를 선택한다.
- 코드 라인 20에서 suspend용 클럭 소스로 @cs를 지정한다.
- “always-on” 속성이 있는 클럭 소스만 가능하다.
__clocksource_update_freq_hz()
include/linux/clocksource.h
static inline void __clocksource_update_freq_hz(struct clocksource *cs, u32 hz)
{
__clocksource_updatefreq_scale(cs, 1, hz);
}
현재 클럭소스의 주파수가 요청한 hz로 변경 시 관련된 mult, shift, maxadj, max_idle_ns 등을 산출한다.
__clocksource_update_freq_khz()
include/linux/clocksource.h
static inline void __clocksource_update_freq_khz(struct clocksource *cs, u32 khz)
{
__clocksource_updatefreq_scale(cs, 1000, khz);
}
현재 클럭소스의 주파수가 요청한 khz로 변경 시 관련된 mult, shift, maxadj, max_idle_ns 등을 산출한다.
__clocksource_update_freq_scale()
kernel/time/clocksource.c
/** * __clocksource_update_freq_scale - Used update clocksource with new freq * @cs: clocksource to be registered * @scale: Scale factor multiplied against freq to get clocksource hz * @freq: clocksource frequency (cycles per second) divided by scale * * This should only be called from the clocksource->enable() method. * * This *SHOULD NOT* be called directly! Please use the * __clocksource_update_freq_hz() or __clocksource_update_freq_khz() helper * functions. */
void __clocksource_update_freq_scale(struct clocksource *cs, u32 scale, u32 freq)
{
u64 sec;
/*
* Default clocksources are *special* and self-define their mult/shift.
* But, you're not special, so you should specify a freq value.
*/
if (freq) {
/*
* Calc the maximum number of seconds which we can run before
* wrapping around. For clocksources which have a mask > 32-bit
* we need to limit the max sleep time to have a good
* conversion precision. 10 minutes is still a reasonable
* amount. That results in a shift value of 24 for a
* clocksource with mask >= 40-bit and f >= 4GHz. That maps to
* ~ 0.06ppm granularity for NTP.
*/
sec = cs->mask;
do_div(sec, freq);
do_div(sec, scale);
if (!sec)
sec = 1;
else if (sec > 600 && cs->mask > UINT_MAX)
sec = 600;
clocks_calc_mult_shift(&cs->mult, &cs->shift, freq,
NSEC_PER_SEC / scale, sec * scale);
}
/*
* Ensure clocksources that have large 'mult' values don't overflow
* when adjusted.
*/
cs->maxadj = clocksource_max_adjustment(cs);
while (freq && ((cs->mult + cs->maxadj < cs->mult)
|| (cs->mult - cs->maxadj > cs->mult))) {
cs->mult >>= 1;
cs->shift--;
cs->maxadj = clocksource_max_adjustment(cs);
}
/*
* Only warn for *special* clocksources that self-define
* their mult/shift values and don't specify a freq.
*/
WARN_ONCE(cs->mult + cs->maxadj < cs->mult,
"timekeeping: Clocksource %s might overflow on 11%% adjustment\n",
cs->name);
clocksource_update_max_deferment(cs);
pr_info("%s: mask: 0x%llx max_cycles: 0x%llx, max_idle_ns: %lld ns\n",
cs->name, cs->mask, cs->max_cycles, cs->max_idle_ns);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(__clocksource_update_freq_scale);
요청한 배율(scale) 및 주파수(freq)로 클럭소스의 mult, shift, maxadj, max_idle_ns 등을 갱신한다.
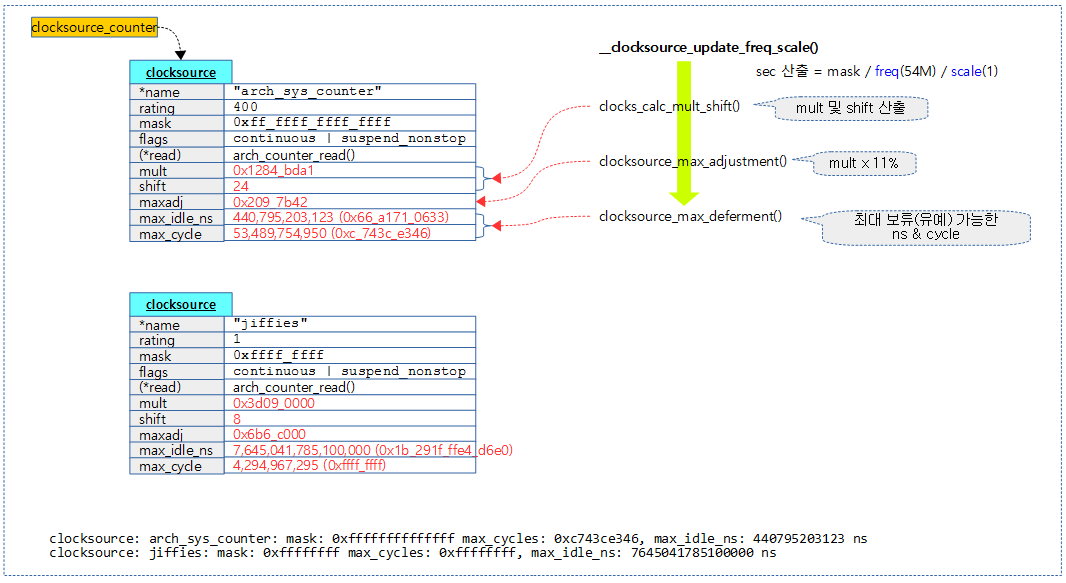
- 코드 라인 19~21에서 클럭소스의 mask 값을 @freq 및 @scale로 나누어 최대 몇 초까지 사용될 수 있는지를 알아와서 sec에 대입한다.
- 코드 라인 22~25에서 sec가 1초도 안되는 경우 1초로 변경한다. 또한 클럭 소스가 32비트 카운터를 초과하는 경우에 한해 sec 값이 600을 초과하면 최대 값 600초로 제한한다.
- jiffies 클럭 소스는 32비트 카운터 값을 사용하므로 600초 제한 없이 계산된다.
- “arch_sys_counter” 클럭 소스는 56비트 카운터를 사용하므로 최대 600초로 제한된다.
- 코드 라인 27~28에서 @freq, @scale 및 산출된 초(sec)로 소요 시간(ns) 계산에 필요한 컨버팅 팩터인 mult 및 shift 값을 구해온다.
- 코드 라인 34에서mult 값의 최대 교정치 값으로 사용하기 위해 mult 값의 11%를 maxadj에 저장한다.
- 코드 라인 35~40에서 최대 교정치 값을 더한 mult 값이 overflow 된 경우 mult 값과 shift 값을 1씩 줄인 후 overflow 되지 않을 때까지 다시 교정한다.
- 코드 라인 50에서 카운터가 overflow되지 않는 범위의 ns 값을 약간 마진 12.5를 줄여 max_idle_ns에 저장한다.
- 소요 시간(delta)이 max_idle_ns 값을 초과하는 경우 카운터가 overflow될 수 있음을 나타낸다.
- 코드 라인 52~53에서 클럭소스의 mask 값, max_cycles 값, max_idle_ns 값등을 정보로 출력한다.
- 예) clocksource: arch_sys_counter: mask: 0xffffffffffffff max_cycles: 0xc743ce346, max_idle_ns: 440795203123 ns
- 예) clocksource: jiffies: mask: 0xffffffff max_cycles: 0xffffffff, max_idle_ns: 7645041785100000 ns
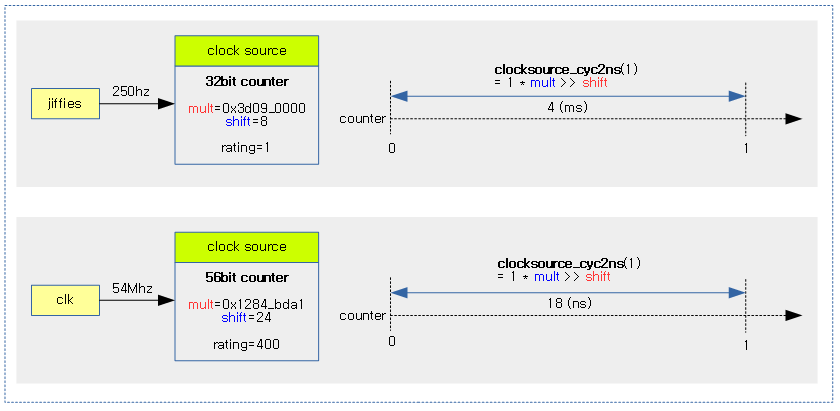
아래 그림은 54Mhz 56비트 카운터와 jiffies 32비트 카운터를 사용하는 경우 설정되는 값들을 보여준다.
mult & shift
“from 값이 to가 되려면 얼마의 컨버팅 비율이 필요할까?”에 대한 대답은 ‘to / from’을 하면 컨버팅 팩터가 산출된다. 다음과 같이 주파수를 사용하는 사례를 적용해본다.
예) 19.2Mhz 주파수를 갖는 카운터의 1 펄스 값이 사용하는 시간은 나노초 단위로 얼마일까?
- 디지탈 클럭 시스템에서 주파수 hz는 1초당 high/low 전압이 반복되는 개수를 의미한다. 따라서 19.2Mhz는 1초에 19.2M 번의 high/low 전압이 바뀌고 펄스 하나가 사용하는 초는 ‘1 초 / 19.2M’ 초를 갖는다. (1 / 19.2M = 52.08333333 (ns))
커널 코드는 성능과 호환성을 유지하기 위해 부동 소숫점(float)을 사용한 나눗셈 연산을 사용하지 않는다. 따라서 이러한 연산을 대체할 수 있는 방법으로 mult와 shift를 사용한다.
먼저 실수(float) 1.0이라는 수를 사용하지 않고 소숫점을 포함한 정수로 변환을 하여 사용할 때 10배를 곱하여 10이라는 정수를 1.0이라고 의미를 붙일 수 있다. 이렇게 실수를 변환하여 사용하는 정수는 이진수 시스템에서는 10진수와 다르게 2의 거듭제곱수를 사용한다. 이 값이 크면 클 수록 소숫점 이하 정밀도를 높여 표현할 수 있다.
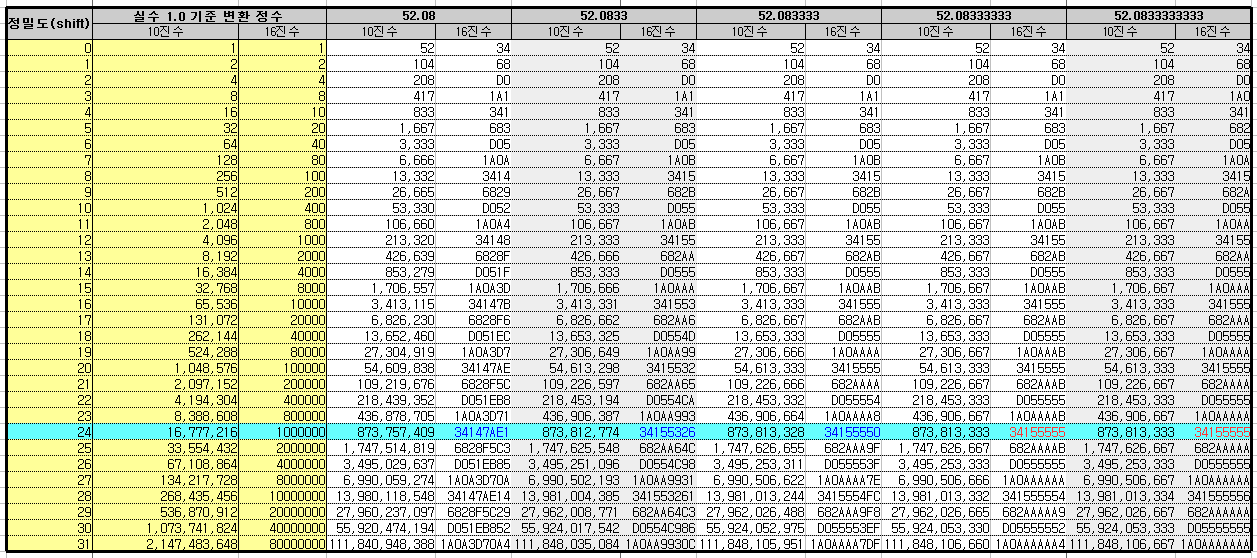
예) 실수 52.08333333에 대해 소숫점이하 8자리의 정밀도를 정수로 표현하기 위해 10E8=100,000,000 배를 곱하여야 한다. 컴퓨터에서는 2 진수의 연산이 더 빠르므로 이를 직접 사용하기 보다는 2의 거듭제곱수를 사용한다. 100,000,000 보다 큰 유사한 2의 n 거듭 제곱수로 2^27=134,217,728을 사용하면 10진수의 8자리 소수를 해결할 수 있다.
다른 정밀도에 따라 사용되는 mult 값들을 살펴본다.
- 아래 파란 라인만 참고해보면실수 1.0 기준으로 정밀도 shift=24를 사용하여 2^24=0x100_0000 기준 정수를 사용한 경우 실수 52.08333333을 변환한 정수는 0x3415_5555(873,813,333)이 된다.
- 10진수의 소숫점 8자리를 해결하는 정밀도이다.
- 참고: Scheduler -1- (Basic)
결국 정밀도가 높아야 하는 경우 float 1.0에 대한 정수 기준 값이 커져야 함을 알 수 있다. 이 정수 기준 값을 shift 연산에 사용할 예정이다.
“x / y 와 같은 형태의 나눗셈을 커널은 어떻게 처리할까?”
y로 나누는 값이 2의 배수일 경우 우측 쉬프트 연산자를 사용하여 간단히 나눗셈을 대체할 수 있으므로 ‘(x * mult) >> shift’ 형태로 바꿔서 사용할 수 있도록 한다. mult 값은 소숫점일 수 있으므로 정수형으로 변환하여 사용한다.
예) 주파수(freq)에 해당하는 from=19.2M를 나노초 단위의 주파수인 to=1G를 대상으로 설명하면
- to(1G) / from(19.2M) = 52.08333333과 같이 from이 52.0833333배가 되어야 to가 됨을 알 수 있다. 따라서 from의 1 펄스를 52.0833333 나노초로 산출해야 함을 알 수 있다.
- 실제 연산은 ‘(to(1G) * mult) >> shift’를 사용하므로 mult와 shift를 산출해야 한다. 먼저 정밀도를 위해 shift를 결정하고 mult 값은 실수를 사용하지 않고 shift 비트 수 만큼 배율 변화한 정수를 사용한다.
mult & shift 산출
clocks_calc_mult_shift()
kernel/time/clocksource.c
/** * clocks_calc_mult_shift - calculate mult/shift factors for scaled math of clocks * @mult: pointer to mult variable * @shift: pointer to shift variable * @from: frequency to convert from * @to: frequency to convert to * @maxsec: guaranteed runtime conversion range in seconds * * The function evaluates the shift/mult pair for the scaled math * operations of clocksources and clockevents. * * @to and @from are frequency values in HZ. For clock sources @to is * NSEC_PER_SEC == 1GHz and @from is the counter frequency. For clock * event @to is the counter frequency and @from is NSEC_PER_SEC. * * The @maxsec conversion range argument controls the time frame in * seconds which must be covered by the runtime conversion with the * calculated mult and shift factors. This guarantees that no 64bit * overflow happens when the input value of the conversion is * multiplied with the calculated mult factor. Larger ranges may * reduce the conversion accuracy by chosing smaller mult and shift * factors. */
void
clocks_calc_mult_shift(u32 *mult, u32 *shift, u32 from, u32 to, u32 maxsec)
{
u64 tmp;
u32 sft, sftacc= 32;
/*
* Calculate the shift factor which is limiting the conversion
* range:
*/
tmp = ((u64)maxsec * from) >> 32;
while (tmp) {
tmp >>=1;
sftacc--;
}
/*
* Find the conversion shift/mult pair which has the best
* accuracy and fits the maxsec conversion range:
*/
for (sft = 32; sft > 0; sft--) {
tmp = (u64) to << sft;
tmp += from / 2;
do_div(tmp, from);
if ((tmp >> sftacc) == 0)
break;
}
*mult = tmp;
*shift = sft;
}
최대초 @maxsec로 @from 주파수를 @to 주파수로 변환할 때 적용할 컨버팅 팩터인 mult 및 shift 값을 구해온다.
- armv7 아키텍처의 로컬 타이머는 32비트 타이머로 from 주파수를 max초 기간만큼 곱하여 64비트로 옮겼을 때 64비트에서 남는 비트들과 배율 차이만큼의 비트들을 뺀 비트를 대상으로 최대 32비트에 한하여 정밀도(shift) 비트를 최대한 올려 사용할 수 있다.
- @from * factor = @to
- 예) 54M * factor = 1G
- factor = @to / @from
- 예) factor = 1G / 54M = 0.185185185…
- @from * mult >> shift = @to
- 코드 라인 11~15에서 from과 maxsec 곱한 후 leading 0 비트 갯 수로 sftacc를 구한다.
- sftacc는 0 ~ 32 범위로 제한한다. 32를 초과하는 경우 32로 계산한다. (최대 정밀도=32bit)
- sftacc는 컨버전 팩터로 정확도를 제한하는데 숫자가 작을 수록 정확도가 낮아진다.
- 측정하는 구간 소요 시간인 maxsec를 높이면 정밀도에 사용할 수 있는 비트가 줄어들므로 정확도가 낮아진다.
- shftacc를 32에서 시작하여, @from * @maxsec 값이 32bit를 초과한 비트 수 만큼 shtacc–
- 코드 라인 21~29에서 to 값을 32 ~ 1까지 좌측 시프트한 값을 from 으로 나눈 값을 다시 sftacc 값 만큼 우측 시프트하여 0을 초과하는 경우 mult 및 shift와 값을 구한다. 만일 0 이하인 경우 to 값을 계속 감소시키며 루프를 돈다.
- sht를 32에서 시작하여 감소시켜 나가며, ((@to << sht) + (반올림 목적: @from / 2)) / @from 값이 shtacc 비트 이내에 포함된 값을 mult 값으로 로 선택한다.
다음은 factor 대신 사용할 정확도 shift 별 mult 값을 보여준다.
from(54000000) * factor(18.518519) = to(1000000000) ---------------------------------- from(54000000) * mult( 18.518519) >> 0 = to(1000000000) from(54000000) * mult( 37.037037) >> 1 = to(1000000000) from(54000000) * mult( 74.074074) >> 2 = to(1000000000) from(54000000) * mult( 148.148148) >> 3 = to(1000000000) from(54000000) * mult( 296.296296) >> 4 = to(1000000000) from(54000000) * mult( 592.592593) >> 5 = to(1000000000) from(54000000) * mult( 1185.185185) >> 6 = to(1000000000) from(54000000) * mult( 2370.370370) >> 7 = to(1000000000) from(54000000) * mult( 4740.740741) >> 8 = to(1000000000) from(54000000) * mult( 9481.481481) >> 9 = to(1000000000) from(54000000) * mult( 18962.962963) >> 10 = to(1000000000) from(54000000) * mult( 37925.925926) >> 11 = to(1000000000) from(54000000) * mult( 75851.851852) >> 12 = to(1000000000) from(54000000) * mult( 151703.703704) >> 13 = to(1000000000) from(54000000) * mult( 303407.407407) >> 14 = to(1000000000) from(54000000) * mult( 606814.814815) >> 15 = to(1000000000) from(54000000) * mult( 1213629.629630) >> 16 = to(1000000000) from(54000000) * mult( 2427259.259259) >> 17 = to(1000000000) from(54000000) * mult( 4854518.518519) >> 18 = to(1000000000) from(54000000) * mult( 9709037.037037) >> 19 = to(1000000000) from(54000000) * mult( 19418074.074074) >> 20 = to(1000000000) from(54000000) * mult( 38836148.148148) >> 21 = to(1000000000) from(54000000) * mult( 77672296.296296) >> 22 = to(1000000000) from(54000000) * mult( 155344592.592593) >> 23 = to(1000000000) from(54000000) * mult( 310689185.185185) >> 24 = to(1000000000) from(54000000) * mult( 621378370.370370) >> 25 = to(1000000000) from(54000000) * mult( 1242756740.740741) >> 26 = to(1000000000) from(54000000) * mult( 2485513481.481482) >> 27 = to(1000000000) from(54000000) * mult( 4971026962.962963) >> 28 = to(1000000000) from(54000000) * mult( 9942053925.925926) >> 29 = to(1000000000) from(54000000) * mult(19884107851.851852) >> 30 = to(1000000000) from(54000000) * mult(39768215703.703705) >> 31 = to(1000000000)
다음은 32비트 이진화 정수(1.0 = 0x1_0000_0000)를 사용한 mult 값을 보여준다.
from(54000000) * factor(18.518519) = to(1000000000) ---------------------------------- from(54000000) * mult(0x 1284bda12f) >> 0 = to(1000000000) from(54000000) * mult(0x 25097b425e) >> 1 = to(1000000000) from(54000000) * mult(0x 4a12f684bc) >> 2 = to(1000000000) from(54000000) * mult(0x 9425ed0978) >> 3 = to(1000000000) from(54000000) * mult(0x 1284bda12f0) >> 4 = to(1000000000) from(54000000) * mult(0x 25097b425e0) >> 5 = to(1000000000) from(54000000) * mult(0x 4a12f684bc0) >> 6 = to(1000000000) from(54000000) * mult(0x 9425ed09780) >> 7 = to(1000000000) from(54000000) * mult(0x 1284bda12f00) >> 8 = to(1000000000) from(54000000) * mult(0x 25097b425e00) >> 9 = to(1000000000) from(54000000) * mult(0x 4a12f684bc00) >> 10 = to(1000000000) from(54000000) * mult(0x 9425ed097800) >> 11 = to(1000000000) from(54000000) * mult(0x 1284bda12f000) >> 12 = to(1000000000) from(54000000) * mult(0x 25097b425e000) >> 13 = to(1000000000) from(54000000) * mult(0x 4a12f684bc000) >> 14 = to(1000000000) from(54000000) * mult(0x 9425ed0978000) >> 15 = to(1000000000) from(54000000) * mult(0x 1284bda12f0000) >> 16 = to(1000000000) from(54000000) * mult(0x 25097b425e0000) >> 17 = to(1000000000) from(54000000) * mult(0x 4a12f684bc0000) >> 18 = to(1000000000) from(54000000) * mult(0x 9425ed09780000) >> 19 = to(1000000000) from(54000000) * mult(0x 1284bda12f00000) >> 20 = to(1000000000) from(54000000) * mult(0x 25097b425e00000) >> 21 = to(1000000000) from(54000000) * mult(0x 4a12f684bc00000) >> 22 = to(1000000000) from(54000000) * mult(0x 9425ed097800000) >> 23 = to(1000000000) from(54000000) * mult(0x1284bda12f000000) >> 24 = to(1000000000) from(54000000) * mult(0x25097b425e000000) >> 25 = to(1000000000) from(54000000) * mult(0x4a12f684bc000000) >> 26 = to(1000000000) from(54000000) * mult(0x9425ed0978000000) >> 27 = to(1000000000) from(54000000) * mult(0x1284bda12f0000000) >> 28 = to(1000000000) from(54000000) * mult(0x25097b425e0000000) >> 29 = to(1000000000) from(54000000) * mult(0x4a12f684bc0000000) >> 30 = to(1000000000) from(54000000) * mult(0x9425ed09780000000) >> 31 = to(1000000000)
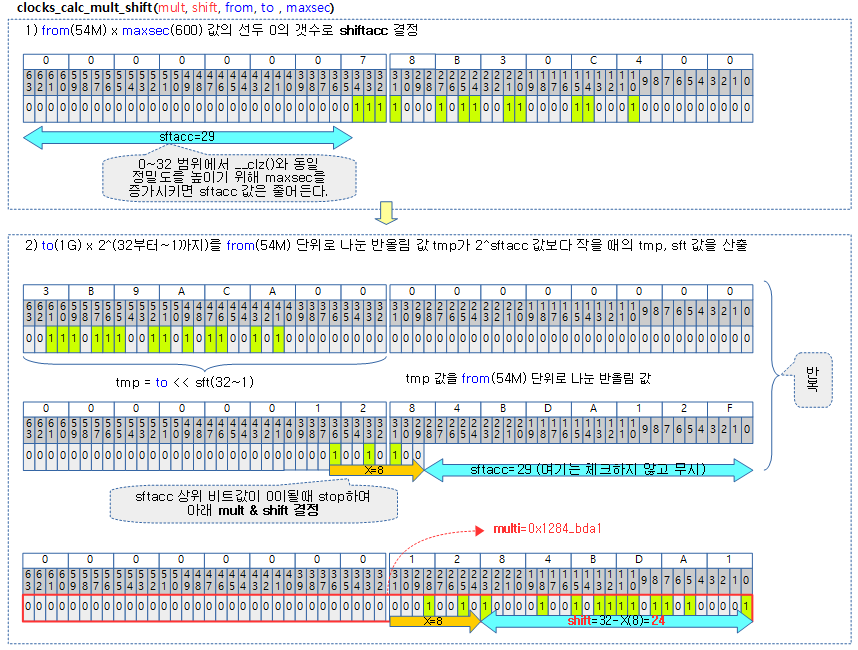
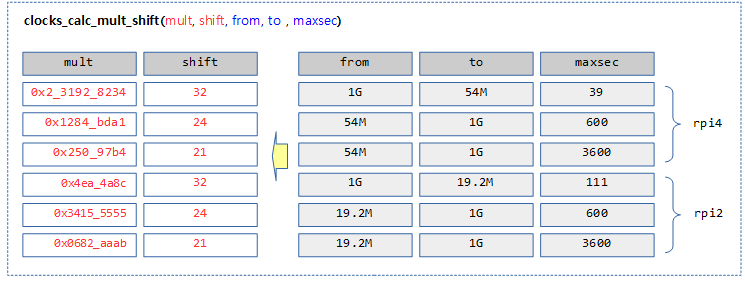
다음 그림은 from=54Mhz, to=1G, maxsec=600 값이 주어질 때 mult=0x1284_bda1/shift=24 값으로 계산되는 모습을 보여준다.
- 1) 54M * 600 = 0x7_8830_C400 값은 32bit를 3bit 만큼 초과하였으므로 shtacc=32-3=29로 결정된다.
- 2) ((1G << 32) + 27M) / @from = 0x12_84bd_a12f 값은 shtacc(29) 비트를 8bit 만큼 초과하였으므로 mult 값으로 8bit 만큼 줄인 값으로 결정하고, shift 값은 32-8=24로 결정한다.
다음 그림은 몇 가지 조건으로 mult/shift 값을 산출한 결과를 보여준다.
clocksource_max_adjustment()
kernel/time/clocksource.c
/** * clocksource_max_adjustment- Returns max adjustment amount * @cs: Pointer to clocksource * */
static u32 clocksource_max_adjustment(struct clocksource *cs)
{
u64 ret;
/*
* We won't try to correct for more than 11% adjustments (110,000 ppm),
*/
ret = (u64)cs->mult * 11;
do_div(ret,100);
return (u32)ret;
}
최대 조정값으로 mult 값의 11%를 반환한다.
clocksource_max_deferment()
kernel/time/clocksource.c
/** * clocksource_update_max_deferment - Updates the clocksource max_idle_ns & max_cycles * @cs: Pointer to clocksource * */
static u64 clocksource_update_max_deferment(struct clocksource *cs)
{
cs->max_idle_ns = clocks_calc_max_nsecs(cs->mult, cs->shift,
cs->maxadj, cs->mask,
&cs->max_cycles);
}
클럭 소스로 cycle 카운터 값을 읽어 ns 값으로 변환하여 사용할 때 최대 사용가능한 보류(유예)할 수 있는 최대 ns 및 cycle 값을 산출한다.
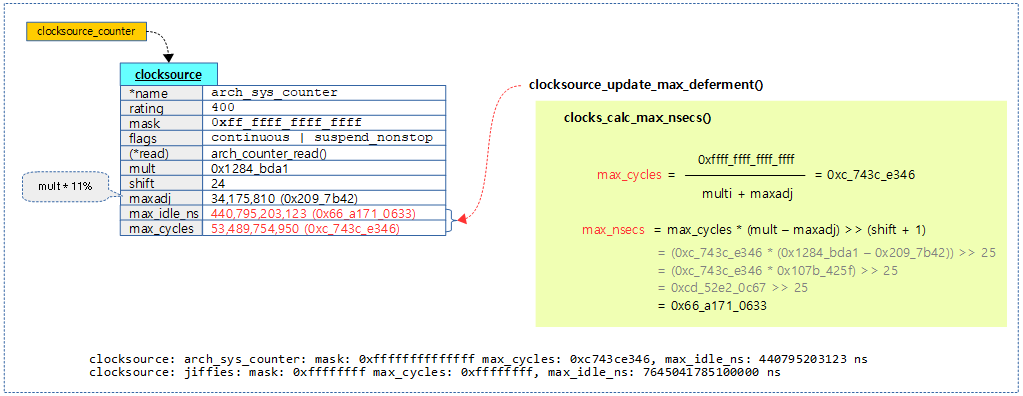
다음 그림은 56비트 클럭 소스로 최대 보류(유예)할 수 있는 ns 및 cycle 값을 산출하는 모습을 보여준다.
- max_idle_ns 값은 약 440초
- max_cycles 값은 약 440억번
clocks_calc_max_nsecs()
kernel/time/clocksource.c
/** * clocks_calc_max_nsecs - Returns maximum nanoseconds that can be converted * @mult: cycle to nanosecond multiplier * @shift: cycle to nanosecond divisor (power of two) * @maxadj: maximum adjustment value to mult (~11%) * @mask: bitmask for two's complement subtraction of non 64 bit counters * @max_cyc: maximum cycle value before potential overflow (does not include * any safety margin) * * NOTE: This function includes a safety margin of 50%, in other words, we * return half the number of nanoseconds the hardware counter can technically * cover. This is done so that we can potentially detect problems caused by * delayed timers or bad hardware, which might result in time intervals that * are larger than what the math used can handle without overflows. */
u64 clocks_calc_max_nsecs(u32 mult, u32 shift, u32 maxadj, u64 mask, u64 *max_cyc)
{
u64 max_nsecs, max_cycles;
/*
* Calculate the maximum number of cycles that we can pass to the
* cyc2ns() function without overflowing a 64-bit result.
*/
max_cycles = ULLONG_MAX;
do_div(max_cycles, mult+maxadj);
/*
* The actual maximum number of cycles we can defer the clocksource is
* determined by the minimum of max_cycles and mask.
* Note: Here we subtract the maxadj to make sure we don't sleep for
* too long if there's a large negative adjustment.
*/
max_cycles = min(max_cycles, mask);
max_nsecs = clocksource_cyc2ns(max_cycles, mult - maxadj, shift);
/* return the max_cycles value as well if requested */
if (max_cyc)
*max_cyc = max_cycles;
/* Return 50% of the actual maximum, so we can detect bad values */
max_nsecs >>= 1;
return max_nsecs;
}
최대 조정 cycle 값을 뺀 mult와 cycle 수로 최대 사용 가능한 시간(ns)의 절반을 구해 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 9~10에서 0xffff_ffff_ffff_ffff / (mult+maxadj)로 max_cycle을 산출한다.
- max_cycle을 산출하는 방법이 커널 v4.1-rc1에서 simple하게 바뀌었다.
- 참고: clocksource: Simplify the clocks_calc_max_nsecs() logic (2015, v4.1-rc1)
- 코드 라인 18에서 max_cycles가 mask 값을 초과하지 않게 한다.
- 코드 라인 19에서 계산된 max_cycles에 maxadj를 뺀 mult를 곱한 수를 우측으로 shift 하여 최대 소요 시간(ns)을 구해 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 22~23에서 출력 인자 @max_cyc가 지정된 경우 max_cycles 값을 출력한다.
- 코드 라인 26~28에서 최대 소요 시간(ns)의 절반을 반환한다.
clocksource_cyc2ns()
include/linux/clocksource.h
/** * clocksource_cyc2ns - converts clocksource cycles to nanoseconds * @cycles: cycles * @mult: cycle to nanosecond multiplier * @shift: cycle to nanosecond divisor (power of two) * * Converts clocksource cycles to nanoseconds, using the given @mult and @shift. * The code is optimized for performance and is not intended to work * with absolute clocksource cycles (as those will easily overflow), * but is only intended to be used with relative (delta) clocksource cycles. * * XXX - This could use some mult_lxl_ll() asm optimization */
static inline s64 clocksource_cyc2ns(u64 cycles, u32 mult, u32 shift)
{
return ((u64) cycles * mult) >> shift;
}
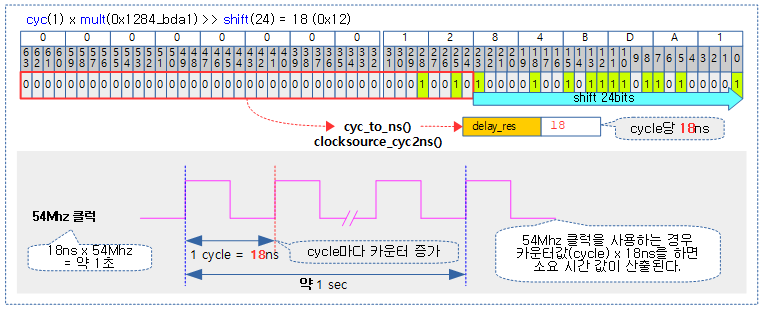
cycle 값에 @mult를 곱하고 @shift한 나노초를 반환한다.
- 예) 1 cycle, mult=0x682_aaab, shift=21
- =52ns
- 예) 256 cycle, mult=0x682a_aaab, shift=21
- =13,333ns
다음 그림은 mult=0x1284_bda1, shift=24인 상황에서 cycle=1이 주어진 경우 18ns의 소요 시간을 산출하는 모습을 보여준다.
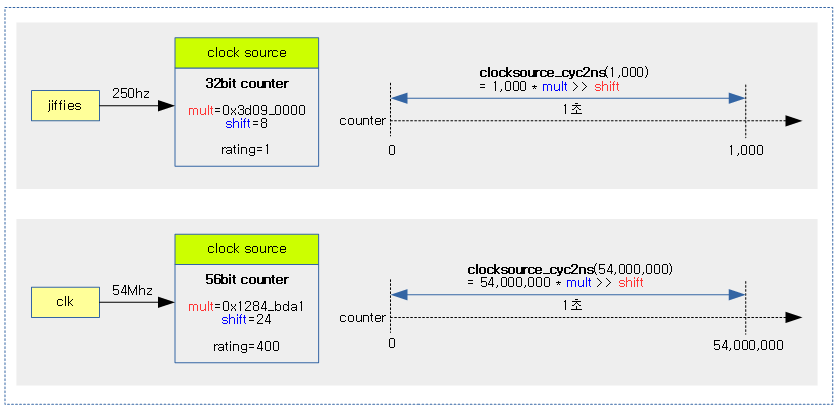
다음 그림은 해상도가 다른 두 개의 클럭 소스에 대해 1초 동안 카운터가 증가된 경우를 보여준다.
다음 그림은 해상도가 다른 두 개의 클럭 소스에 대해 1 사이클의 카운터가 증가된 경우에 대해 처리 가능한 최소 시간을 보여준다.
- 해상도가 낮은 jiffies를 사용하는 클럭 소스는 최소 단위로 4ms의 해상도를 갖음을 알 수 있다.
클럭 소스 등록 및 선택
clocksource_enqueue()
kernel/time/clocksource.c
/* * Enqueue the clocksource sorted by rating */
static void clocksource_enqueue(struct clocksource *cs)
{
struct list_head *entry = &clocksource_list;
struct clocksource *tmp;
list_for_each_entry(tmp, &clocksource_list, list)
/* Keep track of the place, where to insert */
if (tmp->rating >= cs->rating)
entry = &tmp->list;
list_add(&cs->list, entry);
}
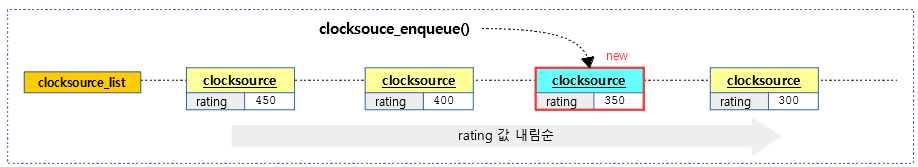
요청한 클럭 소스를 clocksource_list에 추가할 때 rating 값이 큰 순서대로 정렬한다. (descending sort)
다음 그림은 클럭 소스를 추가할 때 rating 값 순으로 소팅되어 등록되는 것을 보여준다.
clocksource_select()
kernel/time/clocksource.c
/** * clocksource_select - Select the best clocksource available * * Private function. Must hold clocksource_mutex when called. * * Select the clocksource with the best rating, or the clocksource, * which is selected by userspace override. */
static void clocksource_select(void)
{
__clocksource_select(false);
}
현재 지정된 클럭을 포함하여 best 클럭 소스를 찾아 선택한다.
__clocksource_select()
kernel/time/clocksource.c
static void __clocksource_select(bool skipcur)
{
bool oneshot = tick_oneshot_mode_active();
struct clocksource *best, *cs;
/* Find the best suitable clocksource */
best = clocksource_find_best(oneshot, skipcur);
if (!best)
return;
if (!strlen(override_name))
goto found;
/* Check for the override clocksource. */
list_for_each_entry(cs, &clocksource_list, list) {
if (skipcur && cs == curr_clocksource)
continue;
if (strcmp(cs->name, override_name) != 0)
continue;
/*
* Check to make sure we don't switch to a non-highres
* capable clocksource if the tick code is in oneshot
* mode (highres or nohz)
*/
if (!(cs->flags & CLOCK_SOURCE_VALID_FOR_HRES) && oneshot) {
/* Override clocksource cannot be used. */
if (cs->flags & CLOCK_SOURCE_UNSTABLE) {
pr_warn("Override clocksource %s is not HRT compatible - cannot switch while in HRT/NOHZ mode\n",
cs->name);
override_name[0] = 0;
} else {
/*
* The override cannot be currently verified.
* Deferring to let the watchdog check.
*/
pr_info("Override clocksource %s is not currently HRT compatible - deferring\n",
cs->name);
}
} else
/* Override clocksource can be used. */
best = cs;
break;
}
found:
if (curr_clocksource != best && !timekeeping_notify(best)) {
pr_info("Switched to clocksource %s\n", best->name);
curr_clocksource = best;
}
}
best 클럭 소스를 선택한다. skip_cur에 true를 요청하는 경우 현재 선택된 클럭 소스는 제외하고 다른 best 클럭 소스를 찾아 선택한다.
- 코드 라인 3에서 현재 cpu의 tick_cpu_device 모드가 oneshot을 지원하는지 여부를 알아온다.
- 코드 라인 7~9에서 먼저 best 클럭 소스를 알아온다. 만일 찾지 못한 경우 함수를 빠져나간다.
- 코드 라인 10~11에서 “clocksource=” 커널 파라미터로 지정된 클럭 소스가 없으면 found: 레이블로 이동한다.
- 코드 라인 13~41에서 “clocksource=” 커널 파라미터로 지정된 클럭 소스를 best 클럭 소스로 지정한다.
- 고해상도를 지원하는 클럭 소스가 아니면서 oneshot을 지원해야 하는 경우 고해상도 모드가 아니다라는 메시지를 출력한다.
- 코드 라인 43~47에서 found: 레이블이다. 현재 클럭 소스가 best 클럭 소스로 변경된 경우 클럭 소스가 바뀌었다는 정보를 출력한다.
다음 그림은 “t4” 클럭 소스를 지정하여 선택하는 것을 보여준다.
clocksource_find_best()
kernel/time/clocksource.c
static struct clocksource *clocksource_find_best(bool oneshot, bool skipcur)
{
struct clocksource *cs;
if (!finished_booting || list_empty(&clocksource_list))
return NULL;
/*
* We pick the clocksource with the highest rating. If oneshot
* mode is active, we pick the highres valid clocksource with
* the best rating.
*/
list_for_each_entry(cs, &clocksource_list, list) {
if (skipcur && cs == curr_clocksource)
continue;
if (oneshot && !(cs->flags & CLOCK_SOURCE_VALID_FOR_HRES))
continue;
return cs;
}
return NULL;
}
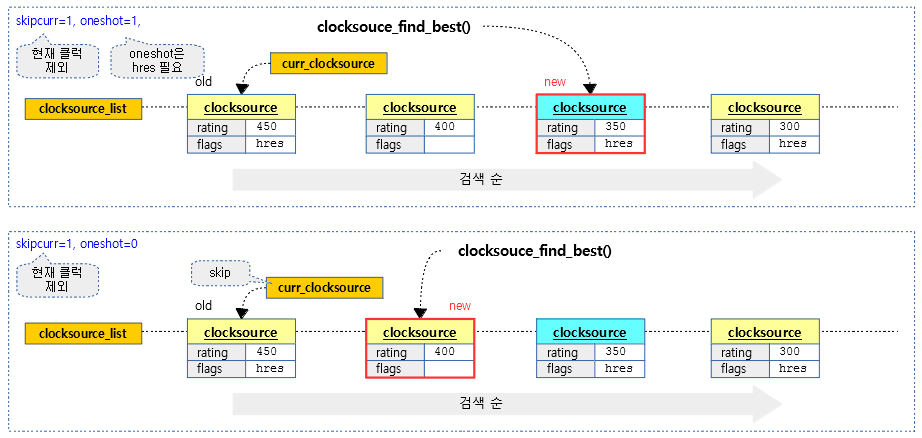
best 클럭 소스를 찾아 반환한다. oneshot=1이 요청되는 경우 hrtimer에서만 찾는다. skipcur=true인 경우 현재 선택된 클럭 소스는 제외한다.
- 코드 라인 5~6에서 아직 부트업으로 인한 초기화가 안되었거나 등록된 클럭 소스가 없는 경우 함수를 빠져나간다.
- 코드 라인 13에서 rating 값 순으로 등록되어 있는 클럭 소스 리스트에서 조건을 만족하는 처음 클럭 소스를 찾는다. 현재 지정된 클럭 소스와 oneshot 요청 시 valid_for_hires 플래그가 없는 클럭 소스인 경우는 skip하는 조건이다.
다음 그림은 oneshot 설정 유무에 따라 best 클럭 소스를 찾는 과정을 보여준다.
최종 best 클럭 소스 선택
clocksource_done_booting()
kernel/time/clocksource.c
/* * clocksource_done_booting - Called near the end of core bootup * * Hack to avoid lots of clocksource churn at boot time. * We use fs_initcall because we want this to start before * device_initcall but after subsys_initcall. */
static int __init clocksource_done_booting(void)
{
mutex_lock(&clocksource_mutex);
curr_clocksource = clocksource_default_clock();
finished_booting = 1;
/*
* Run the watchdog first to eliminate unstable clock sources
*/
__clocksource_watchdog_kthread();
clocksource_select();
mutex_unlock(&clocksource_mutex);
return 0;
}
fs_initcall(clocksource_done_booting);
최종 best 클럭 소스를 찾아 선택한다.
- 코드 라인 4에서 jiffies를 default 클럭 소스로 일단 선택한다.
- 코드 라인 9에서 워치독 타이머를 가동하여 unstable 클럭 소스를 제거한다.
- 코드 라인 10에서 best 클럭 소스를 찾아 선택한다.
- 코드 라인 12에서 0을 반환한다.
sysfs를 통한 clocksource 현황 확인
다음과 같이 rpi2의 clocksource를 확인해 보았다.
# cd /sys/devices/system/clocksource # ls clocksource0 power uevent # ls clocksource0 available_clocksource power/ uevent current_clocksource subsystem/ unbind_clocksource # cat clocksource0/available_clocksource arch_sys_counter # cat clocksource0/current_clocksource arch_sys_counter
구조체
clocksource 구조체
include/linux/clocksource.h
/** * struct clocksource - hardware abstraction for a free running counter * Provides mostly state-free accessors to the underlying hardware. * This is the structure used for system time. * * @name: ptr to clocksource name * @list: list head for registration * @rating: rating value for selection (higher is better) * To avoid rating inflation the following * list should give you a guide as to how * to assign your clocksource a rating * 1-99: Unfit for real use * Only available for bootup and testing purposes. * 100-199: Base level usability. * Functional for real use, but not desired. * 200-299: Good. * A correct and usable clocksource. * 300-399: Desired. * A reasonably fast and accurate clocksource. * 400-499: Perfect * The ideal clocksource. A must-use where * available. * @read: returns a cycle value, passes clocksource as argument * @enable: optional function to enable the clocksource * @disable: optional function to disable the clocksource * @mask: bitmask for two's complement * subtraction of non 64 bit counters * @mult: cycle to nanosecond multiplier * @shift: cycle to nanosecond divisor (power of two) * @max_idle_ns: max idle time permitted by the clocksource (nsecs) * @maxadj: maximum adjustment value to mult (~11%) * @max_cycles: maximum safe cycle value which won't overflow on multiplication * @flags: flags describing special properties * @archdata: arch-specific data * @suspend: suspend function for the clocksource, if necessary * @resume: resume function for the clocksource, if necessary * @mark_unstable: Optional function to inform the clocksource driver that * the watchdog marked the clocksource unstable * @owner: module reference, must be set by clocksource in modules * * Note: This struct is not used in hotpathes of the timekeeping code * because the timekeeper caches the hot path fields in its own data * structure, so no line cache alignment is required, * * The pointer to the clocksource itself is handed to the read * callback. If you need extra information there you can wrap struct * clocksource into your own struct. Depending on the amount of * information you need you should consider to cache line align that * structure. */
struct clocksource {
u64 (*read)(struct clocksource *cs);
u64 mask;
u32 mult;
u32 shift;
u64 max_idle_ns;
u32 maxadj;
#ifdef CONFIG_ARCH_CLOCKSOURCE_DATA
struct arch_clocksource_data archdata;
#endif
u64 max_cycles;
const char *name;
struct list_head list;
int rating;
int (*enable)(struct clocksource *cs);
void (*disable)(struct clocksource *cs);
unsigned long flags;
void (*suspend)(struct clocksource *cs);
void (*resume)(struct clocksource *cs);
void (*mark_unstable)(struct clocksource *cs);
void (*tick_stable)(struct clocksource *cs);
/* private: */
#ifdef CONFIG_CLOCKSOURCE_WATCHDOG
/* Watchdog related data, used by the framework */
struct list_head wd_list;
u64 cs_last;
u64 wd_last;
#endif
struct module *owner;
};
- (*read)
- cycle 값을 알아온다.
- mask
- 타이머에 유효한 카운터 비트 마스크
- 56비트 카운터 사용 시 mask=0xff_ffff_ffff_ffff
- 타이머에 유효한 카운터 비트 마스크
- mult
- 1 cycle을 nano second로 변경 시 곱할 수
- shift
- 1 cycle을 nano second로 변경 시 우측 시프트할 수
- max_idle_ns
- clocksource가 최대 idle할 수 있는 nano second
- maxadj
- 최대 조정 값 (mult의 11% 까지)
- archdata
- 아키텍처 종속적인 데이터
- max_cycle
- clocksource 유효성 확인을 용이하게하기 위해 잠재적으로 오버플로를 일으키지 않고 안전하게 곱할 수있는 최대 사이클 값
- 커널 v4.1-rc1에서 추가되었다.
- 참고: clocksource: Add ‘max_cycles’ to ‘struct clocksource’
- *name
- clocksource 명
- list
- 등록 시 리스트에 연결
- rating
- 선택 등급으로 수치가 높을 수록 좋다.
- (*enable)
- clocksource를 enable할 수 있는 경우 사용된다. (option)
- (*disable)
- clocksource를 disable할 수 있는 경우 사용된다. (option)
- flags
- 플래그
- CLOCK_SOURCE_IS_CONTINUOUS(0x01)
- CLOCK_SOURCE_MUST_VERIFY(0x02)
- x86 TSC에서 사용
- CLOCK_SOURCE_WATCHDOG(0x10)
- CLOCK_SOURCE_VALID_FOR_HRES(0x20)
- CLOCK_SOURCE_UNSTABLE(0x40)
- CLOCK_SOURCE_SUSPEND_NONSTOP(0x80)
- CLOCK_SOURCE_RESELECT(0x100)
- 플래그
- (*suspend)
- suspend 시 closksource를 suspend 할 수 있는 경우 사용된다. (option)
- (*resume)
- resume 시 closksource를 resume 할 수 있는 경우 사용된다. (option)
- (*mark_unstable)
- 워치독에 의해 unstable한 상태가 된 클럭소스에 대해 호출된다.
- 현재 x86 TSC 클럭에서 구현되어 사용된다.
- 참고: sched/clock, clocksource: Add optional cs::mark_unstable() method (2016, v4.11-rc1)
- (*tick_stable)
- 워치독에 의해 stable한 상태가 된 클럭 소스에 대해 호출된다.
- 현재 x86 TSC 클럭에서 구현되어 사용된다.
- 참고: x86/tsc, sched/clock, clocksource: Use clocksource watchdog to provide stable sync points (2017, v4.13-rc1)
- wd_list
- 워치독 리스트
- cs_last
- 워치독에서 사용
- 현재 클럭 소스의 카운터 값
- wd_last
- 워치독에서 사용
- 워치독 중인 클럭 소스의 카운터 값
- owner
- 모듈에서 사용 시 반드시 설정되어야 하는 레퍼런스
참고
- Timer -1- (Lowres Timer) | 문c
- Timer -2- (HRTimer) | 문c
- Timer -3- (Clock Sources Subsystem) | 문c – 현재 글
- Timer -4- (Clock Sources Watchdog) | 문c
- Timer -5- (Clock Events Subsystem) | 문c
- Timer -6- (Clock Source & Timer Driver) | 문c
- Timer -7- (Sched Clock & Delay Timers) | 문c
- Timer -8- (Timecounter) | 문c
- Timer -9- (Tick Device) | 문c
- Timer -10- (Timekeeping) | 문c
- Timer -11- (Posix Clock & Timers) | 문c
- time_init() | 문c
- sched_clock_postinit() | 문c
- tick_init() | 문c
- timekeeping_init() | 문c
- calibrate_delay() | 문c
- ARM Archectected Timer | kernel.org