<kernel v5.4>
Tick Device Subsystem
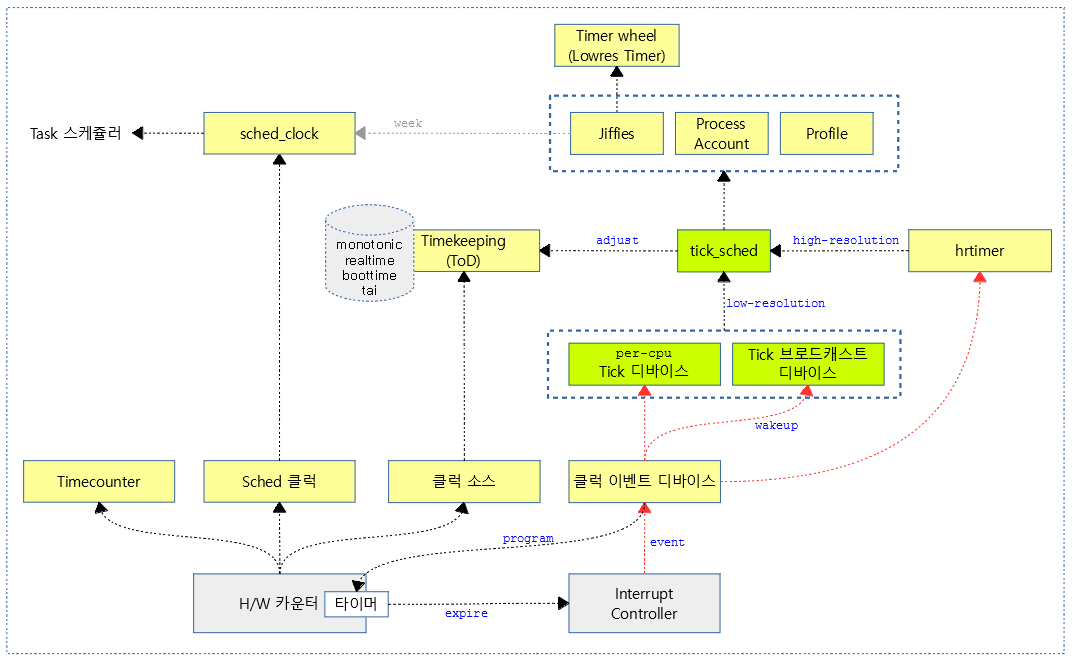
Tick Device Subsystem은 CONFIG_HZ 주기에 해당하는 타이머 스케줄 틱을 발생시키고, 이 스케줄 틱을 이용하는 다음과 같은 여러 루틴들을 처리한다.
- jiffies
- jiffies 값을 증가시킨다. (jiffies 담당 cpu가 처리하며 nohz를 위해 담당 cpu는 변경될 수 있다.)
- timer
- lowres timer wheel을 검색하여 만료된 타이머의 함수를 호출한다.
- 스케줄러 틱
- 런큐의 로드 값을 갱신하고, 현재 동작 중인 태스크 스케줄러(cfs, rt, deadline, …)의 (*task_tick)을 호출한다.
- rcu
- rcu core를 처리한다.
- process account
- cpu 사용 시간을 계량한다.
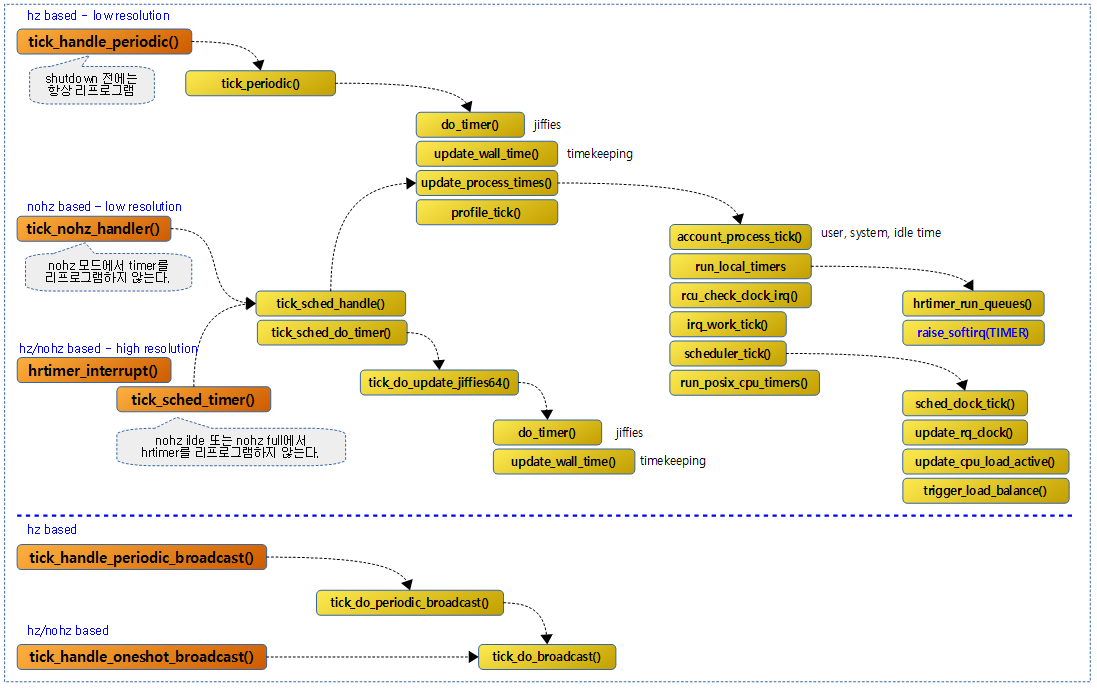
다음 그림은 generic timer sybsystem을 모두 보여준다.
틱 디바이스의 모드 운영
주기적으로 틱을 발생하기 위해 다음과 같이 두 가지 모드를 사용한다.
- hz 기반의 periodic 모드로 운영
- periodic 또는 oneshot 기능을 가진 클럭 이벤트 디바이스 모두 동작할 수 있다.
- legacy 하드웨어에서는 low-resolution 타이머가 oneshot을 지원하지 않고 지속적(periodic)으로 틱을 만드는 hw를 호환하여 운영하기 위해 커널은 처음 부트업시 항상 이 모드로 시작한다.
- nohz 기반의 oneshot 모드로 운영
- oneshot 기능을 가진 high-resolution 타이머를 가진 클럭 이벤트 디바이스만 운영 가능하다.
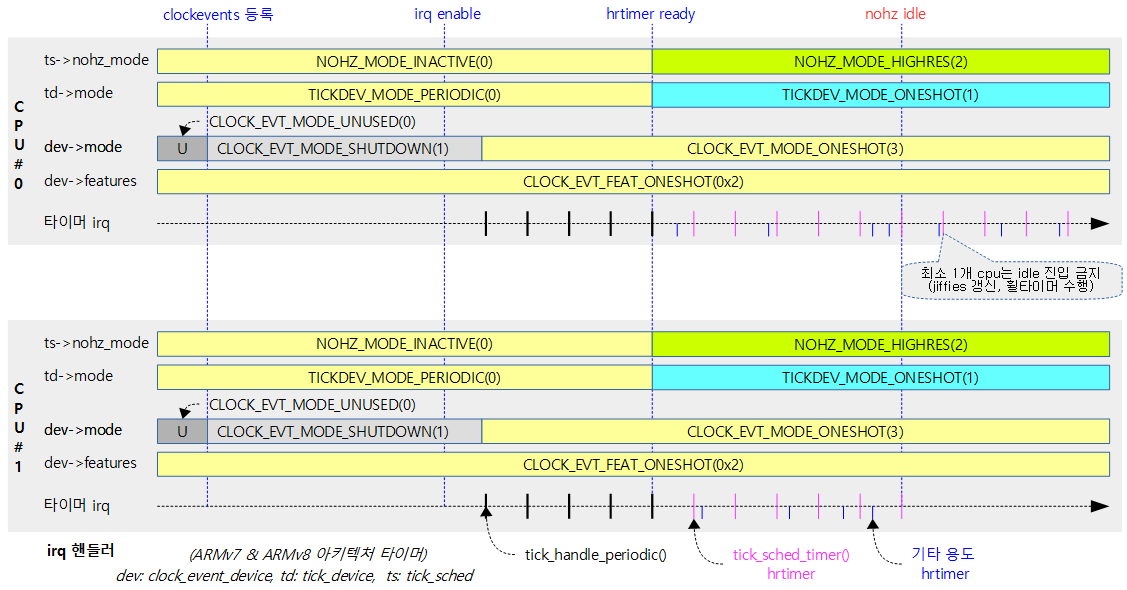
- 틱 모드는 처음에 periodic으로 운영하다가 hrtimer가 준비된 후에 틱 디바이스의 모드를 oneshot 모드로 변경하여 운영한다. 이 과정에서 tick 핸들러가 다음과 같은 순으로 바뀐다.
- tick_handle_periodic() -> clockevents_handle_noop() -> tick_sched_timer()
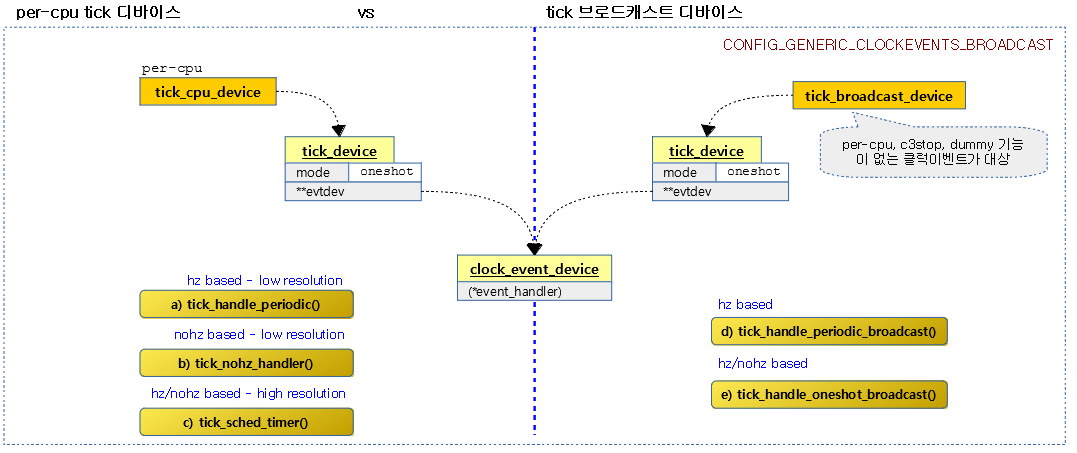
다음 그림은 tick devices subsystem이 동작하는 과정을 보여준다.
Per-cpu Tick Device 및 Tick Broadcast Device
틱을 관리하는 드라이버들로 클럭 이벤트 디바이스의 기능에 따라 각 cpu들은 틱 cpu 디바이스 또는 틱 브로드캐스트 디바이스 둘 중 하나에 연결하여 사용한다.
- Per-cpu Tick 디바이스 (전역 변수 per-cpu tick_cpu_device)
- per-cpu 타이머, 절전기능(c3stop) 타이머와 dummy 타이머를 사용한 클럭 이벤트 디바이스들로 사용 가능하다.
- Tick 브로드캐스트 디바이스 (전역 변수 tick_broadcast_device)
- per-cpu 타이머, 절전기능(c3stop) 타이머 및 dummy 타이머를 사용하지 않는 클럭 이벤트 디바이스만 사용 가능하다.
- 틱 브로드캐스트 모드가 oneshot인 경우 클럭 이벤트 디바이스도 oneshot 기능이 준비되어 있어야 한다.
- 시스템에서 nohz 구현을 위해 Tick 브로드캐스트 디바이스를 사용하지 않는 경우도 있다. (rpi2, rpi3도 사용하지 않는다.)
c3stop (절전 상태 진입하여 코어, IC 및 타이머 등 파워 다운)
arm 아키텍처에 내장된 타이머 중 CP15 레지스터를 통해 제어되는 경우 cpu가 c3(deep-sleep) 절전 상태로 진입하면 절전을 위해 코어, IC 및 타이머의 power를 다운시킨다. 이렇게 타이머 전원을 다운시키면 해당 타이머에 의해 틱 처리를 하기 위해 스스로 wake-up할 수 없으므로 다른 깨어있는 cpu의 도움을 받아야 한다. arm 아키텍처의 내장 타이머는 기본적으로 c3stop을 지원하는데 cpu가 c3(deep-sleep) 상태로 진입할 때 최소 한 개의 cpu는 지속적으로 tick을 처리하고 c3 상태에 진입한 cpu를 대신해서 틱의 만료시간을 계산하여 알릴 필요가 있다. 이렇게 만료된 cpu를 깨워 틱을 처리하게 하기 위해 틱 브로드캐스트 디바이스를 사용한다.
- 현재까지 armv7, armv8 아키텍처의 대부분은 core 단위의 idle에서는 wfi를 사용하여 절전활동을 하고, 클러스터에 소속한 모든 core가 idle되는 경우 deep-sleep 상태로 진입한다. suspend와 동일하게 클러스터 내의 파워를 끄는 형태인데 이 때 시스템에 따라 해당 클러스터의 타이머 및 인터럽트 컨트롤러도 같이 전원이 꺼질 수 있다.
- arm 아키텍처에 내장된 CP15로 제어되는 타이머라 하더라도 특정 시스템은 절전 설계되지 않아 항상 타이머 전원이 on되어 있다. 이러한 경우 c3stop을 false(“always-on”)로 설정하여 내부적으로 스케줄 틱의 관리에 틱 브로드캐스트 디바이스를 사용할 필요 없이 그냥 틱 cpu 디바이스를 사용한다.
c3stop 기능을 사용하는 클럭소스
- x86의 LAPIC 타이머
- ARM 내장 generic 타이머
- arm_arch_timer
- 기타
- mips-gic-timer
- clps711x-timer
절전을 위한 전원 관리 시스템이 없는 SoC에서는 c3stop 기능을 사용하면 안된다. 이러한 시스템에서 절전을 위해 타이머의 전원을 off 후 on 하는 경우 타이머의 comparison 레지스터의 내용이 유실되는 현상이 벌어진다. 이러한 증상으로 인해 리눅스 커널은 디바이스 트리 스크립트의 타이머 노드에 “always-on;” 속성을 추가하여 c3stop 기능을 사용하지 못하게 막는다. (항상 전원이 켜져서 동작하는 타이머로 인식한다.)
- rpi2, rpi3: “always-on;” 속성을 사용하여 브로드캐스트 기능을 사용하지 못하게 한다.
틱 브로드캐스트
절전을 위해 tick을 발생시키지 않는 nohz-idle을 구현할 때 cpu가 c3(deep-sleep) 상태에 진입되면 타이머 전원도 같이 꺼지는 시스템을 위해 다음과 같은 브로드캐스트 구현이 필요하다.
- cpu가 처리할 일이 없어 idle 상태로 진입하기 전에 브로드캐스트를 수신하기 위해 해당 cpu의 비트를 설정한다.
- 브로드캐스트 디바이스의 모드가 periodic인 경우 shutdown 한다.
- 모든 cpu가 처리할 일이 없어도 최소 하나의 대표 cpu는 브로드캐스트 디바이스가 아니라 틱 디바이스로 동작해야 한다.
- 대표 cpu는 c3(deep-sleep) 상태의 cpu를 깨우기 위해 broadcast를 한다.
- c3 상태에 있는 cpu를 깨울 때 IPI(Inter Process Interrupt)를 통해 브로드캐스트하여 해당 cpu를 깨운다.
- 깨어난 cpu는 더 이상 브로드캐스트를 수신하지 않아도 되므로 해당 cpu의 비트를 클리어한다.
- 브로드캐스트 디바이스의 모드가 periodic인 경우 다시 프로그램한다.
C-State
인텔에서 정의한 절전 상태 (참고: Everything You Need to Know About the CPU C-States Power Saving Modes
- C0
- 풀 파워로 인스트럭션을 수행한다.
- C1
- 내부 코어 클럭을 정지시킨 halt 상태
- 외부 클럭과 ACPI는 동작 중으로 인터럽트는 처리할 수 있는 상태
- C2
- Stop-Grant & Stop-Clock 상태로 내부 및 외부 클럭이 정지된 상태
- ACPI는 동작중으로 인터럽트는 처리할 수 있는 상태
- C3
- 플러시 캐시. 내부 클럭 및 외부 클럭도 받아들이지 않고 deep sleep 상태
- ACPI를 통한 인터럽트도 받아들이지 않으며, 특별히 wake-up을 통한 장치를 통해서만 깨울 수 있다.
- c3stop이라고도 한다.
- C4/C5
- 인텔 듀오프로세서에서 멀티 코어 전체가 deep sleep 상태
- C6
- 인텔 Core i7에서 모든 코어가 좀 더 deeper sleep 상태
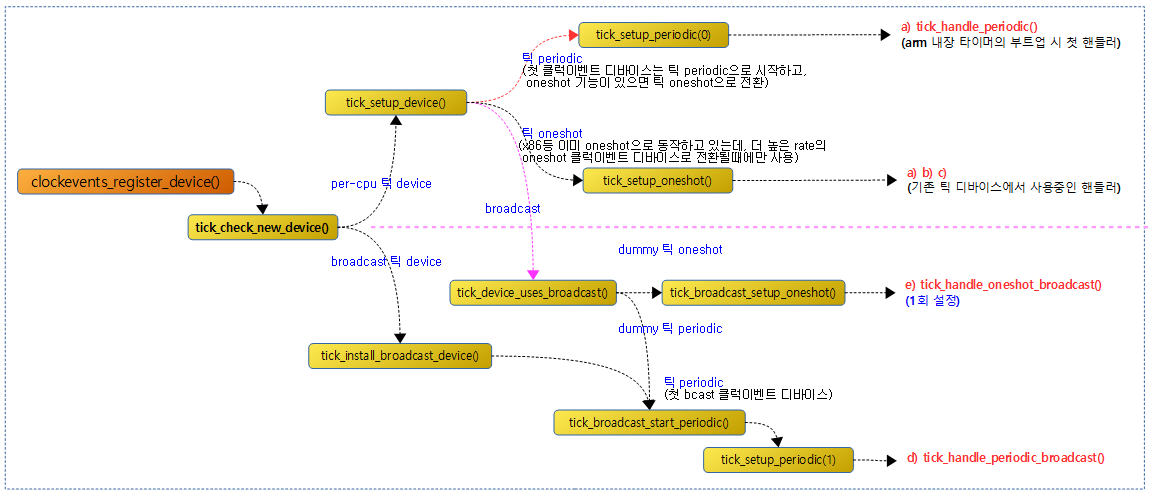
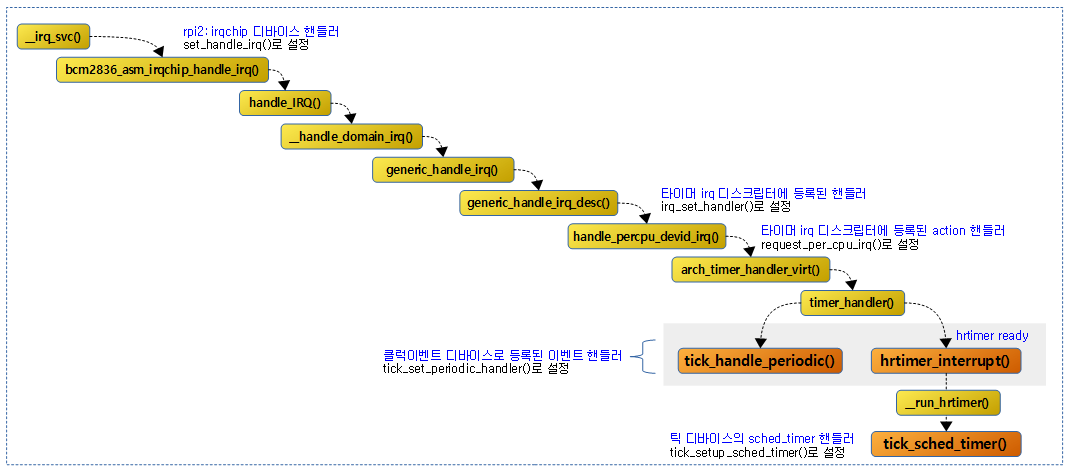
다음 그림은 tick 핸들러가 처음 설정되는 모습을 보여준다.
- arm 아키텍처에 내장된 타이머는 부트업 시 틱 periodic 모드로 출발하므로 tick_handle_periodic() 핸들러가 선택된다.
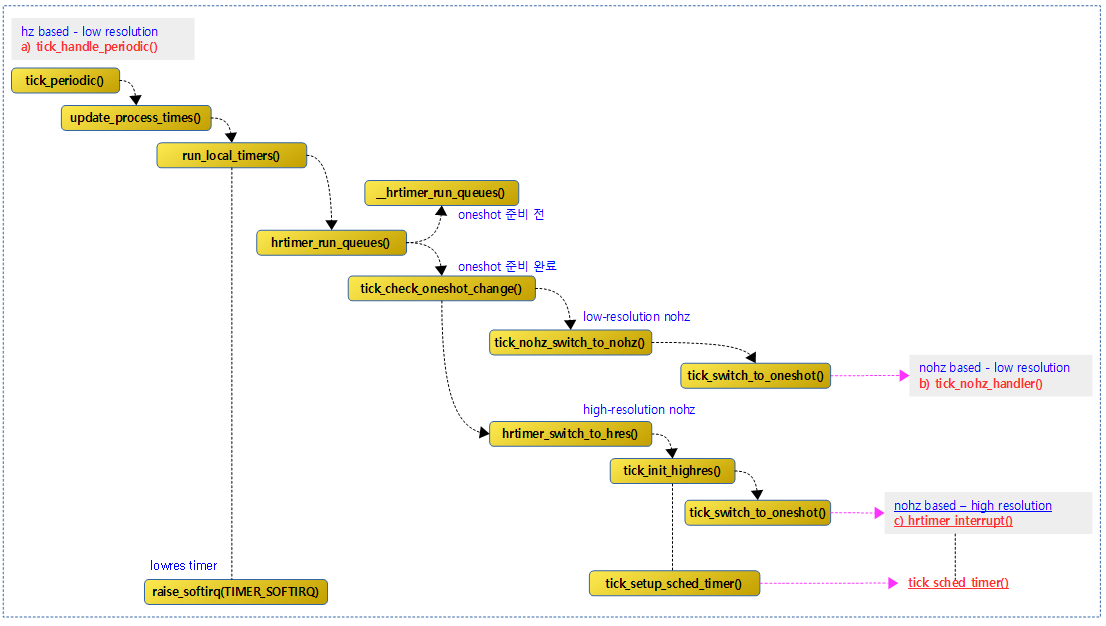
다음 그림은 tick_periodic_handler()가 호출된 후 high-resolution 타이머가 준비되고, nohz oneshot 모드로 전환되어 hrtimer_interrupt() 핸들러가 선택된다. hrtimer_intrerrupt() 내부에서 스케줄 틱 타이머 함수인 tick_sched_timer() 함수가 호출된다.
다음 그림은 틱 cpu 디바이스 및 틱 브로드캐스트 디바이스가 사용하는 틱 핸들러들이다.
- hz/nohz 기반의 high resolution을 사용하는 핸들러는 hrtimer_interrupt이지만 틱 디바이스와 별개로 모든 hrtimer의 만료 시간을 관리한다. 따라서 틱 디바이스만을 대상으로 좁히는 경우 실제 틱 처리에 대한 핸들러는 tick_sched_timer()라고 할 수 있다.
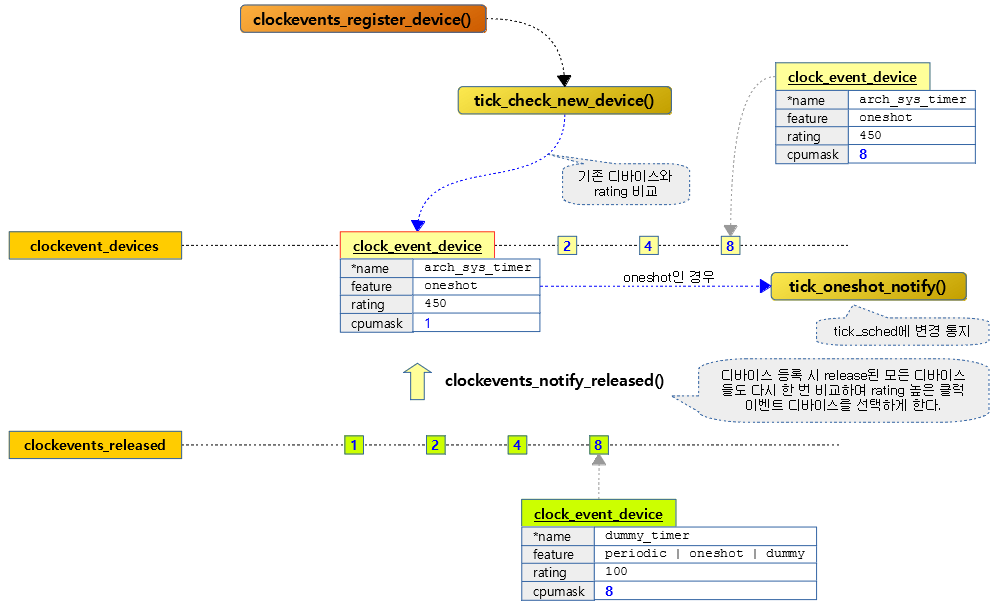
틱 cpu 디바이스 또는 틱 브로드캐스트 디바이스 등록
tick_check_new_device()
kernel/time/tick-common.c
/* * Check, if the new registered device should be used. Called with * clockevents_lock held and interrupts disabled. */
void tick_check_new_device(struct clock_event_device *newdev)
{
struct clock_event_device *curdev;
struct tick_device *td;
int cpu;
cpu = smp_processor_id();
td = &per_cpu(tick_cpu_device, cpu);
curdev = td->evtdev;
/* cpu local device ? */
if (!tick_check_percpu(curdev, newdev, cpu))
goto out_bc;
/* Preference decision */
if (!tick_check_preferred(curdev, newdev))
goto out_bc;
if (!try_module_get(newdev->owner))
return;
/*
* Replace the eventually existing device by the new
* device. If the current device is the broadcast device, do
* not give it back to the clockevents layer !
*/
if (tick_is_broadcast_device(curdev)) {
clockevents_shutdown(curdev);
curdev = NULL;
}
clockevents_exchange_device(curdev, newdev);
tick_setup_device(td, newdev, cpu, cpumask_of(cpu));
if (newdev->features & CLOCK_EVT_FEAT_ONESHOT)
tick_oneshot_notify();
return;
out_bc:
/*
* Can the new device be used as a broadcast device ?
*/
tick_install_broadcast_device(newdev);
}
현재 cpu의 tick 디바이스로 기존 tick 디바이스보다 새 tick 디바이스가 더 좋은 rating 등급인 경우 변경하여 사용할지 체크한다.
- 처음 호출 시에는 요청 clock event 디바이스가 tick 디바이스로 사용된다.
- nohz 구현을 위해 경우에 따라 등록되는 클럭 이벤트 디바이스가 틱 브로드캐스트 디바이스로 동작할 수도 있다.
- 코드 라인 12~13에서 현재 cpu의 틱 디바이스에 사용중인 clock event 디바이스를 새 디바이스로 변경 가능한지 체크한다. 사용할 수 없으면 out_bc 레이블로 이동한다.
- 코드 라인 16~17에서 기존 디바이스와 새 디바이스를 비교하여 새 디바이스의 rating이 더 높은 경우가 아니면 out_bc 레이블로 이동한다.
- 코드 라인 19~20에서 새 clock event 디바이스 모듈에 대한 참조 카운터를 증가시킨다.
- 코드 라인 27~30에서 기존 디바이스가 브로드 캐스트 디바이스인 경우 shutdown 시킨다.
- 코드 라인 31~32에서 틱 디바이스에 사용할 새 클럭 이벤트 디바이스로 변경한다.
- 코드 라인 33~35에서 새 디바이스에 oneshot 기능이 있는 경우 클럭 이벤트 디바이스가 변경되었음을 틱 스케쥴 정보에 async하게 알리고 함수를 빠져나간다.
- 코드 라인 37~41에서 out_bc 레이블이다. 새 클럭 이벤트 디바이스를 체크하여 브로드 캐스트 디바이스로 지정한다.
다음 그림은 각 cpu별로 여러 개의 틱 이벤트 디바이스가 존재하는 경우 best rating 디바이스를 선택하고 그 나머지들은 release 리스트에 두는 모습을 보여준다.
틱 디바이스 조건 체크
tick_check_percpu()
kernel/time/tick-common.c
static bool tick_check_percpu(struct clock_event_device *curdev,
struct clock_event_device *newdev, int cpu)
{
if (!cpumask_test_cpu(cpu, newdev->cpumask))
return false;
if (cpumask_equal(newdev->cpumask, cpumask_of(cpu)))
return true;
/* Check if irq affinity can be set */
if (newdev->irq >= 0 && !irq_can_set_affinity(newdev->irq))
return false;
/* Prefer an existing cpu local device */
if (curdev && cpumask_equal(curdev->cpumask, cpumask_of(cpu)))
return false;
return true;
}
새 클럭 이벤트 디바이스를 tick 디바이스로 설정할 수 있는지 여부를 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 4~5에서 요청 cpu가 새 클럭 이벤트 디바이스가 허용하는 cpu가 아닌 경우 false를 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 6~7에서 요청 cpu가 새 디바이스에 per-cpu로 등록된 경우 true를 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 9~10에서 새 디바이스가 취급하는 irq로 affinity 설정할 수 없으면 false를 반환한다.
- FEAT_DYNTICK이 부여된 드라이버들
- armv7 아키텍처에 내장된 generic 타이머의 메모리 mapped 드라이버 – “arm,armv7-timer-mem”
- “st,nomadik-mtu” 드라이버
- FEAT_DYNTICK이 부여된 드라이버들
- 코드 라인 12~13에서 요청 cpu가 현재 디바이스에 이미 per-cpu로 등록되어 있는 경우 false를 반환한다.
tick_check_preferred()
kernel/time/tick-common.c
static bool tick_check_preferred(struct clock_event_device *curdev,
struct clock_event_device *newdev)
{
/* Prefer oneshot capable device */
if (!(newdev->features & CLOCK_EVT_FEAT_ONESHOT)) {
if (curdev && (curdev->features & CLOCK_EVT_FEAT_ONESHOT))
return false;
if (tick_oneshot_mode_active())
return false;
}
/*
* Use the higher rated one, but prefer a CPU local device with a lower
* rating than a non-CPU local device
*/
return !curdev ||
newdev->rating > curdev->rating ||
!cpumask_equal(curdev->cpumask, newdev->cpumask);
}
기존 틱 디바이스와 새 디바이스를 비교하여 새 디바이스의 동작 모드 및 등급(rating)이 더 높은 경우 true를 반환한다. (oneshot -> rating 순)
- 코드 라인 5~7에서 기존 틱 디바이스는 oneshot 기능이 있는데 새 디바이스가 oneshot 기능이 없는 경우 false를 반환한다. (oneshot 우선)
- 코드 라인 8~9에서 기존 틱 디바이스가 이미 oneshot 모드로 동작하는데 새 디바이스가 oneshot 기능이 없는 경우 false를 반환한다. (oneshot 우선)
- 코드 라인 16~18에서 새 디바이스의 rating이 더 높은 경우 true를 반환한다.
다음 그림은 새 클럭 이벤트 디바이스가 기존보다 더 구형(periodic) 모드로 동작하거나 rating이 더 낮을 때 선호되지 않는 케이스들을 보여준다.
- 성공 case:
- 기존 틱 디바이스로 등록된 클럭 이벤트 디바이스가 하나도 없는 경우
- 기존 틱 디바이스에 등록된 클럭 이벤트 디바이스의 등급(rating)보다 높고 feature도 서로 같거나 더 높은 oneshot인 경우
tick_oneshot_mode_active()
kernel/time/tick-oneshot.c
/** * tick_check_oneshot_mode - check whether the system is in oneshot mode * * returns 1 when either nohz or highres are enabled. otherwise 0. */
int tick_oneshot_mode_active(void)
{
unsigned long flags;
int ret;
local_irq_save(flags);
ret = __this_cpu_read(tick_cpu_device.mode) == TICKDEV_MODE_ONESHOT;
local_irq_restore(flags);
return ret;
}
현재 cpu의 tick 디바이스가 oneshot 모드인지 여부를 반환한다.
Tick 디바이스로 지정
tick_setup_device()
kernel/time/tick-common.c
/* * Setup the tick device */
static void tick_setup_device(struct tick_device *td,
struct clock_event_device *newdev, int cpu,
const struct cpumask *cpumask)
{
void (*handler)(struct clock_event_device *) = NULL;
ktime_t next_event = 0;
/*
* First device setup ?
*/
if (!td->evtdev) {
/*
* If no cpu took the do_timer update, assign it to
* this cpu:
*/
if (tick_do_timer_cpu == TICK_DO_TIMER_BOOT) {
tick_do_timer_cpu = cpu;
tick_next_period = ktime_get();
tick_period = NSEC_PER_SEC / HZ;
#ifdef CONFIG_NO_HZ_FULL
/*
* The boot CPU may be nohz_full, in which case set
* tick_do_timer_boot_cpu so the first housekeeping
* secondary that comes up will take do_timer from
* us.
*/
if (tick_nohz_full_cpu(cpu))
tick_do_timer_boot_cpu = cpu;
} else if (tick_do_timer_boot_cpu != -1 &&
!tick_nohz_full_cpu(cpu)) {
tick_take_do_timer_from_boot();
tick_do_timer_boot_cpu = -1;
WARN_ON(tick_do_timer_cpu != cpu);
#endif
}
/*
* Startup in periodic mode first.
*/
td->mode = TICKDEV_MODE_PERIODIC;
} else {
handler = td->evtdev->event_handler;
next_event = td->evtdev->next_event;
td->evtdev->event_handler = clockevents_handle_noop;
}
td->evtdev = newdev;
/*
* When the device is not per cpu, pin the interrupt to the
* current cpu:
*/
if (!cpumask_equal(newdev->cpumask, cpumask))
irq_set_affinity(newdev->irq, cpumask);
/*
* When global broadcasting is active, check if the current
* device is registered as a placeholder for broadcast mode.
* This allows us to handle this x86 misfeature in a generic
* way. This function also returns !=0 when we keep the
* current active broadcast state for this CPU.
*/
if (tick_device_uses_broadcast(newdev, cpu))
return;
if (td->mode == TICKDEV_MODE_PERIODIC)
tick_setup_periodic(newdev, 0);
else
tick_setup_oneshot(newdev, handler, next_event);
}
요청한 클럭 이벤트 디바이스를 현재 cpu에 대한 틱 디바이스로 지정한다. 현재 cpu에 대해 처음 틱 디바이스가 지정된 경우 틱 디바이스의 모드를 periodic으로 시작한다. (hrtimer가 초기화되어 사용되기 전에는 oneshot 모드로 바꾸지 않는다.)
- 코드 라인 11~42에서 현재 cpu에 대해 tick 디바이스의 클럭 이벤트 디바이스가 설정되지 않은 경우 모드를 periodic으로 설정한다. 그리고 모든 cpu를 대상으로 가장 처음 틱 디바이스가 설정되면 틱에 대한 주기 등 관련 값들을 설정한다. (tick_do_timer_cpu, tick_next_period, tick_period)
- tick_do_timer_cpu는 디폴트 값으로 TICK_DO_TIMER_BOOT 값으로 설정되어 cpu가 아직 지정되지 않았음을 의미한다.
- 코드 라인 43~47에서 tick 디바이스의 클럭 이벤트 디바이스가 이미 설정되어 있지만 새로운 요청이 있는 경우 틱 이벤트 핸들러에 빈 함수를 지정한 후 기존 이벤트 핸들러에서 사용 중인 핸들러를 사용할 준비를 한다.
- 해당 cpu에 대한 틱 디바이스의 클럭 이벤트 디바이스가 변경되는 과정에서 이벤트 핸들러가 동작되어야 할 때 자연스럽게 아무것도 처리하지 않게 한다.
- 코드 라인 49에서 tick 디바이스에 클럭 이벤트 디바이스를 연결한다.
- 코드 라인 55~56에서 새 클럭 이벤트 디바이스가 cpu 내장형(per-cpu)이 아니면 현재 cpu에서 새 틱 디바이스의 irq를 처리할 수 있도록 affinity 설정을 한다.
- FEAT_IRQDYN 기능이 있는 클럭 이벤트 디바이스만이 irq를 요청한 cpu로 연결할 수 있다.
- 브로드캐스트 목적의 인터럽트가 특정 cpu에 고정되지 않고 cpu를 선택(set_irq_affinity)하여 사용할 수 있으며 다음 드라이버에서 사용되고 있다.
- armv7 또는 armv8 아키텍처에 내장된 generic 타이머의 메모리 mapped 드라이버 – “arm,armv7-timer-mem”
- “st,nomadik-mtu”
- 코드 라인 65~66에서 새 클럭 이벤트 디바이스가 브로드캐스트 디바이스로 동작하는 경우 처리가 완료되었으므로 함수를 빠져나간다.
- 코드 라인 68~71에서 tick 디바이스의 모드에 맞게 틱 디바이스를 periodic 및 oneshot 모드로 설정한다.
tick_nohz_full_cpu()
include/linux/tick.h
static inline bool tick_nohz_full_cpu(int cpu)
{
if (!tick_nohz_full_enabled())
return false;
return cpumask_test_cpu(cpu, tick_nohz_full_mask);
}
현재 cpu가 nohz full로 운영되는지 여부를 반환한다.
tick_nohz_full_enabled()
include/linux/tick.h
static inline bool tick_nohz_full_enabled(void)
{
if (!context_tracking_is_enabled())
return false;
return tick_nohz_full_running;
}
nohz full로 운영되는지 여부를 반환한다.
틱 디바이스를 브로드캐스트 디바이스로 등록
tick_device_uses_broadcast()
kernel/time/tick-broadcast.c
/* * Check, if the device is disfunctional and a place holder, which * needs to be handled by the broadcast device. */
int tick_device_uses_broadcast(struct clock_event_device *dev, int cpu)
{
struct clock_event_device *bc = tick_broadcast_device.evtdev;
unsigned long flags;
int ret = 0;
raw_spin_lock_irqsave(&tick_broadcast_lock, flags);
/*
* Devices might be registered with both periodic and oneshot
* mode disabled. This signals, that the device needs to be
* operated from the broadcast device and is a placeholder for
* the cpu local device.
*/
if (!tick_device_is_functional(dev)) {
dev->event_handler = tick_handle_periodic;
tick_device_setup_broadcast_func(dev);
cpumask_set_cpu(cpu, tick_broadcast_mask);
if (tick_broadcast_device.mode == TICKDEV_MODE_PERIODIC)
tick_broadcast_start_periodic(bc);
else
tick_broadcast_setup_oneshot(bc);
ret = 1;
} else {
/*
* Clear the broadcast bit for this cpu if the
* device is not power state affected.
*/
if (!(dev->features & CLOCK_EVT_FEAT_C3STOP))
cpumask_clear_cpu(cpu, tick_broadcast_mask);
else
tick_device_setup_broadcast_func(dev);
/*
* Clear the broadcast bit if the CPU is not in
* periodic broadcast on state.
*/
if (!cpumask_test_cpu(cpu, tick_broadcast_on))
cpumask_clear_cpu(cpu, tick_broadcast_mask);
틱 디바이스 상태에 따라 브로드캐스트 디바이스로 동작시킬지 아닐지 여부를 다음과 같이 결정한다.
- 더미 틱 디바이스인 경우 현재 cpu에 대해 브로드캐스트 디바이스로 동작시킨다. 결과=1
- oneshot 틱 디바이스인 경우 현재 cpu를 브로드캐스트에서 제외한다. 결과=0
- periodic 모드인 경우 브로드캐스트할 cpu가 없는 경우 shutdown한다. 결과=현재 cpu가 브로드캐스트에 포함되어 있는지 여부
- 코드 라인 15~23에서 클럭 이벤트 디바이스가 periodic 및 oneshot 기능이 없는 더미인 경우 핸들러 함수와 브로드캐스트 함수를 설정한다. 그리고 현재 cpu를 tick_broadcast_mask에 추가한다.
- 틱 브로드캐스트 디바이스가 더미 디바이스 상태에 있을 때에도 핸들러 함수가 정상적으로 호출되도록 설정한다.
- 더미 디바이스를 틱 브로드캐스트 디바이스로 사용하고 결과로 1을 반환한다. 모드가 periodic을 지원하면 periodic 모드로 동작시키고 그렇지 않으면 oneshot 모드로 동작시킨다.
- 코드 라인 24~32에서 절전을 위한 c3stop 기능이 없는 경우 tick_broadcast_mask에서 요청 cpu를 제외시킨다. 반대로 c3stop 기능이 있는 경우 현재 디바이스에 브로드캐스트 함수를 설정한다.
- c3stop 기능이 없으면 타이머 전원을 끄지 않고 계속 동작시킨다.
- 코드 라인 38~39에서 periodic용 tick_broadcast_on에 현재 cpu가 포함되지 않은 경우 tick_broadcast_mask에서 현재 cpu를 클리어한다.
switch (tick_broadcast_device.mode) {
case TICKDEV_MODE_ONESHOT:
/*
* If the system is in oneshot mode we can
* unconditionally clear the oneshot mask bit,
* because the CPU is running and therefore
* not in an idle state which causes the power
* state affected device to stop. Let the
* caller initialize the device.
*/
tick_broadcast_clear_oneshot(cpu);
ret = 0;
break;
case TICKDEV_MODE_PERIODIC:
/*
* If the system is in periodic mode, check
* whether the broadcast device can be
* switched off now.
*/
if (cpumask_empty(tick_broadcast_mask) && bc)
clockevents_shutdown(bc);
/*
* If we kept the cpu in the broadcast mask,
* tell the caller to leave the per cpu device
* in shutdown state. The periodic interrupt
* is delivered by the broadcast device, if
* the broadcast device exists and is not
* hrtimer based.
*/
if (bc && !(bc->features & CLOCK_EVT_FEAT_HRTIMER))
ret = cpumask_test_cpu(cpu, tick_broadcast_mask);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
raw_spin_unlock_irqrestore(&tick_broadcast_lock, flags);
return ret;
}
- 코드 라인 1~13에서 틱 브로드캐스트 디바이스가 oneshot 모드로 동작하는 경우 요청 cpu를 브로드캐스트 대상에서 제외하고 결과로 0을 반환한다.
- tick_broadcast_oneshot_mask와 tick_broadcast_pending_mask에서 요청 cpu를 제외시킨다.
- 코드 라인 15~33에서 틱 브로드캐스트 디바이스가 periodic 모드로 동작하는 경우 요청 cpu가 브로드캐스트 대상에 포함되어 있는지 여부를 반환한다. 만일 브로드캐스트 대상이 없는 경우 디바이스를 shutdown 한다.
tick_device_is_functional()
kernel/time/tick-internal.h
/*
* Check, if the device is functional or a dummy for broadcast
*/
static inline int tick_device_is_functional(struct clock_event_device *dev)
{
return !(dev->features & CLOCK_EVT_FEAT_DUMMY);
}
클럭 이벤트 디바이스가 periodic 및 oneshot 기능 중 하나가 있는 경우 true를 반환한다.
- dummy 디바이스는 periodic 및 oneshot 기능 모두 없다.
tick_device_setup_broadcast_func()
kernel/time/tick-broadcast.c
static void tick_device_setup_broadcast_func(struct clock_event_device *dev)
{
if (!dev->broadcast)
dev->broadcast = tick_broadcast;
if (!dev->broadcast) {
pr_warn_once("%s depends on broadcast, but no broadcast function available\n",
dev->name);
dev->broadcast = err_broadcast;
}
}
틱 디바이스에 브로드캐스트 함수가 설정되지 않은 경우 브로드캐스트 함수를 설정한다.
- 틱 브로드캐스트 함수에서 대상 cpu로 IPI(Inter Process Interrupt)를 발생시킨다.
tick_broadcast()
arch/arm/kernel/smp.c
#ifdef CONFIG_GENERIC_CLOCKEVENTS_BROADCAST
void tick_broadcast(const struct cpumask *mask)
{
smp_cross_call(mask, IPI_TIMER);
}
#endif
대상 cpu들을 IPI(Inter Process Interrupt)로 깨워 IPI _TIMER 기능에 대한 처리를 수행하게 요청한다.
tick_broadcast_start_periodic()
kernel/time/tick-broadcast.c
/*
* Start the device in periodic mode
*/
static void tick_broadcast_start_periodic(struct clock_event_device *bc)
{
if (bc)
tick_setup_periodic(bc, 1);
}
요청한 클럭 이벤트 디바이스를 periodic 모드의 브로드캐스트 디바이스로 사용하여 tick을 발생시킨다.
틱 디바이스 모드 설정
틱 디바이스를 periodic 모드로 설정
tick_setup_periodic()
/* * Setup the device for a periodic tick */
void tick_setup_periodic(struct clock_event_device *dev, int broadcast)
{
tick_set_periodic_handler(dev, broadcast);
/* Broadcast setup ? */
if (!tick_device_is_functional(dev))
return;
if ((dev->features & CLOCK_EVT_FEAT_PERIODIC) &&
!tick_broadcast_oneshot_active()) {
clockevents_set_mode(dev, CLOCK_EVT_MODE_PERIODIC);
} else {
unsigned long seq;
ktime_t next;
do {
seq = read_seqbegin(&jiffies_lock);
next = tick_next_period;
} while (read_seqretry(&jiffies_lock, seq));
clockevents_set_mode(dev, CLOCK_EVT_MODE_ONESHOT);
for (;;) {
if (!clockevents_program_event(dev, next, false))
return;
next = ktime_add(next, tick_period);
}
}
}
요청한 클럭 이벤트 디바이스를 periodic 모드의 틱 디바이스로 사용하여 tick을 발생시킨다. broadcast=1로 요청한 경우 브로드캐스트 핸들러를 준비한다.
- 코드 라인 3에서 periodic 핸들러 함수를 지정한다. @broadcast가 요청된 경우 broadcast용 periodic 핸들러 함수를 지정한다.
- 코드 라인 6~7에서 클럭 이벤트 디바이스가 dummy 디바이스인 경우 이미 브로드 캐스트 디바이스이므로 함수를 빠져나간다.
- 코드 라인 9~11에서 클럭 이벤트 디바이스 기능에 periodic이 있고 틱 브로드캐스트 디바이스가 oneshot 모드가 아닌 경우 클럭 이벤트 디바이스를 periodic로 설정한다.
- 코드 라인 12~21에서 1 tick을 더해 다음 만료 시간을 지정한 후 클럭 이벤트 디바이스를 oneshot 모드로 설정한다.
- 코드 라인 23~27에서 클럭 이벤트 디바이스에 프로그램하여 성공하면 함수를 빠져나간다. 만일 실패하는 경우 1 tick 만큼 만료 시간을 더해 성공할 때까지 루프를 돌며 시도한다.
tick_set_periodic_handler()
kernel/time/tick-broadcast.c
/* * Set the periodic handler depending on broadcast on/off */
void tick_set_periodic_handler(struct clock_event_device *dev, int broadcast)
{
if (!broadcast)
dev->event_handler = tick_handle_periodic;
else
dev->event_handler = tick_handle_periodic_broadcast;
}
periodic 핸들러 함수를 지정한다. @broadcast가 요청된 경우 broadcast용 periodic 핸들러 함수를 지정한다.
틱 디바이스를 oneshot 모드로 설정
tick_setup_oneshot()
kernel/time/tick-oneshot.c
/** * tick_setup_oneshot - setup the event device for oneshot mode (hres or nohz) */
void tick_setup_oneshot(struct clock_event_device *newdev,
void (*handler)(struct clock_event_device *),
ktime_t next_event)
{
newdev->event_handler = handler;
clockevents_set_mode(newdev, CLOCK_EVT_MODE_ONESHOT);
clockevents_program_event(newdev, next_event, true);
}
oneshot 모드로 클럭이벤트 디바이스를 설정하고 핸들러를 대입한 후 이벤트를 프로그램한다.
tick_is_broadcast_device()
kernel/time/tick-broadcast.c
/* * Check, if the device is the broadcast device */
int tick_is_broadcast_device(struct clock_event_device *dev)
{
return (dev && tick_broadcast_device.evtdev == dev);
}
요청한 클럭 이벤트 디바이스가 브로드캐스트 디바이스인지 여부를 반환한다.
틱 디바이스 이벤트 핸들러
틱 디바이스 핸들러 -1- (hz based, 저해상도 타이머)
tick_handle_periodic()
kernel/time/tick-common.c
/* * Event handler for periodic ticks */
void tick_handle_periodic(struct clock_event_device *dev)
{
int cpu = smp_processor_id();
ktime_t next = dev->next_event;
tick_periodic(cpu);
#if defined(CONFIG_HIGH_RES_TIMERS) || defined(CONFIG_NO_HZ_COMMON)
/*
* The cpu might have transitioned to HIGHRES or NOHZ mode via
* update_process_times() -> run_local_timers() ->
* hrtimer_run_queues().
*/
if (dev->event_handler != tick_handle_periodic)
return;
#endif
if (dev->mode != CLOCK_EVT_MODE_ONESHOT)
return;
for (;;) {
/*
* Setup the next period for devices, which do not have
* periodic mode:
*/
next = ktime_add(next, tick_period);
if (!clockevents_program_event(dev, next, false))
return;
/*
* Have to be careful here. If we're in oneshot mode,
* before we call tick_periodic() in a loop, we need
* to be sure we're using a real hardware clocksource.
* Otherwise we could get trapped in an infinite
* loop, as the tick_periodic() increments jiffies,
* which then will increment time, possibly causing
* the loop to trigger again and again.
*/
if (timekeeping_valid_for_hres())
tick_periodic(cpu);
}
}
틱 디바이스가 periodic 모드로 동작하여 인터럽트가 발생하면 이 함수가 호출되며 이 때 tick_periodic() 함수를 호출한다. oneshot 모드를 사용하는 클럭 이벤트 디바이스인 경우 다음 tick을 프로그램한다.
- 코드 라인 6에서 정규 틱 마다 할 일(스케줄, account process, rcu, irq work, posix cpu 타이머 등)을 처리한다. 추가로 현재 cpu가 do_timer() 호출 전담인 경우 jiffies를 1 증가시키고 wall time 등을 갱신한다.
- 코드 라인 13~14에서 periodic 핸들러가 아닌 경우 함수를 빠져나간다.
- 코드 라인 16~17에서 클럭 이벤트 디바이스가 이미 oneshot 모드가 아닌 경우 더 이상 처리를 할 필요 없으므로 핸들러를 빠져나간다.
- 결국 periodic 모드에서는 tick 마다 인터럽트 발생하고 jiffies++하고 wall time 만 갱신한다.
- 코드 라인 18~38에서 tick에 대한 시간을 추가하여 oneshot 이벤트를 프로그램 한다. 프로그램에 실패한 경우 timekeeping용 클럭 소스에서 CLOCK_SOURCE_VALID_FOR_HRES 플래그를 사용했으면 다시 한 번 jiffies를 1 증가시키고 wall time 등을 갱신하게 한다. 그 후 다시 반복한다.
tick_periodic()
kernel/time/tick-common.c
/* * Periodic tick */
static void tick_periodic(int cpu)
{
if (tick_do_timer_cpu == cpu) {
write_seqlock(&jiffies_lock);
/* Keep track of the next tick event */
tick_next_period = ktime_add(tick_next_period, tick_period);
do_timer(1);
write_sequnlock(&jiffies_lock);
update_wall_time();
}
update_process_times(user_mode(get_irq_regs()));
profile_tick(CPU_PROFILING);
}
정규 틱 마다 할 일(스케줄, account process, rcu, irq work, posix cpu 타이머 등)을 처리한다. 추가로 현재 cpu가 do_timer() 호출 전담인 경우jiffies를 1 증가시키고 글로벌 로드를 계산하고 wall time 등을 갱신한다
- 코드 라인 3~10에서 현재 cpu가 do_timer() 호출 전담인 경우 다음 틱 시간을 갱신하고 jiffies를 1 증가시키고 global load를 계산한다.
- 32bit arm은 jiffies 증가 시 64비트인 jiffies_64를 사용하므로 접근 시에는 반드시 시퀀스 락을 사용하여야 한다.
- 코드 라인 11에서 wall time을 갱신한다.
- 코드 라인 14에서 cpu 처리 시간을 갱신한다.
- 코드 라인 15에서 cpu profile 정보를 남긴다
do_timer()
kernel/time/timekeeping.c
/* * Must hold jiffies_lock */
void do_timer(unsigned long ticks)
{
jiffies_64 += ticks;
calc_global_load(ticks);
}
jiffies 값을 요청한 ticks 만큼 증가시키고 global load를 계산한다.
- global load 산출
- 계산 간격이 10 tick을 초과한 경우 1min, 5min, 15min 간격의 로드 평균 값을 avenrun[]에 갱신한다.
- 참고:
- Scheduler -2- (cpu load & PELT) | 문c
- Linux kernel load accounting | HAPPY HACKING
profile_tick()
kernel/profile.c
void profile_tick(int type)
{
struct pt_regs *regs = get_irq_regs();
if (!user_mode(regs) && prof_cpu_mask != NULL &&
cpumask_test_cpu(smp_processor_id(), prof_cpu_mask))
profile_hit(type, (void *)profile_pc(regs));
}
cpu profile 정보를 남긴다.
- 코드 라인 3에서 마지막 exception 프레임의 주소가 담긴 현재 cpu의 프레임 포인터를 알아온다.
- 코드 라인 5~7에서 커널에서 exception되었으며 prof_cpu_mask에 현재 cpu가 포함된 경우 cpu profile 정보를 남긴다.
profile_hit()
include/linux/profile.h
/* * Single profiler hit: */
static inline void profile_hit(int type, void *ip)
{
/*
* Speedup for the common (no profiling enabled) case:
*/
if (unlikely(prof_on == type))
profile_hits(type, ip, 1);
}
커널이 요청 타입에 대한 profile 타입을 준비한 경우 ip 주소에 대해 profile 정보를 남긴다.
- 요청 타입이 profiling 중인 타입이 아닌 거나 profile 버퍼가 설정되지 않은 경우 처리를 포기한다.
- cpu, sched, sleep, kvm profiling 중 하나를 선택할 수 있다.
- “profile=[schedule,]<number>”
- 스케쥴 포인트에 대해 profile
- <number>
- step/bucket 사이즈를 2의 차수 값을 사용하며 통계 시간 기반 profile
- “profile=sleep”
- D-state sleeping (ms)에 대한 profile
- “profile=kvm”
- VM 종료에 대한 profile
- 참고:
- Profiling the kernel
- kerneltop | LWN.net
update_process_times()
kernel/time/timer.c
/* * Called from the timer interrupt handler to charge one tick to the current * process. user_tick is 1 if the tick is user time, 0 for system. */
void update_process_times(int user_tick)
{
struct task_struct *p = current;
/* Note: this timer irq context must be accounted for as well. */
account_process_tick(p, user_tick);
run_local_timers();
rcu_sched_clock_irq(user_tick);
#ifdef CONFIG_IRQ_WORK
if (in_irq())
irq_work_tick();
#endif
scheduler_tick();
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_POSIX_TIMERS))
run_posix_cpu_timers();
}
매 틱마다 호출되는 처리해야 하는 루틴들을 묶어놓은 함수이다.
- 코드 라인 6에서 cpu가 처리되는 시간 비율을 측정한다. user, system 및 idle 타임으로 구분하여 측정한다
- 코드 라인 7에서 만료된 hrtimer 및 timer 함수를 호출한다.
- hrtimer는 periodic 모드에서만 호출된다. oneshot 모드는 별도의 hrtimer_interrupt() 핸들러에서 직접 처리한다.
- timer는 softirq에서 처리하도록 raise 한다.
- 코드 라인 8에서 rcu core에 대한 처리를 수행한다.
- 코드 라인 10~11에서 enque되어 대기중인 irq_work를 처리한다.
- 코드 라인 13에서 현재 동작중인 태스크의 스캐줄러에 스케줄 틱을 호출한다.
- 코드 라인 14~15에서 posix cpu 타이머에 대한 처리를 수행한다.
run_local_timers()
kernel/time/timer.c
/* * Called by the local, per-CPU timer interrupt on SMP. */
void run_local_timers(void)
{
struct timer_base *base = this_cpu_ptr(&timer_bases[BASE_STD]);
hrtimer_run_queues();
/* Raise the softirq only if required. */
if (time_before(jiffies, base->clk)) {
if (!IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_NO_HZ_COMMON))
return;
/* CPU is awake, so check the deferrable base. */
base++;
if (time_before(jiffies, base->clk))
return;
}
raise_softirq(TIMER_SOFTIRQ);
}
만료된 hrtimer 및 timer를 처리한다.
- 코드 라인 5에서 periodic 모드에서 호출된 경우 hrtimer 해시 리스트에서 대기중인 만료된 hrtimer 함수들을 처리하도록 호출한다.
- 코드 라인 7~14에서 jiffies 까지 모든 timer가 처리된 경우 함수를 빠져나간다.
- 코드 라인 15에서 타이머 휠을 처리하도록 softirq를 raise 한다.
틱 디바이스 핸들러 -2- (nohz 기반, 저해상도 타이머)
tick_nohz_handler()
kernel/time/tick-sched.c
/* * The nohz low res interrupt handler */
static void tick_nohz_handler(struct clock_event_device *dev)
{
struct tick_sched *ts = this_cpu_ptr(&tick_cpu_sched);
struct pt_regs *regs = get_irq_regs();
ktime_t now = ktime_get();
dev->next_event.tv64 = KTIME_MAX;
tick_sched_do_timer(now);
tick_sched_handle(ts, regs);
/* No need to reprogram if we are running tickless */
if (unlikely(ts->tick_stopped))
return;
while (tick_nohz_reprogram(ts, now)) {
now = ktime_get();
tick_do_update_jiffies64(now);
}
}
nohz 기반의 저해상도 타이머를 사용한 틱 인터럽트 핸들러 루틴이다.
- 코드 라인 9에서 jiffies를 update하고 wall time을 조정한다.
- 코드 라인 10에서 process accounting 및 profile에 관련한 일들을 처리한다.
- 코드 라인 13~14에서 낮은 확률로 tick이 정지된 경우 함수를 빠져나간다.
- 코드 라인 16~19에서 tick을 재프로그램한다. 실패 시 반복한다.
틱 디바이스 핸들러 -3- (hz/nohz 기반, 고해상도 타이머)
hrtimer를 사용하여 tick을 프로그래밍한 인터럽트로 인해 hrtimer_interrupt()가 호출되면 등록된 tick 스케쥴 핸들러에 도달한다.
tick_sched_timer()
kernel/time/tick-sched.c
/* * We rearm the timer until we get disabled by the idle code. * Called with interrupts disabled. */
static enum hrtimer_restart tick_sched_timer(struct hrtimer *timer)
{
struct tick_sched *ts =
container_of(timer, struct tick_sched, sched_timer);
struct pt_regs *regs = get_irq_regs();
ktime_t now = ktime_get();
tick_sched_do_timer(now);
/*
* Do not call, when we are not in irq context and have
* no valid regs pointer
*/
if (regs)
tick_sched_handle(ts, regs);
else
ts->next_tick = 0;
/* No need to reprogram if we are in idle or full dynticks mode */
if (unlikely(ts->tick_stopped))
return HRTIMER_NORESTART;
hrtimer_forward(timer, now, tick_period);
return HRTIMER_RESTART;
}
hz/nohz 기반의 고해상도 타이머를 사용한 틱 인터럽트 핸들러 루틴이다.
- 코드 라인 8에서 jiffies를 update하고 wall time을 조정한다.
- 코드 라인 14~17에서 process accounting 및 profile에 관련한 일들을 처리한다.
- 코드 라인 20~21에서 틱 스케쥴러에서 틱을 멈춰달라는 요청이 있는 경우 HRTIMER_NORESTART를 결과로 함수를 빠져나간다.
- 코드 라인 23~25에서 틱을 다시 프로그램하고 HRTIMER_RESTART를 결과로 함수를 빠져나간다.
Tick 디바이스의 Oneshot 모드 전환
periodic 틱에서 매번 oneshot 준비 상태 확인
틱 디바이스가 periodic 모드로 동작할 때 매 tick 인터럽트마다 호출되어 처리되는 함수 중 update_process_times() -> run_local_timers() -> hrtimer_run_queues() 함수 내에서 periodic 모드용 hrtimer(for hardirq)를 처리한다. hrtimer_run_queues() 함수 내부에서 high-resolution hw 타이머가 준비되어 틱 모드를 oneshot으로 전환할 수 있는지 여부를 체크하는 tick_check_oneshot_change() 함수를 통해 oneshot으로 전환된다. 이렇게 oneshot 모드 전환되면 hrtimer 처리 경로가 바뀌게 된다.
hrtimer_run_queues()
kernel/time/hrtimer.c
/* * Called from run_local_timers in hardirq context every jiffy */
void hrtimer_run_queues(void)
{
struct hrtimer_cpu_base *cpu_base = this_cpu_ptr(&hrtimer_bases);
unsigned long flags;
ktime_t now;
if (__hrtimer_hres_active(cpu_base))
return;
/*
* This _is_ ugly: We have to check periodically, whether we
* can switch to highres and / or nohz mode. The clocksource
* switch happens with xtime_lock held. Notification from
* there only sets the check bit in the tick_oneshot code,
* otherwise we might deadlock vs. xtime_lock.
*/
if (tick_check_oneshot_change(!hrtimer_is_hres_enabled())) {
hrtimer_switch_to_hres();
return;
}
raw_spin_lock_irqsave(&cpu_base->lock, flags);
now = hrtimer_update_base(cpu_base);
if (!ktime_before(now, cpu_base->softirq_expires_next)) {
cpu_base->softirq_expires_next = KTIME_MAX;
cpu_base->softirq_activated = 1;
raise_softirq_irqoff(HRTIMER_SOFTIRQ);
}
__hrtimer_run_queues(cpu_base, now, flags, HRTIMER_ACTIVE_HARD);
raw_spin_unlock_irqrestore(&cpu_base->lock, flags);
}
hrtimer 해시 리스트에서 대기중인 만료된 hrtimer를 처리한다. 이 루틴은 periodic 틱에서만 동작한다.
- 코드 라인 7~8에서 oneshot 모드로 전환하여 이미 hres 타이머가 active된 경우 함수를 빠져나간다.
- 코드 라인 17~20에서 oneshot 모드로 전환한다. 만일 hres 타이머를 사용할 수 있는 경우 hres 타이머용 oneshot/nohz 모드로 전환한다.
- oneshot 모드 전환 시 두 가지 모드 지원
- low-resolution 타이머용 nohz 전환
- high-reslution 타이머용 nohz 전환
- oneshot 모드 전환 시 두 가지 모드 지원
- 코드 라인 23에서 periodic 모드인 경우에만 처리되는데 현재 cpu의 hrtimer 시각을 알아온다.
- 코드 라인 25~29에서 softirq용 hrtimer가 만료된 경우 이를 처리하도록 softirq를 raise 한다.
- 코드 라인 31에서 hardirq용 hrtimer에 대한 처리를 수행한다.
hrtimer_hres_active()
kernel/time/hrtimer.c
static inline int hrtimer_hres_active(void)
{
return __hrtimer_hres_active(this_cpu_ptr(&hrtimer_bases));
}
현재 cpu의 hrtimer가 고해상도 모드로 동작중인지 여부를 반환한다.
/* * Is the high resolution mode active ? */
static inline int __hrtimer_hres_active(struct hrtimer_cpu_base *cpu_base)
{
return IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_HIGH_RES_TIMERS) ?
cpu_base->hres_active : 0;
}
@cpu_base의 hrtimer가 고해상도 모드로 동작중인지 여부를 반환한다.
hrtimer_is_hres_enabled()
kernel/time/hrtimer.c
/* * hrtimer_high_res_enabled - query, if the highres mode is enabled */
static inline int hrtimer_is_hres_enabled(void)
{
return hrtimer_hres_enabled;
}
고해상도모드의 hrtimer가 enable되어 있는지 여부를 반환한다.
- 디폴트 값으로 on되어 있고 “highres=off” 커널 파라메터를 사용하여 disable할 수 있다.
tick_check_oneshot_change()
kernel/time/tick-sched.c
/** * Check, if a change happened, which makes oneshot possible. * * Called cyclic from the hrtimer softirq (driven by the timer * softirq) allow_nohz signals, that we can switch into low-res nohz * mode, because high resolution timers are disabled (either compile * or runtime). Called with interrupts disabled. */
int tick_check_oneshot_change(int allow_nohz)
{
struct tick_sched *ts = this_cpu_ptr(&tick_cpu_sched);
if (!test_and_clear_bit(0, &ts->check_clocks))
return 0;
if (ts->nohz_mode != NOHZ_MODE_INACTIVE)
return 0;
if (!timekeeping_valid_for_hres() || !tick_is_oneshot_available())
return 0;
if (!allow_nohz)
return 1;
tick_nohz_switch_to_nohz();
return 0;
}
oneshot 모드로의 변경이 일어난 경우 체크한다.
- 코드 라인 5~6에서 tick_sched의 check_clocks에서 0번 cpu에 해당하는 비트가 설정된 경우 클리어한다. 설정되지 않은 경우 0을 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 8~9에서 nohz 모드가 활성화되지 않은 경우 0을 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 11~12에서 timekeeping에 사용하는 클럭 이벤트 소스의 플래그에 valid_for_hres가 설정되지 않았거나 틱 이벤트 디바이스가 oneshot 모드가 아닌 경우 0을 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 14~15에서 인수 allow_nohz가 0인 경우 1을 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 17~18에서 low-resolution 타이머용 nohz 모드로 전환하고 hrtimer를 사용하여 다음 스케쥴 틱을 프로그래밍 한다.
oneshot 모드 및 low-resolution nohz 전환
tick_nohz_switch_to_nohz()
kernel/time/tick-sched.c
/** * tick_nohz_switch_to_nohz - switch to nohz mode */
static void tick_nohz_switch_to_nohz(void)
{
struct tick_sched *ts = this_cpu_ptr(&tick_cpu_sched);
ktime_t next;
if (!tick_nohz_enabled)
return;
if (tick_switch_to_oneshot(tick_nohz_handler))
return;
/*
* Recycle the hrtimer in ts, so we can share the
* hrtimer_forward with the highres code.
*/
hrtimer_init(&ts->sched_timer, CLOCK_MONOTONIC, HRTIMER_MODE_ABS_HARD);
/* Get the next period */
next = tick_init_jiffy_update();
hrtimer_set_expires(&ts->sched_timer, next);
hrtimer_forward_now(&ts->sched_timer, tick_period);
tick_program_event(hrtimer_get_expires(&ts->sched_timer), 1);
tick_nohz_activate(ts, NOHZ_MODE_LOWRES);
}
oneshot 및 nohz 모드로 전환하고 hrtimer를 사용하여 다음 스케쥴 틱을 프로그래밍 한다.
- 코드 라인 6~7에서 nohz가 enable되어 있지 않은 경우 함수를 빠져나간다.
- 코드 라인 9~10에서 틱 디바이스를 oneshot 모드로 전환시키고 처리할 핸들러를 준비한다. 만일 전환이 실패하는 경우 함수를 빠져나간다.
- 코드 라인 16~22에서 hrtimer를 사용하여 1 jiffies 틱을 프로그램한다.
- 코드 라인 23에서 nohz 모드가 저해상도 타이머 모드로 동작됨을 틱 sched에 표시한다.
tick_switch_to_oneshot()
kernel/time/tick-oneshot.c
/** * tick_switch_to_oneshot - switch to oneshot mode */
int tick_switch_to_oneshot(void (*handler)(struct clock_event_device *))
{
struct tick_device *td = this_cpu_ptr(&tick_cpu_device);
struct clock_event_device *dev = td->evtdev;
if (!dev || !(dev->features & CLOCK_EVT_FEAT_ONESHOT) ||
!tick_device_is_functional(dev)) {
printk(KERN_INFO "Clockevents: "
"could not switch to one-shot mode:");
if (!dev) {
printk(" no tick device\n");
} else {
if (!tick_device_is_functional(dev))
printk(" %s is not functional.\n", dev->name);
else
printk(" %s does not support one-shot mode.\n",
dev->name);
}
return -EINVAL;
}
td->mode = TICKDEV_MODE_ONESHOT;
dev->event_handler = handler;
clockevents_set_mode(dev, CLOCK_EVT_MODE_ONESHOT);
tick_broadcast_switch_to_oneshot();
return 0;
}
틱 디바이스를 oneshot 모드로 전환시키고 처리할 핸들러를 준비한다.
- 이 함수는 다음 두 군데에서 호출되어 사용된다.
- 고해상도 타이머가 필요할 때 hrtimer_switch_to_hres() 함수 내부의 tick_init_hres() 함수에서 사용된다.
- dynamic tick을 처리하기 위해 nohz 모드로 전환하기 위해 tick_nohz_switch_to_nohz() 함수에서 사용된다.
- 코드 라인 6~21에서 clock_event_device가 준비되지 않았거나 oneshot 모드로 동작하지 않는 경우 에러 메시지를 출력하고 -EINVAL 에러를 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 23~25에서 인수로 받은 이벤트 핸들러를 디바이스에 대입한다. 또한 clock_event_device의 set_mode() 후크를 통해 드라이버에서 oneshot 모드를 설정하게 한다.
- rpi2: arch_timer_set_mode_virt() 호출되는데 shutdown 모드가 아닌 oneshot 모드에서는 특별히 설정하는 것이 없다.
- 코드 라인 26에서 tick broadcast 디바이스를 위해 oneshot 모드로 변경한다.
tick_broadcast_switch_to_oneshot()
kernel/time/tick-broadcast.c
/* * Select oneshot operating mode for the broadcast device */
void tick_broadcast_switch_to_oneshot(void)
{
struct clock_event_device *bc;
unsigned long flags;
raw_spin_lock_irqsave(&tick_broadcast_lock, flags);
tick_broadcast_device.mode = TICKDEV_MODE_ONESHOT;
bc = tick_broadcast_device.evtdev;
if (bc)
tick_broadcast_setup_oneshot(bc);
raw_spin_unlock_irqrestore(&tick_broadcast_lock, flags);
}
tick broadcast 디바이스의 모드를 oneshot 모드로 바꾸고 tick broadcast 디바이스의 클럭 이벤트 디바이스가 준비된 경우 다음 tick을 설정한다.
oneshot 모드 및 high-resolution nohz 전환
hrtimer_switch_to_hres()
kernel/time/hrtimer.c
/* * Switch to high resolution mode */
static void hrtimer_switch_to_hres(void)
{
struct hrtimer_cpu_base *base = this_cpu_ptr(&hrtimer_bases);
if (tick_init_highres()) {
pr_warn("Could not switch to high resolution mode on CPU %u\n",
base->cpu);
return;
}
base->hres_active = 1;
hrtimer_resolution = HIGH_RES_NSEC;
tick_setup_sched_timer();
/* "Retrigger" the interrupt to get things going */
retrigger_next_event(NULL);
}
hrtimer를 high resolution 모드로 설정하고 스케쥴 틱 타이머를 동작시킨다.
- 코드 라인 5~9에서 틱 디바이스를 oneshot 모드로 전환한다. 전환되지 않는 경우 경고 메시지를 출력하고 함수를 빠져나간다.
- 코드 라인 10~11에서 hrtimer가 high resolution 상태임을 설정하고 4 개 클럭의 해상도에 1ns를 대입한다.
- 코드 라인 13에서 스케줄 틱을 설정한다.
- 코드 라인 15에서 hrtimer를 리프로그램하고 1을 반환한다.
tick_init_highres()
kernel/time/tick-oneshot.c
/** * tick_init_highres - switch to high resolution mode * * Called with interrupts disabled. */
int tick_init_highres(void)
{
return tick_switch_to_oneshot(hrtimer_interrupt);
}
고해상도 모드의 oneshot 타이머를 동작시키고 인터럽트 발생 시 hrtimer 인터럽트 핸들러 콜백 함수인 hrtimer_interrupt() 함수를 호출하게 한다.
고해상도 hrtimer를 사용한 Sched Tick 설정
tick_setup_sched_timer()
kernel/time/tick-sched.c
/** * tick_setup_sched_timer - setup the tick emulation timer */
void tick_setup_sched_timer(void)
{
struct tick_sched *ts = this_cpu_ptr(&tick_cpu_sched);
ktime_t now = ktime_get();
/*
* Emulate tick processing via per-CPU hrtimers:
*/
hrtimer_init(&ts->sched_timer, CLOCK_MONOTONIC, HRTIMER_MODE_ABS_HARD);
ts->sched_timer.function = tick_sched_timer;
/* Get the next period (per-CPU) */
hrtimer_set_expires(&ts->sched_timer, tick_init_jiffy_update());
/* Offset the tick to avert jiffies_lock contention. */
if (sched_skew_tick) {
u64 offset = ktime_to_ns(tick_period) >> 1;
do_div(offset, num_possible_cpus());
offset *= smp_processor_id();
hrtimer_add_expires_ns(&ts->sched_timer, offset);
}
hrtimer_forward(&ts->sched_timer, now, tick_period);
hrtimer_start_expires(&ts->sched_timer, HRTIMER_MODE_ABS_PINNED_HARD);
tick_nohz_activate(ts, NOHZ_MODE_HIGHRES);
}
고해상도 hrtimer를 사용하여 틱 스케쥴 타이머를 가동한다. 또한 nohz 모드로 설정한다.
- 코드 라인 9~10에서 틱 스케쥴에서 사용할 hrtimer를 초기화하고 핸들러 함수를 지정한다.
- tick_sched_timer()에서 jiffies 관리 cpu를 지정하고, 매번 틱을 프로그램한다.
- 코드 라인 13에서 틱 스케쥴용 hrtimer의 만료 시간은 1 jiffies 기간으로 한다.
- 코드 라인 16~21에서 jiffies lock 혼잡을 피하기 위해 cpu 마다 offset을 산출하고 추가하여 틱 만료시간을 재설정한다.
- 코드 라인 23~24에서 hrtimer를 forward한 후 프로그램한다.
- 코드 라인 25에서 nohz 모드를 highres로 변경하고 active 되었음을 설정한다.
oneshot 틱 프로그램
tick_program_event()
kernel/time/tick-oneshot.c
/** * tick_program_event */
int tick_program_event(ktime_t expires, int force)
{
struct clock_event_device *dev = __this_cpu_read(tick_cpu_device.evtdev);
return clockevents_program_event(dev, expires, force);
}
요청한 만료 시간에 틱이 발생하도록 해당 cpu의 클럭 이벤트 디바이스에 프로그램한다.
틱 브로드캐스트 디바이스 핸들러
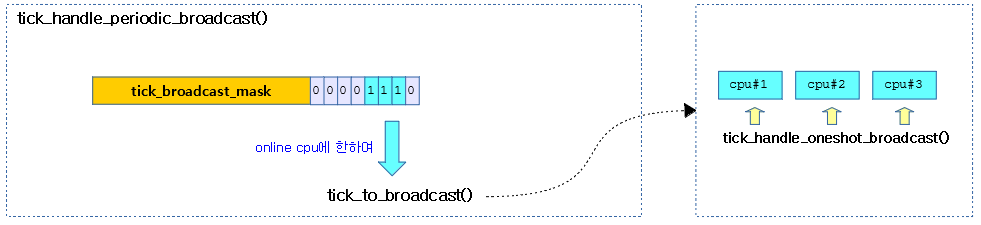
tick_handle_periodic_broadcast()
kernel/time/tick-broadcast.c
/* * Event handler for periodic broadcast ticks */
static void tick_handle_periodic_broadcast(struct clock_event_device *dev)
{
struct tick_device *td = this_cpu_ptr(&tick_cpu_device);
bool bc_local;
raw_spin_lock(&tick_broadcast_lock);
/* Handle spurious interrupts gracefully */
if (clockevent_state_shutdown(tick_broadcast_device.evtdev)) {
raw_spin_unlock(&tick_broadcast_lock);
return;
}
bc_local = tick_do_periodic_broadcast();
if (clockevent_state_oneshot(dev)) {
ktime_t next = ktime_add(dev->next_event, tick_period);
clockevents_program_event(dev, next, true);
}
raw_spin_unlock(&tick_broadcast_lock);
/*
* We run the handler of the local cpu after dropping
* tick_broadcast_lock because the handler might deadlock when
* trying to switch to oneshot mode.
*/
if (bc_local)
td->evtdev->event_handler(td->evtdev);
}
브로드캐스트가 필요한 cpu를 대상으로 브로드캐스트하여 cpu를 idle 상태에서 깨운다. 클럭 이벤트 디바이스의 모드가 oneshot인 경우 틱을 프로그램한다.
- 코드 라인 9~12에서 브로드 캐스트에 사용할 클럭 이벤트 디바이스가 shutdown된 상태라면 함수를 빠져나간다.
- 코드 라인 14에서 브로드캐스트가 필요한 cpu를 대상으로 브로드캐스트하여 cpu를 idle 상태에서 깨운다.
- 코드 라인 16~20에서 클럭 이벤트 디바이스가 oneshot 모드인 경우 틱을 프로그래밍한다.
- 코드 라인 28~29에서 브로드 캐스트용 이벤트 핸들러를 호출한다.
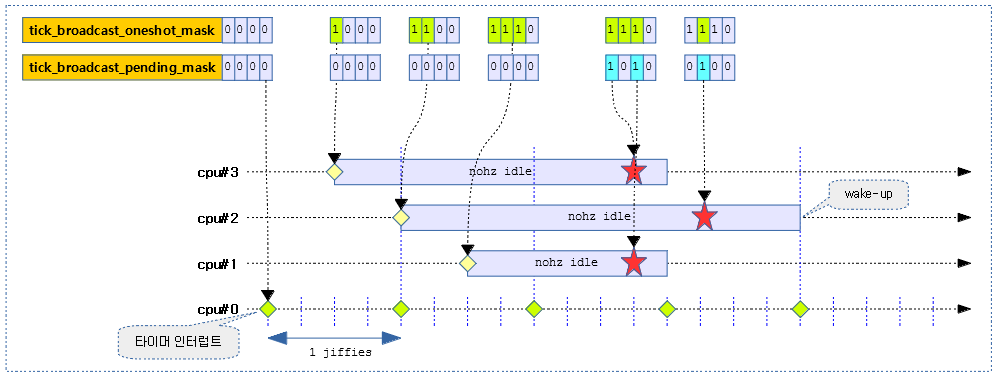
다음 그림은 nohz idle 상태에 있는 cpu#1~#3 들을 깨우도록 브로드캐스트 하는 과정을 보여준다.
- 틱 브로드캐스트 디바이스가 periodic 모드로 동작
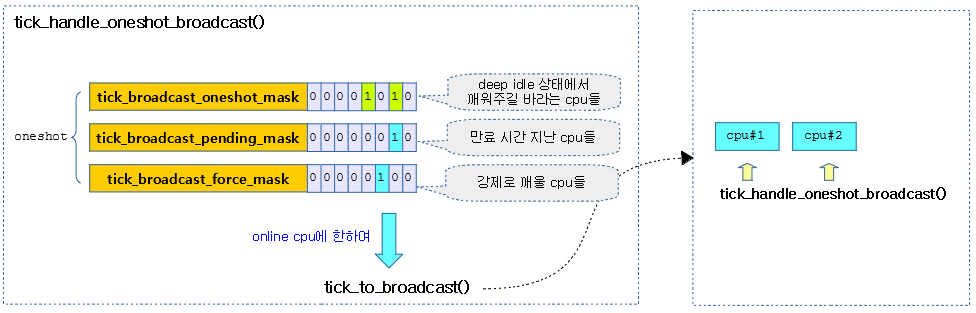
tick_handle_oneshot_broadcast()
kernel/time/tick-broadcast.c
/* * Handle oneshot mode broadcasting */
static void tick_handle_oneshot_broadcast(struct clock_event_device *dev)
{
struct tick_device *td;
ktime_t now, next_event;
int cpu, next_cpu = 0;
bool bc_local;
raw_spin_lock(&tick_broadcast_lock);
dev->next_event = KTIME_MAX;
next_event = KTIME_MAX;
cpumask_clear(tmpmask);
now = ktime_get();
/* Find all expired events */
for_each_cpu(cpu, tick_broadcast_oneshot_mask) {
/*
* Required for !SMP because for_each_cpu() reports
* unconditionally CPU0 as set on UP kernels.
*/
if (!IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_SMP) &&
cpumask_empty(tick_broadcast_oneshot_mask))
break;
td = &per_cpu(tick_cpu_device, cpu);
if (td->evtdev->next_event <= now) {
cpumask_set_cpu(cpu, tmpmask);
/*
* Mark the remote cpu in the pending mask, so
* it can avoid reprogramming the cpu local
* timer in tick_broadcast_oneshot_control().
*/
cpumask_set_cpu(cpu, tick_broadcast_pending_mask);
} else if (td->evtdev->next_event < next_event) {
next_event = td->evtdev->next_event;
next_cpu = cpu;
}
}
/*
* Remove the current cpu from the pending mask. The event is
* delivered immediately in tick_do_broadcast() !
*/
cpumask_clear_cpu(smp_processor_id(), tick_broadcast_pending_mask);
/* Take care of enforced broadcast requests */
cpumask_or(tmpmask, tmpmask, tick_broadcast_force_mask);
cpumask_clear(tick_broadcast_force_mask);
/*
* Sanity check. Catch the case where we try to broadcast to
* offline cpus.
*/
if (WARN_ON_ONCE(!cpumask_subset(tmpmask, cpu_online_mask)))
cpumask_and(tmpmask, tmpmask, cpu_online_mask);
/*
* Wakeup the cpus which have an expired event.
*/
bc_local = tick_do_broadcast(tmpmask);
/*
* Two reasons for reprogram:
*
* - The global event did not expire any CPU local
* events. This happens in dyntick mode, as the maximum PIT
* delta is quite small.
*
* - There are pending events on sleeping CPUs which were not
* in the event mask
*/
if (next_event != KTIME_MAX)
tick_broadcast_set_event(dev, next_cpu, next_event);
raw_spin_unlock(&tick_broadcast_lock);
if (bc_local) {
td = this_cpu_ptr(&tick_cpu_device);
td->evtdev->event_handler(td->evtdev);
}
}
브로드캐스트가 필요한 cpu를 대상으로 브로드캐스트하여 cpu를 idle 상태에서 깨운다. 클럭 이벤트 디바이스의 모드가 oneshot인 경우 틱을 프로그램한다.
- 코드 라인 14~36에서 브로드 캐스트가 필요한 cpu들에 대해 틱 만료된 cpu들을 tmp 마스크에 알아온다.
- 코드 라인 42~46에서 현재 cpu는 pending 마스크에서 제거하고 tmp 마스크 대상에 force 마스크를 추가한다.
- 코드 라인 52~53에서 tmp 마스크에서 online된 cpu들은 제거한다.
- 코드 라인 58에서 tmp 마스크를 대상으로 브로드캐스트를 수행하여 idle 상태에 있는 cpu들을 모두 깨운다.
- 코드 라인 70~71에서 남아있는 이벤트가 있는 경우 브로드캐스트 디바이스로 사용되는 클럭 이벤트 디바이스의 모드를 oneshot으로 변경하고 프로그램한다.
- 코드 라인 75~78에서 등록된 브로드 캐스트용 이벤트 핸들러를 호출한다.
다음 그림은 nohz idle 상태에 있는 cpu#1~#3 들을 깨우도록 브로드캐스트 하는 과정을 보여준다.
- 틱 브로드캐스트 디바이스가 oneshot 모드로 동작
다음 그림은 nohz를 사용하여 idle 상태에 있는 3개의 cpu가 브로드캐스트에 의해 각 만료시간마다 깨어나는 과정을 보여준다.
- 별표와 같이 프로그램된 틱들이 브로드캐스트를 발송하는 cpu의 틱 타임에 맞춰 약간씩 지연되는 모습을 볼 수 있다.
tick_broadcast_set_event()
kernel/time/tick-broadcast.c
static void tick_broadcast_set_event(struct clock_event_device *bc, int cpu,
ktime_t expires)
{
if (!clockevent_state_oneshot(bc))
clockevents_switch_state(bc, CLOCK_EVT_STATE_ONESHOT);
clockevents_program_event(bc, expires, 1);
tick_broadcast_set_affinity(bc, cpumask_of(cpu));
}
틱 브로드캐스트 디바이스에서 사용되는 클럭 이벤트 디바이스의 모드를 oneshot으로 변경하고 프로그램 한다. 만일 실패하는 경우 요청 cpu로 irq affinity를 설정한다.
tick_broadcast_set_affinity()
kernel/time/tick-broadcast.c
/* * Set broadcast interrupt affinity */
static void tick_broadcast_set_affinity(struct clock_event_device *bc,
const struct cpumask *cpumask)
{
if (!(bc->features & CLOCK_EVT_FEAT_DYNIRQ))
return;
if (cpumask_equal(bc->cpumask, cpumask))
return;
bc->cpumask = cpumask;
irq_set_affinity(bc->irq, bc->cpumask);
}
클럭 이벤트 디바이스의 인터럽트를 요청한 cpu 들이 수신할 수 있도록 설정한다. 단 FEAT_DYNIRQ 기능이 없는 클럭 이벤트 디바이스는 수행할 수 없다.
C3Stop과 틱 브로드캐스트
타이머의 절전 기능이 구현된 SoC 즉, c3stop이 설정되었거나 per-cpu 타이머가 없는 경우 cpu가 deep idle 상태에 진입하고 나갈 때 마다 전역 비트맵에 알림 요청을 하고 다른 cpu에서 deep idle 상태의 cpu들을 broadcast 기능을 통해 깨울 수 있다.
cpuidle_setup_broadcast_timer()
drivers/cpuidle/driver.c
/** * cpuidle_setup_broadcast_timer - enable/disable the broadcast timer on a cpu * @arg: a void pointer used to match the SMP cross call API * * If @arg is NULL broadcast is disabled otherwise enabled * * This function is executed per CPU by an SMP cross call. It's not * supposed to be called directly. */
static void cpuidle_setup_broadcast_timer(void *arg)
{
if (arg)
tick_broadcast_enable();
else
tick_broadcast_disable();
}
틱 브로드캐스트 기능을 켜거나 끈다.
tick_broadcast_enable()
include/linux/tick.h
static inline void tick_broadcast_enable(void)
{
tick_broadcast_control(TICK_BROADCAST_ON);
}
틱 브로드캐스트 기능을 켠다.
tick_broadcast_disable()
include/linux/tick.h
static inline void tick_broadcast_disable(void)
{
tick_broadcast_control(TICK_BROADCAST_OFF);
}
틱 브로드캐스트 기능을 끈다.
tick_broadcast_control()
kernel/time/tick-broadcast.c
/** * tick_broadcast_control - Enable/disable or force broadcast mode * @mode: The selected broadcast mode * * Called when the system enters a state where affected tick devices * might stop. Note: TICK_BROADCAST_FORCE cannot be undone. */
void tick_broadcast_control(enum tick_broadcast_mode mode)
{
struct clock_event_device *bc, *dev;
struct tick_device *td;
int cpu, bc_stopped;
unsigned long flags;
/* Protects also the local clockevent device. */
raw_spin_lock_irqsave(&tick_broadcast_lock, flags);
td = this_cpu_ptr(&tick_cpu_device);
dev = td->evtdev;
/*
* Is the device not affected by the powerstate ?
*/
if (!dev || !(dev->features & CLOCK_EVT_FEAT_C3STOP))
goto out;
if (!tick_device_is_functional(dev))
goto out;
cpu = smp_processor_id();
bc = tick_broadcast_device.evtdev;
bc_stopped = cpumask_empty(tick_broadcast_mask);
switch (mode) {
case TICK_BROADCAST_FORCE:
tick_broadcast_forced = 1;
/* fall through */
case TICK_BROADCAST_ON:
cpumask_set_cpu(cpu, tick_broadcast_on);
if (!cpumask_test_and_set_cpu(cpu, tick_broadcast_mask)) {
/*
* Only shutdown the cpu local device, if:
*
* - the broadcast device exists
* - the broadcast device is not a hrtimer based one
* - the broadcast device is in periodic mode to
* avoid a hickup during switch to oneshot mode
*/
if (bc && !(bc->features & CLOCK_EVT_FEAT_HRTIMER) &&
tick_broadcast_device.mode == TICKDEV_MODE_PERIODIC)
clockevents_shutdown(dev);
}
break;
case TICK_BROADCAST_OFF:
if (tick_broadcast_forced)
break;
cpumask_clear_cpu(cpu, tick_broadcast_on);
if (cpumask_test_and_clear_cpu(cpu, tick_broadcast_mask)) {
if (tick_broadcast_device.mode ==
TICKDEV_MODE_PERIODIC)
tick_setup_periodic(dev, 0);
}
break;
}
if (bc) {
if (cpumask_empty(tick_broadcast_mask)) {
if (!bc_stopped)
clockevents_shutdown(bc);
} else if (bc_stopped) {
if (tick_broadcast_device.mode == TICKDEV_MODE_PERIODIC)
tick_broadcast_start_periodic(bc);
else
tick_broadcast_setup_oneshot(bc);
}
}
out:
raw_spin_unlock_irqrestore(&tick_broadcast_lock, flags);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(tick_broadcast_control);
현재 cpu의 상태 변화에 따른 브로드캐스트 여부를 결정할 수 있는 비트마스크 설정을 한다.
- 코드 라인 16~17에서 c3stop 기능이 없는 경우 함수를 빠져나간다.
- 코드 라인 19~20에서 기능이 구현되지 않은 dummy 디바이스인 경우 함수를 빠져나간다.
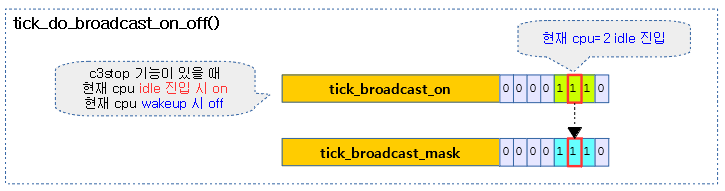
- 코드 라인 30~45에서 broadcast on 요청을 받은 경우 tick_broadcast_on 및 tick_broadcast_mask의 현재 cpu에 해당하는 비트를 설정한다. 만일 틱 브로드캐스트 모드가 periodic 이면서 tick이 발생중이면 tick을 정지시킨다.
- 코드 라인 47~56에서 broadcast off 요청을 받은 경우 tick_broadcast_on 및 tick_broadcast_mask의 현재 cpu에 해당하는 비트를 클리어한다. 만일 틱 브토드캐스트 모드가 periodic이면서 tick이 발생하지 않는 상태인 경우 tick을 발생시키도록 요청한다.
- 코드 라인 60~62에서 브로드캐스트할 cpu가 없는 경우 클럭이벤트 디바이스를 shutdown 한다.
- 코드 라인 63~68에서 브로드캐스트할 cpu가 있는 경우 틱 브로드캐스트 모드에 따라 periodic 또는 oneshot 모드로 설정한다.
다음 그림은 틱 브로드 캐스트를 켜고 끌 때 비트마스크들의 상황을 보여준다.
스케줄 틱 분석
먼저 타이머 인터럽트의 처리 경로를 다시 한 번 살펴보면 여러 개의 경로 중 rpi2의 경우 다음 타이머 인터럽트의 처리 경로가 있다.
- tick_handle_periodic()
- 루틴내에서 bottom-half 처리를 목적으로 softirq를 사용하여 타이머휠에 대한 처리를 수행한다. (run_timer_softirq())
- hrtimer_interrupt() → __run_hrtimer() → tick_sched_timer()
- hrtimer를 사용한 softirq는 커널 4.2.rc1부터 사용하지 않는다.
다음 그림은 스케줄틱이 처음 tick_handle_periodic() 함수로 처리되다가 hrtimer가 준비되면 tick_sched_timer() 함수로 이전되는 것을 보여준다.
nohz 진출입 함수
- tick_nohz_idle_enter()
- tick_nohz_idle_exit()
SMP 시스템에서 타이머 인터럽트가 발생되는 상황에 대해 다음 컴포넌트들의 상태와 비교하여 살펴보자
- cpu 마다 스케줄 틱은 조금씩 어긋나게 프로그램된다.
- 타이머 인터럽트를 발생시키는 틱 디바이스 상태 변화
- SMP 코어 중 하나는 jiffies를 규칙적으로 발생하므로 nohz로 진입할 수 없다. 그 외의 cpu들은 nohz 상태에 진입가능하다.
- 타이머를 프로그램하는 클럭이벤트디바이스 상태 변화
- armv7 & armv8에 내장된 아키텍처 타이머는 oneshot으로만 프로그래밍 가능하므로 매번 CONFIG_HZ 단위로 틱을 프로그래밍해야 한다.
구조체
tick_device 구조체
kernel/time/tick-sched.h
struct tick_device {
struct clock_event_device *evtdev;
enum tick_device_mode mode;
};
- *evtdev
- 틱 디바이스로 사용하는 클럭 이벤트 디바이스
- mode
- TICKDEV_MODE_PERIODIC
- nohz 모드를 사용하지 못하는 틱 디바이스 또는 부트업 과정
- TICKDEV_MODE_ONESHOT
- nohz 모드를 사용할 수 있는 틱 디바이스(possible)
- TICKDEV_MODE_PERIODIC
tick_sched 구조체
kernel/time/tick-sched.h
/** * struct tick_sched - sched tick emulation and no idle tick control/stats * @sched_timer: hrtimer to schedule the periodic tick in high * resolution mode * @check_clocks: Notification mechanism about clocksource changes * @nohz_mode: Mode - one state of tick_nohz_mode * @inidle: Indicator that the CPU is in the tick idle mode * @tick_stopped: Indicator that the idle tick has been stopped * @idle_active: Indicator that the CPU is actively in the tick idle mode; * it is resetted during irq handling phases. * @do_timer_lst: CPU was the last one doing do_timer before going idle * @got_idle_tick: Tick timer function has run with @inidle set * @last_tick: Store the last tick expiry time when the tick * timer is modified for nohz sleeps. This is necessary * to resume the tick timer operation in the timeline * when the CPU returns from nohz sleep. * @next_tick: Next tick to be fired when in dynticks mode. * @idle_jiffies: jiffies at the entry to idle for idle time accounting * @idle_calls: Total number of idle calls * @idle_sleeps: Number of idle calls, where the sched tick was stopped * @idle_entrytime: Time when the idle call was entered * @idle_waketime: Time when the idle was interrupted * @idle_exittime: Time when the idle state was left * @idle_sleeptime: Sum of the time slept in idle with sched tick stopped * @iowait_sleeptime: Sum of the time slept in idle with sched tick stopped, with IO outstanding * @timer_expires: Anticipated timer expiration time (in case sched tick is stopped) * @timer_expires_base: Base time clock monotonic for @timer_expires * @next_timer: Expiry time of next expiring timer for debugging purpose only * @tick_dep_mask: Tick dependency mask - is set, if someone needs the tick */
struct tick_sched {
struct hrtimer sched_timer;
unsigned long check_clocks;
enum tick_nohz_mode nohz_mode;
unsigned int inidle : 1;
unsigned int tick_stopped : 1;
unsigned int idle_active : 1;
unsigned int do_timer_last : 1;
unsigned int got_idle_tick : 1;
ktime_t last_tick;
ktime_t next_tick;
unsigned long idle_jiffies;
unsigned long idle_calls;
unsigned long idle_sleeps;
ktime_t idle_entrytime;
ktime_t idle_waketime;
ktime_t idle_exittime;
ktime_t idle_sleeptime;
ktime_t iowait_sleeptime;
unsigned long last_jiffies;
u64 timer_expires;
u64 timer_expires_base;
u64 next_timer;
ktime_t idle_expires;
atomic_t tick_dep_mask;
};
- sched_timer
- hres timer가 활성된 이후 스케줄 틱을 발생하는 hrtimer
- check_clocks
- 클럭 소스의 변화가 있거나 틱 디바이스 모드가 변경될 때 1로 설정된다.
- nohz_mode
- NOHZ_MODE_INACTIVE
- nohz 모드가 동작하지 않는 경우
- NOHZ_MODE_LOWRES
- low-resolution 타이머를 사용하는 nohz 모드
- NOHZ_MODE_HIGHRES
- high-resolution 타이머를 사용하는 nohz 모드
- NOHZ_MODE_INACTIVE
- inidle:1
- nohz idle 진입 여부
- tick_nohz_idle_enter() 함수에서 1로 설정하고, tick_nohz_idle_exit() 함수에서 0으로 클리어한다.
- tick_stopped:1
- nohz로 인해 tick이 멈춘 상태 여부 (nohz idle & nohz full)
- idle_active:1
- cpu가 틱 idle 모드인지 여부
- do_timer_last:1
- idle 진입 전 do_timer() 함수를 수행했었는지 여부
- last_tick
- 마지막 프로그래밍된 틱 시간(ns)
- nohz를 멈추고 다시 periodic 틱을 발생 시킬 때 기억해둔 이 틱 시간 이후로 틱을 forward하여 사용한다.
- idle_expires
- nohz idle 진입 시 nohz 만료 예정 시각(ns)
참고
- Timer -1- (Lowres Timer) | 문c
- Timer -2- (HRTimer) | 문c
- Timer -3- (Clock Sources Subsystem) | 문c
- Timer -4- (Clock Sources Watchdog) | 문c
- Timer -5- (Clock Events Subsystem) | 문c
- Timer -6- (Clock Source & Timer Driver) | 문c
- Timer -7- (Sched Clock & Delay Timers) | 문c
- Timer -8- (Timecounter) | 문c – 현재 글
- Timer -9- (Tick Device) | 문c
- Timer -10- (Timekeeping) | 문c
- Timer -11- (Posix Clock & Timers) | 문c
- time_init() | 문c
- sched_clock_postinit() | 문c
- tick_init() | 문c
- timekeeping_init() | 문c
- calibrate_delay() | 문c
- The tick broadcast framework | LWN.net