<kernel v5.0>
kmem_cache_shrink()
mm/slab_common.c
/** * kmem_cache_shrink - Shrink a cache. * @cachep: The cache to shrink. * * Releases as many slabs as possible for a cache. * To help debugging, a zero exit status indicates all slabs were released. */
int kmem_cache_shrink(struct kmem_cache *cachep)
{
int ret;
get_online_cpus();
get_online_mems();
ret = __kmem_cache_shrink(cachep);
put_online_mems();
put_online_cpus();
return ret;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(kmem_cache_shrink);
요청한 슬랩 캐시에서 해지가능한 슬랩 페이지들을 찾아 모두 해지시킨다.
__kmem_cache_shrink()
mm/slub.c
/* * kmem_cache_shrink discards empty slabs and promotes the slabs filled * up most to the head of the partial lists. New allocations will then * fill those up and thus they can be removed from the partial lists. * * The slabs with the least items are placed last. This results in them * being allocated from last increasing the chance that the last objects * are freed in them. */
int __kmem_cache_shrink(struct kmem_cache *s)
{
int node;
int i;
struct kmem_cache_node *n;
struct page *page;
struct page *t;
struct list_head discard;
struct list_head promote[SHRINK_PROMOTE_MAX];
unsigned long flags;
int ret = 0;
flush_all(s);
for_each_kmem_cache_node(s, node, n) {
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&discard);
for (i = 0; i < SHRINK_PROMOTE_MAX; i++)
INIT_LIST_HEAD(promote + i);
spin_lock_irqsave(&n->list_lock, flags);
/*
* Build lists of slabs to discard or promote.
*
* Note that concurrent frees may occur while we hold the
* list_lock. page->inuse here is the upper limit.
*/
list_for_each_entry_safe(page, t, &n->partial, lru) {
int free = page->objects - page->inuse;
/* Do not reread page->inuse */
barrier();
/* We do not keep full slabs on the list */
BUG_ON(free <= 0);
if (free == page->objects) {
list_move(&page->lru, &discard);
n->nr_partial--;
} else if (free <= SHRINK_PROMOTE_MAX)
list_move(&page->lru, promote + free - 1);
}
/*
* Promote the slabs filled up most to the head of the
* partial list.
*/
for (i = SHRINK_PROMOTE_MAX - 1; i >= 0; i--)
list_splice(promote + i, &n->partial);
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&n->list_lock, flags);
/* Release empty slabs */
list_for_each_entry_safe(page, t, &discard, lru)
discard_slab(s, page);
if (slabs_node(s, node))
ret = 1;
}
return ret;
}
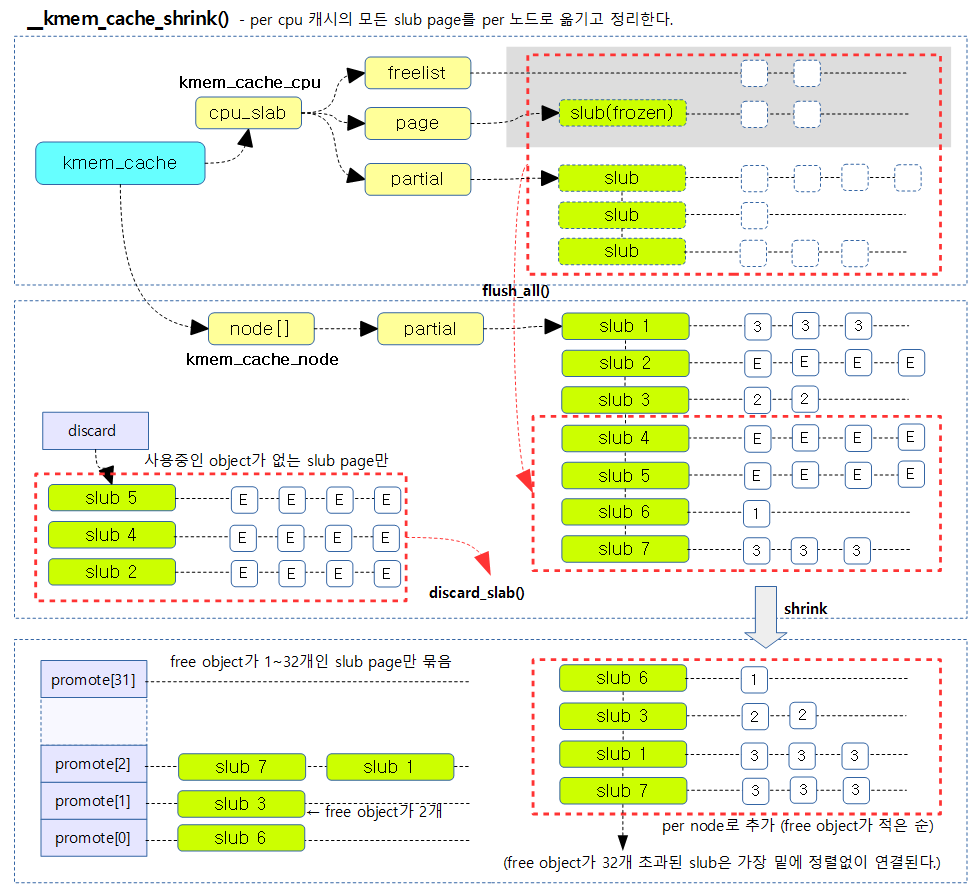
요청한 슬랩 캐시에서 해지가능한 슬랩 페이지들을 찾아 모두 해지시키기 위해 다음과 같은 과정을 수행한다.
- n->partial 리스트의 슬랩 페이지들 중 사용중인 object가 없는 경우 슬랩 페이지들을 버디 시스템으로 되돌린다.
- n->partial 리스트의 슬랩 페이지들 중 32개 미만의 free object들은 asscending 정렬한다.
- 코드 라인 13에서 슬랩 캐시의 per cpu 슬랩 페이지들을 모두 n->partial 리스트로 옮긴다.
- 코드 라인 14~17에서 슬랩 캐시의 노드를 순회하며 discard 리스트를 초기화하고, SHRINK_PROMOTE_MAX(32) 만큼 promote[] 리스트를 초기화한다.
- 코드 라인 27~41에서 n->partial 리스트의 슬랩 페이지들을 순회하며 object가 모두 free object들로 구성된 슬랩 페이지는 discard 리스트에 추가하고, free object 수가 SHRINK_PROMOTE_MAX(32) 이하인 경우 promote[free-1] 리스트에 추가한다.
- 코드 라인 47~48에서 n->partial 리스트의 선두에 promote[i] 리스트를 추가한다.
- 결국 free object가 1~32개 순으로 정렬되어 선두에 추가된다.
- 가장 선두에 free object가 가장 적은 슬랩 페이지를 위로 배치하여 object 할당 시 슬랩 페이지가 리스트 관리에서 빨리 없어질 수 있게 한다.
- 코드 라인 53~54에서 discard 리스트에 있는 슬랩 페이지들을 모두 해제하여 버디 시스템으로 돌려준다.
- 코드 라인 56~57에서 slub 디버그깅 중에 노드에 슬랩이 남아있는 경우 함수 종료 시 1을 반환하게 한다.
다음 그림은 현재 슬랩 캐시의 모든 슬랩 페이지들을 n->partial 리스트로 옮기고 정리하는 모습을 보여준다.
kick_all_cpus_sync()
kernel/smp.c
/** * kick_all_cpus_sync - Force all cpus out of idle * * Used to synchronize the update of pm_idle function pointer. It's * called after the pointer is updated and returns after the dummy * callback function has been executed on all cpus. The execution of * the function can only happen on the remote cpus after they have * left the idle function which had been called via pm_idle function * pointer. So it's guaranteed that nothing uses the previous pointer * anymore. */
void kick_all_cpus_sync(void)
{
/* Make sure the change is visible before we kick the cpus */
smp_mb();
smp_call_function(do_nothing, NULL, 1);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(kick_all_cpus_sync);
IPI call을 사용하여 각 cpu를 호출하여 더미 callback을 수행시키게 한다.
- pm_idle 함수 포인터의 update의 동기화를 하는데 사용된다.
- do_nothing()은 비어 있는 함수이다.
참고
- Slab Memory Allocator -1- (구조) | 문c
- Slab Memory Allocator -2- (캐시 초기화) | 문c
- Slub Memory Allocator -3- (캐시 생성) | 문c
- Slub Memory Allocator -4- (Order 계산) | 문c
- Slub Memory Allocator -5- (Slub 할당) | 문c
- Slub Memory Allocator -6- (Object 할당) | 문c
- Slub Memory Allocator -7- (Object 해제) | 문c
- Slub Memory Allocator -8- (Drain/Flash 캐시) | 문c
- Slub Memory Allocator -9- (캐시 Shrink) | 문c – 현재 글
- Slub Memory Allocator -10- (Slub 해제) | 문c
- Slub Memory Allocator -11- (캐시 삭제) | 문c
- Slub Memory Allocator -12- (Slub 디버깅) | 문c
- Slub Memory Allocator -13- (slabinfo) | 문c