<kernel v5.4>
Interrupts -9- (GIC v3 Driver)
GIC v3 & GIC v4 호환
GIC v3 드라이버 코드는 GIC v4도 같이 사용한다. (GIC v4 its를 위한 코드가 일부 추가됨)
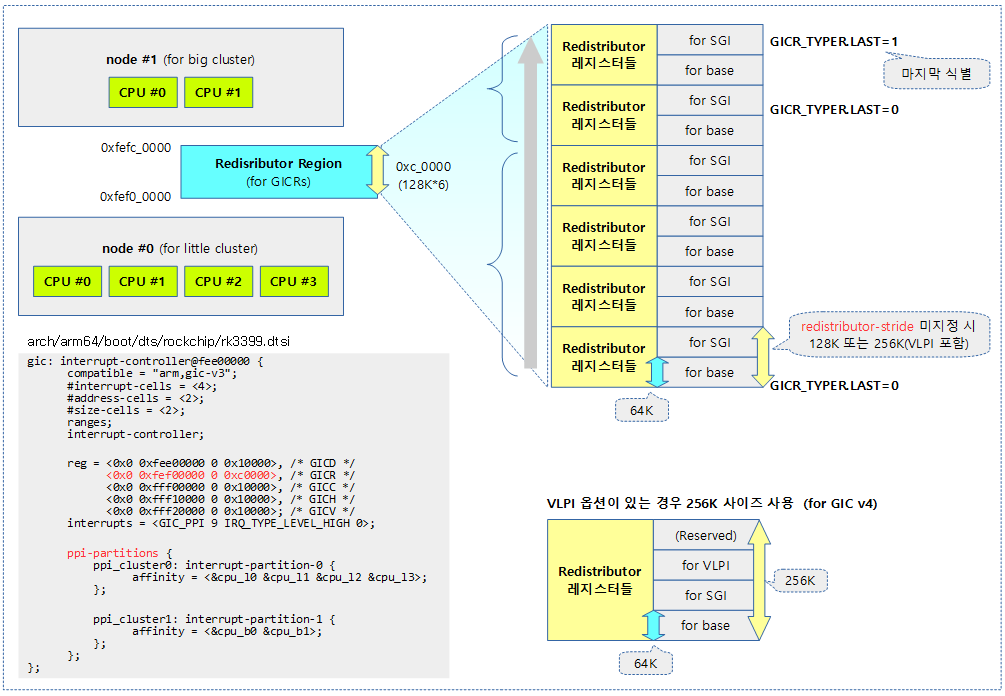
다음은 rock3399 칩에서 사용하는 gic v3 컨트롤러에 대한 디바이스 트리이다.
arch/arm64/boot/dts/rockchip/rk3399.dtsi
gic: interrupt-controller@fee00000 {
compatible = "arm,gic-v3";
#interrupt-cells = <4>;
#address-cells = <2>;
#size-cells = <2>;
ranges;
interrupt-controller;
reg = <0x0 0xfee00000 0 0x10000>, /* GICD */
<0x0 0xfef00000 0 0xc0000>, /* GICR */
<0x0 0xfff00000 0 0x10000>, /* GICC */
<0x0 0xfff10000 0 0x10000>, /* GICH */
<0x0 0xfff20000 0 0x10000>; /* GICV */
interrupts = <GIC_PPI 9 IRQ_TYPE_LEVEL_HIGH 0>;
its: interrupt-controller@fee20000 {
compatible = "arm,gic-v3-its";
msi-controller;
reg = <0x0 0xfee20000 0x0 0x20000>;
};
ppi-partitions {
ppi_cluster0: interrupt-partition-0 {
affinity = <&cpu_l0 &cpu_l1 &cpu_l2 &cpu_l3>;
};
ppi_cluster1: interrupt-partition-1 {
affinity = <&cpu_b0 &cpu_b1>;
};
};
};
- reg
- 기본적으로 GICD(mandatory), GICR(mandatory), GICC(option), GICH(option), GICV(option) 영역 5개를 사용한다.
- interrupts
- VGIC 관리를 위한 인터럽트 소스이다.
- its: interrupt-controller@fee20000
- GIC v3-its 드라이버는 생략한다.
- ppi-partitions
- PPI affnity를 사용하여 파티션을 구성한다.
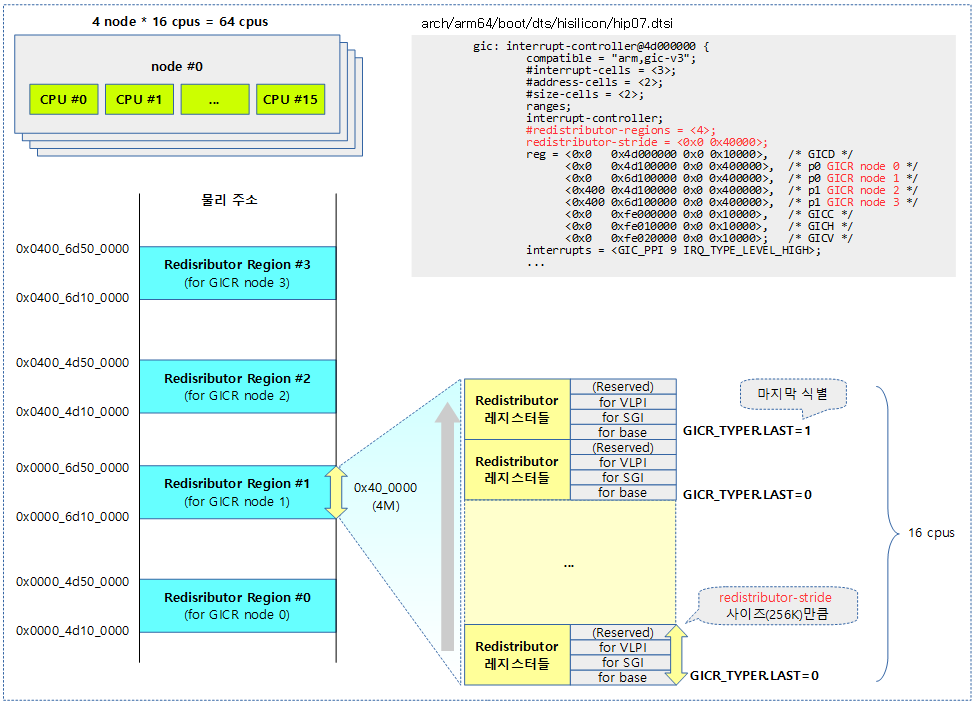
다음은 hisilicon의 hip07 칩에서 사용하는 gic v3 컨트롤러에 대한 디바이스 트리이다.
arch/arm64/boot/dts/hisilicon/hip07.dtsi
gic: interrupt-controller@4d000000 {
compatible = "arm,gic-v3";
#interrupt-cells = <3>;
#address-cells = <2>;
#size-cells = <2>;
ranges;
interrupt-controller;
#redistributor-regions = <4>;
redistributor-stride = <0x0 0x40000>;
reg = <0x0 0x4d000000 0x0 0x10000>, /* GICD */
<0x0 0x4d100000 0x0 0x400000>, /* p0 GICR node 0 */
<0x0 0x6d100000 0x0 0x400000>, /* p0 GICR node 1 */
<0x400 0x4d100000 0x0 0x400000>, /* p1 GICR node 2 */
<0x400 0x6d100000 0x0 0x400000>, /* p1 GICR node 3 */
<0x0 0xfe000000 0x0 0x10000>, /* GICC */
<0x0 0xfe010000 0x0 0x10000>, /* GICH */
<0x0 0xfe020000 0x0 0x10000>; /* GICV */
interrupts = <GIC_PPI 9 IRQ_TYPE_LEVEL_HIGH>;
...
- #redistributor-regions
- GICR 레지스터 영역이 4개의 노드로 구성됨을 알 수 있다.
- redistributor-stride
- GICR 노드 레지스터간에 패딩 간격 페이지 수를 지정한다. 이 값은 64K의 배수여야 한다.
- 위의 예에서는 256K를 사용하였다.
- GICR 노드 레지스터간에 패딩 간격 페이지 수를 지정한다. 이 값은 64K의 배수여야 한다.
- reg
- 기본적으로 GICD, GICR, GICC, GICH, GICV 영역 5개를 사용하지만, 이 컨트롤러는 GICR 영역이 1 -> 4개로 확장되었다.
GIC v3 드라이버 초기화
gic_of_init()
drivers/irqchip/irq-gic-v3.c
static int __init gic_of_init(struct device_node *node, struct device_node *parent)
{
void __iomem *dist_base;
struct redist_region *rdist_regs;
u64 redist_stride;
u32 nr_redist_regions;
int err, i;
dist_base = of_iomap(node, 0);
if (!dist_base) {
pr_err("%pOF: unable to map gic dist registers\n", node);
return -ENXIO;
}
err = gic_validate_dist_version(dist_base);
if (err) {
pr_err("%pOF: no distributor detected, giving up\n", node);
goto out_unmap_dist;
}
if (of_property_read_u32(node, "#redistributor-regions", &nr_redist_regions))
nr_redist_regions = 1;
rdist_regs = kcalloc(nr_redist_regions, sizeof(*rdist_regs),
GFP_KERNEL);
if (!rdist_regs) {
err = -ENOMEM;
goto out_unmap_dist;
}
for (i = 0; i < nr_redist_regions; i++) {
struct resource res;
int ret;
ret = of_address_to_resource(node, 1 + i, &res);
rdist_regs[i].redist_base = of_iomap(node, 1 + i);
if (ret || !rdist_regs[i].redist_base) {
pr_err("%pOF: couldn't map region %d\n", node, i);
err = -ENODEV;
goto out_unmap_rdist;
}
rdist_regs[i].phys_base = res.start;
}
if (of_property_read_u64(node, "redistributor-stride", &redist_stride))
redist_stride = 0;
gic_enable_of_quirks(node, gic_quirks, &gic_data);
err = gic_init_bases(dist_base, rdist_regs, nr_redist_regions,
redist_stride, &node->fwnode);
if (err)
goto out_unmap_rdist;
gic_populate_ppi_partitions(node);
if (static_branch_likely(&supports_deactivate_key))
gic_of_setup_kvm_info(node);
return 0;
out_unmap_rdist:
for (i = 0; i < nr_redist_regions; i++)
if (rdist_regs[i].redist_base)
iounmap(rdist_regs[i].redist_base);
kfree(rdist_regs);
out_unmap_dist:
iounmap(dist_base);
return err;
}
IRQCHIP_DECLARE(gic_v3, "arm,gic-v3", gic_of_init);
GIC v3 인터럽트 컨트롤러 초기화 시작 함수이다. (GIC v4 인터럽트 컨트롤러도 이 함수를 같이 사용한다)
- 코드 라인 9~13에서 Distributor 레지스터 영역인 “reg” 속성의 0번째 주소와 사이즈를 읽어와 가상 주소에 매핑한다.
- 코드 라인 15~19에서 Distributor 레지스터에서 gic v3 또는 v4 여부를 체크한다. (성공 시 0)
- 코드 라인 21~22에서 ReDistributor 영역의 수를 알아오기 위해 “#redistributor-regions” 속성 값을 알아온다. 속성이 없는 경우 디폴트는 1이다.
- 코드 라인 24~29에서 ReDistributor 영역의 수만큼 redist_region 구조체를 할당한다.
- 코드 라인 31~43에서 ReDistributor 영역의 수만큼 “reg” 속성의 두 번째 부터 주소와 사이즈를 읽어 가상 주소에 매핑하고, 매핑한 주소는 rdist_regs[].redist_base에 대입한다. 그리고 rdist_regs[].phys_base에는 물리 주소를 기록한다.
- 코드 라인 45~46에서 GICR 노드 레지스터간에 패딩 간격 페이지 수를 지정하기 위해 “redistributor-stride” 속성 값을 알아온다. 속성이 없는 경우 디폴트는 0이다.
- 코드 라인 48에서 gic 컨트롤러들 중 errata 코드가 있는 경우 이를 호출하여 수행한다.
- 현재 Qualcomm MSM8996, Hisilicon의 hip06 및 hip07이 대상이다.
- 코드 라인 50~53에서 gic 컨트롤러를 초기화한다.
- 코드 라인 55에서 모든 PPI들을 위해 irq 파티션을 생성한다.
- 참고: Interrupts -10- (irq partition) | 문c
- 코드 라인 57~58에서 Guest OS를 위한 KVM 정보를 설정한다.
- 코드 라인 59에서 성공 값 0을 반환한다.
gic_validate_dist_version()
drivers/irqchip/irq-gic-v3.c
static int __init gic_validate_dist_version(void __iomem *dist_base)
{
u32 reg = readl_relaxed(dist_base + GICD_PIDR2) & GIC_PIDR2_ARCH_MASK;
if (reg != GIC_PIDR2_ARCH_GICv3 && reg != GIC_PIDR2_ARCH_GICv4)
return -ENODEV;
return 0;
}
GICD_PIDR2 레지스터의 버전을 읽어 gic v3 또는 v4인지 여부를 알아온다. 성공시 0을 반환한다.
GIC 레지스터들 초기화
gic_init_bases()
drivers/irqchip/irq-gic-v3.c
static int __init gic_init_bases(void __iomem *dist_base,
struct redist_region *rdist_regs,
u32 nr_redist_regions,
u64 redist_stride,
struct fwnode_handle *handle)
{
u32 typer;
int err;
if (!is_hyp_mode_available())
static_branch_disable(&supports_deactivate_key);
if (static_branch_likely(&supports_deactivate_key))
pr_info("GIC: Using split EOI/Deactivate mode\n");
gic_data.fwnode = handle;
gic_data.dist_base = dist_base;
gic_data.redist_regions = rdist_regs;
gic_data.nr_redist_regions = nr_redist_regions;
gic_data.redist_stride = redist_stride;
/*
* Find out how many interrupts are supported.
*/
typer = readl_relaxed(gic_data.dist_base + GICD_TYPER);
gic_data.rdists.gicd_typer = typer;
gic_enable_quirks(readl_relaxed(gic_data.dist_base + GICD_IIDR),
gic_quirks, &gic_data);
pr_info("%d SPIs implemented\n", GIC_LINE_NR - 32);
pr_info("%d Extended SPIs implemented\n", GIC_ESPI_NR);
gic_data.domain = irq_domain_create_tree(handle, &gic_irq_domain_ops,
&gic_data);
irq_domain_update_bus_token(gic_data.domain, DOMAIN_BUS_WIRED);
gic_data.rdists.rdist = alloc_percpu(typeof(*gic_data.rdists.rdist));
gic_data.rdists.has_vlpis = true;
gic_data.rdists.has_direct_lpi = true;
if (WARN_ON(!gic_data.domain) || WARN_ON(!gic_data.rdists.rdist)) {
err = -ENOMEM;
goto out_free;
}
gic_data.has_rss = !!(typer & GICD_TYPER_RSS);
pr_info("Distributor has %sRange Selector support\n",
gic_data.has_rss ? "" : "no ");
if (typer & GICD_TYPER_MBIS) {
err = mbi_init(handle, gic_data.domain);
if (err)
pr_err("Failed to initialize MBIs\n");
}
set_handle_irq(gic_handle_irq);
gic_update_rdist_properties();
gic_smp_init();
gic_dist_init();
gic_cpu_init();
gic_cpu_pm_init();
if (gic_dist_supports_lpis()) {
its_init(handle, &gic_data.rdists, gic_data.domain);
its_cpu_init();
} else {
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_ARM_GIC_V2M))
gicv2m_init(handle, gic_data.domain);
}
gic_enable_nmi_support();
return 0;
out_free:
if (gic_data.domain)
irq_domain_remove(gic_data.domain);
free_percpu(gic_data.rdists.rdist);
return err;
}
- 코드 라인 10~14에서 하이퍼 모드가 운용가능한 상태가 아니면 supports_deactivate_key를 disable 한다.
- 커널이 하이퍼 모드로 동작하는 경우에 따라 EOI 모드를 priority drop과 deactivate를 split하여 운영한다.
- 예) “GIC: Using split EOI/Deactivate mode”
- 참고: 가상화 지원 (하이퍼 모드) | 문c
- 커널이 하이퍼 모드로 동작하는 경우에 따라 EOI 모드를 priority drop과 deactivate를 split하여 운영한다.
- 코드 라인 16~20에서 gic_chip_data 구조체 형태인 전역 gic_data에 인자로 전달된 값들로 초기화한다.
- 코드 라인 25~26에서 GICD_TYPER 레지스터 값을 저장한다.
- 코드 라인 28~29에서 GICD_IIDR 레지스터 값을 읽어 관련 디바이스에 대해서만 errtum 코드를 수행한다.
- 코드 라인 31~32에서 SPI와 확장 SPI 수 정보를 출력한다.
- 코드 라인 33~35에서 하이라키를 지원하는 irq 도메인을 생성하고, DOMAIN_BUS_WIRED 도메인 타입으로 지정한다.
- 코드 라인 36~43에서 Redistributor용 per-cpu 자료 구조를 할당 받고 초기화한다.
- 가상 LPI 지원과 Direct LPI Injection을 true로 미리 설정한다.
- 추후 Redistributor 레지스터들을 읽어 하나라도 VLPI 및 DirectLPI 값이 0인 경우 false로 바뀐다.
- 코드 라인 45~47에서 GICD_TYPER.RSS 비트를 읽어 rss 지원 여부를 알아내고 출력한다.
- 코드 라인 49~53에서 GICD_TYPER.MBIS 비트를 읽어 메시지 기반 인터럽트의 지원하는 경우 mbi 관련 초기화 루틴을 수행한다.
- “msi-controller” 속성 필요
- 코드 라인 55에서 이 컨트롤러에서 관리를 위해 사용하는 인터럽트의 핸들러 함수를 지정한다.
- 코드 라인 57에서 Redistributor 속성을 읽어 갱신한다.
- 코드 라인 59에서 SMP를 지원하기 위한 초기화를 수행한다.
- 코드 라인 60에서 Distributtor 레지스터를 사용한 초기화를 수행한다.
- 코드 라인 61에서 CPU interface 레지스터를 사용한 초기화를 수행한다.
- 코드 라인 62에서 CPU 절전(suspen/resume) 관련한 초기화를 수행한다.
- 코드 라인 64~70에서 LPI를 지원하는 경우 ITS츨 초기화한다. 지원하지 않는 경우 GIC 가상화 지원 초기화를 수행한다.
- 코드 라인 72에서 Pesudo-NNI 기능을 지원하는 경우 이에 대한 초기화를 수행한다.
- 코드 라인 74에서 성공 값 0을 반환한다.
GIC Quirks(ERRATA) 초기화 및 적용
gic_enable_of_quirks()
drivers/irqchip/irq-gic-common.c
void gic_enable_of_quirks(const struct device_node *np,
const struct gic_quirk *quirks, void *data)
{
for (; quirks->desc; quirks++) {
if (!of_device_is_compatible(np, quirks->compatible))
continue;
if (quirks->init(data))
pr_info("GIC: enabling workaround for %s\n",
quirks->desc);
}
}
디바이스 트리로 지정된 디바이스만 erratum 적용한다.
gic_enable_quirks()
drivers/irqchip/irq-gic-common.c
void gic_enable_quirks(u32 iidr, const struct gic_quirk *quirks,
void *data)
{
for (; quirks->desc; quirks++) {
if (quirks->compatible)
continue;
if (quirks->iidr != (quirks->mask & iidr))
continue;
if (quirks->init(data))
pr_info("GIC: enabling workaround for %s\n",
quirks->desc);
}
}
@iidr 값이 일치하는 디바이스만 erratum 적용한다.
gic_quirks
static const struct gic_quirk gic_quirks[] = {
{
.desc = "GICv3: Qualcomm MSM8996 broken firmware",
.compatible = "qcom,msm8996-gic-v3",
.init = gic_enable_quirk_msm8996,
},
{
.desc = "GICv3: HIP06 erratum 161010803",
.iidr = 0x0204043b,
.mask = 0xffffffff,
.init = gic_enable_quirk_hip06_07,
},
{
.desc = "GICv3: HIP07 erratum 161010803",
.iidr = 0x00000000,
.mask = 0xffffffff,
.init = gic_enable_quirk_hip06_07,
},
{
}
};
버그 등으로 인해 erratum 코드가 적용되어야 할 디바이스들이다.
SMP core들 시작시 호출될 함수 지정
gic_smp_init()
drivers/irqchip/irq-gic-v3.c
static void gic_smp_init(void)
{
set_smp_cross_call(gic_raise_softirq);
cpuhp_setup_state_nocalls(CPUHP_AP_IRQ_GIC_STARTING,
"irqchip/arm/gicv3:starting",
gic_starting_cpu, NULL);
}
새로운 cpu가 online될 때 gic에 알려야 할 함수를 지정한다.
gic_starting_cpu()
drivers/irqchip/irq-gic-v3.c
static int gic_starting_cpu(unsigned int cpu)
{
gic_cpu_init();
if (gic_dist_supports_lpis())
its_cpu_init();
return 0;
}
새로운 cpu가 online될 때 콜백 호출되는 함수이다. 해당 cpu interface 레지스터들을 초기화하고, LPI를 지원하는 경우 ITS 초기화 함수를 수행한다.
Distributor 초기화
gic_dist_init()
drivers/irqchip/irq-gic-v3.c
static void __init gic_dist_init(void)
{
unsigned int i;
u64 affinity;
void __iomem *base = gic_data.dist_base;
/* Disable the distributor */
writel_relaxed(0, base + GICD_CTLR);
gic_dist_wait_for_rwp();
/*
* Configure SPIs as non-secure Group-1. This will only matter
* if the GIC only has a single security state. This will not
* do the right thing if the kernel is running in secure mode,
* but that's not the intended use case anyway.
*/
for (i = 32; i < GIC_LINE_NR; i += 32)
writel_relaxed(~0, base + GICD_IGROUPR + i / 8);
/* Extended SPI range, not handled by the GICv2/GICv3 common code */
for (i = 0; i < GIC_ESPI_NR; i += 32) {
writel_relaxed(~0U, base + GICD_ICENABLERnE + i / 8);
writel_relaxed(~0U, base + GICD_ICACTIVERnE + i / 8);
}
for (i = 0; i < GIC_ESPI_NR; i += 32)
writel_relaxed(~0U, base + GICD_IGROUPRnE + i / 8);
for (i = 0; i < GIC_ESPI_NR; i += 16)
writel_relaxed(0, base + GICD_ICFGRnE + i / 4);
for (i = 0; i < GIC_ESPI_NR; i += 4)
writel_relaxed(GICD_INT_DEF_PRI_X4, base + GICD_IPRIORITYRnE + i);
/* Now do the common stuff, and wait for the distributor to drain */
gic_dist_config(base, GIC_LINE_NR, gic_dist_wait_for_rwp);
/* Enable distributor with ARE, Group1 */
writel_relaxed(GICD_CTLR_ARE_NS | GICD_CTLR_ENABLE_G1A | GICD_CTLR_ENABLE_G1,
base + GICD_CTLR);
/*
* Set all global interrupts to the boot CPU only. ARE must be
* enabled.
*/
affinity = gic_mpidr_to_affinity(cpu_logical_map(smp_processor_id()));
for (i = 32; i < GIC_LINE_NR; i++)
gic_write_irouter(affinity, base + GICD_IROUTER + i * 8);
for (i = 0; i < GIC_ESPI_NR; i++)
gic_write_irouter(affinity, base + GICD_IROUTERnE + i * 8);
}
GIC Distributor를 초기화한다.
- 코드 라인 8~9에서 Distributor를 disable하기 위해 GICD_CTRL 값에 0을 기록한다.
- 코드 라인 17~18에서 모든 SPI들을 non-secure group 1으로 설정하기위해 GICD_IGROUPRn들을 모두 0xffff_ffff(1 비트당 1 인터럽트)로 설정한다.
- one security states에서 리눅스 커널이 동작하는 경우 그룹 제어가 가능하다.
- 그러나 two secure states인 경우 그룹 설정은 secure에서 해야 하기 때문에 non-secure에서 동작하느 리눅스 커널에서 제어는 의미 없게 된다.
- 코드 라인 21~24에서 모든 확장 SPI들을 disable 및 deactivate 요청하기 위해 GICD_ICENABLERn 과 GICD_ICACTIVERn들을 모두 0xffff_ffff(1 비트당 1 인터럽트)로 설정한다.
- 코드 라인 26~27에서 모든 확장 SPI들을 non-secure group 1으로 설정하기위해 GICD_IGROUPRnE들을 모두 0xffff_ffff(1 비트당 1 인터럽트)로 설정한다.
- 코드 라인 29~30에서 모든 확장 SPI들을 레벨 sensitive 모드로 설정하기 위해 GICD_ICFGRnE들을 모두 0x0(1 비트당 1 인터럽트)으로 설정한다.
- 코드 라인 32~33에서 모든 확장 SPI들에 대해 우선 순위를 0xd0으로 설정하기 위해 GICD_IPRIORITYRnE에 0xa0을 기록한다. (8 비트당 1 인터럽트)
- non-secure에서 설정한 0xa0은 cpu interface로 올라갈 때 내부 변환하면 0xa0 >> 1 | 0x80 = 0xd0에 해당하는 우선 순위이다.
- 코드 라인 36에서 GIC v1 이상에서 동작하는 공통 Distributor 설정 코드를 수행한다.
- 코드 라인 39~40에서 Distributor를 활성화할 때 ARE(Affinity Routing Enable), group 1도 활성화한다.
- 코드 라인 46에서 boot cpu의 affinity 값들을 읽어오기 위해 MPIDR 레지스터를 알아온다.
- 코드 라인 47~51에서 모든 SPI들 및 확장 SPI들을 대상으로 boot cpu로 라우팅 설정하기 위해 읽어온 affinity 값을 GICD_ROUTERn 및 GICD_ROUTERRnE에 기록한다.
gic_dist_wait_for_rwp()
drivers/irqchip/irq-gic-v3.c
/* Wait for completion of a distributor change */
static void gic_dist_wait_for_rwp(void)
{
gic_do_wait_for_rwp(gic_data.dist_base);
}
distributor 레지스터에 기록한 후 이의 수행이 완료될 때까지 대기한다.
gic_do_wait_for_rwp()
drivers/irqchip/irq-gic-v3.c
static void gic_do_wait_for_rwp(void __iomem *base)
{
u32 count = 1000000; /* 1s! */
while (readl_relaxed(base + GICD_CTLR) & GICD_CTLR_RWP) {
count--;
if (!count) {
pr_err_ratelimited("RWP timeout, gone fishing\n");
return;
}
cpu_relax();
udelay(1);
};
}
GICD_CTLR.RWP 레지스터를 읽어 0이될 때까지 반복한다.
GIC v1 이상 공통 Distributor 설정
gic_dist_config()
drivers/irqchip/irq-gic-v3.c
void gic_dist_config(void __iomem *base, int gic_irqs,
void (*sync_access)(void))
{
unsigned int i;
/*
* Set all global interrupts to be level triggered, active low.
*/
for (i = 32; i < gic_irqs; i += 16)
writel_relaxed(GICD_INT_ACTLOW_LVLTRIG,
base + GIC_DIST_CONFIG + i / 4);
/*
* Set priority on all global interrupts.
*/
for (i = 32; i < gic_irqs; i += 4)
writel_relaxed(GICD_INT_DEF_PRI_X4, base + GIC_DIST_PRI + i);
/*
* Deactivate and disable all SPIs. Leave the PPI and SGIs
* alone as they are in the redistributor registers on GICv3.
*/
for (i = 32; i < gic_irqs; i += 32) {
writel_relaxed(GICD_INT_EN_CLR_X32,
base + GIC_DIST_ACTIVE_CLEAR + i / 8);
writel_relaxed(GICD_INT_EN_CLR_X32,
base + GIC_DIST_ENABLE_CLEAR + i / 8);
}
if (sync_access)
sync_access();
}
모든 GIC 버전에서 동작하는 공통 Distributor 설정 코드를 수행한다.
- 코드 라인 9~11에서 모든 SPI들에 대한 low active 레벨 sensitive 설정을 위해 GICD_ICFGRn에 0x0을 기록한다. (2 비트당 1 인터럽트)
- 코드 라인 16~17에서 모든 SPI들에 대해 우선 순위를 0xd0으로 설정하기 위해 GICD_IPRIORITYRn에 0xa0을 기록한다. (8 비트당 1 인터럽트)
- non-secure에서 설정한 0xa0은 cpu interface로 올라갈 때 내부 변환하면 0xa0 >> 1 | 0x80 = 0xd0에 해당하는 우선 순위이다.
- 코드 라인 23~28에서 모든 확장 SPI들을 disable 및 deactivate 요청하기 위해 GICD_ICENABLERn 과 GICD_ICACTIVERn들을 모두 0xffff_ffff(1 비트당 1 인터럽트)로 설정한다.
- 코드 라인 30~31 Distributor 레지스터 적용이 완료될 때까지 대기하도록 인자로 전달받은 @sync_access 함수를 호출한다.
CPU Interface 관련 초기화
gic_cpu_init()
drivers/irqchip/irq-gic-v3.c
static void gic_cpu_init(void)
{
void __iomem *rbase;
int i;
/* Register ourselves with the rest of the world */
if (gic_populate_rdist())
return;
gic_enable_redist(true);
WARN((gic_data.ppi_nr > 16 || GIC_ESPI_NR != 0) &&
!(gic_read_ctlr() & ICC_CTLR_EL1_ExtRange),
"Distributor has extended ranges, but CPU%d doesn't\n",
smp_processor_id());
rbase = gic_data_rdist_sgi_base();
/* Configure SGIs/PPIs as non-secure Group-1 */
for (i = 0; i < gic_data.ppi_nr + 16; i += 32)
writel_relaxed(~0, rbase + GICR_IGROUPR0 + i / 8);
gic_cpu_config(rbase, gic_data.ppi_nr + 16, gic_redist_wait_for_rwp);
/* initialise system registers */
gic_cpu_sys_reg_init();
}
CPU interface를 초기화한다.
- 코드 라인 7~10에서 Redistributor를 활성화한다.
- 코드 라인 17에서 Redistributor에서 SGI 베이스 레지스터 가상 주소를 알아온다.
- 코드 라인 20~21에서 SGI/PPI들을 모두 non-secure group 1으로 설정하기 위해 GICR_IGROUP0Rn에 0xffff_ffff(1 비트당 1 인터럽트)를 기록한다.
- 코드 라인 23에서 모든 버전의 GIC를 위한 공통 CPU 설정 코드를 수행한다.
- 코드 라인 26에서 시스템 레지스터를 초기화한다.
GIC v1 이상 공통 CPU 관련 설정
gic_cpu_config()
drivers/irqchip/irq-gic-common.c
void gic_cpu_config(void __iomem *base, int nr, void (*sync_access)(void))
{
int i;
/*
* Deal with the banked PPI and SGI interrupts - disable all
* private interrupts. Make sure everything is deactivated.
*/
for (i = 0; i < nr; i += 32) {
writel_relaxed(GICD_INT_EN_CLR_X32,
base + GIC_DIST_ACTIVE_CLEAR + i / 8);
writel_relaxed(GICD_INT_EN_CLR_X32,
base + GIC_DIST_ENABLE_CLEAR + i / 8);
}
/*
* Set priority on PPI and SGI interrupts
*/
for (i = 0; i < nr; i += 4)
writel_relaxed(GICD_INT_DEF_PRI_X4,
base + GIC_DIST_PRI + i * 4 / 4);
/* Ensure all SGI interrupts are now enabled */
writel_relaxed(GICD_INT_EN_SET_SGI, base + GIC_DIST_ENABLE_SET);
if (sync_access)
sync_access();
}
모든 GIC 버전에서 동작하는 공통 CPU 관련 설정을 수행한다.
- 코드 라인 9~14에서 모든 SGI/PPI들을 disable 및 deactivate 요청하기 위해 GICD_ICENABLERn 과 GICD_ICACTIVERn들을 모두 0xffff_ffff(1 비트당 1 인터럽트)로 설정한다.
- 코드 라인 19~21에서 모든 SGI/PPI들에 대해 우선 순위를 0xd0으로 설정하기 위해 GICD_IPRIORITYRn에 0xa0을 기록한다. (8 비트당 1 인터럽트)
- non-secure에서 설정한 0xa0은 cpu interface로 올라갈 때 내부 변환하면 0xa0 >> 1 | 0x80 = 0xd0에 해당하는 우선 순위이다.
- 코드 라인 24에서 모든 SGI들을 enable 요청하기 위해 GICD_ISENABLERn들을 모두 0xffff_ffff(1 비트당 1 인터럽트)로 설정한다.
- 코드 라인 26~27에서 Distributor 레지스터 적용이 완료될 때까지 대기하도록 인자로 전달받은 @sync_access 함수를 호출한다.
gic_cpu_sys_reg_init()
drivers/irqchip/irq-gic-v3.c -1/2-
static void gic_cpu_sys_reg_init(void)
{
int i, cpu = smp_processor_id();
u64 mpidr = cpu_logical_map(cpu);
u64 need_rss = MPIDR_RS(mpidr);
bool group0;
u32 pribits;
/*
* Need to check that the SRE bit has actually been set. If
* not, it means that SRE is disabled at EL2. We're going to
* die painfully, and there is nothing we can do about it.
*
* Kindly inform the luser.
*/
if (!gic_enable_sre())
pr_err("GIC: unable to set SRE (disabled at EL2), panic ahead\n");
pribits = gic_get_pribits();
group0 = gic_has_group0();
/* Set priority mask register */
if (!gic_prio_masking_enabled()) {
write_gicreg(DEFAULT_PMR_VALUE, ICC_PMR_EL1);
} else {
/*
* Mismatch configuration with boot CPU, the system is likely
* to die as interrupt masking will not work properly on all
* CPUs
*/
WARN_ON(gic_supports_nmi() && group0 &&
!gic_dist_security_disabled());
}
/*
* Some firmwares hand over to the kernel with the BPR changed from
* its reset value (and with a value large enough to prevent
* any pre-emptive interrupts from working at all). Writing a zero
* to BPR restores is reset value.
*/
gic_write_bpr1(0);
if (static_branch_likely(&supports_deactivate_key)) {
/* EOI drops priority only (mode 1) */
gic_write_ctlr(ICC_CTLR_EL1_EOImode_drop);
} else {
/* EOI deactivates interrupt too (mode 0) */
gic_write_ctlr(ICC_CTLR_EL1_EOImode_drop_dir);
}
GIC 시스템 레지스터들을 초기화한다.
- 코드 라인 3~5에서 현재 cpu에 대한 mpidr 값을 알아와서 aff0 값이 16을 초과한 경우 need_rss에 1을 대입한다.
- aff0이 16 이상이라는 의미는 최하위 레벨에서 16개 이상의 cpu가 사용되므로 RSS(Range Select Support)=1이되어 최하위 affnity 레벨의 cpu 범위가 0~255까지 라는 의미이다.
- 코드 라인 16~17에서 SRE(System Register Enable)이 0인 경우 에러를 출력한다.
- GICv3 하드웨어가 GIC v1~v2 드라이버 코드를 사용하는 경우 SRE=0로 설정하지만, GIC v3 하드웨어에 GIC v3 드라이버 코드를 사용하는 경우 SRE=1로 하여 시스템 레지스터를 사용하는 것이 정확하고, 또 성능에도 유리하다.
- 코드 라인 19에서 pribits 값을 알아온다.
- ICC_CTLR_EL1.PRIbits + 1 값
- 코드 라인 21에서 커널이 group 0를 사용 가능한지 여부를 알아온다.
- 코드 라인 24~34에서 Pesudo-NMI 기능을 위한 priority masking 기능이 활성화되지 않은 경우 디폴트 priority mask 값 0xf0을 ICC_PMR_EL1.PMR 레지스터에 기록한다.
- 코드 라인 42에서 펌웨어에서 Binary Point 값을 설정하였을 수도 있으므로 커널에선 이를 0으로 기록하여 리셋되는 기능이 있다.
- 코드 라인 44~50에서 EL2 부트 여부에 따라 적절한 EOImode를 설정한다.
- EL2 모드에서 리눅스 커널이 부팅한 경우 호스트 OS로 동작하는 경우이다. 이러한 경우 Guest OS를 지원하기 위해 Host OS는 priority drop과 deactivate를 분리한(ICC_CTLR_EL1_EOImode_drop) EOI 모드를 사용한다.
drivers/irqchip/irq-gic-v3.c -2/2-
/* Always whack Group0 before Group1 */
if (group0) {
switch(pribits) {
case 8:
case 7:
write_gicreg(0, ICC_AP0R3_EL1);
write_gicreg(0, ICC_AP0R2_EL1);
/* Fall through */
case 6:
write_gicreg(0, ICC_AP0R1_EL1);
/* Fall through */
case 5:
case 4:
write_gicreg(0, ICC_AP0R0_EL1);
}
isb();
}
switch(pribits) {
case 8:
case 7:
write_gicreg(0, ICC_AP1R3_EL1);
write_gicreg(0, ICC_AP1R2_EL1);
/* Fall through */
case 6:
write_gicreg(0, ICC_AP1R1_EL1);
/* Fall through */
case 5:
case 4:
write_gicreg(0, ICC_AP1R0_EL1);
}
isb();
/* ... and let's hit the road... */
gic_write_grpen1(1);
/* Keep the RSS capability status in per_cpu variable */
per_cpu(has_rss, cpu) = !!(gic_read_ctlr() & ICC_CTLR_EL1_RSS);
/* Check all the CPUs have capable of sending SGIs to other CPUs */
for_each_online_cpu(i) {
bool have_rss = per_cpu(has_rss, i) && per_cpu(has_rss, cpu);
need_rss |= MPIDR_RS(cpu_logical_map(i));
if (need_rss && (!have_rss))
pr_crit("CPU%d (%lx) can't SGI CPU%d (%lx), no RSS\n",
cpu, (unsigned long)mpidr,
i, (unsigned long)cpu_logical_map(i));
}
/**
* GIC spec says, when ICC_CTLR_EL1.RSS==1 and GICD_TYPER.RSS==0,
* writing ICC_ASGI1R_EL1 register with RS != 0 is a CONSTRAINED
* UNPREDICTABLE choice of :
* - The write is ignored.
* - The RS field is treated as 0.
*/
if (need_rss && (!gic_data.has_rss))
pr_crit_once("RSS is required but GICD doesn't support it\n");
}
- 코드 라인 2~18에서 커널에서 group 0을 사용가능한 경우 pribits에 따라4 개의 Activate Priorities Group 0 레지스터값에 0을 기록하여 리셋하여 사용한다.
- ICC_AP0Rn_EL1 레지스터 4개는 EL2에서 physical fiq를 수신하지 않도록 설정된 경우(EL2.HCR_EL2.FMO=0)에만 non-secure EL1 커널에서 access 가능하다.
- 코드 라인 20~34에서 pribits에 따라4 개의 Activate Priorities Group 1 레지스터값에 0을 기록하여 리셋하여 사용한다.
- ICC_AP1Rn_EL1 레지스터 4개는 EL2에서 physical irq를 수신하지 않도록 설정된 경우(EL2.HCR_EL2.IMO=0)에만 non-secure EL1 커널에서 access 가능하다.
- 코드 라인 37에서 non-secure 커널에서 group1 인터럽트를 활성화하기위해 SYS_ICC_IGRPEN1_EL1에 1을 기록한다.
- 코드 라인 40에서 per-cpu has_rss 변수에 RSS(Range Select Support) 값을 알아온다.
- SGI 사용시 0인 경우 0~15 cpu, 1인 경우 0~255 cpu
- 코드 라인 43~51에서 cpu mpidr 값에서 affinity 0에 해당하는 cpu 번호가 RSS 범위를 벗어나는 경우 이를 체크하여 에러 로그를 출력한다.
- 코드 라인 60~61에서 affinity 0 레벨에서 0~255 cpu 범위를 사용하는데 GIC가 지원하지 않는 경우 에러 로그를 출력한다.
gic_enable_sre()
include/linux/irqchip/arm-gic-v3.h
static inline bool gic_enable_sre(void)
{
u32 val;
val = gic_read_sre();
if (val & ICC_SRE_EL1_SRE)
return true;
val |= ICC_SRE_EL1_SRE;
gic_write_sre(val);
val = gic_read_sre();
return !!(val & ICC_SRE_EL1_SRE);
}
GIC 시스템 레지스터를 사용할 수 있도록 활성화한다.
- ICC_SRE_EL1.SRE=1로 활성화한다.
gic_get_pribits()
drivers/irqchip/irq-gic-v3.c
static u32 gic_get_pribits(void)
{
u32 pribits;
pribits = gic_read_ctlr();
pribits &= ICC_CTLR_EL1_PRI_BITS_MASK;
pribits >>= ICC_CTLR_EL1_PRI_BITS_SHIFT;
pribits++;
return pribits;
}
priority 레벨링의 단계에 사용되는 비트 수를 알아온다.
- ICC_CTRL_EL1.PRIbits + 1
- 이 값이 4인 경우 -> pribits=5가 되고 2^5=32가 된다. (이 칩은 총 32 단계의 priority 레벨을 운영한다.)
gic_has_group0()
drivers/irqchip/irq-gic-v3.c
static bool gic_has_group0(void)
{
u32 val;
u32 old_pmr;
old_pmr = gic_read_pmr();
/*
* Let's find out if Group0 is under control of EL3 or not by
* setting the highest possible, non-zero priority in PMR.
*
* If SCR_EL3.FIQ is set, the priority gets shifted down in
* order for the CPU interface to set bit 7, and keep the
* actual priority in the non-secure range. In the process, it
* looses the least significant bit and the actual priority
* becomes 0x80. Reading it back returns 0, indicating that
* we're don't have access to Group0.
*/
gic_write_pmr(BIT(8 - gic_get_pribits()));
val = gic_read_pmr();
gic_write_pmr(old_pmr);
return val != 0;
}
EL1에서 동작하는 리눅스 커널에서 group 0를 사용할 수 있는지 여부를 알아온다.
- group 0가 EL3에서 통제되는 경우 EL1 에서 동작하는 커널에서 최고 높은 우선 순위를 기록하고 읽을 때 그 값이 읽히는 것이 아니라 0이 읽힌다.
- pribits가 5인 경우 32단계로 priority 레벨링이 동작한다. 그 중 0x00을 제외한 가장 높은 우선 순위인 0x08을 기록해본다.
- 0x00, 0x08, 0x10, 0x18, 0x20, … 0xf8
gic_prio_masking_enabled()
arch/arm64/include/asm/arch_gicv3.h
static inline bool gic_prio_masking_enabled(void)
{
return system_uses_irq_prio_masking();
}
Pesudo-NMI 기능을 위해 시스템이 irq masking 기능을 사용할 수 있는 경우 true를 반환한다.
system_uses_irq_prio_masking()
arch/arm64/include/asm/cpufeature.h
static inline bool system_uses_irq_prio_masking(void)
{
return IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_ARM64_PSEUDO_NMI) &&
cpus_have_const_cap(ARM64_HAS_IRQ_PRIO_MASKING);
}
CONFIG_ARM64_PSEUDO_NMI 커널 옵션과 IRQ_PRIO_MASKING capability를 가진 경우에 true를 반환한다.
Redistributor 초기화
Redistributor 속성들 갱신
gic_update_rdist_properties()
drivers/irqchip/irq-gic-v3.c
static void gic_update_rdist_properties(void)
{
gic_data.ppi_nr = UINT_MAX;
gic_iterate_rdists(__gic_update_rdist_properties);
if (WARN_ON(gic_data.ppi_nr == UINT_MAX))
gic_data.ppi_nr = 0;
pr_info("%d PPIs implemented\n", gic_data.ppi_nr);
pr_info("%sVLPI support, %sdirect LPI support\n",
!gic_data.rdists.has_vlpis ? "no " : "",
!gic_data.rdists.has_direct_lpi ? "no " : "");
}
Redistributor들에서 몇 가지 속성을 갱신한다. 그런 후 관련 속성을 정보 출력한다.
gic_iterate_rdists()
drivers/irqchip/irq-gic-v3.c
static int gic_iterate_rdists(int (*fn)(struct redist_region *, void __iomem *))
{
int ret = -ENODEV;
int i;
for (i = 0; i < gic_data.nr_redist_regions; i++) {
void __iomem *ptr = gic_data.redist_regions[i].redist_base;
u64 typer;
u32 reg;
reg = readl_relaxed(ptr + GICR_PIDR2) & GIC_PIDR2_ARCH_MASK;
if (reg != GIC_PIDR2_ARCH_GICv3 &&
reg != GIC_PIDR2_ARCH_GICv4) { /* We're in trouble... */
pr_warn("No redistributor present @%p\n", ptr);
break;
}
do {
typer = gic_read_typer(ptr + GICR_TYPER);
ret = fn(gic_data.redist_regions + i, ptr);
if (!ret)
return 0;
if (gic_data.redist_regions[i].single_redist)
break;
if (gic_data.redist_stride) {
ptr += gic_data.redist_stride;
} else {
ptr += SZ_64K * 2; /* Skip RD_base + SGI_base */
if (typer & GICR_TYPER_VLPIS)
ptr += SZ_64K * 2; /* Skip VLPI_base + reserved page */
}
} while (!(typer & GICR_TYPER_LAST));
}
return ret ? -ENODEV : 0;
}
Redistributor들에서 몇 가지 속성을 갱신한다.
- 코드 라인 6~16에서 Redistributor 영역 수 만큼 순회하며 GICR_PIDR2.ARCH 값을 읽어 GIC v3 및 v4가 아닌 경우 경고 메시지를 출력하고 에러를 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 18~22에서 Redistributor 레지스터를 읽어 gic 설정 값을 갱신하기 위해 인자로 전달받은 *fn함수를 호출한다.
- GIC v3에서 전달한 함수: __gic_update_rdist_properties()
- 코드 라인 24~25에서 ACPI를 통해 하나의 Residtributor만 구현되었다고 지정된 경우 처리를 중간하고 함수를 빠져나간다.
- 코드 라인 27~33에서 Resistributor 레지스터들 간에 redist_stride 값 만큼 갭을 둔다. 단 redist_stride가 설정되지 않은 경우 128K/256K(LPIS 지원시) 만큼 갭을 둔다.
- 코드 라인 34에서 GICR_TYPER.LAST 비트가 0이면 아직 끝나지 않았으므로 다음을 처리하기 위해 계속 루프를 돈다.
다음 그림은 4개의 노드에 각각 16개의 cpu를 사용하여 Redistributor를 구성한 모습을 보여준다.
- Redistributor 레지스터 세트는 각각 256K를 사용하였고, 전체 64 세트이다. (4 redistributor regions * 16 cpus)
다음 그림은 1개의 노드에 big/little 클러스터가 같이 구현되어 있는 Redistributor를 구성한 모습과 ppi 파티션이 구성된 모습을 보여준다.
- Redistributor 레지스터 세트는 각각 128K를 사용하였고, 전체 6 세트이다. (1 redistributor regions * 6 cpus)
- 2 개의 파티션에 각각 4개 cpu와 2개 cpu가 구성되어 있다.
__gic_update_rdist_properties()
drivers/irqchip/irq-gic-v3.c
static int __gic_update_rdist_properties(struct redist_region *region,
void __iomem *ptr)
{
u64 typer = gic_read_typer(ptr + GICR_TYPER);
gic_data.rdists.has_vlpis &= !!(typer & GICR_TYPER_VLPIS);
gic_data.rdists.has_direct_lpi &= !!(typer & GICR_TYPER_DirectLPIS);
gic_data.ppi_nr = min(GICR_TYPER_NR_PPIS(typer), gic_data.ppi_nr);
return 1;
}
Redistributor 레지스터를 읽어 속성 갑을 갱신한다.
- 코드 라인 4에서 Redistributor 레지스터 베이스를 가리키는 ptr을 기반으로 GICR_TYPER 레지스터 값을 읽어온다.
- 코드 라인 5에서 GICR_TYPER.VLPIS가 하나라도 0이면 false 설정으로 바꾼다.
- 코드 라인 6에서 GICR_TYPER.DirectLPIS가 하나라도 0이면 false 설정으로 바꾼다.
- 코드 라인 7에서 GIC를 통해 읽은 PPI 수와 GICR을 통해 읽은 PPI 수 중 작은 값으로 ppi_nr에 대입한다.
Redistributor 활성화
gic_populate_rdist()
drivers/irqchip/irq-gic-v3.c
static int gic_populate_rdist(void)
{
if (gic_iterate_rdists(__gic_populate_rdist) == 0)
return 0;
/* We couldn't even deal with ourselves... */
WARN(true, "CPU%d: mpidr %lx has no re-distributor!\n",
smp_processor_id(),
(unsigned long)cpu_logical_map(smp_processor_id()));
return -ENODEV;
}
Redistributor들에서 cpu의 affinity와 동일한 경우 rd_base와 phys_base를 갱신한다.
__gic_populate_rdist()
drivers/irqchip/irq-gic-v3.c
static int __gic_populate_rdist(struct redist_region *region, void __iomem *ptr)
{
unsigned long mpidr = cpu_logical_map(smp_processor_id());
u64 typer;
u32 aff;
/*
* Convert affinity to a 32bit value that can be matched to
* GICR_TYPER bits [63:32].
*/
aff = (MPIDR_AFFINITY_LEVEL(mpidr, 3) << 24 |
MPIDR_AFFINITY_LEVEL(mpidr, 2) << 16 |
MPIDR_AFFINITY_LEVEL(mpidr, 1) << 8 |
MPIDR_AFFINITY_LEVEL(mpidr, 0));
typer = gic_read_typer(ptr + GICR_TYPER);
if ((typer >> 32) == aff) {
u64 offset = ptr - region->redist_base;
gic_data_rdist_rd_base() = ptr;
gic_data_rdist()->phys_base = region->phys_base + offset;
pr_info("CPU%d: found redistributor %lx region %d:%pa\n",
smp_processor_id(), mpidr,
(int)(region - gic_data.redist_regions),
&gic_data_rdist()->phys_base);
return 0;
}
/* Try next one */
return 1;
}
MPIDR을 통해 알아온 4단계 affinity 값과 GICR_TYPER을 통해 읽어온 4 단계 affinity 값이 같은 경우에 한해 rd_base와 phys_base를 갱신하고 로그 정보를 출력한다. 성공 시 0을 반환한다.
- GICR_TYPER 레지스터는 64비트 값을 가지고 있고 bits[61:32]에 4단계 affinity 값이 담겨있다.
gic_enable_redist()
drivers/irqchip/irq-gic-v3.c
static void gic_enable_redist(bool enable)
{
void __iomem *rbase;
u32 count = 1000000; /* 1s! */
u32 val;
if (gic_data.flags & FLAGS_WORKAROUND_GICR_WAKER_MSM8996)
return;
rbase = gic_data_rdist_rd_base();
val = readl_relaxed(rbase + GICR_WAKER);
if (enable)
/* Wake up this CPU redistributor */
val &= ~GICR_WAKER_ProcessorSleep;
else
val |= GICR_WAKER_ProcessorSleep;
writel_relaxed(val, rbase + GICR_WAKER);
if (!enable) { /* Check that GICR_WAKER is writeable */
val = readl_relaxed(rbase + GICR_WAKER);
if (!(val & GICR_WAKER_ProcessorSleep))
return; /* No PM support in this redistributor */
}
while (--count) {
val = readl_relaxed(rbase + GICR_WAKER);
if (enable ^ (bool)(val & GICR_WAKER_ChildrenAsleep))
break;
cpu_relax();
udelay(1);
};
if (!count)
pr_err_ratelimited("redistributor failed to %s...\n",
enable ? "wakeup" : "sleep");
}
Redistributor를 깨우거나 슬립시킨다. @enable=1일 때 깨우고, @enable=0일 때 슬립한다.
- 코드 라인 7~8에서 FLAGS_WORKAROUND_GICR_WAKER_MSM8996 워크어라운드 플래그가 설정된 경우 함수를 빠져나간다.
- 코드 라인 10~18에서 GICR_WAKER.ProcessorSleep 필드를 제거(@enable=1)하거나 추가(@enable=0)한다.
- 코드 라인 20~24에서 @enable=0일 때 GICR_WAKER.ProcessorSleep 을 다시 읽어 0인 경우 PM을 지원하지 않으므로 함수를 빠져나간다.
- 코드 라인 26~32에서 최대 1초간 busy wait하며 GICR_WAKER.ChildrenAsleep을 읽은 값과 enable이 서로 다른 경우 루프를 벗어난다.
- 코드 라인 33~35에서 1초 동안 설정되지 않은 경우 “Redistributor failed to (wakeup|sleep)”을 출력한다.
KVM 지원
gic_of_setup_kvm_info()
irq-gic-v3.c
static void __init gic_of_setup_kvm_info(struct device_node *node)
{
int ret;
struct resource r;
u32 gicv_idx;
gic_v3_kvm_info.type = GIC_V3;
gic_v3_kvm_info.maint_irq = irq_of_parse_and_map(node, 0);
if (!gic_v3_kvm_info.maint_irq)
return;
if (of_property_read_u32(node, "#redistributor-regions",
&gicv_idx))
gicv_idx = 1;
gicv_idx += 3; /* Also skip GICD, GICC, GICH */
ret = of_address_to_resource(node, gicv_idx, &r);
if (!ret)
gic_v3_kvm_info.vcpu = r;
gic_v3_kvm_info.has_v4 = gic_data.rdists.has_vlpis;
gic_set_kvm_info(&gic_v3_kvm_info);
}
KVM을 통해 Guest OS를 동작시킬 때 사용할 gic 정보를 저장한다.
gic_set_kvm_info()
drivers/irqchip/irq-gic-common.c
void gic_set_kvm_info(const struct gic_kvm_info *info)
{
BUG_ON(gic_kvm_info != NULL);
gic_kvm_info = info;
}
virt/kvm/arm/vgic/vgic-init.c – kvm_vgic_hyp_init() 함수에서 gic-v3가 제공한 정보를 가져다 virtual gic를 초기화할 떄 사용한다.
GIC v3 Operations
GIC v3용 irq_chip Operations는 가상화 지원 관련하여 두 가지가 사용된다.
- gic_eoimode1_chip
- 호스트 OS용
- gic_chip
- Guest OS용
호스트 OS용 gic_eoimode1_chip
drivers/irqchip/irq-gic-v3.c
static struct irq_chip gic_eoimode1_chip = {
.name = "GICv3",
.irq_mask = gic_eoimode1_mask_irq,
.irq_unmask = gic_unmask_irq,
.irq_eoi = gic_eoimode1_eoi_irq,
.irq_set_type = gic_set_type,
.irq_set_affinity = gic_set_affinity,
.irq_get_irqchip_state = gic_irq_get_irqchip_state,
.irq_set_irqchip_state = gic_irq_set_irqchip_state,
.irq_set_vcpu_affinity = gic_irq_set_vcpu_affinity,
.irq_nmi_setup = gic_irq_nmi_setup,
.irq_nmi_teardown = gic_irq_nmi_teardown,
.flags = IRQCHIP_SET_TYPE_MASKED |
IRQCHIP_SKIP_SET_WAKE |
IRQCHIP_MASK_ON_SUSPEND,
};
Guest OS용 gic_chip
drivers/irqchip/irq-gic-v3.c
static struct irq_chip gic_chip = {
.name = "GICv3",
.irq_mask = gic_mask_irq,
.irq_unmask = gic_unmask_irq,
.irq_eoi = gic_eoi_irq,
.irq_set_type = gic_set_type,
.irq_set_affinity = gic_set_affinity,
.irq_get_irqchip_state = gic_irq_get_irqchip_state,
.irq_set_irqchip_state = gic_irq_set_irqchip_state,
.irq_nmi_setup = gic_irq_nmi_setup,
.irq_nmi_teardown = gic_irq_nmi_teardown,
.flags = IRQCHIP_SET_TYPE_MASKED |
IRQCHIP_SKIP_SET_WAKE |
IRQCHIP_MASK_ON_SUSPEND,
};
인터럽트 Mask & Unmask
gic_eoimode1_mask_irq()
drivers/irqchip/irq-gic-v3.c
static void gic_eoimode1_mask_irq(struct irq_data *d)
{
gic_mask_irq(d);
/*
* When masking a forwarded interrupt, make sure it is
* deactivated as well.
*
* This ensures that an interrupt that is getting
* disabled/masked will not get "stuck", because there is
* noone to deactivate it (guest is being terminated).
*/
if (irqd_is_forwarded_to_vcpu(d))
gic_poke_irq(d, GICD_ICACTIVER);
}
해당 인터럽트를 mask 한다.
- 코드 라인 3에서 GICD_ICENABLERn의 인터럽트 번호에 해당하는 비트에 1을 기록하여 physical 인터럽트를 mask 한다.
- 코드 라인 12~13에서 Guest OS에 vcpu를 통해 인터럽트를 전달 가능한 경우 GICD_ICACTIVERn의 인터럽트 번호에 해당하는 비트에 1을 기록하여 deactivate 요청을 한다.
gic_mask_irq()
drivers/irqchip/irq-gic-v3.c
static void gic_mask_irq(struct irq_data *d)
{
gic_poke_irq(d, GICD_ICENABLER);
}
해당 인터럽트를 mask 한다.
- 코드 라인 3에서 GICD_ICENABLERn의 인터럽트 번호에 해당하는 비트에 1을 기록하여 physical 인터럽트를 mask 한다.
gic_unmask_irq()
drivers/irqchip/irq-gic-v3.c
static void gic_unmask_irq(struct irq_data *d)
{
gic_poke_irq(d, GICD_ISENABLER);
}
해당 인터럽트를 unmask 한다.
- 코드 라인 3에서 GICD_ISENABLERn의 인터럽트 번호에 해당하는 비트에 1을 기록하여 physical 인터럽트를 unmask 한다.
레지스터 Peek & Poke
gic_peek_irq()
drivers/irqchip/irq-gic-v3.c
static int gic_peek_irq(struct irq_data *d, u32 offset)
{
void __iomem *base;
u32 index, mask;
offset = convert_offset_index(d, offset, &index);
mask = 1 << (index % 32);
if (gic_irq_in_rdist(d))
base = gic_data_rdist_sgi_base();
else
base = gic_data.dist_base;
return !!(readl_relaxed(base + offset + (index / 32) * 4) & mask);
}
@offset 위치 레지스터의 해당 인터럽트에 대응하는 비트 값을 읽어온다. (1=설정, 0=클리어)
- 코드 라인 6에서 해당 인터럽트의 @offset에 해당하는 offset을 알아오고, @index에는 세 가지(PPI/SPI, EPPI 및 ESPI) 타입의 0부터 시작하는 값을 알아온다.
- 코드 라인 9~12에서 해당 인터럽트가 Redistributor를 사용해야 하는 per-cpu 타입(PPI/EPPI) 여부에 따라 베이스 주소를 sgi_base로, 그 외의 경우 dist_base로 한다.
- 코드 라인 14에서 레지스터 베이스에 offset을 더한 주소에서 산출된 mask 비트 값을 읽어온다.
gic_poke_irq()
drivers/irqchip/irq-gic-v3.c
static void gic_poke_irq(struct irq_data *d, u32 offset)
{
void (*rwp_wait)(void);
void __iomem *base;
u32 index, mask;
offset = convert_offset_index(d, offset, &index);
mask = 1 << (index % 32);
if (gic_irq_in_rdist(d)) {
base = gic_data_rdist_sgi_base();
rwp_wait = gic_redist_wait_for_rwp;
} else {
base = gic_data.dist_base;
rwp_wait = gic_dist_wait_for_rwp;
}
writel_relaxed(mask, base + offset + (index / 32) * 4);
rwp_wait();
}
@offset 위치 레지스터의 해당 인터럽트에 대응하는 비트에 1을 기록한다.
- clear-request 또는 set-request 타입 레지스터에 사용한다
convert_offset_index()
drivers/irqchip/irq-gic-v3.c
/* * Routines to disable, enable, EOI and route interrupts */
static u32 convert_offset_index(struct irq_data *d, u32 offset, u32 *index)
{
switch (get_intid_range(d)) {
case PPI_RANGE:
case SPI_RANGE:
*index = d->hwirq;
return offset;
case EPPI_RANGE:
/*
* Contrary to the ESPI range, the EPPI range is contiguous
* to the PPI range in the registers, so let's adjust the
* displacement accordingly. Consistency is overrated.
*/
*index = d->hwirq - EPPI_BASE_INTID + 32;
return offset;
case ESPI_RANGE:
*index = d->hwirq - ESPI_BASE_INTID;
switch (offset) {
case GICD_ISENABLER:
return GICD_ISENABLERnE;
case GICD_ICENABLER:
return GICD_ICENABLERnE;
case GICD_ISPENDR:
return GICD_ISPENDRnE;
case GICD_ICPENDR:
return GICD_ICPENDRnE;
case GICD_ISACTIVER:
return GICD_ISACTIVERnE;
case GICD_ICACTIVER:
return GICD_ICACTIVERnE;
case GICD_IPRIORITYR:
return GICD_IPRIORITYRnE;
case GICD_ICFGR:
return GICD_ICFGRnE;
case GICD_IROUTER:
return GICD_IROUTERnE;
default:
break;
}
break;
default:
break;
}
WARN_ON(1);
*index = d->hwirq;
return offset;
}
해당 인터럽트 타입과 @offset 주소로 레지스터에 대한 offset을 알아온다. 그리고 출력 인자 *index에는 hwirq 번호를 대입한다.
- 코드 라인 3~7에서 해당 인터럽트가 PPI 및 SPI 범위인 경우 @offset을 그대로 반환하고, @index에는 d->hwirq역시 그대로 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 8~15에서 해당 인터럽트가 확장 PPI 범위인 경우 @offset을 그대로 반환하고, @index에는 d->hwirq – EPPI_BASE_INTID(1024 + 32) + 32 값을 반환한다.
- 결국 @index = d->hwirq – 1024 (확장 SPI에 대한 @index는 0 ~ 1023)
- 코드 라인 16~36에서 해당 인터럽트가 확장 SPI 범위인 경우 @offset에 따라 레지스터 offset을 반환하고, @index에는 d->hwirq – ESPI_BASE_INTID 값을 반환한다.
- 결국 @index = d->hwirq – 4096 (확장 SPI의 INTID 는 4096 부터 시작, @index는 0부터)
- 코드 라인 37~47에서 그 외의 범위인 경우 @offset을 그대로 반환하고, @index에는 d->hwirq역시 그대로 반환한다.
인터럽트 타입 설정
gic_set_type()
drivers/irqchip/irq-gic-v3.c
static int gic_set_type(struct irq_data *d, unsigned int type)
{
enum gic_intid_range range;
unsigned int irq = gic_irq(d);
void (*rwp_wait)(void);
void __iomem *base;
u32 offset, index;
int ret;
/* Interrupt configuration for SGIs can't be changed */
if (irq < 16)
return -EINVAL;
range = get_intid_range(d);
/* SPIs have restrictions on the supported types */
if ((range == SPI_RANGE || range == ESPI_RANGE) &&
type != IRQ_TYPE_LEVEL_HIGH && type != IRQ_TYPE_EDGE_RISING)
return -EINVAL;
if (gic_irq_in_rdist(d)) {
base = gic_data_rdist_sgi_base();
rwp_wait = gic_redist_wait_for_rwp;
} else {
base = gic_data.dist_base;
rwp_wait = gic_dist_wait_for_rwp;
}
offset = convert_offset_index(d, GICD_ICFGR, &index);
ret = gic_configure_irq(index, type, base + offset, rwp_wait);
if (ret && (range == PPI_RANGE || range == EPPI_RANGE)) {
/* Misconfigured PPIs are usually not fatal */
pr_warn("GIC: PPI INTID%d is secure or misconfigured\n", irq);
ret = 0;
}
return ret;
}
해당 인터럽트에 대한 트리거 타입을 지정한다.
- 코드 라인 11~12에서 SGI는 에러를 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 14~19에서 SPI 또는 확장 SPI 영역인 경우 level high 또는 edge rising 트리거 타입만 지정할 수 있다.
- 코드 라인 21~27에서 해당 인터럽트가 Redistributor를 사용해야 하는 per-cpu 타입(PPI/EPPI) 여부에 따라 sgi_base를 그 외의 경우 dist_base를 레지스터 베이스로 지정한다.
- 코드 라인 29에서 PPI/SPI인 경우 GICD_ICFGRn 또는 EPPI/ESPI인 경우 GICD_ICFGRnE 레지스터에 대한 offset 주소를 알아오고 index에는 해당 인터럽트에 대한 0부터 시작하는 인덱스 값을 알아온다.(n)
- 코드 라인 31~36에서 위에서 알아온 베이스 주소 + offset 주소의 레지스터에 index에 해당하는 인터럽트 위치에 type을 기록하고, rwp_wait 함수를 통해 레지스터에 기록이 완료될 때까지 대기한다.
get_intid_range()
drivers/irqchip/irq-gic-v3.c
static enum gic_intid_range get_intid_range(struct irq_data *d)
{
return __get_intid_range(d->hwirq);
}
해당 인터럽트에 대한 레인지 타입을 알아온다.
__get_intid_range()
drivers/irqchip/irq-gic-v3.c
static enum gic_intid_range __get_intid_range(irq_hw_number_t hwirq)
{
switch (hwirq) {
case 16 ... 31:
return PPI_RANGE;
case 32 ... 1019:
return SPI_RANGE;
case EPPI_BASE_INTID ... (EPPI_BASE_INTID + 63):
return EPPI_RANGE;
case ESPI_BASE_INTID ... (ESPI_BASE_INTID + 1023):
return ESPI_RANGE;
case 8192 ... GENMASK(23, 0):
return LPI_RANGE;
default:
return __INVALID_RANGE__;
}
}
@hwirq 값에 따른 인터럽트에 대한 레인지 타입을 반환한다.
- PPI_RANGE: hwirq 16 ~ 31
- SPI_RANGE: hwirq: 32 ~ 1019
- EPPI_RANGE: 1024 ~ 1024 + 63
- ESPI_RANGE: 4096 ~ 4096 + 1023
- LPI_RANGE: 8192 ~ 0x80_0000 (2^23)
gic_intid_range
drivers/irqchip/irq-gic-v3.c
enum gic_intid_range {
PPI_RANGE,
SPI_RANGE,
EPPI_RANGE,
ESPI_RANGE,
LPI_RANGE,
__INVALID_RANGE__
};
gic_configure_irq()
drivers/irqchip/irq-gic-common.c
int gic_configure_irq(unsigned int irq, unsigned int type,
void __iomem *base, void (*sync_access)(void))
{
u32 confmask = 0x2 << ((irq % 16) * 2);
u32 confoff = (irq / 16) * 4;
u32 val, oldval;
int ret = 0;
unsigned long flags;
/*
* Read current configuration register, and insert the config
* for "irq", depending on "type".
*/
raw_spin_lock_irqsave(&irq_controller_lock, flags);
val = oldval = readl_relaxed(base + confoff);
if (type & IRQ_TYPE_LEVEL_MASK)
val &= ~confmask;
else if (type & IRQ_TYPE_EDGE_BOTH)
val |= confmask;
/* If the current configuration is the same, then we are done */
if (val == oldval) {
raw_spin_unlock_irqrestore(&irq_controller_lock, flags);
return 0;
}
/*
* Write back the new configuration, and possibly re-enable
* the interrupt. If we fail to write a new configuration for
* an SPI then WARN and return an error. If we fail to write the
* configuration for a PPI this is most likely because the GIC
* does not allow us to set the configuration or we are in a
* non-secure mode, and hence it may not be catastrophic.
*/
writel_relaxed(val, base + confoff);
if (readl_relaxed(base + confoff) != val)
ret = -EINVAL;
raw_spin_unlock_irqrestore(&irq_controller_lock, flags);
if (sync_access)
sync_access();
return ret;
}
@irq에 해당하는 2 비트의 @type을 일반/확장 인터럽트 여부에 따라 GICD_TYPERn 또는 GICD_TYPERnE에 기록한다. 기록한 후에는 기록이 완료될 때까지 잠시 대기한다.
Pseudo-NMI 지원
Pseudo-NMI 초기화
gic_enable_nmi_support()
drivers/irqchip/irq-gic-v3.c
static void gic_enable_nmi_support(void)
{
int i;
if (!gic_prio_masking_enabled())
return;
if (gic_has_group0() && !gic_dist_security_disabled()) {
pr_warn("SCR_EL3.FIQ is cleared, cannot enable use of pseudo-NMIs\n");
return;
}
ppi_nmi_refs = kcalloc(gic_data.ppi_nr, sizeof(*ppi_nmi_refs), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!ppi_nmi_refs)
return;
for (i = 0; i < gic_data.ppi_nr; i++)
refcount_set(&ppi_nmi_refs[i], 0);
static_branch_enable(&supports_pseudo_nmis);
if (static_branch_likely(&supports_deactivate_key))
gic_eoimode1_chip.flags |= IRQCHIP_SUPPORTS_NMI;
else
gic_chip.flags |= IRQCHIP_SUPPORTS_NMI;
}
Pesudo-NMI를 지원하는 경우 초기화 한다.
- 코드 라인 5~6에서 Pesudo-NMI 기능을 위해 시스템이 irq masking 기능이 필요한데 사용할 수 없으면 그냥 함수를 빠져나간다.
- 코드 라인 8~11에서 커널에서 gorup 0를 지원하면서 secure를 동작 중인 경우 경고 메시지를 출력하고 함수를 빠져나간다.
- EL3에서 secure가 동작 중이면 SCR_EL3.FIQ가 설정되어 FIQ를 커널에서 처리해야 한다.
- 코드 라인 13~15에서 ppi_nmi_refs 레퍼런스 카운터를 ppi 수 만큼 할당한다.
- 코드 라인 17~18에서 ppi_nmi_refs[]를 모두 0으로 설정한다.
- 코드 라인 20에서 Pesudo-NMI 기능이 동작한다는 static key를 활성화한다.
- 코드 라인 22~25에서 EL2 호스트 OS 운영에 따라 irq_chip operations의 플래그에 NMI 지원을 추가한다.
Pseudo-NMI 인터럽트 설정
gic_irq_nmi_setup()
drivers/irqchip/irq-gic-v3.c
static int gic_irq_nmi_setup(struct irq_data *d)
{
struct irq_desc *desc = irq_to_desc(d->irq);
if (!gic_supports_nmi())
return -EINVAL;
if (gic_peek_irq(d, GICD_ISENABLER)) {
pr_err("Cannot set NMI property of enabled IRQ %u\n", d->irq);
return -EINVAL;
}
/*
* A secondary irq_chip should be in charge of LPI request,
* it should not be possible to get there
*/
if (WARN_ON(gic_irq(d) >= 8192))
return -EINVAL;
/* desc lock should already be held */
if (gic_irq_in_rdist(d)) {
u32 idx = gic_get_ppi_index(d);
/* Setting up PPI as NMI, only switch handler for first NMI */
if (!refcount_inc_not_zero(&ppi_nmi_refs[idx])) {
refcount_set(&ppi_nmi_refs[idx], 1);
desc->handle_irq = handle_percpu_devid_fasteoi_nmi;
}
} else {
desc->handle_irq = handle_fasteoi_nmi;
}
gic_irq_set_prio(d, GICD_INT_NMI_PRI);
return 0;
}
해당 인터럽트를 Pesudo-NMI로 설정한다.
- 코드 라인 5~6에서 Pesudo-NMI를 지원하지 않는 시스템인 경우 -EINVAL 에러를 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 8~11에서 해당 인터럽트가 이미 enable 된 경우 에러 메시지를 출력하고 -EINVAL 에러를 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 17~18에서 LPI인 경우 지원하지 않으므로 -EINVAL을 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 21~31에서 해당 인터럽트가 Redistributor를 사용해야 하는 per-cpu 타입(PPI/EPPI) 여부에 따라 다음과 같이 설정한다.
- PPI/EPPI 타입인 경우 해당 인터럽트 번호별로 첫 번째 설정인 경우에만 핸들러를 handle_percpu_devid_fasteoi_nmi() 함수로 설정한다.
- 그 외 타입인 경우 핸들러를 handle_fasteoi_nmi() 함수로 지정한다.
- 참고: Interrupts -2- (irq chip) | 문c
- 코드 라인 33에서 인터럽트 우선 순위 값을 0x20 (내부 변환 후 0x90)으로 설정한다.
- non-secure EL1에서 동작하는 커널에서 우선 순위 값을 설정하면 group 1 인터럽트들만 설정 가능하며 다음과 같은 기준으로 변경되어 설정된다.
- prio(0x20) >> 1 | 0x80 = 변환 prio(0x90)
- non-secure EL1에서 동작하는 커널에서 우선 순위 값을 설정하면 group 1 인터럽트들만 설정 가능하며 다음과 같은 기준으로 변경되어 설정된다.
gic_supports_nmi()
drivers/irqchip/irq-gic-v3.c
static inline bool gic_supports_nmi(void)
{
return IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_ARM64_PSEUDO_NMI) &&
static_branch_likely(&supports_pseudo_nmis);
}
Pesudo-NMI를 지원하는지 여부를 반환한다.
gic_irq_in_rdist()
drivers/irqchip/irq-gic-v3.c
static inline int gic_irq_in_rdist(struct irq_data *d)
{
enum gic_intid_range range = get_intid_range(d);
return range == PPI_RANGE || range == EPPI_RANGE;
}
해당 인터럽트가 Redistributor를 사용해야 하는지 여부를 알아온다. (PPI 또는 EPPI인 경우)
인터럽트 우선 순위 설정
gic_irq_set_prio()
drivers/irqchip/irq-gic-v3.c
static void gic_irq_set_prio(struct irq_data *d, u8 prio)
{
void __iomem *base = gic_dist_base(d);
u32 offset, index;
offset = convert_offset_index(d, GICD_IPRIORITYR, &index);
writeb_relaxed(prio, base + offset + index);
}
해당 인터럽트의 우선 순위를 설정한다.
- non-secure EL1에서 동작하는 커널에서 우선 순위 값을 설정하면 group 1 인터럽트들만 설정 가능하며 다음과 같은 기준으로 변경되어 설정된다.
- prio >> 1 | 0x80 = 변환 prio (cpu interface로 전달되는 최종 priority 값이다)
Pseudo-NMI 인터럽트 해제
kernel/irq/chip.c
static void gic_irq_nmi_teardown(struct irq_data *d)
{
struct irq_desc *desc = irq_to_desc(d->irq);
if (WARN_ON(!gic_supports_nmi()))
return;
if (gic_peek_irq(d, GICD_ISENABLER)) {
pr_err("Cannot set NMI property of enabled IRQ %u\n", d->irq);
return;
}
/*
* A secondary irq_chip should be in charge of LPI request,
* it should not be possible to get there
*/
if (WARN_ON(gic_irq(d) >= 8192))
return;
/* desc lock should already be held */
if (gic_irq_in_rdist(d)) {
u32 idx = gic_get_ppi_index(d);
/* Tearing down NMI, only switch handler for last NMI */
if (refcount_dec_and_test(&ppi_nmi_refs[idx]))
desc->handle_irq = handle_percpu_devid_irq;
} else {
desc->handle_irq = handle_fasteoi_irq;
}
gic_irq_set_prio(d, GICD_INT_DEF_PRI);
}
해당 인터럽트를 Pesudo-NMI에서 일반 인터럽트로 변경하여 설정한다.
- 코드 라인 5~6에서 Pesudo-NMI를 지원하지 않는 시스템인 경우 -EINVAL 에러를 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 8~11에서 해당 인터럽트가 이미 enable 된 경우 에러 메시지를 출력하고 -EINVAL 에러를 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 17~18에서 LPI인 경우 지원하지 않으므로 -EINVAL을 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 21~29에서 해당 인터럽트가 Redistributor를 사용해야 하는 per-cpu 타입(PPI/EPPI) 여부에 따라 다음과 같이 설정한다.
- PPI/EPPI 타입인 경우 해당 인터럽트 번호별로 첫 번째 설정인 경우에만 핸들러를 handle_percpu_devid_irq() 함수로 설정한다.
- 그 외 타입인 경우 핸들러를 handle_fasteoi_irq() 함수로 지정한다.
- 코드 라인 31에서 인터럽트 우선 순위 값을 0xa0 (내부 변환 후 0xd0)으로 설정한다.
- non-secure EL1에서 동작하는 커널에서 우선 순위 값을 설정하면 group 1 인터럽트들만 설정 가능하며 다음과 같은 기준으로 변경되어 설정된다.
- prio(0xa0) >> 1 | 0x80 = 변환 prio(0xd0)
- non-secure EL1에서 동작하는 커널에서 우선 순위 값을 설정하면 group 1 인터럽트들만 설정 가능하며 다음과 같은 기준으로 변경되어 설정된다.
구조체
gic_chip_data 구조체
drivers/irqchip/irq-gic-v3.c
struct gic_chip_data {
struct fwnode_handle *fwnode;
void __iomem *dist_base;
struct redist_region *redist_regions;
struct rdists rdists;
struct irq_domain *domain;
u64 redist_stride;
u32 nr_redist_regions;
u64 flags;
bool has_rss;
unsigned int ppi_nr;
struct partition_desc **ppi_descs;
};
GIC v3 컨트롤러의 내부 칩 데이터를 구성한다.
- *fwnode
- 펌웨어 노드 정보
- *dist_base
- Distributor 영역 가상 주소 베이스
- *redist_regions
- Redistributor 영역 수 만큼 redist_region 구조체를 할당하여 사용한다.
- *domain
- GIC가 사용하는 irq domain을 가리킨다.
- redist_stride
- Distributor들간의 주소 간격이 지정된다.
- nr_redist_regions
- Redistributor 영역 수
- flags
- has_rss
- affinity 0 레벨에서 0~255 범위의 cpu 번호를 지원해야 하는지 여부 (Range Select Support)
- **ppi_descs
- PPI 파티션을 사용하는 경우 파티션 수 만큼 partition_desc 구조체를 할당하여 사용한다.
redist_region 구조체
drivers/irqchip/irq-gic-v3.c
struct redist_region {
void __iomem *redist_base;
phys_addr_t phys_base;
bool single_redist;
};
하나의 Redistributor 정보를 관리한다.
- *redist_base
- Redistributor 레지스터 가상 주소 베이스
- phys_base
- Redistributor 레지스터 물리 주소 베이스
- single_redist
- Redistributor 영역 내에 single Redistributor인지 여부
rdists 구조체
include/linux/irqchip/arm-gic-v3.h
struct rdists {
struct {
void __iomem *rd_base;
struct page *pend_page;
phys_addr_t phys_base;
bool lpi_enabled;
} __percpu *rdist;
phys_addr_t prop_table_pa;
void *prop_table_va;
u64 flags;
u32 gicd_typer;
bool has_vlpis;
bool has_direct_lpi;
};
하나의 Redistributor region 정보를 관리한다.
- *rdist
- cpu 수 만큼 다음 4 항목을 구성한다.
- *rd_base
- Redistributor 레지스터 가상 주소 베이스
- *pend_page
- phys_base
- Redistributor 레지스터 물리 주소 베이스
- lpi_enabled
- LPI 활성화 여부
- prop_table_pa
- *prop_table_va
- flags
- gicd_typer
- has_vlpis
- VLPIS 지원 여부
- for GIC v4
- has_direct_lpi
- Direct LPI 지원 여부
참고
- Interrupts -1- (Interrupt Controller) | 문c
- Interrupts -2- (irq chip) | 문c
- Interrupts -3- (irq domain) | 문c
- Interrupts -4- (Top-Half & Bottom-Half) | 문c
- Interrupts -5- (Softirq) | 문c
- Interrupts -6- (IPI Cross-call) | 문c
- Interrupts -7- (Workqueue 1) | 문c
- Interrupts -8- (Workqueue 2) | 문c
- Interrupts -9- (GIC v3 Driver) | 문c – 현재 글
- Interrupts -10- (irq partition) | 문c
- Interrupts -11- (RPI2 IC Driver) | 문c
- Interrupts -12- (irq desc) | 문c
- KVM PCIe/MSI Passthrough on Arm/Arm64 (2016) | Eric Auger
- ARM® Interrupt Virtualization | ARM – 다운로드 pdf
- GICv3 and GICv4 Software Overview | ARM – 다운로드 pdf