<kernel v5.4>
IRQ 디스크립터
IRQ 디스크립터를 관리하는 두 가지 방법
CONFIG_SPARSE_IRQ 커널 옵션을 사용유무에 따라 IRQ 번호를 관리하는 방법이 두 가지로 나뉜다.
- Sparse IRQ
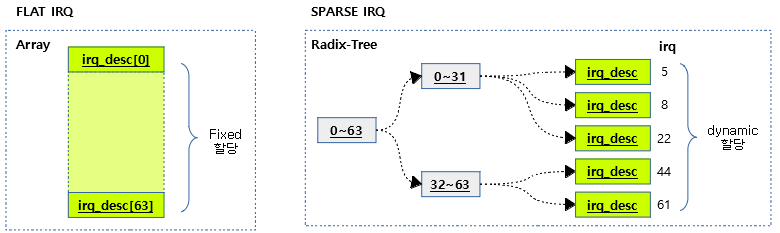
- 커널 옵션을 사용하는 경우 필요한 IRQ 번호에 대한 irq_desc 구조체를 동적으로 할당하고 Radix Tree를 사용하여 관리한다.
- arm64 시스템은 기본적으로 CONFIG_SPARSE_IRQ 커널 옵션을 구성하여 사용한다.
- 관련 함수
- irq_alloc_desc*()
- irq_free_desc*()
- Flat IRQ
- 커널 옵션을 사용하지 않는 경우 max IRQ 번호만큼 irq_dest 구조체 배열을 컴파일 시 정적으로 할당하여 사용한다.
NR_IRQS vs nr_irqs
NR_IRQS는 컴파일 타임에 지정되는 irq 수이고, nr_irqs는 런타임에 결정되어 사용되는 irq 수이다.
- NR_CPUS vs nr_cpus와 동일하게 사용된다.
early irq 초기화
1) Sparse IRQ
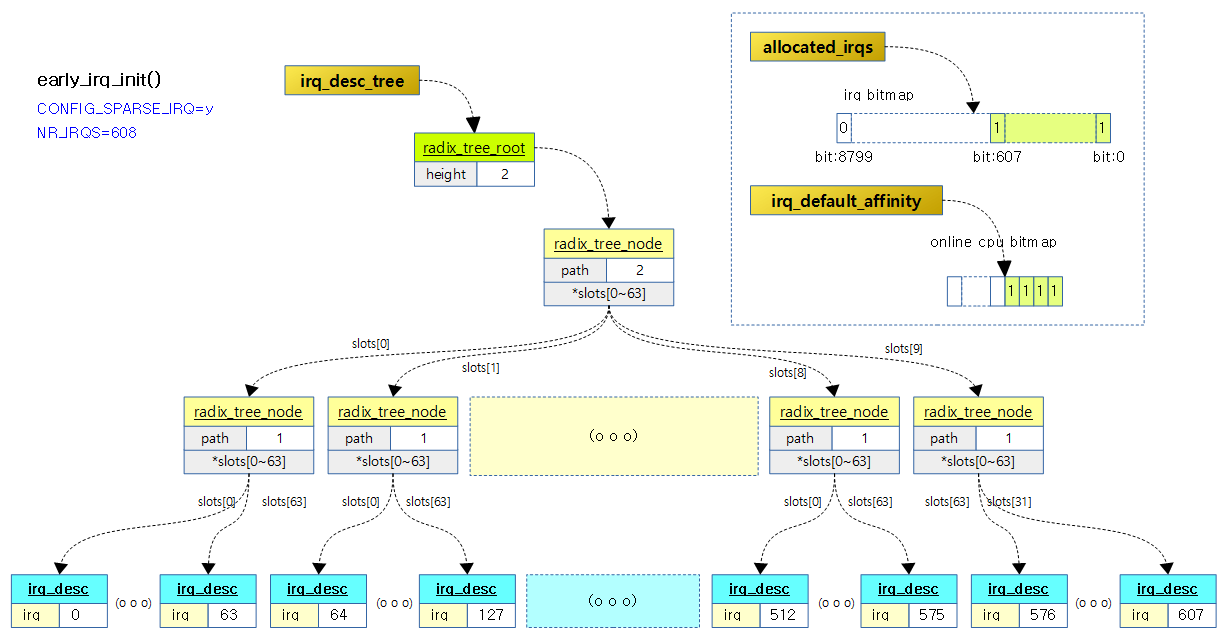
early_irq_init() – Sparse
kernel/irq/irqdesc.c
#ifdef CONFIG_SPARSE_IRQ
int __init early_irq_init(void)
{
int i, initcnt, node = first_online_node;
struct irq_desc *desc;
init_irq_default_affinity();
/* Let arch update nr_irqs and return the nr of preallocated irqs */
initcnt = arch_probe_nr_irqs();
printk(KERN_INFO "NR_IRQS: %d, nr_irqs: %d, preallocated irqs: %d\n",
NR_IRQS, nr_irqs, initcnt);
if (WARN_ON(nr_irqs > IRQ_BITMAP_BITS))
nr_irqs = IRQ_BITMAP_BITS;
if (WARN_ON(initcnt > IRQ_BITMAP_BITS))
initcnt = IRQ_BITMAP_BITS;
if (initcnt > nr_irqs)
nr_irqs = initcnt;
for (i = 0; i < initcnt; i++) {
desc = alloc_desc(i, node, 0, NULL, NULL);
set_bit(i, allocated_irqs);
irq_insert_desc(i, desc);
}
return arch_early_irq_init();
}
#endif
irq 디스크립터를 sparse하게 관리할 수 있는 radix 트리를 구성하고 초기화한다.
- 코드 라인 7에서 모든 cpu를 대상으로 사용하도록 전역 irq_default_affinity 변수에 cpu 비트맵 매스크를 할당하고 모두 1로 설정한다.
- 코드 라인 10에서 사용할 최대 irq 갯수를 알아온다.
- 코드 라인 11~12에서 컴파일 때 지정한 최대 NR_IRQS 값과 재조정된 nr_irqs 값, 그리고 아키텍처에 따라 미리 할당해야 할 irq 수 등을 알아와 로그 정보로 출력한다.
- 예) “NR_IRQS: 64, nr_irqs: 64, preallocated irqs: 0”
- 코드 라인 14~15에서 전역 nr_irqs가 IRQ_BITMAP_BITS를 초과하지 않도록 제한한다.
- IRQ_BITMAP_BITS
- sparse 옵션에서 NR_IRQS+8192개
- flat 옵션에서 NR_IRQS
- IRQ_BITMAP_BITS
- 코드 라인 17~18에서 initcnt가 IRQ_BITMAP_BITS를 초과하지 않도록 제한한다.
- 코드 라인 20~21에서 nr_irqs를 아키텍처에 따라 미리 할당해야 할 irq 수로 제한한다.
- 코드 라인 23~27에서 아키텍처에 따라 미리 할당해야 할 수(initcnt) 수 만큼 순회하며 irq 디스크립터를 할당한다. 전역 allocated_irqs 비트마스크의 irq 번호(0번부터 시작)에 해당하는 비트를 설정하고, 전역 irq_desc_tree에 추가한다.
- 코드 라인 28에서 아키텍처별로 early irq 초기화 루틴을 수행한다.
- 현재 x86, ia64 아키텍처에서 제공된다.
다음 그림은 sparse하게 irq 디스크립터가 관리되는 모습을 보여준다.
2) Flat IRQ
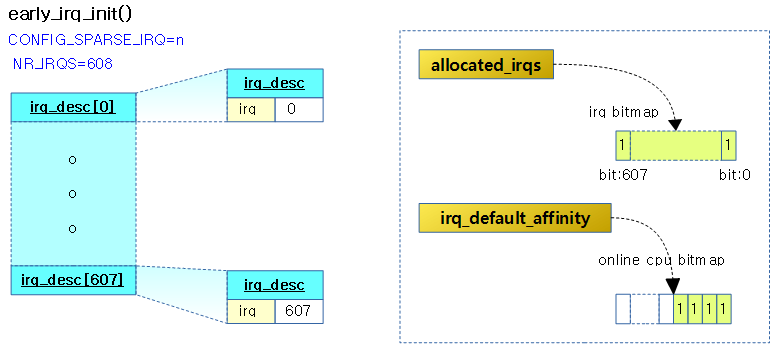
early_irq_init() – Flat
kernel/irq/irqdesc.c
#else /* !CONFIG_SPARSE_IRQ */
struct irq_desc irq_desc[NR_IRQS] __cacheline_aligned_in_smp = {
[0 ... NR_IRQS-1] = {
.handle_irq = handle_bad_irq,
.depth = 1,
.lock = __RAW_SPIN_LOCK_UNLOCKED(irq_desc->lock),
}
};
int __init early_irq_init(void)
{
int count, i, node = first_online_node;
struct irq_desc *desc;
init_irq_default_affinity();
printk(KERN_INFO "NR_IRQS:%d\n", NR_IRQS);
desc = irq_desc;
count = ARRAY_SIZE(irq_desc);
for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {
desc[i].kstat_irqs = alloc_percpu(unsigned int);
alloc_masks(&desc[i], node);
raw_spin_lock_init(&desc[i].lock);
lockdep_set_class(&desc[i].lock, &irq_desc_lock_class);
mutex_init(&desc[i].request_mutex);
desc_set_defaults(i, &desc[i], node, NULL);
}
return arch_early_irq_init();
}
#endif
irq 디스크립터를 flat하게 관리하도록 전역 irq_desc[] 배열을 초기화한다.
- 코드 라인 15에서 모든 cpu를 대상으로 사용하도록 전역 irq_default_affinity 변수에 cpu 비트맵 매스크를 할당하고 모두 1로 설정한다.
- 코드 라인 17에서 컴파일 때 지정한 최대 NR_IRQS 값을 로그 정보로 출력한다.
- 예) “NR_IRQS: 64”
- 코드 라인 19~29에서 NR_IRQS 수만큼 순회하며 irq 디스크립터를 초기화한다.
- 코드 라인 30에서 아키텍처별로 early irq 초기화 루틴을 수행한다.
- 현재 x86, ia64 아키텍처에서 제공된다.
다음 그림은 flat하게 irq 디스크립터가 관리되는 모습을 보여준다.
irq affinity
“irqaffinity=” 커널 파라미터 설정
irq_affinity_setup()
kernel/irq/irqdesc.c
static int __init irq_affinity_setup(char *str)
{
alloc_bootmem_cpumask_var(&irq_default_affinity);
cpulist_parse(str, irq_default_affinity);
/*
* Set at least the boot cpu. We don't want to end up with
* bugreports caused by random comandline masks
*/
cpumask_set_cpu(smp_processor_id(), irq_default_affinity);
return 1;
}
__setup("irqaffinity=", irq_affinity_setup);
“irqaffinity=<cpu ranges>” 커널 파라미터를 설정하여 irq를 처리할 수 있는 cpu를 지정하며, 이외에 기본적으로 boot cpu도 포함시킨다.
- 예) “irqaffinity=0-1,6-7”
디폴트 irq affinity 초기화
init_irq_default_affinity()
kernel/irq/irqdesc.c
static void __init init_irq_default_affinity(void)
{
if (!cpumask_available(irq_default_affinity))
zalloc_cpumask_var(&irq_default_affinity, GFP_NOWAIT);
if (cpumask_empty(irq_default_affinity))
cpumask_setall(irq_default_affinity);
}
“irqaffinity=” 커널 파라미터가 설정되지 않은 경우 디폴트로 모든 cpu에서 동작하도록 제한하지 않는다.
- 코드 라인 3~4에서 할당 방식의 cpu 비트맵 마스크인 경우 비트맵 마스크의 메모리를 할당한다.
- 코드 라인 5~6에서 디폴트 affinity가 설정되지 않은 경우에 한하여 모든 cpu에서 동작하도록 모두 1로 설정한다.
이 루틴은 해당 시스템의 인터럽트 컨트롤러를 초기화하고 각각의 인터럽트 번호에 따른 핸들러들을 준비하는 과정이다. 인터럽트 컨트롤러는 시스템마다 다른 각각의 하드웨어를 사용하므로 분석을하고자 하는 시스템의 하드웨어에 대한 지식이 필요한다. 따라서 각 시스템에서 사용하는 인터럽트 컨틀롤러의 데이터 시트를 참고하기 바란다.
리눅스 커널에서 구현 방법은 크게 다음과 같이 두 가지로 나뉜다.
- 아키텍처 전용 머신 코드를 수행하여 인터럽트 컨트롤러를 초기화하고 핸들러를 구성하는 방법
- arch/arm/mach-로 시작하는 디렉토리
- 대부분의 임베디드 시스템에서 처음 사용된 방식으로 곧장 각 머신의 인터럽트 컨트롤러 설정 등이 구현되어 있다.
-
- rpi 및 rp2 예)
- 내부 인터럽트 초기화 함수는 Device Tree를 사용한다.
- 커널 v4.4 부터는 지원되지 않는다.
- rpi 및 rp2 예)
-
- Device Tree에 설정된 내용을 분석하여 해당 드라이버를 구동하고 인터럽트 컨트롤러 하드웨어를 초기화하고 핸들러를 구성하는 방법
- kernel/chip.c (헬퍼) -> drivers/irqchip 디렉토리의 각 인터럽트 컨트롤러 드라이버
- irq_domain 등을 사용하여 리눅스 irq와 hw irq의 매핑을 지원하는 구조로 복잡해졌지만 점차 시스템들이 이 방향으로 구성하고 있다.
- arm64도 Device Tree 구성을 읽어 인터럽트 초기화 함수들을 호출한다.
- rpi 및 rpi2 예)
- 커널 v4.4 부터 지원하기 시작하였다.
- kernel/chip.c (헬퍼) -> drivers/irqchip 디렉토리의 각 인터럽트 컨트롤러 드라이버
VMAP Stack 지원
64비트 시스템의 경우 vmalloc 공간이 충분하기 때문에 cpu마다 stack 공간으로 vmalloc 공간을 사용할 수 있도록 지원한다.
- 현재 x86, s390, arm64 아키텍처에 적용되어 있다.
- 참고: arm64: add basic VMAP_STACK support (2017, v4.14-rc1)
IRQ 초기화
init_IRQ() – ARM64
arch/arm64/kernel/irq.c
void __init init_IRQ(void)
{
init_irq_stacks();
irqchip_init();
if (!handle_arch_irq)
panic("No interrupt controller found.");
if (system_uses_irq_prio_masking()) {
/*
* Now that we have a stack for our IRQ handler, set
* the PMR/PSR pair to a consistent state.
*/
WARN_ON(read_sysreg(daif) & PSR_A_BIT);
local_daif_restore(DAIF_PROCCTX_NOIRQ);
}
}
인터럽트 처리 핸들러를 위해 인터럽트 컨트롤러의 준비 및 필요한 설정 수행한다.
- 코드 라인 3에서 per-cpu irq용 스택을 할당하여 준비한다.
- 코드 라인 4~6에서 인터럽트 컨트롤러를 초기화하기 위한 irqchip 초기화를 수행한다.
- 참고: Interrupts -2- (irq chip) | 문c
- 코드 라인 8~15에서 시스템이 irq priority 마스킹을 사용할 수 있는 경우 irq를 블럭한다. 단 Pesudo-NMI는 허용한다.
init_irq_stacks()
arch/arm64/kernel/irq.c
#ifdef CONFIG_VMAP_STACK
static void init_irq_stacks(void)
{
int cpu;
unsigned long *p;
for_each_possible_cpu(cpu) {
p = arch_alloc_vmap_stack(IRQ_STACK_SIZE, cpu_to_node(cpu));
per_cpu(irq_stack_ptr, cpu) = p;
}
}
#else
/* irq stack only needs to be 16 byte aligned - not IRQ_STACK_SIZE aligned. */
DEFINE_PER_CPU_ALIGNED(unsigned long [IRQ_STACK_SIZE/sizeof(long)], irq_stack);
static void init_irq_stacks(void)
{
int cpu;
for_each_possible_cpu(cpu)
per_cpu(irq_stack_ptr, cpu) = per_cpu(irq_stack, cpu);
}
#endif
per-cpu irq 스택을 생성한다.
- 디폴트로 사용되는 CONFIG_VMAP_STACK 커널 옵션은 스택을 vmalloc 공간에 매핑하여 사용할 수 있게 한다.
init_IRQ() – ARM32
arch/arm/kernel/irq.c
void __init init_IRQ(void)
{
int ret;
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_OF) && !machine_desc->init_irq)
irqchip_init();
else
machine_desc->init_irq();
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_OF) && IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_CACHE_L2X0) &&
(machine_desc->l2c_aux_mask || machine_desc->l2c_aux_val)) {
if (!outer_cache.write_sec)
outer_cache.write_sec = machine_desc->l2c_write_sec;
ret = l2x0_of_init(machine_desc->l2c_aux_val,
machine_desc->l2c_aux_mask);
if (ret)
pr_err("L2C: failed to init: %d\n", ret);
}
uniphier_cache_init();
}
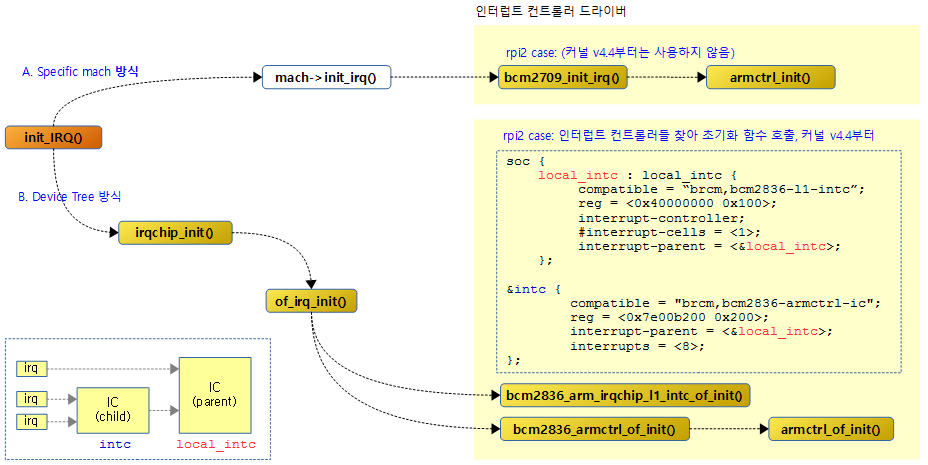
인터럽트 처리 핸들러를 위해 인터럽트 컨트롤러의 준비 및 필요한 설정 수행한다. 시스템 구성에 따라 머신 디스크립터 또는 DTB 둘 중 하나의 방법을 사용하여 초기화 한다.
- 코드 라인 5~8에서 시스템이 Device Tree를 지원하면서 머신 디스크립터에서 init_irq 후크가 설정되어 있지 않으면 Device Tree를 위해 irqchip_init() 함수를 호출하고, 그렇지 않은 경우 머신 디스크립터에 준비한 init_irq 후크에 설정된 콜백 함수를 호출한다.
- rpi2 예)
- 머신의 init_irq에 등록한 bcm2709_init_irq() 함수를 호출한다.
- 참고: A new generic IRQ layer | LWN.net
- rpi2 예)
- 코드 라인 10~18에서 outer 캐시를 가진 시스템에 대해 초기화를 수행한다.
- DTB를 사용할 수 있는 커널에서 L2X0 캐시 컨트롤러를 사용하는 시스템이고 머신에 l2c_aux_mask 또는 l2_aux_val이 설정된 경우 outer 캐시에 대한 콜백함수를 준비하고 초기화 함수를 호출한다.
- 코드 라인 20에서 UniPhier outer 캐시 컨트롤러를 사용하는 시스템을 초기화한다.
arch/arm64/kernel/irq.c – arm64 참고
void __init init_IRQ(void)
{
irqchip_init();
if (!handle_arch_irq)
panic("No interrupt controller found.");
}
arm64에서는 DTB 만을 지원하므로 irqchip_init() 함수를 곧바로 호출한다.
인터럽트 컨트롤러 초기화
시스템에 따라 다양한 종류의 인터럽트 컨트롤러를 사용하는데 rpi2에서 사용하는 bcm2709용 인터럽트 컨트롤러 초기화 함수를 호출하기로 한다.
- Device Tree 미 사용시 (CONFIG_OF=n)
- rpi
- arch/arm/mach-bcm2708/bcm2708.c – bcm2708_init_irq()
- 내부 초기화 함수에서는 device tree를 사용한다.
- arch/arm/mach-bcm2708/bcm2708.c – bcm2708_init_irq()
- rp2
- arch/arm/mach-bcm2709/bcm2709.c – bcm2709_init_irq()
- 내부 초기화 함수에서는 device tree를 사용한다.
- arch/arm/mach-bcm2709/bcm2709.c – bcm2709_init_irq()
- rpi
- Device Tree 사용 시
- of_irq_init() 함수를 통해 Device Tree에 있는 인터럽트 컨트롤러 정보를 읽어오고 해당 드라이버의 초기화 함수들을 호출한다.
- GIC
- drivers/irqchip/irq-gic.c – gic_of_init()
- Exynos Combiner
- drivers/irqchip/exynos-combiner.c – combiner_of_init()
- rpi
- drivers/irqchip/irq-bcm2835.c – armctrl_of_init()
- rpi2
- 두 개의 드라이버를 사용한다. (커널 v4.4 부터 적용)
- drivers/irqchip/irq-bcm2835.c – bcm2836_armctrl_of_init()
- drivers/irqchip/irq-bcm2836.c – bcm2836_arm_irqchip_l1_intc_of_init()
- 두 개의 드라이버를 사용한다. (커널 v4.4 부터 적용)
IRQ 디스크립터 할당
irq_alloc_descs()
include/linux/irq.h
#define irq_alloc_descs(irq, from, cnt, node) \
__irq_alloc_descs(irq, from, cnt, node, THIS_MODULE, NULL)
요청 @irq 번호부터 @cnt 수 만큼 irq 디스크립터를 @node에 할당한다. 요청한 @irq 번호가 지정되지 않은 값(-1)이면 @from 번호부터 검색하여 배정한다. 그리고 현재 모듈을 irq 디스크립터의 owner로 설정한다.
irq_alloc_descs_from()
include/linux/irq.h
#define irq_alloc_descs_from(from, cnt, node) \
irq_alloc_descs(-1, from, cnt, node)
새로운 irq 번호로, @from에서 검색하여 @cnt 수 만큼 irq 디스크립터를 @node에 할당한다. 그리고 현재 모듈을 irq 디스크립터의 owner로 설정한다.
__irq_alloc_descs()
kernel/irq/irqdesc.c
/** * irq_alloc_descs - allocate and initialize a range of irq descriptors * @irq: Allocate for specific irq number if irq >= 0 * @from: Start the search from this irq number * @cnt: Number of consecutive irqs to allocate. * @node: Preferred node on which the irq descriptor should be allocated * @owner: Owning module (can be NULL) * @affinity: Optional pointer to an affinity mask array of size @cnt which * hints where the irq descriptors should be allocated and which * default affinities to use * * Returns the first irq number or error code */
int __ref
__irq_alloc_descs(int irq, unsigned int from, unsigned int cnt, int node,
struct module *owner, const struct irq_affinity_desc *affinity)
{
int start, ret;
if (!cnt)
return -EINVAL;
if (irq >= 0) {
if (from > irq)
return -EINVAL;
from = irq;
} else {
/*
* For interrupts which are freely allocated the
* architecture can force a lower bound to the @from
* argument. x86 uses this to exclude the GSI space.
*/
from = arch_dynirq_lower_bound(from);
}
mutex_lock(&sparse_irq_lock);
start = bitmap_find_next_zero_area(allocated_irqs, IRQ_BITMAP_BITS,
from, cnt, 0);
ret = -EEXIST;
if (irq >=0 && start != irq)
goto unlock;
if (start + cnt > nr_irqs) {
ret = irq_expand_nr_irqs(start + cnt);
if (ret)
goto unlock;
}
ret = alloc_descs(start, cnt, node, affinity, owner);
unlock:
mutex_unlock(&sparse_irq_lock);
return ret;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(__irq_alloc_descs);
요청 @irq 번호부터 @cnt 수 만큼 irq 디스크립터를 @node에 할당한다. 요청한 @irq 번호가 지정되지 않은 값(-1)이면 @from 번호부터 검색하여 배정한다. 그리고 현재 모듈을 irq 디스크립터의 owner로 설정한다.
- 코드 라인 7~8에서 @cnt가 지정되지 않은 경우 -EINVAL 에러로 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 10~13에서 @irq 번호(0번 이상)를 지정한 경우 검색 시작할 번호 @from에 @irq 번호를 대입한다. 단 @from이 고정 irq 번호보다 큰 경우 -EINVAL 에러로 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 14~21에서 @irq 번호(0번 이상)를 지정하지 않은 경우 새 irq 번호를 발부받기 위해 @from 부터 시작하도록 한다. 단 아키텍처에 따라 from 값이 바뀔 수 있다.
- x86 아키텍처에서는 GSI 공간을 피해야 한다.
- 코드 라인 25~26에서 인터럽트 할당 비트맵에서 @from 비트부터 연속된 @cnt 수 만큼의 할당되지 않은 비트를 찾는다.
- 참고: Bitmap Operations | 문c
- 예) 0b0000_0000_1111_0000_1111_0000
- from=5, cnt=2 -> start=8
- from=5, cnt=5 -> start=16
- 코드 라인 28~29에서 @irq 번호를 지정하였고, 찾은 시작 irq 번호와 다른 경우 -EEXIST 에러를 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 31~35에서 할당할 공간이 부족한 경우 irq 공간을 필요한 수 만큼 확장한다. 확장이 불가능한 경우 -EEXIST 에러를 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 36~39에서start irq 디스크립터 부터 @cnt 수 만큼 @node에 할당한다. 그리고 모듈 owner를 설정하고 start irq 번호를 반환한다.
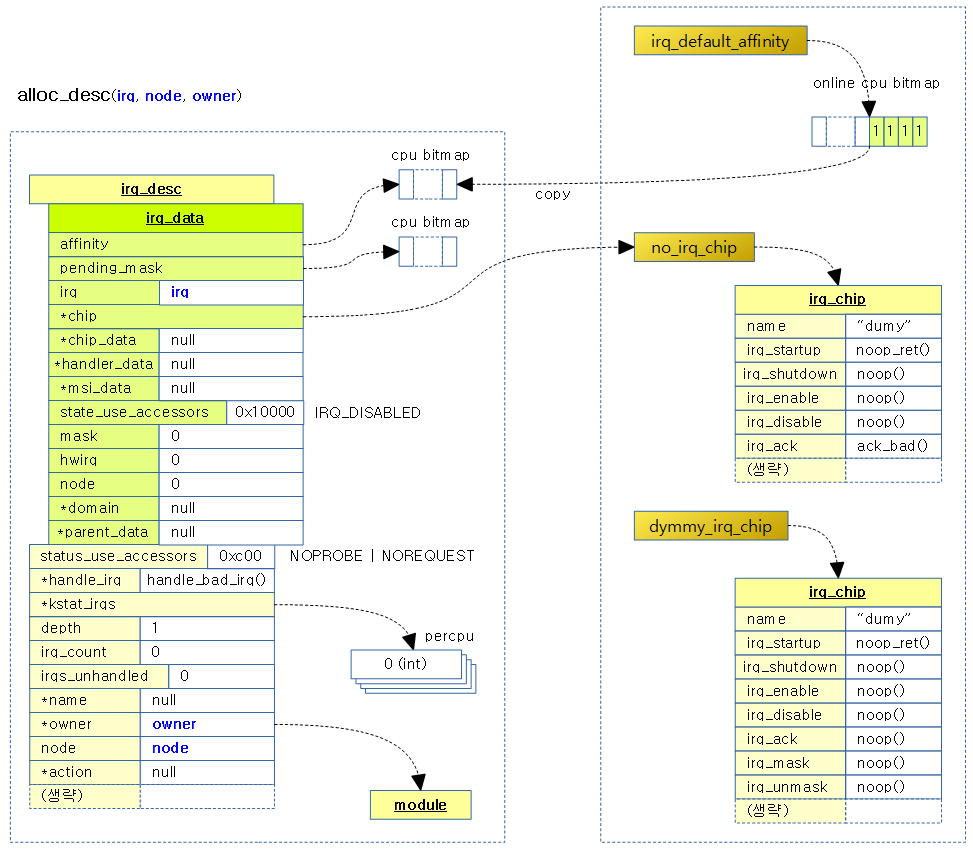
alloc_descs() – FLAT IRQ 용
kernel/irq/irqdesc.c
static inline int alloc_descs(unsigned int start, unsigned int cnt, int node,
const struct irq_affinity_desc *affinity,
struct module *owner)
{
u32 i;
for (i = 0; i < cnt; i++) {
struct irq_desc *desc = irq_to_desc(start + i);
desc->owner = owner;
}
bitmap_set(allocated_irqs, start, cnt);
return start;
}
flat irq의 경우 irq 디스크립터가 이미 준비되어 있으므로 별도로 생성할 필요 없고, 사용할 @start irq 번호부터 @cnt 수 만큼 할당 비트들만을 설정한다. 반환하는 값은 @start 값과 동일하다.
alloc_descs() – SPARSE IRQ 용
kernel/irq/irqdesc.c
static int alloc_descs(unsigned int start, unsigned int cnt, int node,
const struct irq_affinity_desc *affinity,
struct module *owner)
{
struct irq_desc *desc;
int i;
/* Validate affinity mask(s) */
if (affinity) {
for (i = 0; i < cnt; i++) {
if (cpumask_empty(&affinity[i].mask))
return -EINVAL;
}
}
for (i = 0; i < cnt; i++) {
const struct cpumask *mask = NULL;
unsigned int flags = 0;
if (affinity) {
if (affinity->is_managed) {
flags = IRQD_AFFINITY_MANAGED |
IRQD_MANAGED_SHUTDOWN;
}
mask = &affinity->mask;
node = cpu_to_node(cpumask_first(mask));
affinity++;
}
desc = alloc_desc(start + i, node, flags, mask, owner);
if (!desc)
goto err;
irq_insert_desc(start + i, desc);
irq_sysfs_add(start + i, desc);
irq_add_debugfs_entry(start + i, desc);
}
bitmap_set(allocated_irqs, start, cnt);
return start;
err:
for (i--; i >= 0; i--)
free_desc(start + i);
return -ENOMEM;
}
@start irq 디스크립터 부터 @cnt 수 만큼 irq 디스크립터를 @node에 할당한다. 그리고 모듈 owner를 설정한 후 radix tree에 추가한다. 반환 값은 @start irq 번호이다.
- 코드 라인 9~14에서 @affinity가 지정된 경우 @cnt 수만큼 @affinity[i].mask가 모두 설정되어 있는지 확인한다. 하나라도 설정되지 않은 경우 -EINVAL 에러를 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 16에서 에서 인터럽트 수인 @cnt 수만큼 반복한다.
- 코드 라인 20~28에서 @affinity 정보가 있는 경우 인자로 받은 @node 대신 affinity[i].mask에 지정된 첫 cpu에 대한 노드를 사용한다.
- affinity++하여 다음 구조체를 선택한다.
- 코드 라인 30~32에서 @start+i 번호의 irq 디스크립터를 @node에 할당한다. 그리고 모듈 owner를 설정한다.
- 코드 라인 33에서 할당한 irq 디스크립터를 radix tree에 추가한다.
- 코드 라인 34에서 할당한 irq 디스크립터를 sysfs에 추가한다.
- 코드 라인 35에서 할당한 riq 디스크립터를 debugfs에 추가한다.
- 코드 라인 37에서 전역 allocated_irqs 비트맵에 할당된 인터럽트 번호에 해당하는 비트들을 설정한다.
- 코드 라인 38에서 성공 하였으므로 @start irq 번호를 반환한다.
다음 그림은 하나의 irq descriptor가 할당되고 초기화되는 모습을 보여준다.
alloc_masks()
kernel/irq/irqdesc.c
static int alloc_masks(struct irq_desc *desc, int node)
{
if (!zalloc_cpumask_var_node(&desc->irq_common_data.affinity,
GFP_KERNEL, node))
return -ENOMEM;
#ifdef CONFIG_GENERIC_IRQ_EFFECTIVE_AFF_MASK
if (!zalloc_cpumask_var_node(&desc->irq_common_data.effective_affinity,
GFP_KERNEL, node)) {
free_cpumask_var(desc->irq_common_data.affinity);
return -ENOMEM;
}
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_GENERIC_PENDING_IRQ
if (!zalloc_cpumask_var_node(&desc->pending_mask, GFP_KERNEL, node)) {
#ifdef CONFIG_GENERIC_IRQ_EFFECTIVE_AFF_MASK
free_cpumask_var(desc->irq_common_data.effective_affinity);
#endif
free_cpumask_var(desc->irq_common_data.affinity);
return -ENOMEM;
}
#endif
return 0;
}
irq 디스크립터에서 사용하는 여러 cpu 비트맵 마스크를 할당받는다.
desc_set_defaults()
kernel/irq/irqdesc.c
static void desc_set_defaults(unsigned int irq, struct irq_desc *desc, int node,
const struct cpumask *affinity, struct module *owner)
{
int cpu;
desc->irq_common_data.handler_data = NULL;
desc->irq_common_data.msi_desc = NULL;
desc->irq_data.common = &desc->irq_common_data;
desc->irq_data.irq = irq;
desc->irq_data.chip = &no_irq_chip;
desc->irq_data.chip_data = NULL;
irq_settings_clr_and_set(desc, ~0, _IRQ_DEFAULT_INIT_FLAGS);
irqd_set(&desc->irq_data, IRQD_IRQ_DISABLED);
irqd_set(&desc->irq_data, IRQD_IRQ_MASKED);
desc->handle_irq = handle_bad_irq;
desc->depth = 1;
desc->irq_count = 0;
desc->irqs_unhandled = 0;
desc->tot_count = 0;
desc->name = NULL;
desc->owner = owner;
for_each_possible_cpu(cpu)
*per_cpu_ptr(desc->kstat_irqs, cpu) = 0;
desc_smp_init(desc, node, affinity);
}
요청한 @irq 번호에 해당하는 irq 디스크립터 @desc를 디폴트 값으로 초기화하고, @affinity와 @owner를 지정한다.
- 코드 라인 6에서 인터럽트 핸들러 데이터를 null로 초기화한다.
- 코드 라인 7에서 msi 디스크립터가 없는 상태로 초기화한다.
- 코드 라인 9에서 irq 디스크립터의 하이라키를 표현하는 irq_data의 가장 상위에서 irq 디스크립터에 있는 irq 공통 데이터 구조체를 가리킨다.
- 코드 라인 10에서 irq 디스크립터에 인자로 받은 @irq 번호를 지정한다.
- 코드 라인 11~12에서 irq를 처리할 irqchip과 chip_data는 지정되지 않은 상태로 초기화한다.
- 지정되지 않은 경우 no_irq_chip() 함수를 가리킨다.
- 코드 라인 13에서 irq 디스크립터의 플래그를 모드 제거하고, 디폴트 초기화 플래그를 설정한다.
- arm32: IRQ_NOPROBE | IRQ_NOREQUEST
- arm64: 없음
- 코드 라인 14~15에서 irq 디스크립터에 disabled, masked 플래그들을 설정한다.
- 코드 라인 16에서 인터럽트 핸들러 함수를 지정하지 않은 상태로 초기화한다.
- 지정되지 않은 경우 handle_bad_irq() 함수를 가리킨다.
- 코드 라인 17~24에서 irq 디스크립터의 각종 값들을 초기화한다.
- 코드 라인 25에서 irq 디스크립터에 @affinity를 적용한다. 지정되지 않은 경우 전역 irq_default_affinity 값을 적용한다.
irq_settings_clr_and_set()
kernel/irq/settings.h
static inline void
irq_settings_clr_and_set(struct irq_desc *desc, u32 clr, u32 set)
{
desc->status_use_accessors &= ~(clr & _IRQF_MODIFY_MASK);
desc->status_use_accessors |= (set & _IRQF_MODIFY_MASK);
}
irq 디스크립터의 status_use_accessors에서 인수 @clr로 요청한 비트들을 clear하고 인수 @set으로 요청한 비트들을 설정한다.
irqd_set()
kernel/irq/internals.h
static inline void irqd_set(struct irq_data *d, unsigned int mask)
{
d->state_use_accessors |= mask;
}
irq 디스크립터의 status_use_accessors에서 인수 @mask로 요청한 비트들을 설정한다.
desc_smp_init()
kernel/irq/irqdesc.c
static void desc_smp_init(struct irq_desc *desc, int node,
const struct cpumask *affinity)
{
if (!affinity)
affinity = irq_default_affinity;
cpumask_copy(desc->irq_common_data.affinity, affinity);
#ifdef CONFIG_GENERIC_PENDING_IRQ
cpumask_clear(desc->pending_mask);
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_NUMA
desc->irq_common_data.node = node;
#endif
}
요청한 irq 디스크립터 @desc에서 사용 가능한 cpu들을 지정하기 위해 @affinity 비트마스크를 지정한다. @affinity가 null인 경우 디폴트 affinity가 사용된다.
irq_insert_desc()
kernel/irq/irqdesc.c
static void irq_insert_desc(unsigned int irq, struct irq_desc *desc)
{
radix_tree_insert(&irq_desc_tree, irq, desc);
}
전역 irq_desc_tree에 요청 @irq 번호를 키로 irq 디스크립터 @desc를 추가한다.
Local IRQ 제어
- local
- 현재 cpu
- raw
- 커널 옵션에 따른 논리적인 구현의 차이
- arch
- 아키텍처 의존적인 구현의 차이
Local IRQ Disable
local_irq_disable()
include/linux/irqflags.h
#define local_irq_disable() do { raw_local_irq_disable(); } while (0)
현재 CPU의 인터럽트를 disable
raw_local_irq_disable()
include/linux/irqflags.h
#define raw_local_irq_disable() arch_local_irq_disable()
arch_local_irq_disable() – ARM32
arch/arm/include/asm/irqflags.h
static inline void arch_local_irq_disable(void)
{
asm volatile(
" cpsid i @ arch_local_irq_disable"
:
:
: "memory", "cc");
}
arch_local_irq_disable() – ARM64
arch/arm64/include/asm/irqflags.h
static inline void arch_local_irq_disable(void)
{
if (system_has_prio_mask_debugging()) {
u32 pmr = read_sysreg_s(SYS_ICC_PMR_EL1);
WARN_ON_ONCE(pmr != GIC_PRIO_IRQON && pmr != GIC_PRIO_IRQOFF);
}
asm volatile(ALTERNATIVE(
"msr daifset, #2 // arch_local_irq_disable",
__msr_s(SYS_ICC_PMR_EL1, "%0"),
ARM64_HAS_IRQ_PRIO_MASKING)
:
: "r" ((unsigned long) GIC_PRIO_IRQOFF)
: "memory");
}
- Pesudo-NMI를 지원하는 경우 Priority Mask 레지스터를 사용하여 디폴트 irq만 disable하고, nmi에 사용하는 irq는 통과시키는 기법을 사용한다.
- Pesudo-NMI를 지원하지 않는 경우 PSTATE.I 플래그를 설정하여 irq를 disable 한다.
Local IRQ Enable
local_irq_enable()
include/linux/irqflags.h”
#define local_irq_enable() do { raw_local_irq_enable(); } while (0)
현재 CPU의 인터럽트를 enable
raw_local_irq_enaable()
include/linux/irqflags.h
#define raw_local_irq_enable() arch_local_irq_enable()
arch_local_irq_enable() – ARM32
arch/arm/include/asm/irqflags.h
static inline void arch_local_irq_enable(void)
{
asm volatile(
" cpsie i @ arch_local_irq_enable"
:
:
: "memory", "cc");
}
arch_local_irq_enable() – ARM64
arch/arm64/include/asm/irqflags.h
static inline void arch_local_irq_enable(void)
{
if (system_has_prio_mask_debugging()) {
u32 pmr = read_sysreg_s(SYS_ICC_PMR_EL1);
WARN_ON_ONCE(pmr != GIC_PRIO_IRQON && pmr != GIC_PRIO_IRQOFF);
}
asm volatile(ALTERNATIVE(
"msr daifclr, #2 // arch_local_irq_enable\n"
"nop",
__msr_s(SYS_ICC_PMR_EL1, "%0")
"dsb sy",
ARM64_HAS_IRQ_PRIO_MASKING)
:
: "r" ((unsigned long) GIC_PRIO_IRQON)
: "memory");
}
- Pesudo-NMI를 지원하는 경우 Priority Mask 레지스터를 사용하여 디폴트 irq와 nmi에 사용하는 irq 모두 통과시킨다.
- Pesudo-NMI를 지원하지 않는 경우 PSTATE.I 플래그를 클리어하여 irq를 enable 한다.
Local IRQ 백업
local_irq_save()
include/linux/irqflags.h
#define local_irq_save(flags) \
do { \
raw_local_irq_save(flags); \
} while (0)
현재 CPU의 irq 상태를 백업하고 disable 한다.
raw_local_irq_save()
include/linux/irqflags.h
#define raw_local_irq_save(flags) \
do { \
typecheck(unsigned long, flags); \
flags = arch_local_irq_save(); \
} while (0)
현재 CPU의 cpsr값을 변수에 저장한다.
arch_local_irq_save() – ARM32
arch/arm/include/asm/irqflags.h
static inline unsigned long arch_local_irq_save(void)
{
unsigned long flags;
asm volatile(
" mrs %0, " IRQMASK_REG_NAME_R " @ arch_local_irq_save\n"
" cpsid i"
: "=r" (flags) : : "memory", "cc");
return flags;
}
arch_local_irq_save() – ARM64
arch/arm64/include/asm/irqflags.h
static inline unsigned long arch_local_irq_save(void)
{
unsigned long flags;
flags = arch_local_save_flags();
/*
* There are too many states with IRQs disabled, just keep the current
* state if interrupts are already disabled/masked.
*/
if (!arch_irqs_disabled_flags(flags))
arch_local_irq_disable();
return flags;
}
arch_local_irq_save_flags() – ARM64
arch/arm64/include/asm/irqflags.h
static inline unsigned long arch_local_save_flags(void)
{
unsigned long flags;
asm volatile(ALTERNATIVE(
"mrs %0, daif",
__mrs_s("%0", SYS_ICC_PMR_EL1),
ARM64_HAS_IRQ_PRIO_MASKING)
: "=&r" (flags)
:
: "memory");
return flags;
}
Local IRQ 복구
local_irq_restore()
include/linux/irqflags.h
#define local_irq_restore(flags) do { raw_local_irq_restore(flags); } while (0)
현재 cpu에서 백업해둔 irq 상태를 복구한다.
raw_local_irq_restore()
#define raw_local_irq_restore(flags) \
do { \
typecheck(unsigned long, flags); \
arch_local_irq_restore(flags); \
} while (0)
변수에 저장된 cpsr값을 읽어 현재 CPU의 cpsr_c 부분을 변경(현재 CPU의 인터럽트 상태를 저장되었던 상태로 되돌림)
arch_local_irq_restore() – ARM32
arch/arm/include/asm/irqflags.h
static inline void arch_local_irq_restore(unsigned long flags)
{
asm volatile(
" msr " IRQMASK_REG_NAME_W ", %0
:
: "r" (flags)
: "memory", "cc");
}
#define IRQMASK_REG_NAME_W "cpsr_c"
arch_local_irq_restore() – ARM64
arch/arm64/include/asm/irqflags.h
static inline void arch_local_irq_restore(unsigned long flags)
{
asm volatile(ALTERNATIVE(
"msr daif, %0\n"
"nop",
__msr_s(SYS_ICC_PMR_EL1, "%0")
"dsb sy",
ARM64_HAS_IRQ_PRIO_MASKING)
:
: "r" (flags)
: "memory");
}
APIs
irq 디스크립터 할당 & 해제
- irq_alloc_descs()
- irq_alloc_descs_from()
- __irq_alloc_descs()
- alloc_descs()
- irq_free_descs()
- irq_alloc_hwirqs()
- irq_free_hwirqs()
irq 핸들러
- generic_handle_irq()
- generic_handle_irq_desc()
- __handle_domain_irq()
- __irq_set_preflow_handler()
기타
- irq_data_to_desc()
- irq_desc_get_irq()
- irq_desc_get_irq_data()
- irq_desc_get_chip()
- irq_desc_get_chip_data()
- irq_desc_get_handler_data()
- irq_desc_has_action()
- irq_has_action()
- irq_set_handler_locked()
- irq_set_chip_handler_name_locked()
- irq_balancing_disabled()
- irq_is_percpu()
- irq_is_percpu_devid()
- irq_get_percpu_devid_partition()
구조체 및 데이터
IRQ 디스크립터
include/linux/irqdesc.h
/** * struct irq_desc - interrupt descriptor * @irq_common_data: per irq and chip data passed down to chip functions * @kstat_irqs: irq stats per cpu * @handle_irq: highlevel irq-events handler * @preflow_handler: handler called before the flow handler (currently used by sparc) * @action: the irq action chain * @status: status information * @core_internal_state__do_not_mess_with_it: core internal status information * @depth: disable-depth, for nested irq_disable() calls * @wake_depth: enable depth, for multiple irq_set_irq_wake() callers * @tot_count: stats field for non-percpu irqs * @irq_count: stats field to detect stalled irqs * @last_unhandled: aging timer for unhandled count * @irqs_unhandled: stats field for spurious unhandled interrupts * @threads_handled: stats field for deferred spurious detection of threaded handlers * @threads_handled_last: comparator field for deferred spurious detection of theraded handlers * @lock: locking for SMP * @affinity_hint: hint to user space for preferred irq affinity * @affinity_notify: context for notification of affinity changes * @pending_mask: pending rebalanced interrupts * @threads_oneshot: bitfield to handle shared oneshot threads * @threads_active: number of irqaction threads currently running * @wait_for_threads: wait queue for sync_irq to wait for threaded handlers * @nr_actions: number of installed actions on this descriptor * @no_suspend_depth: number of irqactions on a irq descriptor with * IRQF_NO_SUSPEND set * @force_resume_depth: number of irqactions on a irq descriptor with * IRQF_FORCE_RESUME set * @rcu: rcu head for delayed free * @kobj: kobject used to represent this struct in sysfs * @request_mutex: mutex to protect request/free before locking desc->lock * @dir: /proc/irq/ procfs entry * @debugfs_file: dentry for the debugfs file * @name: flow handler name for /proc/interrupts output */
struct irq_desc {
struct irq_common_data irq_common_data;
struct irq_data irq_data;
unsigned int __percpu *kstat_irqs;
irq_flow_handler_t handle_irq;
#ifdef CONFIG_IRQ_PREFLOW_FASTEOI
irq_preflow_handler_t preflow_handler;
#endif
struct irqaction *action; /* IRQ action list */
unsigned int status_use_accessors;
unsigned int core_internal_state__do_not_mess_with_it;
unsigned int depth; /* nested irq disables */
unsigned int wake_depth; /* nested wake enables */
unsigned int tot_count;
unsigned int irq_count; /* For detecting broken IRQs */
unsigned long last_unhandled; /* Aging timer for unhandled count */
unsigned int irqs_unhandled;
atomic_t threads_handled;
int threads_handled_last;
raw_spinlock_t lock;
struct cpumask *percpu_enabled;
const struct cpumask *percpu_affinity;
#ifdef CONFIG_SMP
const struct cpumask *affinity_hint;
struct irq_affinity_notify *affinity_notify;
#ifdef CONFIG_GENERIC_PENDING_IRQ
cpumask_var_t pending_mask;
#endif
#endif
unsigned long threads_oneshot;
atomic_t threads_active;
wait_queue_head_t wait_for_threads;
#ifdef CONFIG_PM_SLEEP
unsigned int nr_actions;
unsigned int no_suspend_depth;
unsigned int cond_suspend_depth;
unsigned int force_resume_depth;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_PROC_FS
struct proc_dir_entry *dir;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_GENERIC_IRQ_DEBUGFS
struct dentry *debugfs_file;
const char *dev_name;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_SPARSE_IRQ
struct rcu_head rcu;
struct kobject kobj;
#endif
struct mutex request_mutex;
int parent_irq;
struct module *owner;
const char *name;
} ____cacheline_internodealigned_in_smp;
한 개의 irq 디스크립터이다.
- irq_common_data
- irq 공통 정보
- 아래 irq_data 같이 부모 관계로 연결되는 곳에서도 공통으로 사용되는 정보이다.
- irq_data
- chip 기능에 전달되는 irq와 chip 데이터
- 이 구조체들은 하이라키 도메인 구성된 경우 부모 관계로 연결된다.
- *kstat_irqs
- cpu 별 irq 통계 카운터
- handle_irq
- 하이 레벨 irq 이벤트 핸들러
- preflow_handler
- preflow 핸들러
- *action
- irq action 체인으로 유저 디바이스가 요청한 인터럽트 핸들러가 추가되는 리스트이다.
- status_use_accessors
- irq 상태 정보
- core_internal_state__do_not_mess_with_it
- 코어 내부 상태 정보
- irqd->state으로 표현( state가 매크로)
- depth
- 네스트된 irq_disable() 호출을 위한 disable depth
- wake_depth
- 다중 irq_set_irq_wake() 호출을 위한 enable depth
- irq_count
- stalled irq들을 감지하기 위한 상태 필드
- last_unhandled
- 언핸들드 카운트를 위한 aging 타이머
- irqs_unhandled
- 가짜 언핸들된 인터럽트들을 위한 상태 필드
- threads_handled
- 스레드 핸들러의 연기된 가짜 감지를 위한 상태 필드
- threads_handled_last
- 스레드 핸들러의 연기된 가짜 감지를 위한 비교 필드
- lock
- SMP lock
- *percpu_enabled
- cpu 비트마스크
- *percpu_affinity
- cpu 제한된 경우 cpu affinity를 표현한 비트마스크
- *affinity_hint
- 권장 irq affinity를 위한 user space 힌트
- 참고: genirq: Add CPU mask affinity hint
- *affinity_notify
- affnity가 변경 시 통지를 위한 context
- pending_mask
- 지연된 리밸런스된 인터럽트들
- threads_oneshot
- 공유 oneshot 스레드들을 다룰 비트필드
- 참고: genirq: Add oneshot support
- threads_active
- 현재 동작중인 irqaction 스레드의 수
- wait_for_threads
- 스레드된 핸들러를 위해 기다릴 sync_irq를 위한 대기큐
- nr_actions
- 이 irq 디스크립터에 설치된 액션 수
- no_suspend_depth
- IRQF_NO_SUSPEND 셋을 가진 irq 디스크립터의 irqactions 수
- cond_suspend_depth
- force_resume_depth
- IRQF_FORCE_RESUME 셋을 가진 irq 디스크립터의 irqactions 수
- dir
- /proc/irq/에 표시될 procfs 엔트리
- default로 irq 숫자 (예: /proc/irq/83)
- *debugfs_file
- 디버그용 (/sys/fs/debug)
- *dev_name
- 디버그용
- rcu
- kobj
- request_mutex
- parent_irq
- cascade 연결 시 부모 irq 번호
- *owner
- 모듈을 가리킨다.
- name
- /proc/interrupts에 출력될 flow 핸들러 이름
- 예) uart-pl011
irq_data 구조체
include/linux/irq.h
/** * struct irq_data - per irq chip data passed down to chip functions * @mask: precomputed bitmask for accessing the chip registers * @irq: interrupt number * @hwirq: hardware interrupt number, local to the interrupt domain * @common: point to data shared by all irqchips * @chip: low level interrupt hardware access * @domain: Interrupt translation domain; responsible for mapping * between hwirq number and linux irq number. * @parent_data: pointer to parent struct irq_data to support hierarchy * irq_domain * @chip_data: platform-specific per-chip private data for the chip * methods, to allow shared chip implementations */
struct irq_data {
u32 mask;
unsigned int irq;
unsigned long hwirq;
struct irq_common_data *common;
struct irq_chip *chip;
struct irq_domain *domain;
#ifdef CONFIG_IRQ_DOMAIN_HIERARCHY
struct irq_data *parent_data;
#endif
void *chip_data;
};
이 구조체는 irqchip들에 제공될 정보들이다. irq 디스크립터에 기본 내장되어 있고, 하이라키 도메인을 구성하는 경우 추가 생성되어 부모 관계로 연결된다.
- mask
- chip 레지스터들에 접근하기 위한 미리 계산된 비트마스크
- irq
- 리눅스가 관리하는 인터럽트 번호 (virq)
- hwirq
- 하드웨어 인터럽트 번호
- *common
- irq 디스크립터에 있는 공통 정보 구조체를 가리킨다.
- *chip
- 로우 레벨 인터럽트 컨트롤러 하드웨어 제어를 담당하는 irq_chip 구조체를 가리킨다.
- *domain
- irq 도메인을 가리킨다. (hwirq -> irq 변환)
- *parent_data
- 하이라키 irq 도메인을 지원하기 위한 부모 irq_data를 가리킨다.
- chip_data
- chip 메소드와 공유 chip 구현을 허락하기 위한 플랫폼 specific per-chip private 데이터
irq_common_data 구조체
include/linux/irq.h
/** * struct irq_common_data - per irq data shared by all irqchips * @state_use_accessors: status information for irq chip functions. * Use accessor functions to deal with it * @node: node index useful for balancing * @handler_data: per-IRQ data for the irq_chip methods * @affinity: IRQ affinity on SMP. If this is an IPI * related irq, then this is the mask of the * CPUs to which an IPI can be sent. * @effective_affinity: The effective IRQ affinity on SMP as some irq * chips do not allow multi CPU destinations. * A subset of @affinity. * @msi_desc: MSI descriptor * @ipi_offset: Offset of first IPI target cpu in @affinity. Optional. */
struct irq_common_data {
unsigned int __private state_use_accessors;
#ifdef CONFIG_NUMA
unsigned int node;
#endif
void *handler_data;
struct msi_desc *msi_desc;
cpumask_var_t affinity;
#ifdef CONFIG_GENERIC_IRQ_EFFECTIVE_AFF_MASK
cpumask_var_t effective_affinity;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_GENERIC_IRQ_IPI
unsigned int ipi_offset;
#endif
};
하이라키 irq 도메인을 구성하는 irq data들이 사용하는 irq 공통 정보이다.
- state_use_accessors
- irq chip 기능들에 제공할 irq 디스크립터의 accessor 정보
- node
- 노드 인덱스
- *handler_data
- irq_chip 메소드를 위한 per-IRQ 데이터
- *msi_desc
- MSI 디스크립터를 가리킨다.
- affinity
- SMP에서의 IRQ affinity
- effective_affinity
- ipi_offset
IRQ Data 상태
include/linux/irq.h
/* * Bit masks for irq_common_data.state_use_accessors * * IRQD_TRIGGER_MASK - Mask for the trigger type bits * IRQD_SETAFFINITY_PENDING - Affinity setting is pending * IRQD_ACTIVATED - Interrupt has already been activated * IRQD_NO_BALANCING - Balancing disabled for this IRQ * IRQD_PER_CPU - Interrupt is per cpu * IRQD_AFFINITY_SET - Interrupt affinity was set * IRQD_LEVEL - Interrupt is level triggered * IRQD_WAKEUP_STATE - Interrupt is configured for wakeup * from suspend * IRQD_MOVE_PCNTXT - Interrupt can be moved in process * context * IRQD_IRQ_DISABLED - Disabled state of the interrupt * IRQD_IRQ_MASKED - Masked state of the interrupt * IRQD_IRQ_INPROGRESS - In progress state of the interrupt * IRQD_WAKEUP_ARMED - Wakeup mode armed * IRQD_FORWARDED_TO_VCPU - The interrupt is forwarded to a VCPU * IRQD_AFFINITY_MANAGED - Affinity is auto-managed by the kernel * IRQD_IRQ_STARTED - Startup state of the interrupt * IRQD_MANAGED_SHUTDOWN - Interrupt was shutdown due to empty affinity * mask. Applies only to affinity managed irqs. * IRQD_SINGLE_TARGET - IRQ allows only a single affinity target * IRQD_DEFAULT_TRIGGER_SET - Expected trigger already been set * IRQD_CAN_RESERVE - Can use reservation mode */
enum {
IRQD_TRIGGER_MASK = 0xf,
IRQD_SETAFFINITY_PENDING = (1 << 8),
IRQD_ACTIVATED = (1 << 9),
IRQD_NO_BALANCING = (1 << 10),
IRQD_PER_CPU = (1 << 11),
IRQD_AFFINITY_SET = (1 << 12),
IRQD_LEVEL = (1 << 13),
IRQD_WAKEUP_STATE = (1 << 14),
IRQD_MOVE_PCNTXT = (1 << 15),
IRQD_IRQ_DISABLED = (1 << 16),
IRQD_IRQ_MASKED = (1 << 17),
IRQD_IRQ_INPROGRESS = (1 << 18),
IRQD_WAKEUP_ARMED = (1 << 19),
IRQD_FORWARDED_TO_VCPU = (1 << 20),
IRQD_AFFINITY_MANAGED = (1 << 21),
IRQD_IRQ_STARTED = (1 << 22),
IRQD_MANAGED_SHUTDOWN = (1 << 23),
IRQD_SINGLE_TARGET = (1 << 24),
IRQD_DEFAULT_TRIGGER_SET = (1 << 25),
IRQD_CAN_RESERVE = (1 << 26),
};
irq_common_data.state_use_accessors에서 사용되는 플래그들이다.
- IRQD_TRIGGER_MASK
- 트리거 타입 마스크 (4비트)
- IRQD_SETAFFINITY_PENDING
- affinity 설정이 지연되는 중
- IRQD_NO_BALANCING
- no 밸런싱
- IRQD_PER_CPU
- 코어별 전용 인터럽트 배정되는 경우 per-cpu 인터럽트로 구성
- IRQD_AFFINITY_SET
- affnity 설정된 경우
- IRQD_LEVEL
- 레벨 트리거 설정된 경우 (그렇지 않으면 edge 트리거)
- IRQD_WAKERUP_STATE
- suspend된 작업을 깨워 동작시키는 인터럽트 형태로 설정
- IRQD_MOVE_PCNTXT
- 인터럽트가 process context로 이동된 경우
- IRQD_IRQ_DISABLED
- 인터럽트를 disable한 상태
- IRQD_IRQ_MASKED
- 인터럽트의 masked 상태
- IRQD_IRQ_INPROGRESS
- 인터럽트가 진행중인 상태
- IRQD_WAKERUP_ARMED
- 꺠우는 모드 armed
- IRQD_FORWARDED_TO_VCPU
- 가상화를 담당하는 vCPU 인터페이스로 전달 가능
- IRQD_IRQ_STARTED
- 인터럽트가 서비스 시작된 상태
- IRQD_MANAGED_SHUTDOWN
- affinity가 지정되지 않아 인터럽트가 shutdown된 상태
- IRQD_SINGLE_TARGET
- 하나의 cpu(affinity target)만 지정 가능한 상태
- IRQD_DEFAULT_TRIGGER_SET
- 트리거가 설정된 상태
- IRQD_CAN_RESERVE
- 예약 모드 사용 가능한 상태
참고
- Interrupts -1- (Interrupt Controller) | 문c
- Interrupts -2- (irq chip) | 문c
- Interrupts -3- (irq domain) | 문c
- Interrupts -4- (Top-Half & Bottom-Half) | 문c
- Interrupts -5- (Softirq) | 문c
- Interrupts -6- (IPI Cross-call) | 문c
- Interrupts -7- (Workqueue 1) | 문c
- Interrupts -8- (Workqueue 2) | 문c
- Interrupts -9- (GIC v3 Driver) | 문c
- Interrupts -10- (irq partition) | 문c
- Interrupts -11- (RPI2 IC Driver) | 문c
- Interrupts -12- (irq desc) | 문c – 현재 글