<kernel v5.4>
가상화 지원 (하이퍼 모드)
하이퍼바이저라는 용어는 VM(Virtual Machine)을 생성하고, 관리하고 스케줄링 하기 위해 사용되는 소프트웨어이다.
ARM 시스템에서 가상화를 지원하기 위해서는 AVE(Architecture Virtualization Extension)가 필요하다.
- ARM32에서는 SoC 마다 탑재 여부가 다르다.
- ARM64에서는 대부분 내장되어 있다.
ARM32와 ARM64 시스템의에서 다음과 같은 하이퍼 바이저 운영 모드들이 지원된다. 대부분의 설명은 ARM64를 디폴트로 한다.
- ARM32
- 하이퍼 바이저는 HYP 모드에서 운영
- Guest OS는 SVC 모드에서 운영
- ARM64
- 하이퍼 바이저는 EL2에서 운영
- Guest OS는 EL1 모드에서 운영
하이퍼 바이저를 운영하는 방법은 다음과 같이 두 가지가 있다.
- Type 1 (Standalone)
- EL2에서 Host OS 없이 전용 하이퍼바이저를 운영하고, Host OS 없이 EL1에서 Guest OS를 운영한다.
- 예) Xen Server, VMWare ESXi, VMWare vSphere, Oracle VM Server, Hyper-V
- EL2에서 Host OS 없이 전용 하이퍼바이저를 운영하고, Host OS 없이 EL1에서 Guest OS를 운영한다.
- Type 2 (Hypervisors and Hosted)
- EL2에서 하이퍼바이저와 Host OS를 같이 운영하고, EL1에서 Guest OS를 운영한다.
- 예) VMware worksataion, Virtual Box, QEMU/KVM
- EL2에서 하이퍼바이저와 Host OS를 같이 운영하고, EL1에서 Guest OS를 운영한다.
VHE(Virutalization Host Extension)
ARM 리눅스를 Type 2 하이퍼 바이저로 운영될 때 ARMv8 VHE 지원 여부에 따라 EL2 모드와 EL1 모드를 사용한다.
- VHE 미지원시
- EL2 스위칭 + EL1 Host & Guest OS
- Host OS를 EL2로 부팅한 후 EL2에 관련 스위칭(irq 라우팅 포함) stub 코드만 남겨 놓고 EL1으로 전환하여 운영한다.
- 예) Host용 리눅스 커널이 EL2에서 부팅되고, EL1으로 전환한다.
- VHE 지원시
- EL2 Host OS + EL1 Guest OS
- Host OS를 EL2로 부팅 및 운영하는 것으로 EL2 및 EL1 간 많은 스위칭을 제거해 성능을 향상시켰다.
- 예) 지원을 통해 Host용 리눅스 커널이 EL2에서 부팅 및 운영을 한다.
- VHE 기능을 사용하는 동안 EL1 레지스터를 사용하는 리눅스 커널의 코드 변경없이 EL2 모드에서 사용할 수 있게 하였다.즉 코드에서 접근하는 *_EL1 레지스터들은 실제 *_EL2 레지스터와 동일한 동작을 한다.
- HCR_EL2.E2H 비트를 설정할 때에 사용할 수 있다.
- EL2 모드에서 원래 EL0 및 EL1 레지스터를 사용하기 위해서는 *_EL02 및 *_EL12 레지스터를 사용한다.
- 참고:
- Virtualization Host Extension support (2015) | LWN.net
- To EL2, and Beyond! | Christoffer Dall, Shih-Wei Li – 다운로드 pdf
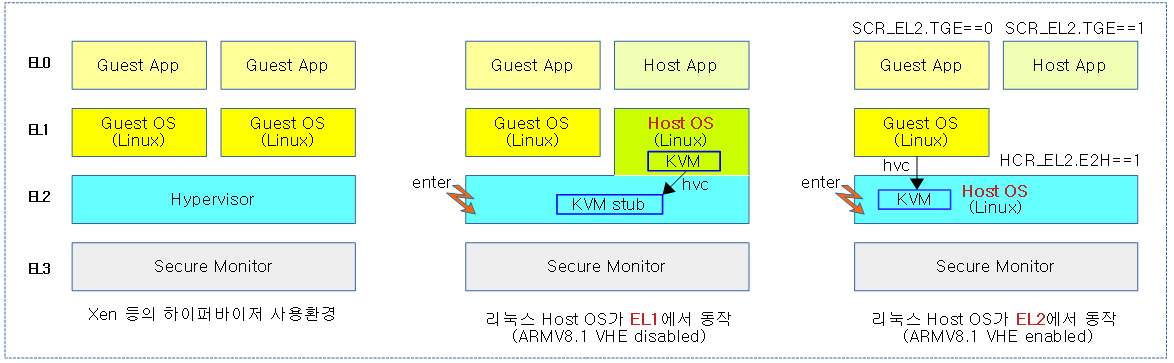
다음 그림은 리눅스 커널등의 OS가 다양한 하이퍼바이저 운영 상황에서 동작하는 모습을 보여준다.
- 좌측 그림은 Xen, VMware/ESX 같은 전용 하이퍼바이저가 동작하고, guest 운영 체제들은 EL1에서 동작한다.
- 중앙 및 우측 그림은 VHE 지원여부에 따라 각각 EL2 및 EL1에서 호스트 운영체제가 동작하고, guest 운영 체제들은 EL1에서 동작한다.
- SCR_EL2.E2H==1 (VHE 운영) 에서 Host OS가 운영되는 cpu는 SCR_EL2.TGE 값이 1이고, Guest OS가 운영되는 cpu는 0이다.
하이퍼모드 지원 유무 확인
하이퍼모드로 부팅된 경우인지 아닌지 메시지(dmesg)를 출력하여 안내한다.
ARM64 예)
- EL2 부팅
- “CPU: All CPU(s) started at EL2“
- EL1 부팅
- “CPU: All CPU(s) started at EL1”
ARM32 예)
- HYP 모드 부팅
- “CPU: All CPU(s) started in HYP mode.”
- “CPU: Virtualization extensions available.”
- SVC 모드 부팅
- “CPU: All CPU(s) started in SVC mode.”
Secure EL2 support
- ARMv8.4 아키텍처부터 Secure EL2를 지원하기 시작하였다.
Full-virtualization vs Para-virtualization
한글로는 전가상화 또는 반가상화라고 불리운다. 오늘 날 가상화를 위한 하드웨어 지원이 있는 cpu에서 Guest OS들은 Guest OS 코드 변경 없이 전가상화를 지원하도록 빠르게 동작하고 있다.
- 현재 전가상화와 반가상화를 구분하여 사용하지 않는다.
- Guest OS를 보다 효과적인 성능으로 사용하기 위해 대부분의 운영체제에 반가상화용 드라이버(virtio)들이 포함되어 있다.
Stage 2 변환
하이퍼 모드를 사용하는 경우 운영체제 별로 매핑된 Stage 2 테이블을 사용는 변환을 통해 물리주소(PA)를 얻어낸다.
- 하이퍼 모드 사용하지 않을 때
- VA —-> (Stage 1 Transalation MMU) —-> PA
- 하이퍼 모드 사용할 때
- VA —-> (Stage 1 Transalation MMU) —-> IPA —-> (Stage 2 Transalation MMU) —-> PA
ASID(Address Space IDentifier)
Stage 1 변환에서 VA에 대해 application을 식별하기 위해 ASID를 사용한다.
VMID(Virtual Machine IDentifier)
Stage 2 변환에서 IPA에 대해 운영체제를 식별하기 위해 VMID를 사용한다.
속성 병합(Combining)
Stage 1과 Stage 2의 매핑은 각각 메모리 타입과 속성을 가지고 있고, 이들은 각각의 제한을 가지고 있는데 병합(Combining)하여 더 많은 제한을 가진다.
- 예) 디바이스 + 메모리 = 디바이스
속성 오버라이딩(Overinding)
Stage 1과 Stage 2의 매핑은 각각 메모리 타입과 속성에 대해 동작 방식을 결정할 수 있는 레지스터가 있다.
- HCR_EL2.CD
- Stage 1 속성을 모두 Non-cacheable로 운영한다.
- HCR_EL2.DC
- Stage 1 속성을 모두 Normal, Write-Back 캐시 속성으로 운영한다.
- HCR_EL2.FWB
- 속성 병합대신 Stage 1 속성으로 오버라이딩한다. (forARMv8.4)
Virtual CPU
vCPU
하이퍼 바이저를 운영하면 cpu core를 각각의 운영체제가 공유하여 사용할 수 있도록 가상 cpu 개념이 사용된다. 즉 1개의 cpu를 여러 개의 vcpu로 나누어 운용할 수 있다.
예) 4 개의 core에 리눅스 Guest OS를 vcpu0~3까지 4개의 코어에서 운용하고, 또 다른 리눅스 Guest OS를 vcpu0~1까지 2개의 코어에서 운용할 수 있다.
Virtual Exception
vIRQ, vFIQ 및 vSErrors
하이퍼 바이저를 운영하면 EL2에서 수신된 물리 인터럽트를 vCPU로 forwarding할 때 가상 Exception인 vIRQ, vFIQ 및 vSErrors가 사용된다.
하이퍼 모드 체크
hyp_mode_check() – ARM64
arch/arm64/kernel/setup.c
static void __init hyp_mode_check(void)
{
if (is_hyp_mode_available())
pr_info("CPU: All CPU(s) started at EL2\n");
else if (is_hyp_mode_mismatched())
WARN_TAINT(1, TAINT_CPU_OUT_OF_SPEC,
"CPU: CPUs started in inconsistent modes");
else
pr_info("CPU: All CPU(s) started at EL1\n");
}
커널이 EL2로 부팅되었는지 EL1으로 부팅되었는지 여부를 메시지로 출력한다.
hyp_mode_check() – ARM32
arch/arm/kernel/setup.c
#ifndef ZIMAGE
void __init hyp_mode_check(void)
{
#ifdef CONFIG_ARM_VIRT_EXT
sync_boot_mode();
if (is_hyp_mode_available()) {
pr_info("CPU: All CPU(s) started in HYP mode.\n");
pr_info("CPU: Virtualization extensions available.\n");
} else if (is_hyp_mode_mismatched()) {
pr_warn("CPU: WARNING: CPU(s) started in wrong/inconsistent modes (primary CPU mode 0x%x)\n",
__boot_cpu_mode & MODE_MASK);
pr_warn("CPU: This may indicate a broken bootloader or firmware.\n");
} else
pr_info("CPU: All CPU(s) started in SVC mode.\n");
#endif
}
#endif
커널이 HYP 모드로 부팅되었는지 SVC 모드로 부팅되었는지 여부를 메시지로 출력한다.
하이퍼 모드 운영 여부
is_hyp_mode_available() – ARM64
arch/arm64/include/asm/virt.h
/* Reports the availability of HYP mode */
static inline bool is_hyp_mode_available(void)
{
return (__boot_cpu_mode[0] == BOOT_CPU_MODE_EL2 &&
__boot_cpu_mode[1] == BOOT_CPU_MODE_EL2);
}
boot cpu가 EL2로 부팅되었는지 여부를 알아온다.
- __boot_cpu_mode[] 저장 루틴은 다음을 참고한다.
- 참고: head.S 전체 | 문c
is_hyp_mode_available() – ARM32
arch/arm/include/asm/virt.h
/* Reports the availability of HYP mode */
static inline bool is_hyp_mode_available(void)
{
return ((__boot_cpu_mode & MODE_MASK) == HYP_MODE &&
!(__boot_cpu_mode & BOOT_CPU_MODE_MISMATCH));
}
boot cpu가 EL2로 부팅되었는지 여부를 알아온다.
기타
sync_boot_mode()
arch/arm/include/asm/virt.h
/* * __boot_cpu_mode records what mode the primary CPU was booted in. * A correctly-implemented bootloader must start all CPUs in the same mode: * if it fails to do this, the flag BOOT_CPU_MODE_MISMATCH is set to indicate * that some CPU(s) were booted in a different mode. * * This allows the kernel to flag an error when the secondaries have come up. */
extern int __boot_cpu_mode;
static inline void sync_boot_mode(void)
{
/*
* As secondaries write to __boot_cpu_mode with caches disabled, we
* must flush the corresponding cache entries to ensure the visibility
* of their writes.
*/
sync_cache_r(&__boot_cpu_mode);
}
- 전역 __boot_cpu_mode 변수 영역에 대해 inner & outer 캐시 flush를 수행한다.
sync_cache_r()
arch/arm/include/asm/cacheflush.h
#define sync_cache_r(ptr) __sync_cache_range_r(ptr, sizeof *(ptr))
- long으로 선언된 전역 __boot_cpu_mode 변수 위치에 대해 inner & outer 캐시 flush를 수행한다.
- long 값이므로 32bit 시스템에서는 4 byte , 64bit 시스템에서는 8 byte 영역만큼에 대해 flush를 수행하게 된다.
__sync_cache_range_r()
arch/arm/include/asm/cacheflush.h
/* * Ensure preceding writes to *p by other CPUs are visible to * subsequent reads by this CPU. We must be careful not to * discard data simultaneously written by another CPU, hence the * usage of flush rather than invalidate operations. */
static inline void __sync_cache_range_r(volatile void *p, size_t size)
{
char *_p = (char *)p;
#ifdef CONFIG_OUTER_CACHE
if (outer_cache.flush_range) {
/*
* Ensure dirty data migrated from other CPUs into our cache
* are cleaned out safely before the outer cache is cleaned:
*/
__cpuc_clean_dcache_area(_p, size);
/* Clean and invalidate stale data for *p from outer ... */
outer_flush_range(__pa(_p), __pa(_p + size));
}
#endif
/* ... and inner cache: */
__cpuc_flush_dcache_area(_p, size);
}
지정된 range에 대해 inner & outer 캐시 flush를 수행한다.
- CONFIG_OUTER_CACHE
- outer 캐시가 사용되는 시스템에서 사용하는 커널 옵션
- rpi2: outer 캐시를 사용하지 않는다.
- if (outer_cache.flush_range) {
- outer 캐시를 사용하는 시스템에서 flush_range에 연결된 함수가 존재하는 경우
- __cpuc_clean_dcache_area(_p, size);
- 지정 range의 outer 캐시를 flush하기 전에 먼저 cpu 캐시 즉 inner 캐시를 먼저 clean 작업을 해야한다.
- ARMv7:
- inner d-cache 영역에 대해 clean 오퍼레이션 대신 flush를 구현하였다.
- outer_flush_range(__pa(_p), __pa(_p + size));
- 지정 range의 outer cache에 대한 flush(clean & invalidate)를 수행한다.
- __cpuc_flush_dcache_area(_p, size);
- 지정 range의 inner d-cache에 대한 flush(clean & invalidate)를 수행한다.
arch/arm/include/asm/cacheflush.h
/* * There is no __cpuc_clean_dcache_area but we use it anyway for * code intent clarity, and alias it to __cpuc_flush_dcache_area. */
#define __cpuc_clean_dcache_area __cpuc_flush_dcache_area
- ARMv7에서는 clean 구현을 따로 준비하지 않았고 따라서 flush 구현을 사용한다.
arch/arm/include/asm/cacheflush.h
#define __cpuc_flush_dcache_area cpu_cache.flush_kern_dcache_area
- ARMv7: v7_flush_kern_dcache_area()
outer_flush_range()
arch/arm/include/asm/outercache.h
/** * outer_flush_range - clean and invalidate outer cache lines * @start: starting physical address, inclusive * @end: end physical address, exclusive */
static inline void outer_flush_range(phys_addr_t start, phys_addr_t end)
{
if (outer_cache.flush_range)
outer_cache.flush_range(start, end);
}
- outer_cache가 구현된 머신에서 지정 range의 outer cache에 대한 flush(clean & invalidate)를 수행한다.
is_hyp_mode_mismatched()
arch/arm/include/asm/virt.h
/* Check if the bootloader has booted CPUs in different modes */
static inline bool is_hyp_mode_mismatched(void)
{
return !!(__boot_cpu_mode & BOOT_CPU_MODE_MISMATCH);
}
arch/arm/include/asm/virt.h
/* * Flag indicating that the kernel was not entered in the same mode on every * CPU. The zImage loader stashes this value in an SPSR, so we need an * architecturally defined flag bit here. */
#define BOOT_CPU_MODE_MISMATCH PSR_N_BIT
arch/arm/include/uapi/asm/ptrace.h
/* * PSR bits * Note on V7M there is no mode contained in the PSR */
#define USR26_MODE 0x00000000 #define FIQ26_MODE 0x00000001 #define IRQ26_MODE 0x00000002 #define SVC26_MODE 0x00000003 #if defined(__KERNEL__) && defined(CONFIG_CPU_V7M) /* * Use 0 here to get code right that creates a userspace * or kernel space thread. */ #define USR_MODE 0x00000000 #define SVC_MODE 0x00000000 #else #define USR_MODE 0x00000010 #define SVC_MODE 0x00000013 #endif #define FIQ_MODE 0x00000011 #define IRQ_MODE 0x00000012 #define ABT_MODE 0x00000017 #define HYP_MODE 0x0000001a #define UND_MODE 0x0000001b #define SYSTEM_MODE 0x0000001f #define MODE32_BIT 0x00000010 #define MODE_MASK 0x0000001f
arch/arm/include/uapi/asm/ptrace.h
/* * Use 0 here to get code right that creates a userspace * or kernel space thread. */
#define USR_MODE 0x00000000 #define SVC_MODE 0x00000000 #else #define USR_MODE 0x00000010 #define SVC_MODE 0x00000013 #endif #define FIQ_MODE 0x00000011 #define IRQ_MODE 0x00000012 #define ABT_MODE 0x00000017 #define HYP_MODE 0x0000001a #define UND_MODE 0x0000001b #define SYSTEM_MODE 0x0000001f #define MODE32_BIT 0x00000010 #define MODE_MASK 0x0000001f
전역 변수
__boot_cpu_mode – ARM64
arch/arm64/include/asm/virt.h
/* * __boot_cpu_mode records what mode CPUs were booted in. * A correctly-implemented bootloader must start all CPUs in the same mode: * In this case, both 32bit halves of __boot_cpu_mode will contain the * same value (either 0 if booted in EL1, BOOT_CPU_MODE_EL2 if booted in EL2). * * Should the bootloader fail to do this, the two values will be different. * This allows the kernel to flag an error when the secondaries have come up. */
extern u32 __boot_cpu_mode[2];
arch/arm64/kernel/hyp-stub.S
/* * We need to find out the CPU boot mode long after boot, so we need to * store it in a writable variable. * * This is not in .bss, because we set it sufficiently early that the boot-time * zeroing of .bss would clobber it. */
ENTRY(__boot_cpu_mode)
.long BOOT_CPU_MODE_EL2
.long BOOT_CPU_MODE_EL1
__boot_cpu_mode – ARM32
arch/arm/include/asm/virt.h
/* * __boot_cpu_mode records what mode the primary CPU was booted in. * A correctly-implemented bootloader must start all CPUs in the same mode: * if it fails to do this, the flag BOOT_CPU_MODE_MISMATCH is set to indicate * that some CPU(s) were booted in a different mode. * * This allows the kernel to flag an error when the secondaries have come up. */
extern int __boot_cpu_mode;
arch/arm/kernel/hyp-stub.S
/* * For the kernel proper, we need to find out the CPU boot mode long after * boot, so we need to store it in a writable variable. * * This is not in .bss, because we set it sufficiently early that the boot-time * zeroing of .bss would clobber it. */
.data
ENTRY(__boot_cpu_mode)
.long 0
참고
- Next steps in KVM enablement on ARM (2015) | ARM
- Isolation using virtualization in the Secure world (2018) | ARM – 다운로드 pdf, 다운로드 pdf
- Virtualization Host Extension support (2015) | LWN.net
- To EL2, and Beyond! | Christoffer Dall, Shih-Wei Li – 다운로드 pdf
- Armv8-A virtualization (2019) | ARM – 다운로드 pdf