<kernel v5.0>
MPIDR Hash Bits
MPIDR 해시 비트를 구성하고 사용하는 단계를 알아본다.
- 1단계: MPIDR 읽어오기
- a) smp_setup_processor_id() 함수를 통해 부트 cpu에 대해 affinity 레벨이 표현된 MPIDR 값을 읽어 __cpu_logical_map[0] 배열에 저장한다. 저장된 값은 cpu_logical_map(cpu) 함수를 사용하여 @cpu에 해당하는 저장된 mpidr 값을 읽어온다.
- mpidr 값은 물리 cpu id를 포함한 affinity 단계별 id가 담겨있는 값이다.
- 참고: smp_setup_processor_id() | 문c
- b) smp_init_cpus() 함수에서 디바이스 트리 또는 ACPI 테이블에 지정된 cpu 노드의 “reg” 값에서 읽은 mpidr 값을 __cpu_logical_map[] 배열에 저장한다.
- 참고: smp_init_cpus() | 문c
- a) smp_setup_processor_id() 함수를 통해 부트 cpu에 대해 affinity 레벨이 표현된 MPIDR 값을 읽어 __cpu_logical_map[0] 배열에 저장한다. 저장된 값은 cpu_logical_map(cpu) 함수를 사용하여 @cpu에 해당하는 저장된 mpidr 값을 읽어온다.
- 2단계: MPIDR 해시 구성하기
- smp_build_mpidr_hash() 함수를 사용하여 각 cpu에서 읽어온 mpidr 값들로 각 affinity 레벨별로 분석하여 전역 mpidr_hash 구조체 객체를 구성한다. 이 mpidr_hash 구조체는 각 affinity 레벨별로 필요한 비트 수 및 shift 비트 수와 전체 비트 수 등을 관리한다.
- 참고로 ARM32에서는 최대 3 단계 그리고 ARM64에서는 최대 4 단계의affinity 레벨을 관리한다.
- 3단계: MPIDR 해시 사용하기
- 이렇게 미리 계산된 mpidr_hash는 cpu_suspend() 및 cpu_resume() 내부의 어셈블리 코드에서 사용된다.
- sleep 또는 resume 할 cpu에 해당하는 mpidr 값을 읽어 산출된 mpidr_hash를 사용하여 각 affinity 레벨에서 사용하는 비트 들을 우측 시프트한 최종 값을 얻어낸다.
- 이렇게 미리 계산된 mpidr_hash는 cpu_suspend() 및 cpu_resume() 내부의 어셈블리 코드에서 사용된다.
MPIDR 해시 산출
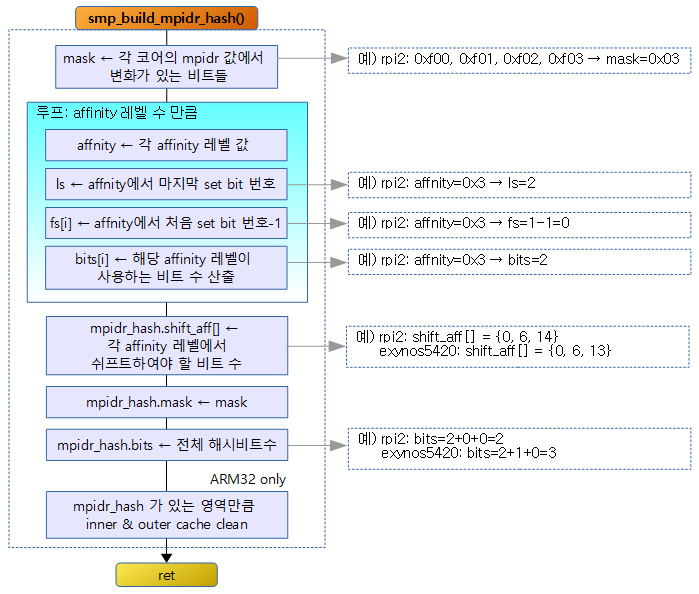
다음 그림은 mpidr_hash를 산출하는 과정을 보여준다.
smp_build_mpidr_hash() – ARM32
arch/arm/kernel/setup.c
/** * smp_build_mpidr_hash - Pre-compute shifts required at each affinity * level in order to build a linear index from an * MPIDR value. Resulting algorithm is a collision * free hash carried out through shifting and ORing */
static void __init smp_build_mpidr_hash(void)
{
u32 i, affinity;
u32 fs[3], bits[3], ls, mask = 0;
/*
* Pre-scan the list of MPIDRS and filter out bits that do
* not contribute to affinity levels, ie they never toggle.
*/
for_each_possible_cpu(i)
mask |= (cpu_logical_map(i) ^ cpu_logical_map(0));
pr_debug("mask of set bits 0x%x\n", mask);
/*
* Find and stash the last and first bit set at all affinity levels to
* check how many bits are required to represent them.
*/
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
affinity = MPIDR_AFFINITY_LEVEL(mask, i);
/*
* Find the MSB bit and LSB bits position
* to determine how many bits are required
* to express the affinity level.
*/
ls = fls(affinity);
fs[i] = affinity ? ffs(affinity) - 1 : 0;
bits[i] = ls - fs[i];
}
/*
* An index can be created from the MPIDR by isolating the
* significant bits at each affinity level and by shifting
* them in order to compress the 24 bits values space to a
* compressed set of values. This is equivalent to hashing
* the MPIDR through shifting and ORing. It is a collision free
* hash though not minimal since some levels might contain a number
* of CPUs that is not an exact power of 2 and their bit
* representation might contain holes, eg MPIDR[7:0] = {0x2, 0x80}.
*/
mpidr_hash.shift_aff[0] = fs[0];
mpidr_hash.shift_aff[1] = MPIDR_LEVEL_BITS + fs[1] - bits[0];
mpidr_hash.shift_aff[2] = 2*MPIDR_LEVEL_BITS + fs[2] -
(bits[1] + bits[0]);
mpidr_hash.mask = mask;
mpidr_hash.bits = bits[2] + bits[1] + bits[0];
pr_debug("MPIDR hash: aff0[%u] aff1[%u] aff2[%u] mask[0x%x] bits[%u]\n",
mpidr_hash.shift_aff[0],
mpidr_hash.shift_aff[1],
mpidr_hash.shift_aff[2],
mpidr_hash.mask,
mpidr_hash.bits);
/*
* 4x is an arbitrary value used to warn on a hash table much bigger
* than expected on most systems.
*/
if (mpidr_hash_size() > 4 * num_possible_cpus())
pr_warn("Large number of MPIDR hash buckets detected\n");
sync_cache_w(&mpidr_hash);
}
전체 logical cpu id에 대한 mpidr 값을 읽어 3 개의 affinity 레벨별로 분석하여 전역 mpidr_hash 구조체 객체를 구성한다. 구성된 mpidr_hash에는 cpi id 값으로 affinity 레벨로 변환을 할 수 있는 shift 값을 가지고 있는데 이렇게 구성한 mpidr_hash 구조체는 __cpu_suspend() 및 __cpu_resume() 등에서 사용된다.
- 코드 라인 9~11에서 전체 possible cpu 수만큼 순회하며 해당 로지컬 cpu의 mpidr 값이 저장된 값을 읽어 변화되는 비트들 만을 추출하여 mask에 저장하고 디버그 정보로 출력한다.
- 모든 코어에 설정되어 변화되지 않는 값들을 제거한다.
- 코드 라인 16~26에서 각 affinity 레벨을 순회하며 mask 값에서 각 affinity 레벨에서 변동되는 비트들만을 추출하여 해당 affnity 레벨에 필요한 hash 비트를 구해 bits[]에 저장한다.
- 처음 3 개의 affnity 레벨을 순회하며 mask에 대해 각 affnity 레벨별로 값을 추출한다. (0~255)
- affnity 값에서 가장 마지막 세트된 비트 번호와 가장 처음 세트된 비트 번호 -1을 알아온다.
- 예) affnity=0xc
- ls=4
- fs=2
- 코드 라인 37~48에서 각 affinity 레벨별로 shift 되야할 비트 수를 산출하고, mask와 전체 hash 비트수를 저장한다. 그런 후 이들 값들을 디버그 출력한다.
- 코드 라인 55에서 mpidr_hash 객체 영역에 대해 inner & outer 캐시 클린을 수행 한다.
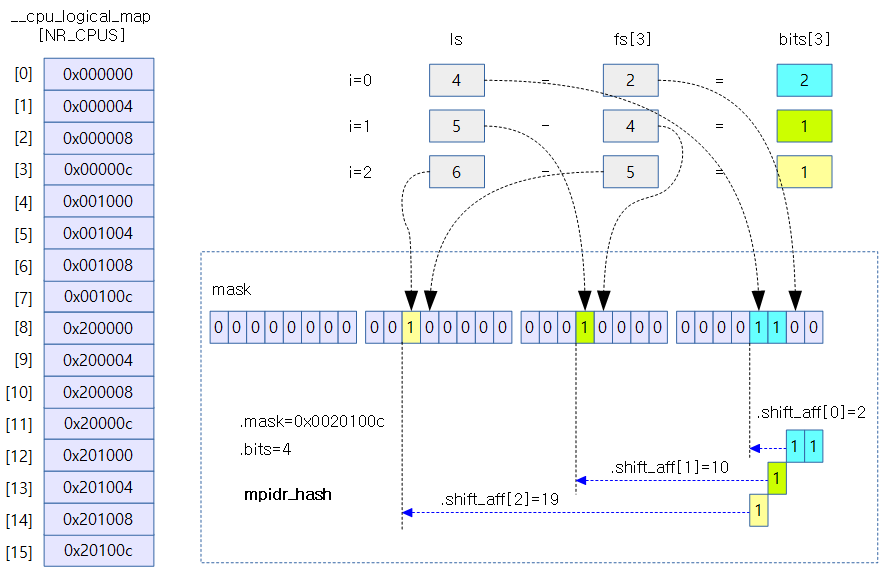
아래 그림은 cluster x 2개, cpu core x 4개, virtual core 4개(실제가 아닌 가상)로 이루어진 시스템에 대해 전역 mpidr_hash 객체가 구성되는 것을 보여준다.
- mpidr hash bits는 4개가 필요하고 각각의 레벨에 대해 쉬프트가 필요한 수는 2, 10, 19이다.
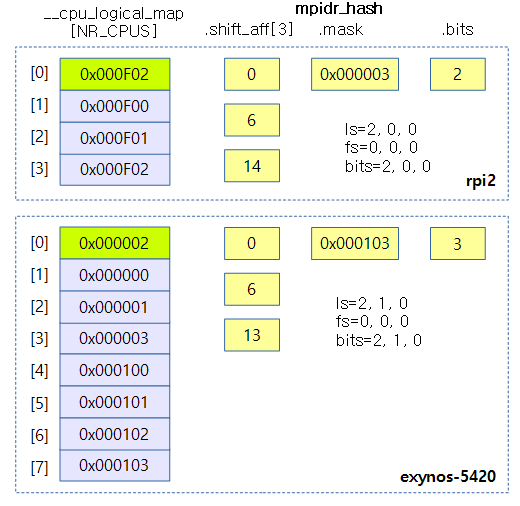
아래 그림은rpi2 및 exynos-5420 시스템에 대해 전역 mpidr_hash 객체가 구성되는 것을 보여준다.
- rpi2: mpidr hash bits는 2개가 필요하고 각각의 레벨에 대해 쉬프트가 필요한 수는 0, 6, 14이다.
- exynos-5420: mpidr hash bits는 3개가 필요하고 각각의 레벨에 대해 쉬프트가 필요한 수는 0, 6, 13이다.
smp_build_mpidr_hash() – ARM64
arch/arm64/kernel/setup.c
/** * smp_build_mpidr_hash - Pre-compute shifts required at each affinity * level in order to build a linear index from an * MPIDR value. Resulting algorithm is a collision * free hash carried out through shifting and ORing */
static void __init smp_build_mpidr_hash(void)
{
u32 i, affinity, fs[4], bits[4], ls;
u64 mask = 0;
/*
* Pre-scan the list of MPIDRS and filter out bits that do
* not contribute to affinity levels, ie they never toggle.
*/
for_each_possible_cpu(i)
mask |= (cpu_logical_map(i) ^ cpu_logical_map(0));
pr_debug("mask of set bits %#llx\n", mask);
/*
* Find and stash the last and first bit set at all affinity levels to
* check how many bits are required to represent them.
*/
for (i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
affinity = MPIDR_AFFINITY_LEVEL(mask, i);
/*
* Find the MSB bit and LSB bits position
* to determine how many bits are required
* to express the affinity level.
*/
ls = fls(affinity);
fs[i] = affinity ? ffs(affinity) - 1 : 0;
bits[i] = ls - fs[i];
}
/*
* An index can be created from the MPIDR_EL1 by isolating the
* significant bits at each affinity level and by shifting
* them in order to compress the 32 bits values space to a
* compressed set of values. This is equivalent to hashing
* the MPIDR_EL1 through shifting and ORing. It is a collision free
* hash though not minimal since some levels might contain a number
* of CPUs that is not an exact power of 2 and their bit
* representation might contain holes, eg MPIDR_EL1[7:0] = {0x2, 0x80}.
*/
mpidr_hash.shift_aff[0] = MPIDR_LEVEL_SHIFT(0) + fs[0];
mpidr_hash.shift_aff[1] = MPIDR_LEVEL_SHIFT(1) + fs[1] - bits[0];
mpidr_hash.shift_aff[2] = MPIDR_LEVEL_SHIFT(2) + fs[2] -
(bits[1] + bits[0]);
mpidr_hash.shift_aff[3] = MPIDR_LEVEL_SHIFT(3) +
fs[3] - (bits[2] + bits[1] + bits[0]);
mpidr_hash.mask = mask;
mpidr_hash.bits = bits[3] + bits[2] + bits[1] + bits[0];
pr_debug("MPIDR hash: aff0[%u] aff1[%u] aff2[%u] aff3[%u] mask[%#llx] bits[%u]\n",
mpidr_hash.shift_aff[0],
mpidr_hash.shift_aff[1],
mpidr_hash.shift_aff[2],
mpidr_hash.shift_aff[3],
mpidr_hash.mask,
mpidr_hash.bits);
/*
* 4x is an arbitrary value used to warn on a hash table much bigger
* than expected on most systems.
*/
if (mpidr_hash_size() > 4 * num_possible_cpus())
pr_warn("Large number of MPIDR hash buckets detected\n");
}
3 단계 affinity 단계를 4 단계 까지 관리하는 것만 다르고 ARM32와 동일한 방법을 사용한다.
캐시 싱크(clean) – ARM32
sync_cache_w() – ARM32
arch/arm/include/asm/cacheflush.h
#define sync_cache_w(ptr) __sync_cache_range_w(ptr, sizeof *(ptr))
ptr 영역을 cache clean 한다.
__sync_cache_range_w()
arch/arm/include/asm/cacheflush.h
/*
* Ensure preceding writes to *p by this CPU are visible to
* subsequent reads by other CPUs:
*/
static inline void __sync_cache_range_w(volatile void *p, size_t size)
{
char *_p = (char *)p;
__cpuc_clean_dcache_area(_p, size);
outer_clean_range(__pa(_p), __pa(_p + size));
}
- p 주소 위치 부터 해당 size 만큼의 영역에 대해 inner 캐시 및 outer cache를 clean 한다.
arch/arm/include/asm/cacheflush.h
/* * There is no __cpuc_clean_dcache_area but we use it anyway for * code intent clarity, and alias it to __cpuc_flush_dcache_area. */ #define __cpuc_clean_dcache_area __cpuc_flush_dcache_area
arch/arm/include/asm/cacheflush.h
#define __cpuc_flush_dcache_area cpu_cache.flush_kern_dcache_area
- MULTI_CPU가 선택된 경우 cpu_cache 구조체를 통해 cache 핸들러 함수를 호출한다.
- rpi2도 이를 사용한다.
outer_clean_range()
arch/arm/include/asm/outercache.h
/**
* outer_clean_range - clean dirty outer cache lines
* @start: starting physical address, inclusive
* @end: end physical address, exclusive
*/
static inline void outer_clean_range(phys_addr_t start, phys_addr_t end)
{
if (outer_cache.clean_range)
outer_cache.clean_range(start, end);
}
- start ~ end 주소 까지 outer cache를 clean 한다.
#ifdef CONFIG_OUTER_CACHE struct outer_cache_fns outer_cache __read_mostly; EXPORT_SYMBOL(outer_cache); #endif
- 전역 outer_cache는 outer_cache_fns 구조체를 가리키며 outer cache 핸들러 코드를 관리한다.
구조체
mpidr_hash 구조체 – ARM32
arch/arm/include/asm/smp_plat.h
/*
* NOTE ! Assembly code relies on the following
* structure memory layout in order to carry out load
* multiple from its base address. For more
* information check arch/arm/kernel/sleep.S
*/
struct mpidr_hash {
u32 mask; /* used by sleep.S */
u32 shift_aff[3]; /* used by sleep.S */
u32 bits;
};
- 전체 logical cpu id 값에서 변화되는 비트들만을 추출한다.
- rpi2 예) 0xf00, 0xf01, 0xf02, 0xf03 -> mask=0x03 (lsb 두 개만 변화됨)
- shift_aff[3]
- mpidr hash bit를 logical cpu id 값으로 쉬프트하기 위한 비트 수
- rpi2 예) mpir hash bit = 전체 2 개 비트 (affinity0=2, affnity1=0, affnity2=0)
- shift_aff[0]=0, shift_aff[1]=6, shift_aff[2]=14
- bits
- mpidr hash bit 수
mpidr_hash 구조체 – ARM64
arch/arm64/include/asm/smp_plat.h
struct mpidr_hash {
u64 mask;
u32 shift_aff[4];
u32 bits;
};
ARM32와 유사하고, shift_aff[] 배열만 3에서 4로 확장됨을 알 수 있다.
- affinity 레벨만 3 단계에서 4 단계까지 관리한다.
outer_cache_fns 구조체 – ARM32 only
arch/arm/include/asm/outercache.h
struct outer_cache_fns {
void (*inv_range)(unsigned long, unsigned long);
void (*clean_range)(unsigned long, unsigned long);
void (*flush_range)(unsigned long, unsigned long);
void (*flush_all)(void);
void (*disable)(void);
#ifdef CONFIG_OUTER_CACHE_SYNC
void (*sync)(void);
#endif
void (*resume)(void);
/* This is an ARM L2C thing */
void (*write_sec)(unsigned long, unsigned);
void (*configure)(const struct l2x0_regs *);
};
- outer 캐시 핸들러 함수들로 구성된다.
- rpi2: 사용하지 않는다.
- l2 또는 l3 캐시를 outer 캐시로 활용하는 특수한 arm 머신들이 몇 개 있다.
참고
- Bit Operations | 문c
- smp_setup_processor_id() | 문c
- smp_init_cpus() | 문c