<kernel v5.0>
SMP(Symetric Multi Processor) Operations
SMP 전용 명령어 핸들러를 위한 구조체 smp_operations를 준비하여 전역 smp_ops의 각 기능별 후크 함수를 갖는다.
smp 오퍼레이션은 다음과 같이 크게 3가지 타입으로 구성된다.
- 머신 디스크립터를 사용하는 SMP operations (ARM32 only)
- PSCI용 SMP operations
- spin-table을 사용하는 SMP operations
부트 CPU Operations 결정 – ARM64
cpu_read_bootcpu_ops() – ARM64
arch/arm64/include/asm/cpu_ops.h
static inline void __init cpu_read_bootcpu_ops(void)
{
cpu_read_ops(0);
}
boot cpu가 사용할 operations를 결정한다.
cpu_read_ops() – ARM64
arch/arm64/kernel/cpu_ops.c
/* * Read a cpu's enable method and record it in cpu_ops. */
int __init cpu_read_ops(int cpu)
{
const char *enable_method = cpu_read_enable_method(cpu);
if (!enable_method)
return -ENODEV;
cpu_ops[cpu] = cpu_get_ops(enable_method);
if (!cpu_ops[cpu]) {
pr_warn("Unsupported enable-method: %s\n", enable_method);
return -EOPNOTSUPP;
}
return 0;
}
인자로 요청받은 @cpu가 사용할 operations를 결정한다. 이 때 디바이스 트리 또는 ACPI를 통해 enable_method 속성 값을 읽어온다.
cpu_read_enable_method() – ARM64
arch/arm64/kernel/cpu_ops.c
static const char *__init cpu_read_enable_method(int cpu)
{
const char *enable_method;
if (acpi_disabled) {
struct device_node *dn = of_get_cpu_node(cpu, NULL);
if (!dn) {
if (!cpu)
pr_err("Failed to find device node for boot cpu\n");
return NULL;
}
enable_method = of_get_property(dn, "enable-method", NULL);
if (!enable_method) {
/*
* The boot CPU may not have an enable method (e.g.
* when spin-table is used for secondaries).
* Don't warn spuriously.
*/
if (cpu != 0)
pr_err("%pOF: missing enable-method property\n",
dn);
}
} else {
enable_method = acpi_get_enable_method(cpu);
if (!enable_method) {
/*
* In ACPI systems the boot CPU does not require
* checking the enable method since for some
* boot protocol (ie parking protocol) it need not
* be initialized. Don't warn spuriously.
*/
if (cpu != 0)
pr_err("Unsupported ACPI enable-method\n");
}
}
return enable_method;
}
인자로 요청받은 @cpu가 사용할 enable-method를 알아온다. 발견되지 않는 경우에는 null을 가져온다.
- 코드 라인 5~24에서 디바이스 트리의 cpu 노드에서 “enable-method” 속성 값을 읽어온다.
- “psci” 또는 “spin-table”을 알아온다. rpi3 시스템의 경우 “brcm,bcm2836-smp” 값을 사용한다.
- 코드 라인 25~37에서 ACPI를 사용하는 경우엔 acpi 테이블에서 enable-method 속성 값을 읽어온다.
- “psci” 또는 “parking-protocol”을 알아온다.
SMP CPU 초기화 – ARM64
다음 그림은 SMP cpu에 대한 초기화를 수행한다.
smp_init_cpus() – ARM64
arch/arm64/kernel/smp.c
/* * Enumerate the possible CPU set from the device tree or ACPI and build the * cpu logical map array containing MPIDR values related to logical * cpus. Assumes that cpu_logical_map(0) has already been initialized. */
void __init smp_init_cpus(void)
{
int i;
if (acpi_disabled)
of_parse_and_init_cpus();
else
acpi_parse_and_init_cpus();
if (cpu_count > nr_cpu_ids)
pr_warn("Number of cores (%d) exceeds configured maximum of %u - clipping\n",
cpu_count, nr_cpu_ids);
if (!bootcpu_valid) {
pr_err("missing boot CPU MPIDR, not enabling secondaries\n");
return;
}
/*
* We need to set the cpu_logical_map entries before enabling
* the cpus so that cpu processor description entries (DT cpu nodes
* and ACPI MADT entries) can be retrieved by matching the cpu hwid
* with entries in cpu_logical_map while initializing the cpus.
* If the cpu set-up fails, invalidate the cpu_logical_map entry.
*/
for (i = 1; i < nr_cpu_ids; i++) {
if (cpu_logical_map(i) != INVALID_HWID) {
if (smp_cpu_setup(i))
cpu_logical_map(i) = INVALID_HWID;
}
}
}
SMP cpu에 대해 로지컬 cpu -> 물리 cpu 매핑과 cpu -> 노드 매핑 설정 및 cpu의 초기화를 수행한다.
- 코드 라인 5~6에서 디바이스 트리의 cpu 노드에서 cpu 정보를 읽어 로지컬 cpu -> 물리 cpu 매핑과 cpu -> 노드 매핑을 설정한다.
- 코드 라인 7~8에서 ACPI 테이블에서 cpu 정보를 읽어 로지컬 cpu -> 물리 cpu 매핑과 cpu -> 노드 매핑을 설정한다.
- 코드 라인 26~31에서 각 cpu의 초기화를 수행한다.
of_parse_and_init_cpus() – ARM64
arch/arm64/kernel/smp.c
/* * Enumerate the possible CPU set from the device tree and build the * cpu logical map array containing MPIDR values related to logical * cpus. Assumes that cpu_logical_map(0) has already been initialized. */
static void __init of_parse_and_init_cpus(void)
{
struct device_node *dn;
for_each_of_cpu_node(dn) {
u64 hwid = of_get_cpu_mpidr(dn);
if (hwid == INVALID_HWID)
goto next;
if (is_mpidr_duplicate(cpu_count, hwid)) {
pr_err("%pOF: duplicate cpu reg properties in the DT\n",
dn);
goto next;
}
/*
* The numbering scheme requires that the boot CPU
* must be assigned logical id 0. Record it so that
* the logical map built from DT is validated and can
* be used.
*/
if (hwid == cpu_logical_map(0)) {
if (bootcpu_valid) {
pr_err("%pOF: duplicate boot cpu reg property in DT\n",
dn);
goto next;
}
bootcpu_valid = true;
early_map_cpu_to_node(0, of_node_to_nid(dn));
/*
* cpu_logical_map has already been
* initialized and the boot cpu doesn't need
* the enable-method so continue without
* incrementing cpu.
*/
continue;
}
if (cpu_count >= NR_CPUS)
goto next;
pr_debug("cpu logical map 0x%llx\n", hwid);
cpu_logical_map(cpu_count) = hwid;
early_map_cpu_to_node(cpu_count, of_node_to_nid(dn));
next:
cpu_count++;
}
}
디바이스 트리의 cpu 노드에서 cpu 정보를 읽어 로지컬 cpu -> 물리 cpu 매핑과 cpu -> 노드 매핑을 설정한다.
- 코드 라인 5~9에서 cpu 노드들을 순회하며 reg 속성 값에서 hwid를 읽어온다.
- 코드 라인 11~15에서 hwid가 중복되는 경우 에러 메시지를 출력하고 skip 한다.
- 코드 라인 23~40에서 부트 cpu에 대한 cpu -> 노드 변환을 지원하기 위해 매핑을 하고, 노드 들에 부트 cpu가 하나만 있는지 체크한다.
- 코드 라인 42~43에서 디바이스 트리에서 읽은 cpu 노드 수가 컴파일 당시 설정한 최대 cpu 수를 초과하는 경우 skip 한다.
- 코드 라인 45~46에서 로지컬 cpu id 번호를 디버그 정보로 출력하고 로지컬 cpu -> 물리 cpu 변환을 지원하기 위해 매핑한다.
- 코드 라인 48에서 cpu -> 노드 변환을 지원하기 위해 매핑을 한다.
다음은 boradcom 사의 northstart2 칩에서 사용된 cpu 노드들을 보여준다.
- 4개의 코어가 시큐어 펌웨어에 psci 콜을 사용하는 것을 알 수 있다.
cpus {
#address-cells = <2>;
#size-cells = <0>;
A57_0: cpu@0 {
device_type = "cpu";
compatible = "arm,cortex-a57", "arm,armv8";
reg = <0 0>;
enable-method = "psci";
next-level-cache = <&CLUSTER0_L2>;
};
A57_1: cpu@1 {
device_type = "cpu";
compatible = "arm,cortex-a57", "arm,armv8";
reg = <0 1>;
enable-method = "psci";
next-level-cache = <&CLUSTER0_L2>;
};
A57_2: cpu@2 {
device_type = "cpu";
compatible = "arm,cortex-a57", "arm,armv8";
reg = <0 2>;
enable-method = "psci";
next-level-cache = <&CLUSTER0_L2>;
};
A57_3: cpu@3 {
device_type = "cpu";
compatible = "arm,cortex-a57", "arm,armv8";
reg = <0 3>;
enable-method = "psci";
next-level-cache = <&CLUSTER0_L2>;
};
CLUSTER0_L2: l2-cache@0 {
compatible = "cache";
};
};
psci {
compatible = "arm,psci-1.0";
method = "smc";
};
early_map_cpu_to_node() – ARM64
arch/arm64/mm/numa.c
void __init early_map_cpu_to_node(unsigned int cpu, int nid)
{
/* fallback to node 0 */
if (nid < 0 || nid >= MAX_NUMNODES || numa_off)
nid = 0;
cpu_to_node_map[cpu] = nid;
/*
* We should set the numa node of cpu0 as soon as possible, because it
* has already been set up online before. cpu_to_node(0) will soon be
* called.
*/
if (!cpu)
set_cpu_numa_node(cpu, nid);
}
cpu -> node 변환을 위해 요청한 @cpu에 대한 @nid를 설정한다.
- NUMA 노드에서 0번 cpu의 경우 이미 online 상태이므로 추가로 cpu에 대한 numa 노드 설정도 한다.
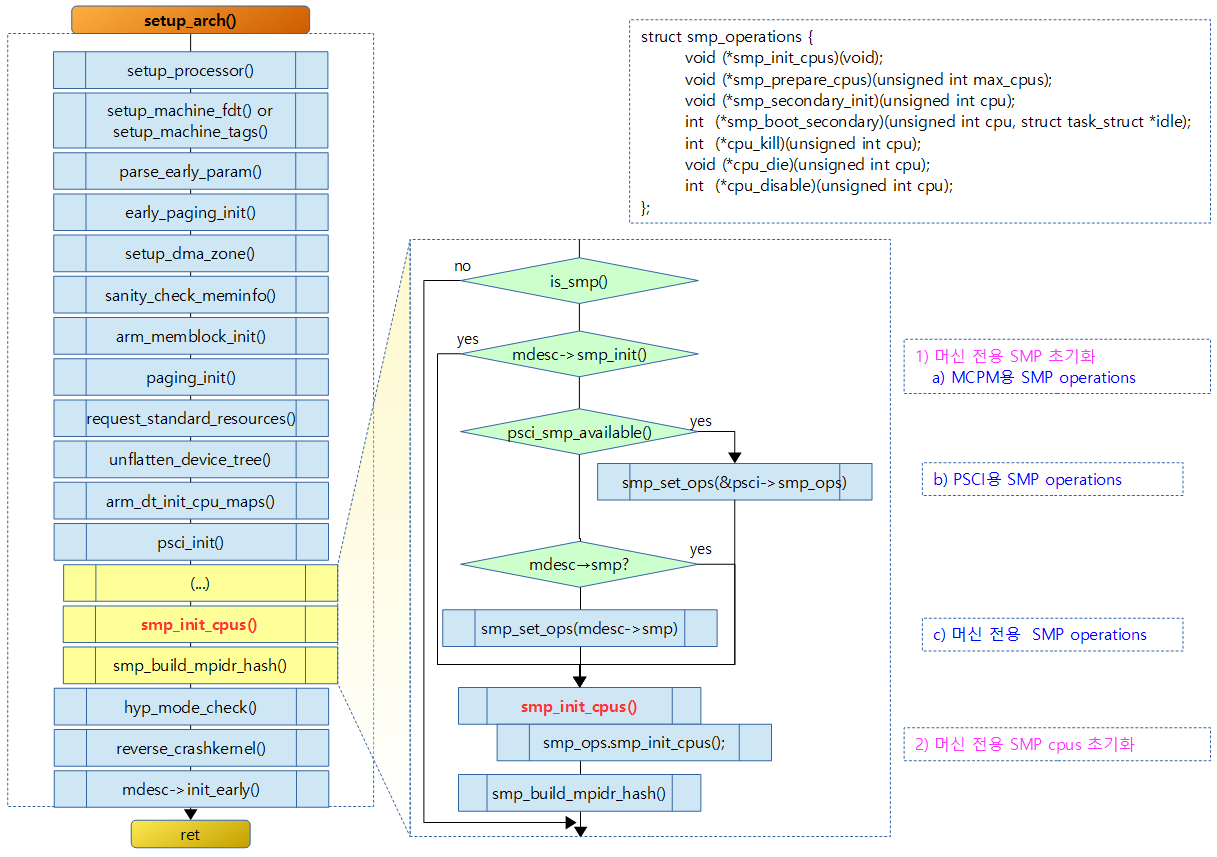
SMP CPU opearations 지정 및 초기화 – ARM32
setup_arch() 함수 중반 smp_init_cpus() 함수를 호출하기 직전
PSCI가 동작 상태에 따라 전역 smp_ops가 가리키는 구조체가 다르다.
- PSCI 동작 시 smp_ops는 psci_smp_ops를 가리키게 한다.
- PSCI 동작하지 않고 mdesc->smp가 존재하는 경우 smp_ops는 mdesc->smp를 가리킨다.
SMP cpu의 operations 지정
setup_arch() 중반 – ARM32
arch/arm/kernel/setup.c
#ifdef CONFIG_SMP
if (is_smp()) {
if (!mdesc->smp_init || !mdesc->smp_init()) {
if (psci_smp_available())
smp_set_ops(&psci_smp_ops);
else if (mdesc->smp)
smp_set_ops(mdesc->smp);
}
- 코드 라인 3에서 SMP 머신에서 smp_init 멤버 변수가 null 이거나 머신의 smp_init() 함수 수행 결과가 실패한 경우
- A) PSCI 방식 보다 먼저 사용될 수 있도록 MCPM(Multiple Cluster Power Management) 기능을 사용할 수 있도록 smp_ops가 mcpm_smp_ops 객체를 가리키게 한다.
- vexpress 예)
- mdesc->smp_init = vexpress_smp_init_ops() 함수를 가리키고 수행한다.
- DT 에서 “cci-400” 이라는 cache coherent interface 400 series 디바이스 장치가 발견되고 “status” 속성이 “ok”일 때 smp_ops를 mcpm_smp_ops 객체를 가리키게 한다.
- mcpm_smp_ops.smp_init_cpus = null
- DT 에서 “cci-400” 이라는 cache coherent interface 400 series 디바이스 장치가 발견되고 “status” 속성이 “ok”일 때 smp_ops를 mcpm_smp_ops 객체를 가리키게 한다.
- mdesc->smp_init = vexpress_smp_init_ops() 함수를 가리키고 수행한다.
- vexpress 예)
- A) PSCI 방식 보다 먼저 사용될 수 있도록 MCPM(Multiple Cluster Power Management) 기능을 사용할 수 있도록 smp_ops가 mcpm_smp_ops 객체를 가리키게 한다.
- 코드 라인 4~5에서 CONFIG_ARM_PSCI 커널 옵션이 설정되어 있고 PSCI가 동작 가능하면
- B) PSCI(Power State Cordination Interface) 기능을 사용할 수 있도록 전역 smp_ops가 psci_smp_ops를 가리키게 한다.
- psci_smp_ops.smp_init_cpus = null
- B) PSCI(Power State Cordination Interface) 기능을 사용할 수 있도록 전역 smp_ops가 psci_smp_ops를 가리키게 한다.
- 코드 라인 6~7에서 C) MCPM이나 PSCI가 동작 가능 상태가 아니면 smp_set_ops() 함수를 통해 smp_ops가 mdesc->smp를 대입한다.
- 예) rpi2:
- smp_ops가 bcm2709_smp_ops.ops 를 가리킨다.
- 예) rpi2:
mdesc->smp 및 mdesc->smp_init을 사용하는 시스템 예)
arch/arm/mach-vexpress/v2m.c
static const char * const v2m_dt_match[] __initconst = {
"arm,vexpress",
NULL,
};
DT_MACHINE_START(VEXPRESS_DT, "ARM-Versatile Express")
.dt_compat = v2m_dt_match,
.l2c_aux_val = 0x00400000,
.l2c_aux_mask = 0xfe0fffff,
.smp = smp_ops(vexpress_smp_dt_ops),
.smp_init = smp_init_ops(vexpress_smp_init_ops),
MACHINE_END
- Versatile Express 시스템에서 DT 머신 정의
- .smp가 전역 vexpress_smp_dt_ops 객체를 가리킴
- .smp_init_ops가 vexpress_smp_init_ops() 함수를 가리킴
smp_ops()
#define smp_ops(ops) (&(ops))
vexpress_smp_dt_ops 전역 객체
arch/arm/mach-vexpress/platsmp.c
struct smp_operations __initdata vexpress_smp_dt_ops = {
.smp_prepare_cpus = vexpress_smp_dt_prepare_cpus,
.smp_secondary_init = versatile_secondary_init,
.smp_boot_secondary = versatile_boot_secondary,
#ifdef CONFIG_HOTPLUG_CPU
.cpu_die = vexpress_cpu_die,
#endif
};
smp_init_ops()
arch/arm/include/asm/mach/arch.h
#define smp_init_ops(ops) (&(ops))
vexpress_smp_init_ops()
arch/arm/mach-vexpress/platsmp.c
bool __init vexpress_smp_init_ops(void)
{
#ifdef CONFIG_MCPM
/*
* The best way to detect a multi-cluster configuration at the moment
* is to look for the presence of a CCI in the system.
* Override the default vexpress_smp_ops if so.
*/
struct device_node *node;
node = of_find_compatible_node(NULL, NULL, "arm,cci-400");
if (node && of_device_is_available(node)) {
mcpm_smp_set_ops();
return true;
}
#endif
return false;
}
- CONFIG_MCPM
- Multi-Cluster Power Management로 big.LITTLE 등의 클러스터 기반의 파워를 관리하는 기능이다.
- node = of_find_compatible_node(NULL, NULL, “arm,cci-400”);
- DT 전체 노드 중 compatible 속성이 “arm,cci-400” 인 노드를 찾는다.
- if (node && of_device_is_available(node)) {
- 노드의 디바이스가 사용 가능하면
- 노드의 “status” 속성이 “ok”이면
- 노드의 디바이스가 사용 가능하면
- mcpm_smp_set_ops();
- 전역 smp_ops가 mcpm_smp_ops를 가리키게 한다.
vexpress-v2p-ca15_a7.dts 에서 “arm,cci-400” Cache Coherent Interface 400 series 디바이스에 대한 스크립트 정의를 보여준다.
- 2개의 a15 cpu와 3개의 a7 cpu가 big.LITTLE 클러스터 구성되어 있다.
cci@2c090000 {
compatible = "arm,cci-400";
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <1>;
reg = <0 0x2c090000 0 0x1000>;
ranges = <0x0 0x0 0x2c090000 0x10000>;
cci_control1: slave-if@4000 {
compatible = "arm,cci-400-ctrl-if";
interface-type = "ace";
reg = <0x4000 0x1000>;
};
cci_control2: slave-if@5000 {
compatible = "arm,cci-400-ctrl-if";
interface-type = "ace";
reg = <0x5000 0x1000>;
};
};
psci_smp_available()
arch/arm/kernel/psci_smp.c
bool __init psci_smp_available(void)
{
/* is cpu_on available at least? */
return (psci_ops.cpu_on != NULL);
}
psci_ops.cpu_on에 함수가 연결되어 있는 경우 PSCI가 동작하는 것으로 간주할 수 있다.
mcpm_smp_set_ops()
arch/arm/common/mcpm_platsmp.c
static struct smp_operations __initdata mcpm_smp_ops = {
.smp_boot_secondary = mcpm_boot_secondary,
.smp_secondary_init = mcpm_secondary_init,
#ifdef CONFIG_HOTPLUG_CPU
.cpu_kill = mcpm_cpu_kill,
.cpu_disable = mcpm_cpu_disable,
.cpu_die = mcpm_cpu_die,
#endif
};
void __init mcpm_smp_set_ops(void)
{
smp_set_ops(&mcpm_smp_ops);
}
전역 smp_ops가 mcpm_smp_ops 객체를 가리키게 한다.
smp_init_cpus() – ARM32
arch/arm/kernel/smp.c
/* platform specific SMP operations */
void __init smp_init_cpus(void)
{
if (smp_ops.smp_init_cpus)
smp_ops.smp_init_cpus();
}
smp_ops.smp_init_cpus에 함수가 연결되어 있는 경우 호출한다.
- smp_ops.smp_init_cpus에 등록된 함수를 호출하여 해당 SMP 머신에 대한 초기화를 진행한다.
- 보통 SCU(Snoop Control Unit) 즉 Cache Coherent Interface에 대한 설정이나 cpu possible bitmap 설정 등을 수행한다.
- exynos 예)
- exynos_smp_init_cpus()
- rpi2 예)
- bcm2709_smp_init_cpus()
아래는 smp_ops에 bcm2709_smp_ops.smp 가 연결되어 있어서 bcm2709_smp_init_cpus() 함수를 호출하는 과정을 보여준다.
arch/arm/mach-bcm2709/bcm2709.c
struct smp_operations bcm2709_smp_ops __initdata = {
.smp_init_cpus = bcm2709_smp_init_cpus,
.smp_prepare_cpus = bcm2709_smp_prepare_cpus,
.smp_secondary_init = bcm2709_secondary_init,
.smp_boot_secondary = bcm2709_boot_secondary,
};
#endif
static const char * const bcm2709_compat[] = {
"brcm,bcm2709",
"brcm,bcm2708", /* Could use bcm2708 in a pinch */
NULL
};
MACHINE_START(BCM2709, "BCM2709")
/* Maintainer: Broadcom Europe Ltd. */
#ifdef CONFIG_SMP
.smp = smp_ops(bcm2709_smp_ops),
#endif
.map_io = bcm2709_map_io,
.init_irq = bcm2709_init_irq,
.init_time = bcm2709_timer_init,
.init_machine = bcm2709_init,
.init_early = bcm2709_init_early,
.reserve = board_reserve,
.restart = bcm2709_restart,
.dt_compat = bcm2709_compat,
MACHINE_END
bcm2709_smp_init_cpus()
arch/arm/mach-bcm2709/bcm2709.c
void __init bcm2709_smp_init_cpus(void)
{
void secondary_startup(void);
unsigned int i, ncores;
ncores = 4; // xxx scu_get_core_count(NULL);
printk("[%s] enter (%x->%x)\n", __FUNCTION__, (unsigned)virt_to_phys((void *)secondary_startup), (unsigned)__io_address(ST_BASE + 0x10));
printk("[%s] ncores=%d\n", __FUNCTION__, ncores);
for (i = 0; i < ncores; i++) {
set_cpu_possible(i, true);
/* enable IRQ (not FIQ) */
writel(0x1, __io_address(ARM_LOCAL_MAILBOX_INT_CONTROL0 + 0x4 * i));
//writel(0xf, __io_address(ARM_LOCAL_TIMER_INT_CONTROL0 + 0x4 * i));
}
set_smp_cross_call(bcm2835_send_doorbell);
}
- ncores를 4로 고정시켰다.
- 각 코어 번호에 대해 cpu possible 비트를 설정한다.
- writel(0x1, __io_address(ARM_LOCAL_MAILBOX_INT_CONTROL0 + 0x4 * i));
- 각 core에 대해 IRQ enable (not FIQ)
- set_smp_cross_call(bcm2835_send_doorbell);
- 전역 __smp_cross_call이 bcm2835_send_doorbell() 함수를 가리키게 한다.
set_smp_cross_call()
arch/arm/kernel/smp.c
static void (*__smp_cross_call)(const struct cpumask *, unsigned int);
void __init set_smp_cross_call(void (*fn)(const struct cpumask *, unsigned int))
{
if (!__smp_cross_call)
__smp_cross_call = fn;
}
- 전역 __smp_cross_call이 설정되어 있지 않으면 fn으로 설정한다.
smp_cross_call()
다음의 함수들에서 호출된다.
- arch_send_call_function_ipi_mask()
- arch_send_wakeup_ipi_mask()
- arch_send_call_function_single_ipi()
- arch_irq_work_raise()
- tick_broadcast()
- smp_send_reschedule()
- smp_send_stop()
arm/kernel/smp.c
static void smp_cross_call(const struct cpumask *target, unsigned int ipinr)
{
trace_ipi_raise(target, ipi_types[ipinr]);
__smp_cross_call(target, ipinr);
}
bcm2835_send_doorbell()
arch/arm/kernel/smp.c
static void bcm2835_send_doorbell(const struct cpumask *mask, unsigned int irq)
{
int cpu;
/*
* Ensure that stores to Normal memory are visible to the
* other CPUs before issuing the IPI.
*/
dsb();
/* Convert our logical CPU mask into a physical one. */
for_each_cpu(cpu, mask)
{
/* submit softirq */
writel(1<<irq, __io_address(ARM_LOCAL_MAILBOX0_SET0 + 0x10 * MPIDR_AFFINITY_LEVEL(cpu_logical_map(cpu), 0)));
}
}
writel()
arch/arm/include/asm/io.h
#define writel(v,c) ({ __iowmb(); writel_relaxed(v,c); })
#define __iowmb() wmb()
#define writel_relaxed(v,c) __raw_writel((__force u32) cpu_to_le32(v),c)
__raw_writel()
arch/arm/include/asm/io.h
static inline void __raw_writel(u32 val, volatile void __iomem *addr)
{
asm volatile("str %1, %0"
: "+Qo" (*(volatile u32 __force *)addr)
: "r" (val));
}
CPU 관련 API
get_cpu()
include/linux/smp.h
#define get_cpu() ({ preempt_disable(); smp_processor_id(); })
cpu id를 알아온다. cpu가 바뀌지 않도록 Preemption을 disable한다.
- 이 함수를 사용하는 경우 사용 후에 반드시 짝이되는 put_cpu()를 사용하여 preemption을 다시 enable 해줘야 한다.
put_cpu()
include/linux/smp.h
#define put_cpu() preempt_enable()
cpu id 사용이 완료되었으므로 Preemption을 enable한다.
smp_processor_id()
include/linux/smp.h
/* * smp_processor_id(): get the current CPU ID. * * if DEBUG_PREEMPT is enabled then we check whether it is * used in a preemption-safe way. (smp_processor_id() is safe * if it's used in a preemption-off critical section, or in * a thread that is bound to the current CPU.) * * NOTE: raw_smp_processor_id() is for internal use only * (smp_processor_id() is the preferred variant), but in rare * instances it might also be used to turn off false positives * (i.e. smp_processor_id() use that the debugging code reports but * which use for some reason is legal). Don't use this to hack around * the warning message, as your code might not work under PREEMPT. */ #ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_PREEMPT extern unsigned int debug_smp_processor_id(void); # define smp_processor_id() debug_smp_processor_id() #else # define smp_processor_id() raw_smp_processor_id() #endif
- CONFIG_DEBUG_PREEMPT를 사용하는 경우 이 함수를 호출하기 전에 preempt가 이미 enable되어 있는 경우 경고를 한다. 그리고 사용을 하지 않는 경우 raw_smp_processor_id() 매크로를 호출한다.
raw_smp_processor_id() – ARM32
arch/arm/include/asm/smp.h
#define raw_smp_processor_id() (current_thread_info()->cpu)
- 현재 태스크가 동작하고 있는 cpu 번호를 리턴한다.
raw_smp_processor_id() – ARM64
arch/arm64/include/asm/smp.h
/* * We don't use this_cpu_read(cpu_number) as that has implicit writes to * preempt_count, and associated (compiler) barriers, that we'd like to avoid * the expense of. If we're preemptible, the value can be stale at use anyway. * And we can't use this_cpu_ptr() either, as that winds up recursing back * here under CONFIG_DEBUG_PREEMPT=y. */ #define raw_smp_processor_id() (*raw_cpu_ptr(&cpu_number))
per-cpu로 관리되는 cpu_number를 통해 cpu id를 알아온다.
참고
- Linux Kernel Power Management (PM) Framework for ARM 64-bit Processors | arm – 다운로드
- Multi-cluster power management | LWN.net
- Linux support for ARM big.LITTLE | LWN.net