<kernel v5.4>
Extable
Exception Table(extable)에는 프로세스 주소 공간(process address space)을 access하는 커널 API를 사용한 코드의 주소와 해당 API의 예외 처리 코드의 주소가 함께 담겨 있다.
- 커널이 프로세스용으로 할당된 페이지를 읽다 에러가 발생한 경우 페이지 테이블에 아직 로드(lazy load)가 되어 있지 않아 추가적으로 로드를 해야 하는 경우도 있고 그렇지 않고 정말 access 할 수 없는 공간으로 access를 시도하다 발생한 exception인 경우도 있다. 따라서 이에 대한 처리를 하기 위한 코드들이 호출될 수 있도록 설계되었다.
프로세스가 특정 주소를 access 하다가 exception이 발생하는 여러 fault(ARM32에서는 fsr_info[], ARM64에서는 fault_info[])별 처리 핸들러 함수를 실행시킬 때 extable을 검사하여 에러 진원지와 동일한 엔트리를 찾은 경우 해당 fixup 코드를 실행시킨다.
- 다음은 fsr_info[]에 연결되어 있는 처리함수들이다.
- do_translation_fault()
- “section translation fault”
- do_page_fault()
- “page translation fault”
- “page permission fault”
- do_sect_fault()
- “section permission fault”
- do_translation_fault()
다음 함수들에서 .fixup 섹션과 __ex_table 섹션을 사용한다.
- get_user(), strlen_user(), strnlen_user()
- __get_user_asm()
- put_user(), clear_user()
- __put_user_asm()
- 이 외에 영역 검사 및 futex 등 몇 개 더 있다.
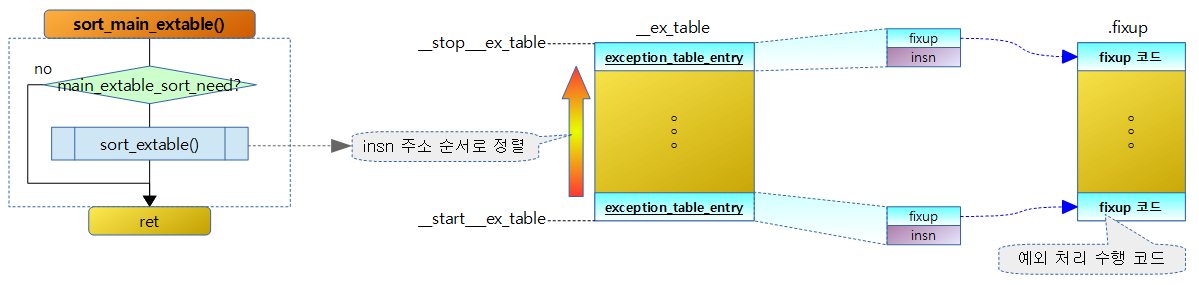
초기화 (정렬)
Main Exception Table이 정렬되어 있지 않은 경우 정렬한다.
- Exception Table은 다음 두 가지가 있다.
- Main Exception Table
- 각 Driver에서 사용하는 Exception Table
- 컴파일 타임에 툴에 의해 Exception table을 정렬하고, 툴에 의해 main_extable_sort_needed 변수 값까지 1로 바꿔주면 커널 부트업 처리 시 정렬을 할 필요가 없다.
- CONFIG_BUILDTIME_EXTABLE_SORT 커널 옵션을 사용하여 빌드 타임에 Exception table을 정렬하게 한다.
sort_main_extable()
kernel/extable.c
/* Sort the kernel's built-in exception table */
void __init sort_main_extable(void)
{
if (main_extable_sort_needed && __stop___ex_table > __start___ex_table) {
pr_notice("Sorting __ex_table...\n");
sort_extable(__start___ex_table, __stop___ex_table);
}
}
Main 커널에서 사용하는 Exception table을 정렬되어 있지 않은 경우 정렬한다.
kernel/extable.c
/* Cleared by build time tools if the table is already sorted. */ u32 __initdata __visible main_extable_sort_needed = 1;
sort_extable()
kernel/extable.c
void sort_extable(struct exception_table_entry *start,
struct exception_table_entry *finish)
{
sort(start, finish - start, sizeof(struct exception_table_entry),
cmp_ex_sort, swap_ex);
}
Exception table의 시작 부터 끝 까지 정렬한다.
- swap_ex 매크로는 ARCH_HAS_RELATIVE_EXTABLE이 사용되는 x86, powerpc, s390, arm64 아키텍처 등에서만 generic한 swap_ex() 함수를 사용하고, 그렇지 않은 경우 NULL로 치환된다.
cmp_ex_sort() – generic
lib/extable.c
/* * The exception table needs to be sorted so that the binary * search that we use to find entries in it works properly. * This is used both for the kernel exception table and for * the exception tables of modules that get loaded. */
static int cmp_ex(const void *a, const void *b)
{
const struct exception_table_entry *x = a, *y = b;
/* avoid overflow */
if (ex_to_insn(x) > ex_to_insn(y))
return 1;
if (ex_to_insn(x) < ex_to_insn(y))
return -1;
return 0;
}
a와 b를 비교한다.
- sort_extable() 함수가 ARCH_HAS_SORT_EXTABLE 가 사용되지 않는 아키텍처에서 사용할 수 있는 generic 루틴이다.
- sparc 아키텍처만 ARCH_HAS_SORT_EXTABLE을 지원하고, 나머지는 위의 generic 함수를 사용한다.
swap_ex() – generic
lib/extable.c
static void swap_ex(void *a, void *b, int size)
{
struct exception_table_entry *x = a, *y = b, tmp;
int delta = b - a;
tmp = *x;
x->insn = y->insn + delta;
y->insn = tmp.insn - delta;
#ifdef swap_ex_entry_fixup
swap_ex_entry_fixup(x, y, tmp, delta);
#else
x->fixup = y->fixup + delta;
y->fixup = tmp.fixup - delta;
#endif
}
a와 b를 치환한다.
__ex_table – ARM
arch/arm/kernel/vmlinux.lds.S
#ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_RODATA
. = ALIGN(1<<SECTION_SHIFT);
#endif
RO_DATA(PAGE_SIZE)
. = ALIGN(4);
__ex_table : AT(ADDR(__ex_table) - LOAD_OFFSET) {
__start___ex_table = .;
#ifdef CONFIG_MMU
*(__ex_table)
#endif
__stop___ex_table = .;
}
__ex_table은 .rodata 섹션 뒤에 위치한다.
__ex_table – ARM64
arch/arm64/kernel/vmlinux.lds.S
.text : { /* Real text segment */
_stext = .; /* Text and read-only data */
__exception_text_start = .;
*(.exception.text)
__exception_text_end = .;
IRQENTRY_TEXT
SOFTIRQENTRY_TEXT
ENTRY_TEXT
TEXT_TEXT
SCHED_TEXT
CPUIDLE_TEXT
LOCK_TEXT
KPROBES_TEXT
HYPERVISOR_TEXT
IDMAP_TEXT
HIBERNATE_TEXT
TRAMP_TEXT
*(.fixup)
*(.gnu.warning)
. = ALIGN(16);
*(.got) /* Global offset table */
}
. = ALIGN(SEGMENT_ALIGN);
_etext = .; /* End of text section */
RO_DATA(PAGE_SIZE) /* everything from this point to */
EXCEPTION_TABLE(8) /* __init_begin will be marked RO NX */
NOTES
__ex_table은 EXCEPTION_TABLE() 매크로로 정의되고, .rodata 섹션 뒤에 위치한다.
include/asm-generic/vmlinux.lds.h
/* * Exception table */
define EXCEPTION_TABLE(align) \
. = ALIGN(align); \
__ex_table : AT(ADDR(__ex_table) - LOAD_OFFSET) { \
__start___ex_table = .; \
KEEP(*(__ex_table)) \
__stop___ex_table = .; \
}
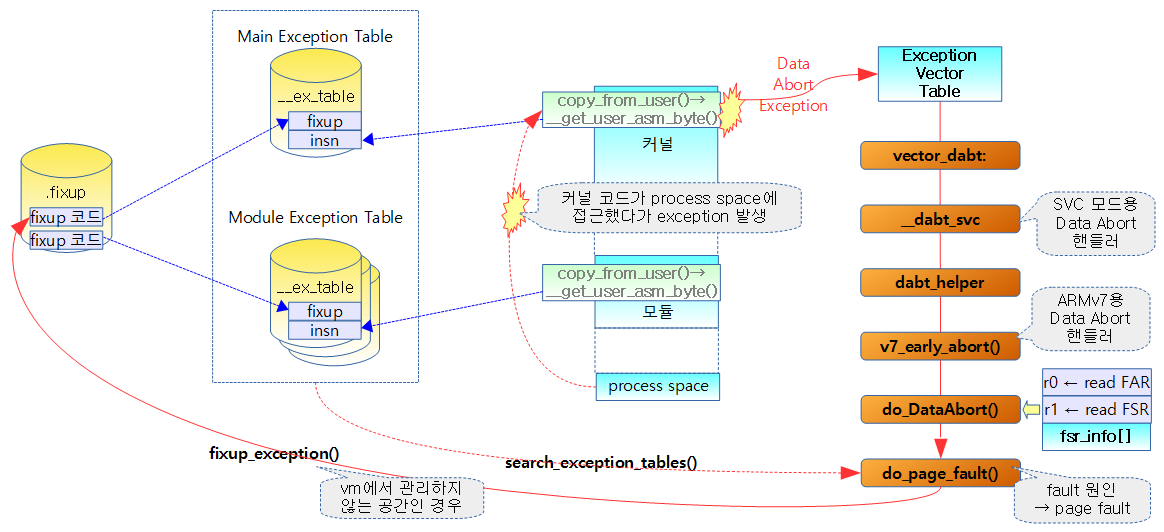
Exception 처리
다음 그림은 커널 코드가 process space에 있는 한 페이지에 접근하다 exception이 발생한 경우를 보여준다.
- 페이지를 access할 때 exception이 발생하는 경우 Data Abort 또는 Prefetch Abort 등의 exception이 발생하고 해당 exception vector로 jump를 하여 관련 함수를 수행한다.
search_exception_tables()
kernel/extable.c
/* Given an address, look for it in the exception tables. */
const struct exception_table_entry *search_exception_tables(unsigned long addr)
{
const struct exception_table_entry *e;
e = search_kernel_exception_table(addr);
if (!e)
e = search_module_extables(addr);
return e;
}
Main exception table과 전체 모듈에 있는 exception table의 insn 가상주소가 인수 addr와 같은 경우 해당 엔트리를 반환하고 검색되지 않는 경우 null을 리턴한다.
search_kernel_exception_table()
lib/extable.c
/* Given an address, look for it in the kernel exception table */
const
struct exception_table_entry *search_kernel_exception_table(unsigned long addr)
{
return search_extable(__start___ex_table,
__stop___ex_table - __start___ex_table, addr);
}
메인 커널에 위치한 exception table을 대상으로 가상 주소 @addr가 검색되는 경우 해당 엔트리를 반환한다. 그 외의 경우 null을 반환한다.
search_extable() – generic
lib/extable.c
/* * Search one exception table for an entry corresponding to the * given instruction address, and return the address of the entry, * or NULL if none is found. * We use a binary search, and thus we assume that the table is * already sorted. */
const struct exception_table_entry *
search_extable(const struct exception_table_entry *base,
const size_t num,
unsigned long value)
{
return bsearch(&value, base, num,
sizeof(struct exception_table_entry), cmp_ex_search);
}
@base에 위치한 exception 테이블에서 가상 주소 @value를 검색하되 최대 @num 엔트리 수만큼 검색한다.
- ARCH_HAS_SEARCH_EXTABLE을 사용하는 sparc 등의 아키텍처를 제외한 아키텍처들은 위의 generic 함수를 사용한다.
bsearch()
lib/bsearch.c
/* * bsearch - binary search an array of elements * @key: pointer to item being searched for * @base: pointer to first element to search * @num: number of elements * @size: size of each element * @cmp: pointer to comparison function * * This function does a binary search on the given array. The * contents of the array should already be in ascending sorted order * under the provided comparison function. * * Note that the key need not have the same type as the elements in * the array, e.g. key could be a string and the comparison function * could compare the string with the struct's name field. However, if * the key and elements in the array are of the same type, you can use * the same comparison function for both sort() and bsearch(). */
void *bsearch(const void *key, const void *base, size_t num, size_t size,
int (*cmp)(const void *key, const void *elt))
{
const char *pivot;
int result;
while (num > 0) {
pivot = base + (num >> 1) * size;
result = cmp(key, pivot);
if (result == 0)
return (void *)pivot;
if (result > 0) {
base = pivot + size;
num--;
}
num >>= 1;
}
return NULL;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(bsearch);
NOKPROBE_SYMBOL(bsearch);
바이너리 검색을 수행한다.
search_module_extables()
kernel/module.c
/* Given an address, look for it in the module exception tables. */
const struct exception_table_entry *search_module_extables(unsigned long addr)
{
const struct exception_table_entry *e = NULL;
struct module *mod;
preempt_disable();
mod = __module_address(addr);
if (!mod)
goto out;
if (!mod->num_exentries)
goto out;
e = search_extable(mod->extable,
mod->num_exentries,
addr);
out:
preempt_enable();
/*
* Now, if we found one, we are running inside it now, hence
* we cannot unload the module, hence no refcnt needed.
*/
return e;
}
전체 모듈을 루프를 돌며 각각의 모듈에 있는 exception table의 insn 가상주소가 인수 addr와 같은 경우 해당 엔트리를 반환하고 검색되지 않는 경우 null을 리턴한다.
구조체 및 전역변수
exception_table_entry 구조체 – generic
include/asm-generic/extable.h
/*
* The exception table consists of pairs of addresses: the first is the
* address of an instruction that is allowed to fault, and the second is
* the address at which the program should continue. No registers are
* modified, so it is entirely up to the continuation code to figure out
* what to do.
*
* All the routines below use bits of fixup code that are out of line
* with the main instruction path. This means when everything is well,
* we don't even have to jump over them. Further, they do not intrude
* on our cache or tlb entries.
*/
struct exception_table_entry
{
unsigned long insn, fixup;
};
- insn
- process(user) space에 접근하는 커널 API의 가상 주소
- fixup
- 해당 API에 대한 예외 처리 코드를 가리키는 가상 주소
exception_table_entry 구조체 – ARM64
arch/arm64/include/asm/extable.h
struct exception_table_entry
{
int insn, fixup;
};
ARM64의 경우 generic 코드와 다르게 unsigned long 대신 int를 사용하는 것을 알 수 있다.
fsr_info[] – ARM32
arch/arm/mm/fsr-2level.c
static struct fsr_info fsr_info[] = {
/*
* The following are the standard ARMv3 and ARMv4 aborts. ARMv5
* defines these to be "precise" aborts.
*/
{ do_bad, SIGSEGV, 0, "vector exception" },
{ do_bad, SIGBUS, BUS_ADRALN, "alignment exception" },
{ do_bad, SIGKILL, 0, "terminal exception" },
{ do_bad, SIGBUS, BUS_ADRALN, "alignment exception" },
{ do_bad, SIGBUS, 0, "external abort on linefetch" },
{ do_translation_fault, SIGSEGV, SEGV_MAPERR, "section translation fault" },
{ do_bad, SIGBUS, 0, "external abort on linefetch" },
{ do_page_fault, SIGSEGV, SEGV_MAPERR, "page translation fault" },
{ do_bad, SIGBUS, 0, "external abort on non-linefetch" },
{ do_bad, SIGSEGV, SEGV_ACCERR, "section domain fault" },
{ do_bad, SIGBUS, 0, "external abort on non-linefetch" },
{ do_bad, SIGSEGV, SEGV_ACCERR, "page domain fault" },
{ do_bad, SIGBUS, 0, "external abort on translation" },
{ do_sect_fault, SIGSEGV, SEGV_ACCERR, "section permission fault" },
{ do_bad, SIGBUS, 0, "external abort on translation" },
{ do_page_fault, SIGSEGV, SEGV_ACCERR, "page permission fault" },
/*
* The following are "imprecise" aborts, which are signalled by bit
* 10 of the FSR, and may not be recoverable. These are only
* supported if the CPU abort handler supports bit 10.
*/
{ do_bad, SIGBUS, 0, "unknown 16" },
{ do_bad, SIGBUS, 0, "unknown 17" },
{ do_bad, SIGBUS, 0, "unknown 18" },
{ do_bad, SIGBUS, 0, "unknown 19" },
{ do_bad, SIGBUS, 0, "lock abort" }, /* xscale */
{ do_bad, SIGBUS, 0, "unknown 21" },
{ do_bad, SIGBUS, BUS_OBJERR, "imprecise external abort" }, /* xscale */
{ do_bad, SIGBUS, 0, "unknown 23" },
{ do_bad, SIGBUS, 0, "dcache parity error" }, /* xscale */
{ do_bad, SIGBUS, 0, "unknown 25" },
{ do_bad, SIGBUS, 0, "unknown 26" },
{ do_bad, SIGBUS, 0, "unknown 27" },
{ do_bad, SIGBUS, 0, "unknown 28" },
{ do_bad, SIGBUS, 0, "unknown 29" },
{ do_bad, SIGBUS, 0, "unknown 30" },
{ do_bad, SIGBUS, 0, "unknown 31" },
};
exception이 발생했을 때 fault가 32개로 구분되며 해당 fault 핸들러 함수가 등록된다.
- 3레벨 페이지 테이블을 사용하는 경우 arch/arm/mm/fsr-3level.c 파일을 참고한다.
fault_info[] – ARM64
arch/arm64/mm/fault.c
static const struct fault_info fault_info[] = {
{ do_bad, SIGKILL, SI_KERNEL, "ttbr address size fault" },
{ do_bad, SIGKILL, SI_KERNEL, "level 1 address size fault" },
{ do_bad, SIGKILL, SI_KERNEL, "level 2 address size fault" },
{ do_bad, SIGKILL, SI_KERNEL, "level 3 address size fault" },
{ do_translation_fault, SIGSEGV, SEGV_MAPERR, "level 0 translation fault" },
{ do_translation_fault, SIGSEGV, SEGV_MAPERR, "level 1 translation fault" },
{ do_translation_fault, SIGSEGV, SEGV_MAPERR, "level 2 translation fault" },
{ do_translation_fault, SIGSEGV, SEGV_MAPERR, "level 3 translation fault" },
{ do_bad, SIGKILL, SI_KERNEL, "unknown 8" },
{ do_page_fault, SIGSEGV, SEGV_ACCERR, "level 1 access flag fault" },
{ do_page_fault, SIGSEGV, SEGV_ACCERR, "level 2 access flag fault" },
{ do_page_fault, SIGSEGV, SEGV_ACCERR, "level 3 access flag fault" },
{ do_bad, SIGKILL, SI_KERNEL, "unknown 12" },
{ do_page_fault, SIGSEGV, SEGV_ACCERR, "level 1 permission fault" },
{ do_page_fault, SIGSEGV, SEGV_ACCERR, "level 2 permission fault" },
{ do_page_fault, SIGSEGV, SEGV_ACCERR, "level 3 permission fault" },
{ do_sea, SIGBUS, BUS_OBJERR, "synchronous external abort" },
{ do_bad, SIGKILL, SI_KERNEL, "unknown 17" },
{ do_bad, SIGKILL, SI_KERNEL, "unknown 18" },
{ do_bad, SIGKILL, SI_KERNEL, "unknown 19" },
{ do_sea, SIGKILL, SI_KERNEL, "level 0 (translation table walk)" },
{ do_sea, SIGKILL, SI_KERNEL, "level 1 (translation table walk)" },
{ do_sea, SIGKILL, SI_KERNEL, "level 2 (translation table walk)" },
{ do_sea, SIGKILL, SI_KERNEL, "level 3 (translation table walk)" },
{ do_sea, SIGBUS, BUS_OBJERR, "synchronous parity or ECC error" }, // RR
eserved when RAS is implemented
{ do_bad, SIGKILL, SI_KERNEL, "unknown 25" },
{ do_bad, SIGKILL, SI_KERNEL, "unknown 26" },
{ do_bad, SIGKILL, SI_KERNEL, "unknown 27" },
{ do_sea, SIGKILL, SI_KERNEL, "level 0 synchronous parity error (translatii
on table walk)" }, // Reserved when RAS is implemented
{ do_sea, SIGKILL, SI_KERNEL, "level 1 synchronous parity error (translatii
on table walk)" }, // Reserved when RAS is implemented
{ do_sea, SIGKILL, SI_KERNEL, "level 2 synchronous parity error (translatii
on table walk)" }, // Reserved when RAS is implemented
{ do_sea, SIGKILL, SI_KERNEL, "level 3 synchronous parity error (translatii
on table walk)" }, // Reserved when RAS is implemented
{ do_bad, SIGKILL, SI_KERNEL, "unknown 32" },
{ do_alignment_fault, SIGBUS, BUS_ADRALN, "alignment fault" },
{ do_bad, SIGKILL, SI_KERNEL, "unknown 34" },
{ do_bad, SIGKILL, SI_KERNEL, "unknown 35" },
{ do_bad, SIGKILL, SI_KERNEL, "unknown 36" },
{ do_bad, SIGKILL, SI_KERNEL, "unknown 37" },
{ do_bad, SIGKILL, SI_KERNEL, "unknown 38" },
{ do_bad, SIGKILL, SI_KERNEL, "unknown 39" },
{ do_bad, SIGKILL, SI_KERNEL, "unknown 40" },
{ do_bad, SIGKILL, SI_KERNEL, "unknown 41" },
{ do_bad, SIGKILL, SI_KERNEL, "unknown 42" },
{ do_bad, SIGKILL, SI_KERNEL, "unknown 43" },
{ do_bad, SIGKILL, SI_KERNEL, "unknown 44" },
{ do_bad, SIGKILL, SI_KERNEL, "unknown 45" },
{ do_bad, SIGKILL, SI_KERNEL, "unknown 46" },
{ do_bad, SIGKILL, SI_KERNEL, "unknown 47" },
{ do_bad, SIGKILL, SI_KERNEL, "TLB conflict abort" },
{ do_bad, SIGKILL, SI_KERNEL, "Unsupported atomic hardware update fault"
},
{ do_bad, SIGKILL, SI_KERNEL, "unknown 50" },
{ do_bad, SIGKILL, SI_KERNEL, "unknown 51" },
{ do_bad, SIGKILL, SI_KERNEL, "implementation fault (lockdown abort)" },
{ do_bad, SIGBUS, BUS_OBJERR, "implementation fault (unsupported exclusivee
)" },
{ do_bad, SIGKILL, SI_KERNEL, "unknown 54" },
{ do_bad, SIGKILL, SI_KERNEL, "unknown 55" },
{ do_bad, SIGKILL, SI_KERNEL, "unknown 56" },
{ do_bad, SIGKILL, SI_KERNEL, "unknown 57" },
{ do_bad, SIGKILL, SI_KERNEL, "unknown 58" },
{ do_bad, SIGKILL, SI_KERNEL, "unknown 59" },
{ do_bad, SIGKILL, SI_KERNEL, "unknown 60" },
{ do_bad, SIGKILL, SI_KERNEL, "section domain fault" },
{ do_bad, SIGKILL, SI_KERNEL, "page domain fault" },
{ do_bad, SIGKILL, SI_KERNEL, "unknown 63" },
};
참고
- Exception -1- (ARM32 Vector)
- Exception -2- (ARM32 Handler 1)
- Exception -3- (ARM32 Handler 2)
- Exception -4- (ARM32 VFP & FPE)
- Exception -5- (Extable) – 현재 글
- Exception -6- (MM Fault Handler)
- Exception -7- (ARM64 Vector)
- Exception -8- (ARM64 Handler)
- copy_from_user() | 문c
- 시스템 콜 | 김태훈 – pptx 다운로드