Radix Tree
- Dynamic하게 정수 index key에 해당하는 slot에 포인터 값을 저장할 수 있다.
- 처음부터 큰 index key를 사용하면 트리 단계가 확장되어 느려지므로 작은 정수 index key를 사용하는 것이 좋다.
- 커널 버전 2.6.17에서 lockless한 구현을 하였다.
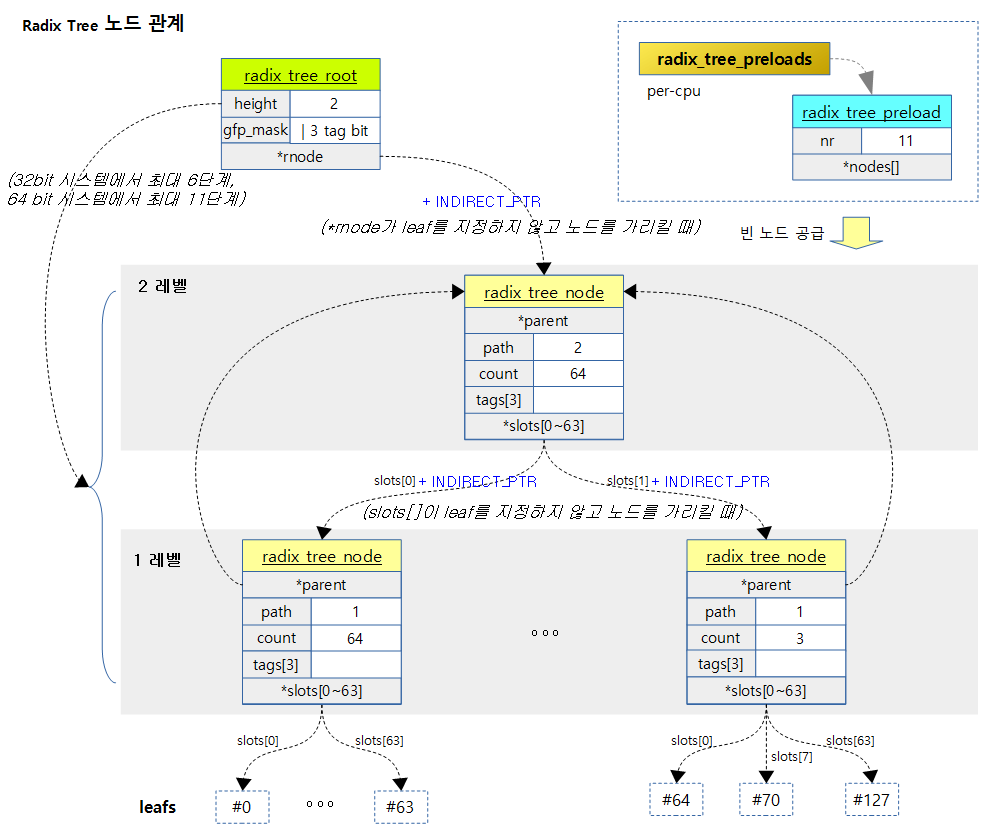
다음 그림은 2단계 Radix Tree의 구조를 표현하였다.
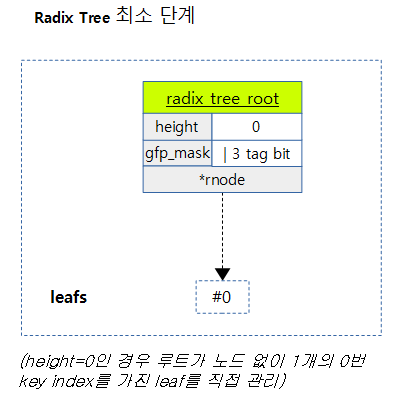
다음 그림은 Radix Tree의 최소 0단계로 index key 0번만을 등록시킬 수 있다. 이 상태에서 다른 번호의 index key를 추가하게 되면 radix 트리 단계(height)가 필요한 단계만큼 확장된다.
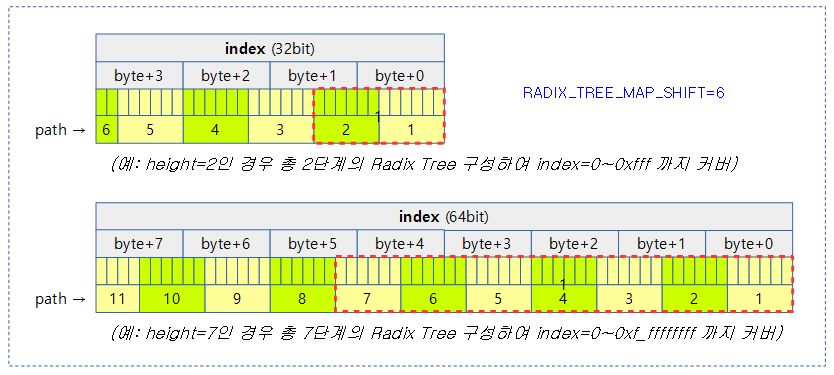
다음 그림은 index 값 크기에 따라 Radix Tree의 단계가 결정되는 것을 보여준다. (단계별 6bit 사용)
Radix 트리 선언
Radix 트리를 선언하고 초기화하는 방법은 다음과 같이 두 가지가 준비되어 있다.
- RADIX_TREE(name, mask);
- struct radix_tree_root my_tree; INIT_RADIX_TREE(my_tree, gfp_mask);
include/linux/radix-tree.h
#define RADIX_TREE(name, mask) \
struct radix_tree_root name = RADIX_TREE_INIT(mask)
요청한 name으로 radix_tree_root 구조체를 선언하고 gfp_mask를 대입하여 초기화한다.
include/linux/radix-tree.h
#define RADIX_TREE_INIT(mask) { \
.height = 0, \
.gfp_mask = (mask), \
.rnode = NULL, \
}
include/linux/radix-tree.h
#define INIT_RADIX_TREE(root, mask) \
do { \
(root)->height = 0; \
(root)->gfp_mask = (mask); \
(root)->rnode = NULL; \
} while (0)
Radix 트리 추가 및 삭제
Radix 트리에 항목을 추가하고 삭제하는 명령이 준비되어 있다.
- radix_tree_insert(root, index, item)
- radix_tree_delete(root, index)
radix_tree_insert()
lib/radix-tree.c
/**
* radix_tree_insert - insert into a radix tree
* @root: radix tree root
* @index: index key
* @item: item to insert
*
* Insert an item into the radix tree at position @index.
*/
int radix_tree_insert(struct radix_tree_root *root,
unsigned long index, void *item)
{
struct radix_tree_node *node;
void **slot;
int error;
BUG_ON(radix_tree_is_indirect_ptr(item));
error = __radix_tree_create(root, index, &node, &slot);
if (error)
return error;
if (*slot != NULL)
return -EEXIST;
rcu_assign_pointer(*slot, item);
if (node) {
node->count++;
BUG_ON(tag_get(node, 0, index & RADIX_TREE_MAP_MASK));
BUG_ON(tag_get(node, 1, index & RADIX_TREE_MAP_MASK));
} else {
BUG_ON(root_tag_get(root, 0));
BUG_ON(root_tag_get(root, 1));
}
return 0;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(radix_tree_insert);
radix 트리의 index에 해당하는 슬롯에 item 포인터를 대입한다.
- error = __radix_tree_create(root, index, &node, &slot);
- index 키 번호로 radix 트리 slot을 준비한다.
- if (error) return error;
- if (*slot != NULL) return -EEXIST;
- slot이 null이 아니면 이미 존재한다고 에러를 반환한다.
- rcu_assign_pointer(*slot, item);
__radix_tree_create()
lib/radix-tree.c
/**
* __radix_tree_create - create a slot in a radix tree
* @root: radix tree root
* @index: index key
* @nodep: returns node
* @slotp: returns slot
*
* Create, if necessary, and return the node and slot for an item
* at position @index in the radix tree @root.
*
* Until there is more than one item in the tree, no nodes are
* allocated and @root->rnode is used as a direct slot instead of
* pointing to a node, in which case *@nodep will be NULL.
*
* Returns -ENOMEM, or 0 for success.
*/
int __radix_tree_create(struct radix_tree_root *root, unsigned long index,
struct radix_tree_node **nodep, void ***slotp)
{
struct radix_tree_node *node = NULL, *slot;
unsigned int height, shift, offset;
int error;
/* Make sure the tree is high enough. */
if (index > radix_tree_maxindex(root->height)) {
error = radix_tree_extend(root, index);
if (error)
return error;
}
slot = indirect_to_ptr(root->rnode);
height = root->height;
shift = (height-1) * RADIX_TREE_MAP_SHIFT;
offset = 0; /* uninitialised var warning */
while (height > 0) {
if (slot == NULL) {
/* Have to add a child node. */
if (!(slot = radix_tree_node_alloc(root)))
return -ENOMEM;
slot->path = height;
slot->parent = node;
if (node) {
rcu_assign_pointer(node->slots[offset], slot);
node->count++;
slot->path |= offset << RADIX_TREE_HEIGHT_SHIFT;
} else
rcu_assign_pointer(root->rnode, ptr_to_indirect(slot));
}
/* Go a level down */
offset = (index >> shift) & RADIX_TREE_MAP_MASK;
node = slot;
slot = node->slots[offset];
shift -= RADIX_TREE_MAP_SHIFT;
height--;
}
if (nodep)
*nodep = node;
if (slotp)
*slotp = node ? node->slots + offset : (void **)&root->rnode;
return 0;
}
index 키에 해당하는 노드와 슬롯을 알아온다. 만일 확장이 필요한 경우 확장도 수행한다.
- if (index > radix_tree_maxindex(root->height)) { error = radix_tree_extend(root, index); if (error) return error; }
- index 키가 최대 값을 넘어가는 경우 radix 트리를 확장시킨다. 만일 에러인 경우 에러를 반환한다.
- slot = indirect_to_ptr(root->rnode);
- ptr에서 RADIX_TREE_INDIRECT_PTR(1)이 위치한 비트(bit0)를 제거한다.
- height = root->height; shift = (height-1) * RADIX_TREE_MAP_SHIFT;
- 현재 radix tree의 height(레벨)로 shift 값을 정한다.
- 예) height=3, RADIX_TREE_MAP_SHIFT=6
- while (height > 0) {
- if (slot == NULL) {
- if (!(slot = radix_tree_node_alloc(root))) return -ENOMEM;
- radix 트리 노드를 할당받는다. 에러가 발생하면 메모리 부족 에러를 반환한다.
- slot->path = height; slot->parent = node;
- slot의 path에 height를 대입하고, parent에 노드를 대입한다.
- if (node) { rcu_assign_pointer(node->slots[offset], slot); node->count++; slot->path |= offset << RADIX_TREE_HEIGHT_SHIFT;
- 루트 노드가 아닌 경우 노드의 slots[offset]에 slot을 대입하고, count를 증가시키며, path에 offset 값을 RADIX_TREE_HEIGHT_SHIFT만큼 좌로 쉬프트한 값을 대입한다.
- } else rcu_assign_pointer(root->rnode, ptr_to_indirect(slot));
- 루트 노드인 경우 root->rnode에 slot 포인터에 RADIX_TREE_INDEIRECT_PTR(1)을 더한 값을 대입한다.
- offset = (index >> shift) & RADIX_TREE_MAP_MASK;
- index 값에서 다음 레벨에 처리할 index bit 만큼을 offset에 대입한다.
- node = slot; slot = node->slots[offset];
- shift -= RADIX_TREE_MAP_SHIFT; height–;
- shift를 RADIX_TREE_MAP_SHIFT 만큼 감소시키고 height도 1 감소시킨다.
- if (nodep) *nodep = node;
- 인수 nodep가 주어진 경우 node를 대입한다.
- if (slotp) *slotp = node ? node->slots + offset : (void **)&root->rnode;
- 인수 slotp가 주어진 경우 슬롯을 대입한다.
- node가 null인 경우는 radix_tree_root 노드가 radix_tree_node 없이 직접 leaf를 관리하는 경우이다.
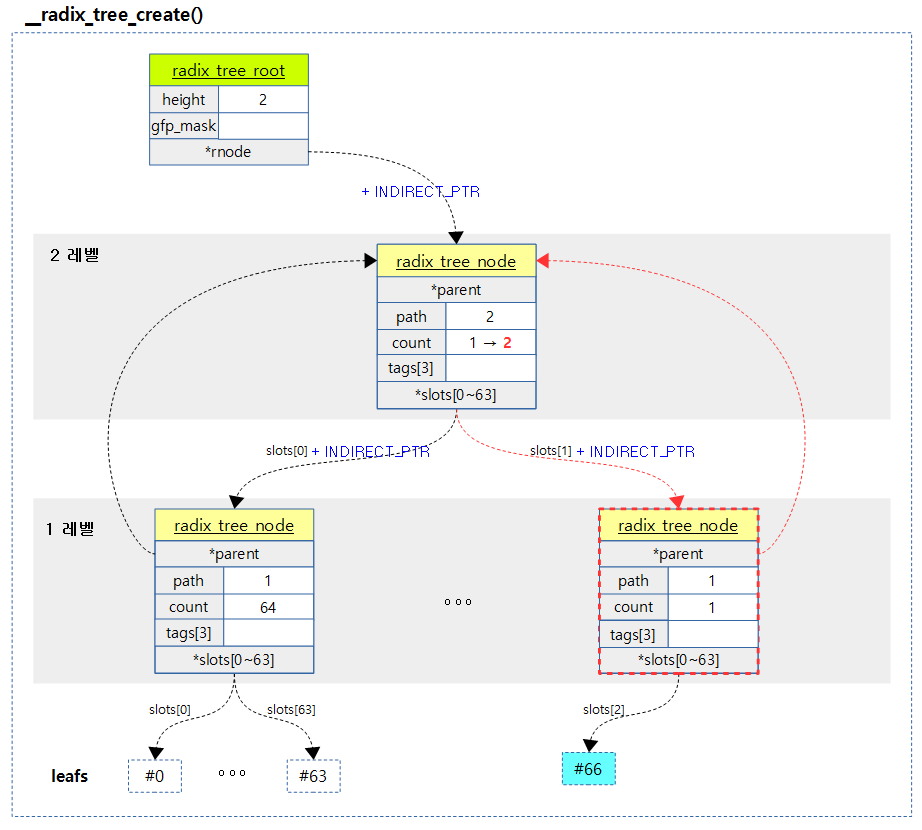
다음 그림은 필요한 index key를 추가하기 위해 필요로하는 중간 노드들을 만들고 구성하는 과정을 보여준다.
radix_tree_extend()
lib/radix-tree.c
/*
* Extend a radix tree so it can store key @index.
*/
static int radix_tree_extend(struct radix_tree_root *root, unsigned long index)
{
struct radix_tree_node *node;
struct radix_tree_node *slot;
unsigned int height;
int tag;
/* Figure out what the height should be. */
height = root->height + 1;
while (index > radix_tree_maxindex(height))
height++;
if (root->rnode == NULL) {
root->height = height;
goto out;
}
do {
unsigned int newheight;
if (!(node = radix_tree_node_alloc(root)))
return -ENOMEM;
/* Propagate the aggregated tag info into the new root */
for (tag = 0; tag < RADIX_TREE_MAX_TAGS; tag++) {
if (root_tag_get(root, tag))
tag_set(node, tag, 0);
}
/* Increase the height. */
newheight = root->height+1;
BUG_ON(newheight & ~RADIX_TREE_HEIGHT_MASK);
node->path = newheight;
node->count = 1;
node->parent = NULL;
slot = root->rnode;
if (newheight > 1) {
slot = indirect_to_ptr(slot);
slot->parent = node;
}
node->slots[0] = slot;
node = ptr_to_indirect(node);
rcu_assign_pointer(root->rnode, node);
root->height = newheight;
} while (height > root->height);
out:
return 0;
}
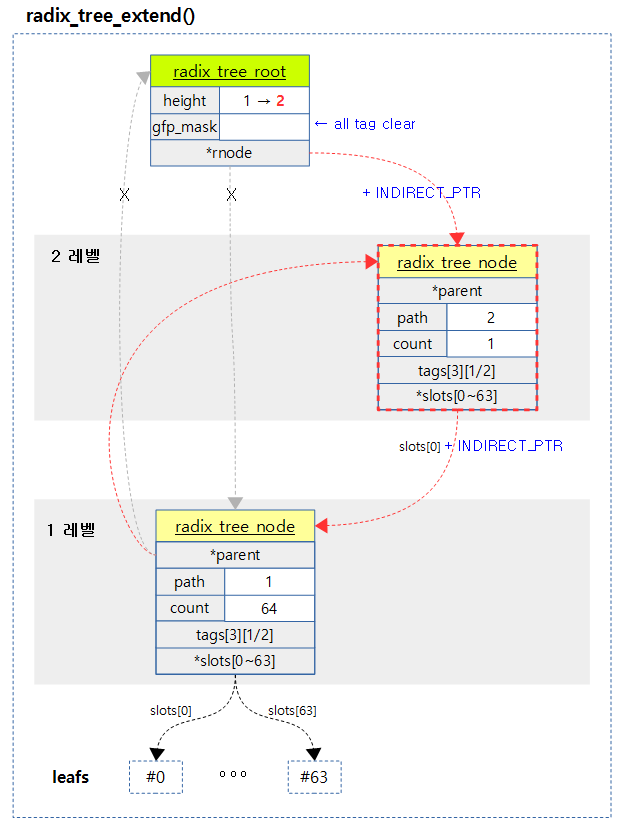
Radix 트리 노드를 확장하기 위해 새로운 루트 노드를 추가하고 기존 노드를 새로 만든 노드의 첫 번째 슬롯에 연결한다. 이러한 과정을 확장이 필요한 단계만큼 수행한다.
- height = root->height + 1; while (index > radix_tree_maxindex(height)) height++;
- 현재 radix tree가 처리할 수 있는 레벨만큼 height 값을 정한다.
- if (root->rnode == NULL) { root->height = height; goto out; }
- 만일 슬롯이 비어 있는 경우 root->height값을 설정하고 함수를 빠져나간다.
- do { unsigned int newheight; if (!(node = radix_tree_node_alloc(root))) return -ENOMEM;
- for (tag = 0; tag < RADIX_TREE_MAX_TAGS; tag++) { if (root_tag_get(root, tag)) tag_set(node, tag, 0); }
- 최대 태그 비트 수 만큼 루프를 돌며 루트 노드의 각 태그 비트가 1인 경우 0으로 초기화한다.
- 태그 비트는 gfp_mask의 비트들 중 __GFP_BITS_SHIFT(25) 비트부터 차례대로 사용된다.
- newheight = root->height+1; node->path = newheight;
- 새로운 루트 노드의 path에 height 값을 1 증가시켜 대입한다.
- node->count = 1; node->parent = NULL;
- 루트 노드의 count에 1을 대입하고 부모 노드가 없다고 지정한다.
- slot = root->rnode; if (newheight > 1) { slot = indirect_to_ptr(slot); slot->parent = node; } node->slots[0] = slot;
- 루트 노드의 첫 번째 슬롯에 기존 루트 노드를 연결한다.
- node = ptr_to_indirect(node); rcu_assign_pointer(root->rnode, node);
- root->height = newheight;
- } while (height > root->height);
- height가 현재 루트 노드의 height보다 큰 경우 새로운 루트 노드를 생성하기 위해 루프를 반복한다.
다음 그림은 1단계의 radix 트리가 2단계로 확장되는 모습을 보여준다.
radix_tree_node_alloc()
lib/radix-tree.c
/*
* This assumes that the caller has performed appropriate preallocation, and
* that the caller has pinned this thread of control to the current CPU.
*/
static struct radix_tree_node *
radix_tree_node_alloc(struct radix_tree_root *root)
{
struct radix_tree_node *ret = NULL;
gfp_t gfp_mask = root_gfp_mask(root);
/*
* Preload code isn't irq safe and it doesn't make sence to use
* preloading in the interrupt anyway as all the allocations have to
* be atomic. So just do normal allocation when in interrupt.
*/
if (!(gfp_mask & __GFP_WAIT) && !in_interrupt()) {
struct radix_tree_preload *rtp;
/*
* Provided the caller has preloaded here, we will always
* succeed in getting a node here (and never reach
* kmem_cache_alloc)
*/
rtp = this_cpu_ptr(&radix_tree_preloads);
if (rtp->nr) {
ret = rtp->nodes[rtp->nr - 1];
rtp->nodes[rtp->nr - 1] = NULL;
rtp->nr--;
}
/*
* Update the allocation stack trace as this is more useful
* for debugging.
*/
kmemleak_update_trace(ret);
}
if (ret == NULL)
ret = kmem_cache_alloc(radix_tree_node_cachep, gfp_mask);
BUG_ON(radix_tree_is_indirect_ptr(ret));
return ret;
}
radix 트리 노드를 할당받아온다.
- radix_tree_preloads에 준비된 노드를 반환한다.
- 만일 radix_tree_preloads에 준비된 노드가 없으면 slub 캐시에서 할당 받아온다.
- gfp_t gfp_mask = root_gfp_mask(root);
- 루트 노드의 gfp_mask에서 태그를 제외한 값을 알아온다.
- if (!(gfp_mask & __GFP_WAIT) && !in_interrupt()) {
- 인터럽트 처리중이 아니면서 __GFP_WAIT 요청도 없는 경우
- rtp = this_cpu_ptr(&radix_tree_preloads); if (rtp->nr) { ret = rtp->nodes[rtp->nr – 1]; rtp->nodes[rtp->nr – 1] = NULL; rtp->nr–; }
- 전역 radix_tree_preloads 구조체가 관리하는 노드가 존재하는 경우 노드 하나를 빼온다.
- if (ret == NULL) ret = kmem_cache_alloc(radix_tree_node_cachep, gfp_mask);
- 노드가 preload에 의해 준비되지 않은 경우 slub 캐시로부터 할당받아온다.
radix_tree_delete()
lib/radix-tree.c
/**
* radix_tree_delete - delete an item from a radix tree
* @root: radix tree root
* @index: index key
*
* Remove the item at @index from the radix tree rooted at @root.
*
* Returns the address of the deleted item, or NULL if it was not present.
*/
void *radix_tree_delete(struct radix_tree_root *root, unsigned long index)
{
return radix_tree_delete_item(root, index, NULL);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(radix_tree_delete);
Radix 트리에서 요청 index 키 항목을 제거한다.
radix_tree_delete_item()
lib/radix-tree.c
/**
* radix_tree_delete_item - delete an item from a radix tree
* @root: radix tree root
* @index: index key
* @item: expected item
*
* Remove @item at @index from the radix tree rooted at @root.
*
* Returns the address of the deleted item, or NULL if it was not present
* or the entry at the given @index was not @item.
*/
void *radix_tree_delete_item(struct radix_tree_root *root,
unsigned long index, void *item)
{
struct radix_tree_node *node;
unsigned int offset;
void **slot;
void *entry;
int tag;
entry = __radix_tree_lookup(root, index, &node, &slot);
if (!entry)
return NULL;
if (item && entry != item)
return NULL;
if (!node) {
root_tag_clear_all(root);
root->rnode = NULL;
return entry;
}
offset = index & RADIX_TREE_MAP_MASK;
/*
* Clear all tags associated with the item to be deleted.
* This way of doing it would be inefficient, but seldom is any set.
*/
for (tag = 0; tag < RADIX_TREE_MAX_TAGS; tag++) {
if (tag_get(node, tag, offset))
radix_tree_tag_clear(root, index, tag);
}
node->slots[offset] = NULL;
node->count--;
__radix_tree_delete_node(root, node);
return entry;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(radix_tree_delete_item);
Radix 트리에서 요청 index 키 항목을 제거하고 제거한 항목을 반환한다.
- entry = __radix_tree_lookup(root, index, &node, &slot);
- Radix 트리에서 요청 index 키 항목을 검색한다.
- if (item && entry != item) return NULL;
- 검색하여 찾은 entry 주소와 item 주소가 다른(mismatch) 경우 null을 반환한다.
- if (!node) { root_tag_clear_all(root); root->rnode = NULL; return entry; }
- 노드가 아닌 경우, 즉 키 인덱스가 0인 경우 루트에서 태그와 ptr 값을 지우고 해당 데이터 ptr 값을 반환한다.
- offset = index & RADIX_TREE_MAP_MASK;
- 현재 노드에서 요청한 인덱스 키에 해당하는 offset
- 0~RADIX_TREE_MAP_SIZE(63)
- for (tag = 0; tag < RADIX_TREE_MAX_TAGS; tag++) { if (tag_get(node, tag, offset)) radix_tree_tag_clear(root, index, tag); }
- offset에 위치한 태그가 설정되어 있는 경우 요청한 인덱스 키에 해당하는 3개 태그를 clear한다. 같은 노드가 관리하는 주변 64개의 태그들도 모두 없는 경우 상위노드로 진행하며 태그를 clear해 나간다.
- node->slots[offset] = NULL; node->count–;
- __radix_tree_delete_node(root, node);
- Radix 트리 노드가 필요 없는 경우 삭제한다.
- return entry;
__radix_tree_lookup()
lib/radix-tree.c
/**
* __radix_tree_lookup - lookup an item in a radix tree
* @root: radix tree root
* @index: index key
* @nodep: returns node
* @slotp: returns slot
*
* Lookup and return the item at position @index in the radix
* tree @root.
*
* Until there is more than one item in the tree, no nodes are
* allocated and @root->rnode is used as a direct slot instead of
* pointing to a node, in which case *@nodep will be NULL.
*/
void *__radix_tree_lookup(struct radix_tree_root *root, unsigned long index,
struct radix_tree_node **nodep, void ***slotp)
{
struct radix_tree_node *node, *parent;
unsigned int height, shift;
void **slot;
node = rcu_dereference_raw(root->rnode);
if (node == NULL)
return NULL;
if (!radix_tree_is_indirect_ptr(node)) {
if (index > 0)
return NULL;
if (nodep)
*nodep = NULL;
if (slotp)
*slotp = (void **)&root->rnode;
return node;
}
node = indirect_to_ptr(node);
height = node->path & RADIX_TREE_HEIGHT_MASK;
if (index > radix_tree_maxindex(height))
return NULL;
shift = (height-1) * RADIX_TREE_MAP_SHIFT;
do {
parent = node;
slot = node->slots + ((index >> shift) & RADIX_TREE_MAP_MASK);
node = rcu_dereference_raw(*slot);
if (node == NULL)
return NULL;
shift -= RADIX_TREE_MAP_SHIFT;
height--;
} while (height > 0);
if (nodep)
*nodep = parent;
if (slotp)
*slotp = slot;
return node;
}
Radix 트리에서 요청 index 키 항목을 검색한다. 발견되지 않으면 null을 반환한다.
- node = rcu_dereference_raw(root->rnode); if (node == NULL) return NULL;
- if (!radix_tree_is_indirect_ptr(node)) {
- if (index > 0) return NULL;
- 요청 index가 0보다 크면 못찾은 경우이므로 null을 반환한다.
- 루트가 직접 데이터를 갖는 경우는 key 인덱스가 0인 경우 밖에 없다.
- if (nodep) *nodep = NULL;
- 루트에서 발견된 경우이므로 Radix 트리 노드 없어서 null을 출력인수 nodep에 대입한다.
- if (slotp) *slotp = (void **)&root->rnode; return node;
- 출력인수 slotp에 슬롯 주소(rnode가 단일 슬롯으로 동작) 값을 대입하고 데이터 ptr 값을 반환한다.
- node = indirect_to_ptr(node);
- 불필요한 플래그 비트를 제거하고 실제 노드 주소만 남긴다.
- 현재 node 값은 가장 상위 Radix 트리 노드 주소값이다.
- height = node->path & RADIX_TREE_HEIGHT_MASK; if (index > radix_tree_maxindex(height)) return NULL;
- 요청 인덱스 키값이 최상위 노드의 height 단계가 관리하는 값을 초과하는 경우 null을 반환한다.
- shift = (height-1) * RADIX_TREE_MAP_SHIFT;
- 가장 최상위 노드를 처리하기 위해 쉬프트할 비트 수를 결정한다.
- do { parent = node; slot = node->slots + ((index >> shift) & RADIX_TREE_MAP_MASK); node = rcu_dereference_raw(*slot); if (node == NULL) return NULL; shift -= RADIX_TREE_MAP_SHIFT; height–; } while (height > 0);
- 가장 상위 노드부터 가장 바닥 노드를 거쳐 leaf까지 루프를 돌며 연결된 노드를 찾아간다.
- if (nodep) *nodep = parent;
- 출력인수 nodep에 leaf를 관리하는 가장 마지막 노드를 대입한다.
- if (slotp) *slotp = slot; return node;
- 출력인수 slotp에 슬롯 주소를 대입하고 데이터 ptr 값을 반환한다.
radix_tree_tag_clear()
lib/radix-tree.c
/**
* radix_tree_tag_clear - clear a tag on a radix tree node
* @root: radix tree root
* @index: index key
* @tag: tag index
*
* Clear the search tag (which must be < RADIX_TREE_MAX_TAGS)
* corresponding to @index in the radix tree. If
* this causes the leaf node to have no tags set then clear the tag in the
* next-to-leaf node, etc.
*
* Returns the address of the tagged item on success, else NULL. ie:
* has the same return value and semantics as radix_tree_lookup().
*/
void *radix_tree_tag_clear(struct radix_tree_root *root,
unsigned long index, unsigned int tag)
{
struct radix_tree_node *node = NULL;
struct radix_tree_node *slot = NULL;
unsigned int height, shift;
int uninitialized_var(offset);
height = root->height;
if (index > radix_tree_maxindex(height))
goto out;
shift = height * RADIX_TREE_MAP_SHIFT;
slot = indirect_to_ptr(root->rnode);
while (shift) {
if (slot == NULL)
goto out;
shift -= RADIX_TREE_MAP_SHIFT;
offset = (index >> shift) & RADIX_TREE_MAP_MASK;
node = slot;
slot = slot->slots[offset];
}
if (slot == NULL)
goto out;
while (node) {
if (!tag_get(node, tag, offset))
goto out;
tag_clear(node, tag, offset);
if (any_tag_set(node, tag))
goto out;
index >>= RADIX_TREE_MAP_SHIFT;
offset = index & RADIX_TREE_MAP_MASK;
node = node->parent;
}
/* clear the root's tag bit */
if (root_tag_get(root, tag))
root_tag_clear(root, tag);
out:
return slot;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(radix_tree_tag_clear);
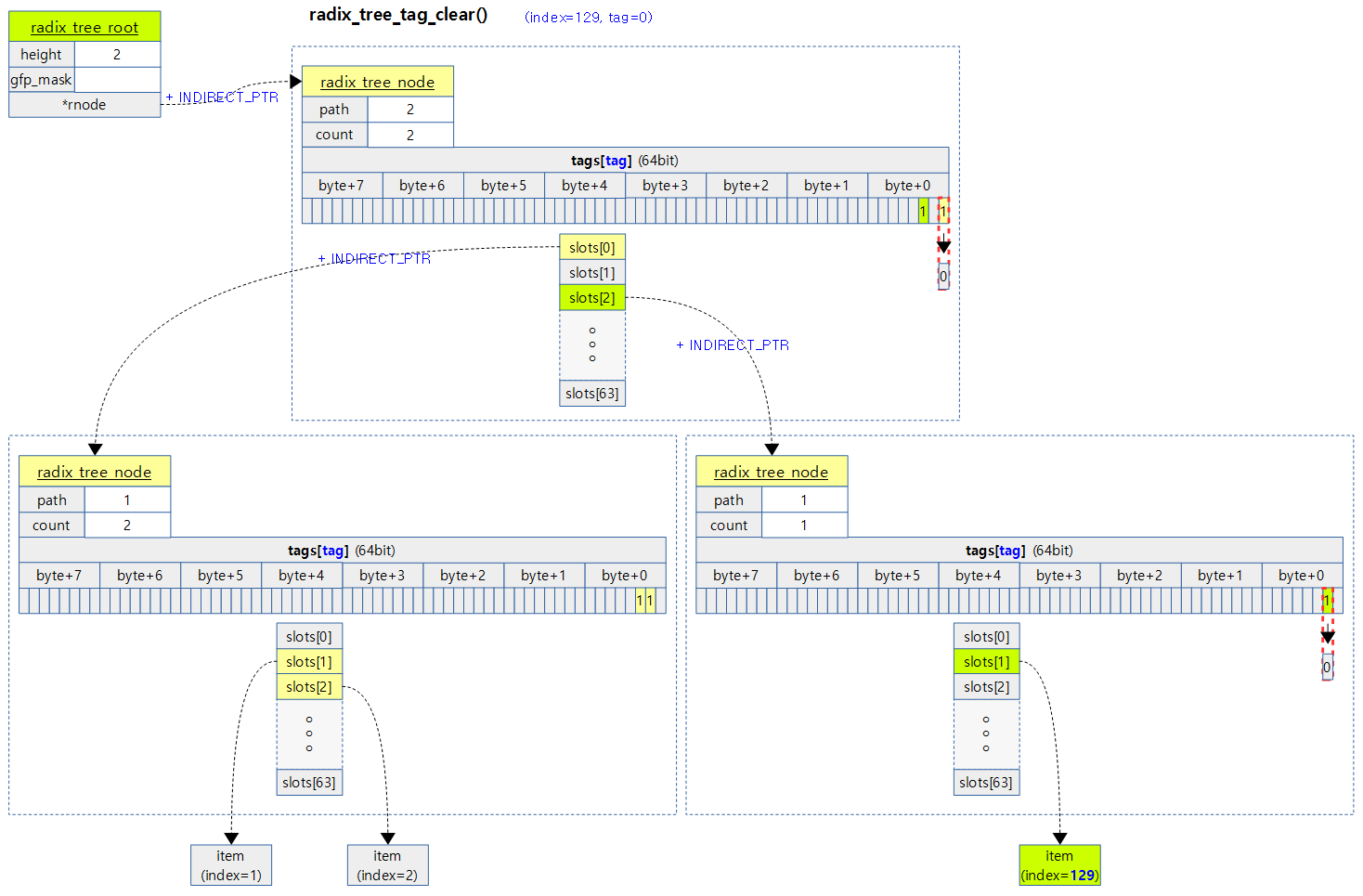
요청한 인덱스 키에 해당하는 태그를 clear한다. 같은 노드가 관리하는 64개의 태그들도 모두 없는 경우 상위노드로 진행하며 태그를 clear해 나간다.
- height = root->height; if (index > radix_tree_maxindex(height)) goto out;
- 요청 index 키 값이 Radix 트리가 관리하는 단계를 초과하는 경우 null을 반환한다.
- shift = height * RADIX_TREE_MAP_SHIFT;
- 잠시 후에 루프를 돌며 index 키에서 각 단계별로 필요한 비트만큼을 쉬프트하여 사용할 것이므로 미리 가장 상위보다 한 단계 더 높은 단계로 쉬프트 값을 정해 놓는다.
- slot = indirect_to_ptr(root->rnode);
- while (shift) { if (slot == NULL) goto out; shift -= RADIX_TREE_MAP_SHIFT; offset = (index >> shift) & RADIX_TREE_MAP_MASK; node = slot; slot = slot->slots[offset]; }
- 가장 바닥 단계까지 루프를 돌아 node와 slot에 가장 최하단 노드 주소와 슬롯 값을 대입하게 한다.
- if (slot == NULL) goto out;
- slot이 이미 비어 있는 경우 null을 반환한다.
- while (node) { if (!tag_get(node, tag, offset)) goto out; tag_clear(node, tag, offset); if (any_tag_set(node, tag)) goto out; index >>= RADIX_TREE_MAP_SHIFT; offset = index & RADIX_TREE_MAP_MASK; node = node->parent; }
- 가장 하위 노드부터 최상위 노드까지 루프를 돌며 index 키와 관련된 태크를 clear한다.
- 진행도중 현재 노드의 index 키와 관련된 태그가 이미 비어 있는 경우 함수를 빠져나간다.
- 진행도중 현재 노드와 관련된 64개의 다른 태그 비트가 여전히 존재하는 경우 상위로 진행하지 않고 함수를 빠져나간다.
- if (root_tag_get(root, tag)) root_tag_clear(root, tag);
- 여기까지 진행이 되었다는 의미는 최상위 노드마저도 모든 태그가 지워졌다는 의미이므로 루트에 있는 태그도 삭제한다.
다음 그림은 index 129번에 대한 0번 태그를 삭제할 때 하위 노드의 태그를 먼저 지운후 같은 노드의 태그가 모두 없는 경우 그 상위 노드의 태그마저 삭제하는 모습을 보여준다.
__radix_tree_delete_node()
lib/radix-tree.c
/**
* __radix_tree_delete_node - try to free node after clearing a slot
* @root: radix tree root
* @node: node containing @index
*
* After clearing the slot at @index in @node from radix tree
* rooted at @root, call this function to attempt freeing the
* node and shrinking the tree.
*
* Returns %true if @node was freed, %false otherwise.
*/
bool __radix_tree_delete_node(struct radix_tree_root *root,
struct radix_tree_node *node)
{
bool deleted = false;
do {
struct radix_tree_node *parent;
if (node->count) {
if (node == indirect_to_ptr(root->rnode)) {
radix_tree_shrink(root);
if (root->height == 0)
deleted = true;
}
return deleted;
}
parent = node->parent;
if (parent) {
unsigned int offset;
offset = node->path >> RADIX_TREE_HEIGHT_SHIFT;
parent->slots[offset] = NULL;
parent->count--;
} else {
root_tag_clear_all(root);
root->height = 0;
root->rnode = NULL;
}
radix_tree_node_free(node);
deleted = true;
node = parent;
} while (node);
return deleted;
}
요청 노드에 대해 shrink를 해본 후 사용 슬롯이 없는 경우 삭제하고 루프를 돌며 상위 노드로 이동하여 반복한다. 하나 이상 삭제된 경우 true를 반환한다.
- do { struct radix_tree_node *parent; if (node->count) { if (node == indirect_to_ptr(root->rnode)) { radix_tree_shrink(root); if (root->height == 0) deleted = true; } return deleted; }
- 요청한 노드의 count가 0보다 큰 경우 shrink를 시도한 후 결과를 반환한다.
- parent = node->parent; if (parent) { unsigned int offset; offset = node->path >> RADIX_TREE_HEIGHT_SHIFT; parent->slots[offset] = NULL; parent->count–;
- 부모 노드가 있는 경우 부모 노드에서 현재 노드로의 연결을 끊고 count를 줄인다.
- } else { root_tag_clear_all(root); root->height = 0; root->rnode = NULL; }
- 최상위 노드를 제거한다.
- 부모 노드가 없는 경우 루트 태그를 모두 clear하고 height를 0으로 만들고 item 연결을 끊는다.
- radix_tree_node_free(node); deleted = true; node = parent; } while (node);
- 현재 노드를 제거하고 그 상위 노드를 선택한 후 계속 진행한다.
- 상위 노드도 카운트가 0이 된 경우 제거한다.
radix_tree_shrink()
lib/radix-tree.c
/**
* radix_tree_shrink - shrink height of a radix tree to minimal
* @root radix tree root
*/
static inline void radix_tree_shrink(struct radix_tree_root *root)
{
/* try to shrink tree height */
while (root->height > 0) {
struct radix_tree_node *to_free = root->rnode;
struct radix_tree_node *slot;
BUG_ON(!radix_tree_is_indirect_ptr(to_free));
to_free = indirect_to_ptr(to_free);
/*
* The candidate node has more than one child, or its child
* is not at the leftmost slot, we cannot shrink.
*/
if (to_free->count != 1)
break;
if (!to_free->slots[0])
break;
/*
* We don't need rcu_assign_pointer(), since we are simply
* moving the node from one part of the tree to another: if it
* was safe to dereference the old pointer to it
* (to_free->slots[0]), it will be safe to dereference the new
* one (root->rnode) as far as dependent read barriers go.
*/
slot = to_free->slots[0];
if (root->height > 1) {
slot->parent = NULL;
slot = ptr_to_indirect(slot);
}
root->rnode = slot;
root->height--;
/*
* We have a dilemma here. The node's slot[0] must not be
* NULLed in case there are concurrent lookups expecting to
* find the item. However if this was a bottom-level node,
* then it may be subject to the slot pointer being visible
* to callers dereferencing it. If item corresponding to
* slot[0] is subsequently deleted, these callers would expect
* their slot to become empty sooner or later.
*
* For example, lockless pagecache will look up a slot, deref
* the page pointer, and if the page is 0 refcount it means it
* was concurrently deleted from pagecache so try the deref
* again. Fortunately there is already a requirement for logic
* to retry the entire slot lookup -- the indirect pointer
* problem (replacing direct root node with an indirect pointer
* also results in a stale slot). So tag the slot as indirect
* to force callers to retry.
*/
if (root->height == 0)
*((unsigned long *)&to_free->slots[0]) |=
RADIX_TREE_INDIRECT_PTR;
radix_tree_node_free(to_free);
}
}
Radix 트리 단계를 줄일 수 있는 경우 불필요한 Radix 트리 노드를 삭제하고 단계를 줄인다.
- 루프를 돌며 최상위 노드를 제거할 수 있는 경우 제거하여 Radix 트리 단계를 줄인다.
- 최상위 노드의 0번 슬롯만 있는 경우 현재 노드를 삭제하고 그 다음 노드를 최상위 노드로 변경한다.
- while (root->height > 0) { struct radix_tree_node *to_free = root->rnode;
- Radix 트리 단계가 1단계 이상인 경우 루트에 연결된 최상위 노드를 가져온다.
- to_free = indirect_to_ptr(to_free);
- 최상위 노드 포인터에서 RADIX_TREE_INDIRECT_PTR 비트를 제거한다.
- if (to_free->count != 1) break;
- 노드가 관리하는 슬롯이 하나가 아니면 그만 shrink를 중지하고 빠져나간다.
- if (!to_free->slots[0]) break;
- 남은 슬롯이 0번이 아닌 경우 그만 shrink를 중지하고 빠져나간다.
- slot = to_free->slots[0]; if (root->height > 1) { slot->parent = NULL; slot = ptr_to_indirect(slot); }root->rnode = slot; root->height–;
- 첫 슬롯에 연결된 다음 노드를 최상위 노드로 만든다.
- parent에 null을 넣고, 루트가 다음 노드를 가리키게 하고 height 값을 감소시킨다.
- if (root->height == 0) *((unsigned long *)&to_free->slots[0]) |= RADIX_TREE_INDIRECT_PTR;
- 루트 height값이 0이면 삭제할 노드의 첫 슬롯에 연결된 값은 item이더라도 RADIX_TREE_INDIRECT_PTR 비트를 더한다.
- radix_tree_node_free(to_free);
radix_tree_node_free()
lib/radix-tree.c
static inline void
radix_tree_node_free(struct radix_tree_node *node)
{
call_rcu(&node->rcu_head, radix_tree_node_rcu_free);
}
Radix 트리 노드를 RCU 방식으로 제거한 후 slub 캐시로 반환한다(free).
radix_tree_node_rcu_free()
lib/radix-tree.c
static void radix_tree_node_rcu_free(struct rcu_head *head)
{
struct radix_tree_node *node =
container_of(head, struct radix_tree_node, rcu_head);
int i;
/*
* must only free zeroed nodes into the slab. radix_tree_shrink
* can leave us with a non-NULL entry in the first slot, so clear
* that here to make sure.
*/
for (i = 0; i < RADIX_TREE_MAX_TAGS; i++)
tag_clear(node, i, 0);
node->slots[0] = NULL;
node->count = 0;
kmem_cache_free(radix_tree_node_cachep, node);
}
Radix 트리 노드의 태그를 제거하고 slots[0]에 null을 대입하고, count를 0으로 만든 후 Radix 트리 노드 slub 캐시에 반환한다.(free)
Preload Radix 트리 노드
radix_tree_preload()
lib/radix-tree.c
/*
* Load up this CPU's radix_tree_node buffer with sufficient objects to
* ensure that the addition of a single element in the tree cannot fail. On
* success, return zero, with preemption disabled. On error, return -ENOMEM
* with preemption not disabled.
*
* To make use of this facility, the radix tree must be initialised without
* __GFP_WAIT being passed to INIT_RADIX_TREE().
*/
int radix_tree_preload(gfp_t gfp_mask)
{
/* Warn on non-sensical use... */
WARN_ON_ONCE(!(gfp_mask & __GFP_WAIT));
return __radix_tree_preload(gfp_mask);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(radix_tree_preload);
전역 per-cpu 타입의 radix tree preload 구조체에 빈 radix 트리 노드를 미리 할당받아 가득 채워 준비한다.
__radix_tree_preload()
lib/radix-tree.c
/*
* Load up this CPU's radix_tree_node buffer with sufficient objects to
* ensure that the addition of a single element in the tree cannot fail. On
* success, return zero, with preemption disabled. On error, return -ENOMEM
* with preemption not disabled.
*
* To make use of this facility, the radix tree must be initialised without
* __GFP_WAIT being passed to INIT_RADIX_TREE().
*/
static int __radix_tree_preload(gfp_t gfp_mask)
{
struct radix_tree_preload *rtp;
struct radix_tree_node *node;
int ret = -ENOMEM;
preempt_disable();
rtp = this_cpu_ptr(&radix_tree_preloads);
while (rtp->nr < ARRAY_SIZE(rtp->nodes)) {
preempt_enable();
node = kmem_cache_alloc(radix_tree_node_cachep, gfp_mask);
if (node == NULL)
goto out;
preempt_disable();
rtp = this_cpu_ptr(&radix_tree_preloads);
if (rtp->nr < ARRAY_SIZE(rtp->nodes))
rtp->nodes[rtp->nr++] = node;
else
kmem_cache_free(radix_tree_node_cachep, node);
}
ret = 0;
out:
return ret;
}
전역 per-cpu 타입의 radix tree preload 구조체에 빈 radix 트리 노드를 미리 할당 받아 가득 채워 준비한다.
- 중간에 slub 캐시로 부터 할당이 실패한 경우 preemption이 enable된 채로 빠져나온다. 성공한 경우 preemption이 disable된 채로 빠져나온다.
- 시스템 크기에 따라 최대 radix 트리 노드 수가 정해진다.
lib/radix-tree.c
/*
* The radix tree is variable-height, so an insert operation not only has
* to build the branch to its corresponding item, it also has to build the
* branch to existing items if the size has to be increased (by
* radix_tree_extend).
*
* The worst case is a zero height tree with just a single item at index 0,
* and then inserting an item at index ULONG_MAX. This requires 2 new branches
* of RADIX_TREE_MAX_PATH size to be created, with only the root node shared.
* Hence:
*/
#define RADIX_TREE_PRELOAD_SIZE (RADIX_TREE_MAX_PATH * 2 - 1)
- RADIX_TREE_PRELOAD_SIZE
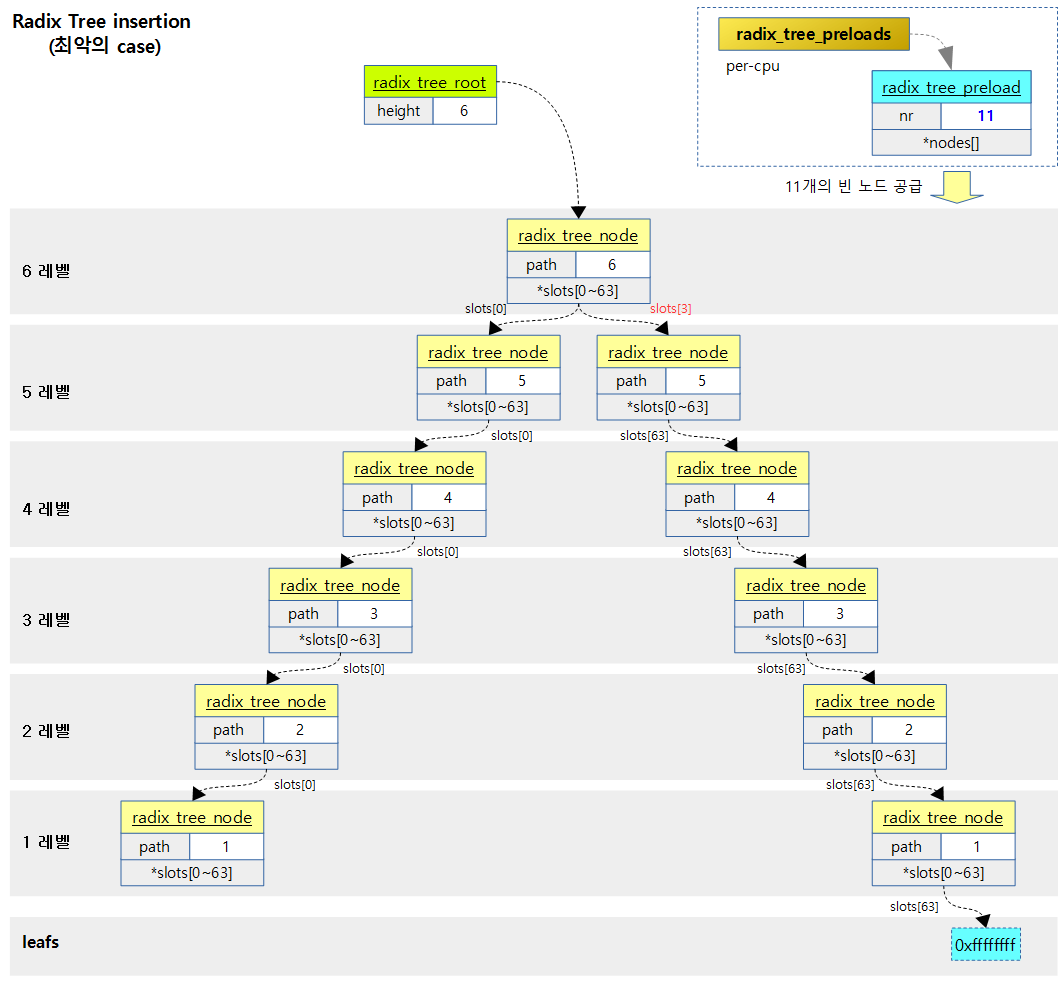
- Radix 트리는 가변 단계(레벨, 높이)로 구성되는데 insert 한 번 수행시 최악의 경우 여러 개의 radix 트리 노드의 할당이 필요하다 따라서 최대 할당이 가능한 수 만큼 미리 radix 트리 프리로드 버퍼에 빈 radix 트리 노드들을 할당 받아 둔다.
- 예) 최악의 32bit 시스템 case
- height가 0인 상태에서 index 키 0xffffffff를 사용하는 경우 최대 11개의 rcu 트리 노드가 필요하다.
- Radix 트리 노드를 6단계까지 6번 확장 시키면서 6개가 필요하다.
- index 키에 맞는 radix 트리 노드를 만들기 위해 6단계를 제외한 1~5단계 각각에 하나씩 하여 5개가 필요하다.
- 따라서 위와 같은 최대로 필요한 수에 맞추어 시스템에 따라 다음과 같이 크기가 결정된다.
다음 그림은 radix_tree_root가 0단계로 동작중에 long 최고 값을 index 키로 요청한 경우 32bit 시스템의 최대 단계인 6단계로 확장되면서 총 11개의 radix_tree_node가 필요한 경우를 보여준다.
기타 함수
ptr_to_indirect()
lib/radix-tree.c
static inline void *ptr_to_indirect(void *ptr)
{
return (void *)((unsigned long)ptr | RADIX_TREE_INDIRECT_PTR);
}
leaf를 가리키지 않고 radix 트리 노드를 가리키는 경우 ptr에 RADIX_TREE_INDIRECT_PTR을 더해 저장한다.
indirect_to_ptr()
lib/radix-tree.c
static inline void *indirect_to_ptr(void *ptr)
{
return (void *)((unsigned long)ptr & ~RADIX_TREE_INDIRECT_PTR);
}
ptr에서 RADIX_TREE_INDIRECT_PTR을 제외한다.
root_gfp_mask()
lib/radix-tree.c
static inline gfp_t root_gfp_mask(struct radix_tree_root *root)
{
return root->gfp_mask & __GFP_BITS_MASK;
}
루트에 저장된 gfp_mask에서 태그 비트를 제외한 순수 gfp_mask를 반환한다.
tag_set()
lib/radix-tree.c
static inline void tag_set(struct radix_tree_node *node, unsigned int tag,
int offset)
{
__set_bit(offset, node->tags[tag]);
}
Radix 트리 노드의 tags[tag]의 offset 비트를 set 한다.
tag_clear()
lib/radix-tree.c
static inline void tag_clear(struct radix_tree_node *node, unsigned int tag,
int offset)
{
__clear_bit(offset, node->tags[tag]);
}
Radix 트리 노드의 tags[tag]의 offset 비트를 clear 한다.
tag_get()
lib/radix-tree.c
static inline int tag_get(struct radix_tree_node *node, unsigned int tag,
int offset)
{
return test_bit(offset, node->tags[tag]);
}
Radix 트리 노드의 tags[tag]의 offset 비트 상태를 가져온다.
root_tag_set()
lib/radix-tree.c
static inline void root_tag_set(struct radix_tree_root *root, unsigned int tag)
{
root->gfp_mask |= (__force gfp_t)(1 << (tag + __GFP_BITS_SHIFT));
}
Radix 트리의 루트에 요청한 tag 비트를 설정한다.
root_tag_clear()
lib/radix-tree.c
static inline void root_tag_clear(struct radix_tree_root *root, unsigned int tag)
{
root->gfp_mask &= (__force gfp_t)~(1 << (tag + __GFP_BITS_SHIFT));
}
Radix 트리의 루트에 요청한 tag 비트를 clear 한다.
root_tag_clear_all()
lib/radix-tree.c
static inline void root_tag_clear_all(struct radix_tree_root *root)
{
root->gfp_mask &= __GFP_BITS_MASK;
}
Radix 트리의 루트에 전체 tag 비트(총 3개)를 clear 한다.
root_tag_get()
lib/radix-tree.c
static inline int root_tag_get(struct radix_tree_root *root, unsigned int tag)
{
return (__force unsigned)root->gfp_mask & (1 << (tag + __GFP_BITS_SHIFT));
}
Radix 트리의 루트의 요청한 tag 비트 상태를 가져온다.
관련 상수
lib/radix-tree.c
#define RADIX_TREE_MAX_TAGS 3
#ifdef __KERNEL__
#define RADIX_TREE_MAP_SHIFT (CONFIG_BASE_SMALL ? 4 : 6)
#else
#define RADIX_TREE_MAP_SHIFT 3 /* For more stressful testing */
#endif
#define RADIX_TREE_MAP_SIZE (1UL << RADIX_TREE_MAP_SHIFT)
#define RADIX_TREE_MAP_MASK (RADIX_TREE_MAP_SIZE-1)
#define RADIX_TREE_TAG_LONGS \
((RADIX_TREE_MAP_SIZE + BITS_PER_LONG - 1) / BITS_PER_LONG)
#define RADIX_TREE_INDEX_BITS (8 /* CHAR_BIT */ * sizeof(unsigned long))
#define RADIX_TREE_MAX_PATH (DIV_ROUND_UP(RADIX_TREE_INDEX_BITS, \
RADIX_TREE_MAP_SHIFT))
/* Height component in node->path */
#define RADIX_TREE_HEIGHT_SHIFT (RADIX_TREE_MAX_PATH + 1)
#define RADIX_TREE_HEIGHT_MASK ((1UL << RADIX_TREE_HEIGHT_SHIFT) - 1)
/* Internally used bits of node->count */
#define RADIX_TREE_COUNT_SHIFT (RADIX_TREE_MAP_SHIFT + 1)
#define RADIX_TREE_COUNT_MASK ((1UL << RADIX_TREE_COUNT_SHIFT) - 1)
아래 값들은 CONFIG_BASE_SMALL 커널 옵션을 사용하지 않을 경우의 값이다.
- RADIX_TREE_MAX_TAGS
- RADIX_TREE_MAP_SHIFT
- RADIX_TREE_MAP_SIZE
- RADIX_TREE_MAP_MASK
- Radix 트리가 사용하는 맵 마스크
- 0x3f
- RADIX_TREE_TAG_LONGS
- Radix 트리 태그 길이
- 32 bit=2, 64 bit=1
- 32 bit 시스템에서 64개의 비트를 위해 2 개의 long 값이 필요
- RADIX_TREE_INDEX_BITS
- RADIX_TREE_MAX_PATH
- RADIX_TREE_HEIGHT_SHIFT
- Radix 트리 height를 위한 shift 수
- 32 bit=7, 64 bit=12
- RADIX_TREE_HEIGHT_MASK
- Radix 트리 height를 위한 마스크
- 32 bit=0x3f, 64 bit=0x7ff
- RADIX_TREE_COUNT_SHIFT
- RADIX_TREE_COUNT_MASK
- Radix 트리 count에 사용하는 마스크
- 0x3f
구조체
radix_tree_root 구조체
include/linux/radix-tree.h
/* root tags are stored in gfp_mask, shifted by __GFP_BITS_SHIFT */
struct radix_tree_root {
unsigned int height;
gfp_t gfp_mask;
struct radix_tree_node __rcu *rnode;
};
- height
- radix 트리가 관리하는 단계 수 (0~N)
- 0 단계에서는 Radix 트리 노드없이 오직 index 키 0 번 1개에 대한 슬롯을 직접 제공한다.
- 시스템 크기에 따라 최대 단계 수가 다르다.
- height가 0인 경우 index key가 하나도 등록이 되지 않았거나 하나의 0번 index key만을 등록한 경우이다.
- gfp_mask
- radix_tree_node 할당을 받을 때 마다 slub 캐시에 메모리 할당을 요청하는데 이 때 사용할 gfp_mask를 담고 있다.
- 추가로 3개의 tag 비트를 사용한다.
- rnode
- 노드를 가리키거나 한 개의 0번 index key에 해당하는 슬롯으로 동작하여 leaf의 포인터를 저장한다.
- 가장 상위 노드인 radix_tree_node를 가리키게 할 경우 RADIX_TREE_INDIRECT_PTR 비트를 추가하여 사용한다.
- 하나의 0번 index key만 사용된 경우 radix_tree_node를 만들지 않고 직접 rnode가 단일 슬롯으로 동작하여 item을 직접 저장한다.
radix_tree_node 구조체
include/linux/radix-tree.h
struct radix_tree_node {
unsigned int path; /* Offset in parent & height from the bottom */
unsigned int count;
union {
struct {
/* Used when ascending tree */
struct radix_tree_node *parent;
/* For tree user */
void *private_data;
};
/* Used when freeing node */
struct rcu_head rcu_head;
};
/* For tree user */
struct list_head private_list;
void __rcu *slots[RADIX_TREE_MAP_SIZE];
unsigned long tags[RADIX_TREE_MAX_TAGS][RADIX_TREE_TAG_LONGS];
};
- path
- 현재 노드의 레벨
- 가장 바닥 레벨은 1부터 시작한다.
- count
- 사용되고 있는 슬롯 수
- 0~최대 RADIX_TREE_MAP_SIZE(64)개까지
- *parent
- *private_data
- rcu_head
- rcu를 이용하여 노드를 삭제할 때 사용한다.
- private_list
- *slots[]
- RADIX_TREE_MAP_SIZE(64)개까지 다음 노드를 가리키거나 leaf에 해당하는 item을 저장한다.
- 노드를 가리키게 할 경우 RADIX_TREE_INDIRECT_PTR을 추가하여 사용한다.
- tags[]
- 총 3개의 태그로 구성된 비트맵
- 각 비트맵은 RADIX_TREE_MAP_SIZE(64)개의 비트를 처리할 수 있는 공간을 가졌다.
- tags[][]의 이중 배열중 마지막은 실제 선언 시에만 사용되고 실제 처리 루틴에서는 tags[] 일차원 배열로만 이용한다.
- slot에 item이 저장되었는지 여부를 비트맵을 사용하여 표현한다.
- 태그 비트가 1이면 해당 비트 위치의 슬롯이 사용되었음을 의미한다.
radix_tree_preload 구조체
lib/radix-tree.c
/*
* Per-cpu pool of preloaded nodes
*/
struct radix_tree_preload {
int nr;
struct radix_tree_node *nodes[RADIX_TREE_PRELOAD_SIZE];
};
- nr
- 현재 cpu에 할당받은 빈 radix_tree_node 구조체의 수
- *nodes
- 할당 받은 radix_tree_node 포인터를 순서대로 배열에 가지고 있다.
참고







