이 함수에서는 등록된 memory memblock에 대해 미리 사전 체크를 하여 early memory allocator로 동작할 수 있도록 다음과 같이 준비한다.
- lowmem 영역만 사용해야 하는 case에 대해 memblock 영역 삭제
- HIGHMEM을 사용하지 않을 경우 또는 캐시가 VIPT aliasing을 사용하는 경우 memory 영역에 등록된 memblock 들이 lowmem 영역을 초과하는 경우 해당 초과 영역들을 제거한다.
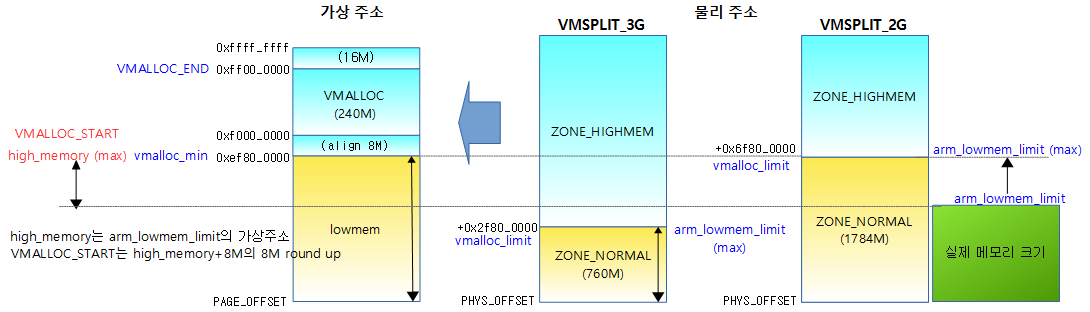
- arm_lowmem_limit 및 high_memory 설정
- memory block의 끝 주소를 arm_lowmem_limit으로 하되 vmalloc_limit(vmalloc_min의 물리주소)을 초과하지 않도록 한다.
- high_memory는 arm_lowmem_limit의 가상 주소 값이다.
- memblock.current_limit 설정
- memory memblock들이 2M 단위로 align되어 있어야 커널 설정 초기에 사용되는 early memory allocator에서 2M 영역을 할당하여 사용하는 reserve memblock을 운영하여야 하므로 각 memory memblock 들이 2M align되어 있지 않은 memblock이 있는 경우 그 지점의 2M round down 주소까지로 사용을 제한하도록 memblock_limit를 설정한다.
sanity_check_meminfo()
arch/arm/mm/mmu.c
void __init sanity_check_meminfo(void)
{
phys_addr_t memblock_limit = 0;
int highmem = 0;
phys_addr_t vmalloc_limit = __pa(vmalloc_min - 1) + 1;
struct memblock_region *reg;
for_each_memblock(memory, reg) {
phys_addr_t block_start = reg->base;
phys_addr_t block_end = reg->base + reg->size;
phys_addr_t size_limit = reg->size;
if (reg->base >= vmalloc_limit)
highmem = 1;
else
size_limit = vmalloc_limit - reg->base;
if (!IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_HIGHMEM) || cache_is_vipt_aliasing()) {
if (highmem) {
pr_notice("Ignoring RAM at %pa-%pa (!CONFIG_HIGHMEM)\n",
&block_start, &block_end);
memblock_remove(reg->base, reg->size);
continue;
}
if (reg->size > size_limit) {
phys_addr_t overlap_size = reg->size - size_limit;
pr_notice("Truncating RAM at %pa-%pa to -%pa",
&block_start, &block_end, &vmalloc_limit);
memblock_remove(vmalloc_limit, overlap_size);
block_end = vmalloc_limit;
}
}
- phys_addr_t vmalloc_limit = __pa(vmalloc_min – 1) + 1;
- vmalloc_min
- VMALLOC_END(0xff00_0000) – (240 << 20) – VMALLOC_OFFSET(8M)
- 0xff00_000 – 240M – 8M = 0xef80_0000
- VMALLOC 영역이 최소 보장되어야 하는 하한 주소로 아키텍처 마다 다르다.
- 32 bit ARM 에서는 0xef80_0000으로 고정되어 사용된다.
- vmalloc_limit
- vmalloc_min의 물리 주소가 담긴다.
- rpi2: 0x6f80_0000
- vmalloc_min
- for_each_memblock(memory, reg) {
- 등록된 전체 memory memblock 영역을 루프로 돈다.
- if (reg->base >= vmalloc_limit)
- 영역의 시작 물리 주소가 vmalloc_limit을 초과한 경우 highmem 영역이라 판단한다.
- if (!IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_HIGHMEM) || cache_is_vipt_aliasing()) {
- HIGHMEM 설정이 안되어 있거나 d-cache가 vipt aliasing을 사용하는 경우
- rpi2: d-cache는 CACHEID_VIPT_NONALIASING
- HIGHMEM 설정이 안되어 있거나 d-cache가 vipt aliasing을 사용하는 경우
- if (highmem) {
- highmem 영역을 사용하는 블럭은 삭제한다.
- if (reg->size > size_limit) {
- size가 lowmem 영역을 넘어가는 경우 넘어가는 부분 만큼을 제거한다.
HIGHMEM을 사용하지 않는 경우 memblock들이 vmalloc_limit을 초과하는 경우 해당 영역을 제거한다.
if (!highmem) {
if (block_end > arm_lowmem_limit) {
if (reg->size > size_limit)
arm_lowmem_limit = vmalloc_limit;
else
arm_lowmem_limit = block_end;
}
- if (block_end > arm_lowmem_limit) {
- 블럭이 arm_lowmem_limit를 초과한 경우
- if (reg->size > size_limit)
- 블럭 사이즈가 lowmem 영역까지 남은 공간을 초과하는 경우 arm_lowmem_limit에 vmalloc_limit을 대입하고 그렇지 않은 경우 블럭의 끝을 지정한다.
/*
* Find the first non-pmd-aligned page, and point
* memblock_limit at it. This relies on rounding the
* limit down to be pmd-aligned, which happens at the
* end of this function.
*
* With this algorithm, the start or end of almost any
* bank can be non-pmd-aligned. The only exception is
* that the start of the bank 0 must be section-
* aligned, since otherwise memory would need to be
* allocated when mapping the start of bank 0, which
* occurs before any free memory is mapped.
*/
if (!memblock_limit) {
if (!IS_ALIGNED(block_start, PMD_SIZE))
memblock_limit = block_start;
else if (!IS_ALIGNED(block_end, PMD_SIZE))
memblock_limit = arm_lowmem_limit;
}
}
}
high_memory = __va(arm_lowmem_limit - 1) + 1;
/*
* Round the memblock limit down to a pmd size. This
* helps to ensure that we will allocate memory from the
* last full pmd, which should be mapped.
*/
if (memblock_limit)
memblock_limit = round_down(memblock_limit, PMD_SIZE);
if (!memblock_limit)
memblock_limit = arm_lowmem_limit;
memblock_set_current_limit(memblock_limit);
}
- if (!memblock_limit) {
- memblock_limit값이 설정되지 않았으면
- if (!IS_ALIGNED(block_start, PMD_SIZE))
- 블럭의 시작 주소가 2M align되어 있지 않은 경우 memblock_limit에 블럭 시작 주소를 대입한다.
- else if (!IS_ALIGNED(block_end, PMD_SIZE))
- 블럭의 끝 주소가 2M align되어 있지 않은 경우 memblock_limit에 블럭 끝 주소를 대입한다.
- memblock_limit = round_down(memblock_limit, PMD_SIZE);
- memblock_limit 주소를 2M round down 한다.
- memblock_set_current_limit(memblock_limit);
- 전역 변수 memblock.current_limit를 설정한다.
- 등록된 memblock은 커널 설정 초기에 2M 단위의 메모리를 할당 받아 사용한다. 따라서 align되지 않은 메모리가 배열에 등록된 경우 align 된 영역까지만 사용하고 나머지 메모리는 사용하지 않도록 memblock_limit를 설정한다.
- 모든 memblock이 2M align 되어 있는 경우 memblock_limit에는 arm_lowmem_limit가 대입된다.
- 반드시 하나 이상의 memblock 영역은 2M align되어 있어야 한다.
- 참고: mm: restrict early_alloc to section-aligned memory
lowmem 영역
- lowmem 영역은 물리 메모리가 1:1로 커널 영역에 매핑되어 사용할 수 있는 영역이다.
- vmalloc_limit
- 현재 커널에서 lowmem 영역을 최대 키울 수 있는 한도내의 물리 메모리 끝 주소
- 메모리 크기와 관계 없이 커널 영역의 크기에 따라 계산되는 물리 주소
- 예)
- VM_SPLIT_3G: 0x2f80_0000 (max lowmem=760M)
- VM_SPLIT_2G: 0x6f80_0000 (max lowmem=1G+760M)
- arm_lowmem_limit
- 물리 메모리 크기가 max lowmem을 초과하는 경우 arm_lowmem_limit는 vmalloc_limit 값과 동일하다.
- 물리 메모리 크기가 max lowmem보다 작은 경우 arm_lowmem_limit는 물리 메모리의 끝 주소가 대입된다.
- high_memory
- arm_lowmem_limit의 가상 주소와 동일하다.
- vmalloc_limit