<kernel v5.0>
Per-cpu -3- (동적 할당)
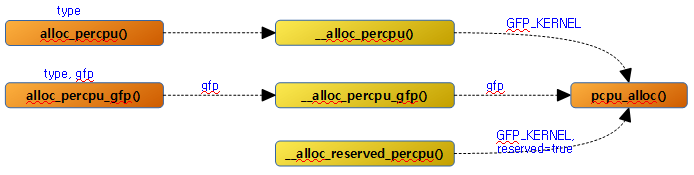
alloc_percpu()
include/linux/percpu.h
#define alloc_percpu(type) \
(typeof(type) __percpu *)__alloc_percpu(sizeof(type), \
__alignof__(type))
요청 타입의 per-cpu 메모리를 할당한다.
__alloc_percpu()
mm/percpu.c
/** * __alloc_percpu - allocate dynamic percpu area * @size: size of area to allocate in bytes * @align: alignment of area (max PAGE_SIZE) * * Equivalent to __alloc_percpu_gfp(size, align, %GFP_KERNEL). */
void __percpu *__alloc_percpu(size_t size, size_t align)
{
return pcpu_alloc(size, align, false, GFP_KERNEL);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(__alloc_percpu);
요청 @size 및 @align 값으로 per-cpu 메모리를 할당한다.
alloc_percpu_gfp()
include/linux/percpu.h
#define alloc_percpu_gfp(type, gfp) \
(typeof(type) __percpu *)__alloc_percpu_gfp(sizeof(type), \
__alignof__(type), gfp)
요청 타입 및 gfp 플래그를 사용하여 per-cpu 메모리를 할당한다.
__alloc_percpu_gfp()
mm/percpu.c
/** * __alloc_percpu_gfp - allocate dynamic percpu area * @size: size of area to allocate in bytes * @align: alignment of area (max PAGE_SIZE) * @gfp: allocation flags * * Allocate zero-filled percpu area of @size bytes aligned at @align. If * @gfp doesn't contain %GFP_KERNEL, the allocation doesn't block and can * be called from any context but is a lot more likely to fail. If @gfp * has __GFP_NOWARN then no warning will be triggered on invalid or failed * allocation requests. * * RETURNS: * Percpu pointer to the allocated area on success, NULL on failure. */
void __percpu *__alloc_percpu_gfp(size_t size, size_t align, gfp_t gfp)
{
return pcpu_alloc(size, align, false, gfp);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(__alloc_percpu_gfp);
요청 size, align 및 gfp 플래그 값으로 per-cpu 메모리를 할당한다.
__alloc_reserved_percpu()
mm/percpu.c
/** * __alloc_reserved_percpu - allocate reserved percpu area * @size: size of area to allocate in bytes * @align: alignment of area (max PAGE_SIZE) * * Allocate zero-filled percpu area of @size bytes aligned at @align * from reserved percpu area if arch has set it up; otherwise, * allocation is served from the same dynamic area. Might sleep. * Might trigger writeouts. * * CONTEXT: * Does GFP_KERNEL allocation. * * RETURNS: * Percpu pointer to the allocated area on success, NULL on failure. */
void __percpu *__alloc_reserved_percpu(size_t size, size_t align)
{
return pcpu_alloc(size, align, true, GFP_KERNEL);
}
컴파일 타임에 모듈에서 사용된 static per-cpu 데이터 선언 영역들은 곧바로 사용될 수 있는 데이터 공간이 아니다. 이들은 런타임에 모듈이 로드될 때 이 함수가 호출되어 first chunk의 reserved 영역 범위내에서 할당한다.
pcpu 동적 할당 메인
pcpu_alloc()
mm/percpu.c -1/3-
/** * pcpu_alloc - the percpu allocator * @size: size of area to allocate in bytes * @align: alignment of area (max PAGE_SIZE) * @reserved: allocate from the reserved chunk if available * @gfp: allocation flags * * Allocate percpu area of @size bytes aligned at @align. If @gfp doesn't * contain %GFP_KERNEL, the allocation is atomic. If @gfp has __GFP_NOWARN * then no warning will be triggered on invalid or failed allocation * requests. * * RETURNS: * Percpu pointer to the allocated area on success, NULL on failure. */
static void __percpu *pcpu_alloc(size_t size, size_t align, bool reserved,
gfp_t gfp)
{
/* whitelisted flags that can be passed to the backing allocators */
gfp_t pcpu_gfp = gfp & (GFP_KERNEL | __GFP_NORETRY | __GFP_NOWARN);
bool is_atomic = (gfp & GFP_KERNEL) != GFP_KERNEL;
bool do_warn = !(gfp & __GFP_NOWARN);
static int warn_limit = 10;
struct pcpu_chunk *chunk;
const char *err;
int slot, off, cpu, ret;
unsigned long flags;
void __percpu *ptr;
size_t bits, bit_align;
/*
* There is now a minimum allocation size of PCPU_MIN_ALLOC_SIZE,
* therefore alignment must be a minimum of that many bytes.
* An allocation may have internal fragmentation from rounding up
* of up to PCPU_MIN_ALLOC_SIZE - 1 bytes.
*/
if (unlikely(align < PCPU_MIN_ALLOC_SIZE))
align = PCPU_MIN_ALLOC_SIZE;
size = ALIGN(size, PCPU_MIN_ALLOC_SIZE);
bits = size >> PCPU_MIN_ALLOC_SHIFT;
bit_align = align >> PCPU_MIN_ALLOC_SHIFT;
if (unlikely(!size || size > PCPU_MIN_UNIT_SIZE || align > PAGE_SIZE ||
!is_power_of_2(align))) {
WARN(do_warn, "illegal size (%zu) or align (%zu) for percpu allocation\n",
size, align);
return NULL;
}
if (!is_atomic) {
/*
* pcpu_balance_workfn() allocates memory under this mutex,
* and it may wait for memory reclaim. Allow current task
* to become OOM victim, in case of memory pressure.
*/
if (gfp & __GFP_NOFAIL)
mutex_lock(&pcpu_alloc_mutex);
else if (mutex_lock_killable(&pcpu_alloc_mutex))
return NULL;
}
spin_lock_irqsave(&pcpu_lock, flags);
/* serve reserved allocations from the reserved chunk if available */
if (reserved && pcpu_reserved_chunk) {
chunk = pcpu_reserved_chunk;
off = pcpu_find_block_fit(chunk, bits, bit_align, is_atomic);
if (off < 0) {
err = "alloc from reserved chunk failed";
goto fail_unlock;
}
off = pcpu_alloc_area(chunk, bits, bit_align, off);
if (off >= 0)
goto area_found;
err = "alloc from reserved chunk failed";
goto fail_unlock;
}
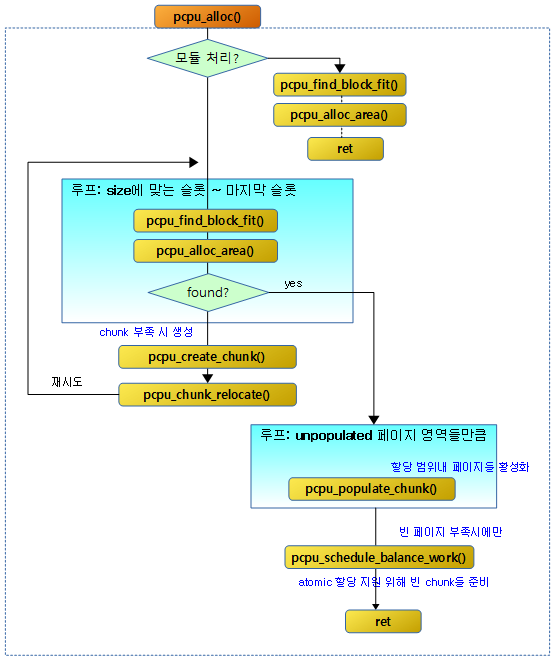
요청 size와 align 값으로 per-cpu 메모리를 동적으로 할당한다. 모듈에서 호출하는 경우 reserved를 true로 호출하여 reserved per-cpu 영역에서 할당하게 한다. 할당받을 공간이 부족한 경우 chunk를 새로 추가하는데, 만일 어토믹 요청인 경우에는 확장하지 않고 실패 처리한다.
- 코드 라인 6에서 어토믹 요청 여부를 파악한다. GFP_KERNEL 옵션을 사용하지 않으면 어토믹 요청이 온 것이다. alloc_percpu( ) 함수 등을 사용하여 호출하는 경우 항상 GFP_KERNEL 옵션을 사용하므로 어토믹 조건을 사용하지 않는다.
- 현재 커널에서 alloc_percpu_gfp( ) 함수를 사용하는 경우에는 gfp 옵션을 바꿀 수 있는데, 실제 적용된 코드에는 아직까지 GFP_KERNEL 옵션 이외의 gfp 옵션을 사용한 경우가 없다. 향후 어토믹 조건을 사용하려고 미리 준비해둔 함수다.
- 어토믹 조건으로 이 함수를 동작시키는 경우 populate된 페이지에서만 per-cpu 데이터를 할당할 수 있게 제한한다. 어토믹 조건이 아닌 경우는 chunk가 부족한 경우 chunk도 생성할 수 있고 unpopulate된 페이지들을 population 과정을 통해 사용할 수 있게 한다.
- 코드 라인 22~23에서 per-cpu 할당의 최소 정렬 단위를 최소 4바이트로 제한한다.
- 코드 라인 25~27에서 할당 사이즈는 per-cpu 최소 정렬 단위로 정렬한다. 그리고 산출된 사이즈 및 정렬 단위로 필요 비트 수를 구한다.
- 예) size=32, align=4
- bits=8, bit_align=1
- 예) size=32, align=4
- 코드 라인 29~34에서 사이즈가 0이거나 유닛 사이즈를 초과하거나 align이 페이지 단위를 초과하거나 2의 제곱승 단위를 사용하지 않는 경우 경고 메시지를 출력하고 null을 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 36~46에서 어토믹 할당 요청이 아닌 경우 OOM 상황에서 per-cpu 할당을 위한 lock을 획득하지 않고 중간에 포기하고 null을 반환할 수 있게 한다.
- 코드 라인 48에서 할당 준비를 하는동안 interrupt를 막는다.
- 코드 라인 51~66에서 모듈을 위해 사용된 static per-cpu 할당은 first chunk의 reserved 영역을 사용하여 관리한다. 이 chunk에서 할당 가능한지 공간을 확인한 후 할당을 시도한다. 만일 적당한 공간을 찾은 경우 area_found: 레이블로 이동하고, 적절한 공간을 찾지 못한 경우 할당 실패 사유를 출력하고 함수를 빠져나가기 위해 faile_unlock: 레이블로 이동한다.
mm/percpu.c -2/3-
restart:
/* search through normal chunks */
for (slot = pcpu_size_to_slot(size); slot < pcpu_nr_slots; slot++) {
list_for_each_entry(chunk, &pcpu_slot[slot], list) {
off = pcpu_find_block_fit(chunk, bits, bit_align,
is_atomic);
if (off < 0)
continue;
off = pcpu_alloc_area(chunk, bits, bit_align, off);
if (off >= 0)
goto area_found;
}
}
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&pcpu_lock, flags);
/*
* No space left. Create a new chunk. We don't want multiple
* tasks to create chunks simultaneously. Serialize and create iff
* there's still no empty chunk after grabbing the mutex.
*/
if (is_atomic) {
err = "atomic alloc failed, no space left";
goto fail;
}
if (list_empty(&pcpu_slot[pcpu_nr_slots - 1])) {
chunk = pcpu_create_chunk(pcpu_gfp);
if (!chunk) {
err = "failed to allocate new chunk";
goto fail;
}
spin_lock_irqsave(&pcpu_lock, flags);
pcpu_chunk_relocate(chunk, -1);
} else {
spin_lock_irqsave(&pcpu_lock, flags);
}
goto restart;
restart: 레이블에서는 dynamic per-cpu 할당에 대한 처리를 수행한다.
- 코드 라인 3에서 적절한 chunk를 먼저 찾기 위해 할당할 사이즈에 해당하는 슬롯 부터 최상위 슬롯까지 순회한다.
- pcpu_size_to_slot()은 size 범위에 해당되는 슬롯 번호를 리턴한다.
- 예) size가 44K이라면 13번 슬롯을 리턴한다.
- pcpu_size_to_slot()은 size 범위에 해당되는 슬롯 번호를 리턴한다.
- 코드 라인 4~8에서 해당 슬롯의 chunk 리스트를 순회하며 할당할 사이즈보다 큰 free 공간이 없으면 skip 한다.
- 코드 라인 10~12에서 할당 요청한 사이즈 만큼 할당된 경우 area_found; 레이블로 이동한다.
- 코드 라인 24~27에서 atomic 요청된 경우 재시도를 하지 않고 fail: 레이블로 이동한다.
- 코드 라인 29~42에서 최상위 슬롯에는 항상 빈 chunk가 있어야 한다. 만일 없는 경우에는 빈 chunk를 생성하고, 최상위 슬롯에 위치시키고 재시도를 하기 위해 restart: 레이블로 이동한다.
mm/percpu.c -3/3-
area_found:
pcpu_stats_area_alloc(chunk, size);
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&pcpu_lock, flags);
/* populate if not all pages are already there */
if (!is_atomic) {
int page_start, page_end, rs, re;
page_start = PFN_DOWN(off);
page_end = PFN_UP(off + size);
pcpu_for_each_unpop_region(chunk->populated, rs, re,
page_start, page_end) {
WARN_ON(chunk->immutable);
ret = pcpu_populate_chunk(chunk, rs, re, pcpu_gfp);
spin_lock_irqsave(&pcpu_lock, flags);
if (ret) {
pcpu_free_area(chunk, off);
err = "failed to populate";
goto fail_unlock;
}
pcpu_chunk_populated(chunk, rs, re, true);
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&pcpu_lock, flags);
}
mutex_unlock(&pcpu_alloc_mutex);
}
if (pcpu_nr_empty_pop_pages < PCPU_EMPTY_POP_PAGES_LOW)
pcpu_schedule_balance_work();
/* clear the areas and return address relative to base address */
for_each_possible_cpu(cpu)
memset((void *)pcpu_chunk_addr(chunk, cpu, 0) + off, 0, size);
ptr = __addr_to_pcpu_ptr(chunk->base_addr + off);
kmemleak_alloc_percpu(ptr, size, gfp);
trace_percpu_alloc_percpu(reserved, is_atomic, size, align,
chunk->base_addr, off, ptr);
return ptr;
fail_unlock:
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&pcpu_lock, flags);
fail:
trace_percpu_alloc_percpu_fail(reserved, is_atomic, size, align);
if (!is_atomic && do_warn && warn_limit) {
pr_warn("allocation failed, size=%zu align=%zu atomic=%d, %s\n",
size, align, is_atomic, err);
dump_stack();
if (!--warn_limit)
pr_info("limit reached, disable warning\n");
}
if (is_atomic) {
/* see the flag handling in pcpu_blance_workfn() */
pcpu_atomic_alloc_failed = true;
pcpu_schedule_balance_work();
} else {
mutex_unlock(&pcpu_alloc_mutex);
}
return NULL;
}
area_found: 레이블에서는 per-cpu 할당이 성공한 경우 후속 처리를 위한 루틴이 있고, fail: 레이블에는 할당이 실패한 경우 원인에 대한 에러 출력을 수행한 후 null을 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 2에서 per-cpu 할당에 대한 stat들을 증가 및 갱신한다.
- 코드 라인 6~29에서 어토믹 처리 요청 중이 아니면 스케줄러를 이용할 필요가 없으므로 즉시 활성화 처리를 한다. 할당받은 페이지의 시작 pfn에서 끝 pfn까지 chunk 내 un-populated 영역의 시작(rs) 주소와 끝(re) 주소들을 알아와서 해당 chunk의 지정된 영역을 populate 한다. 이때 할당된 실제 페이지를 지정된 vmalloc 영역에 매핑한다. 페이지 번호들은 모두 페이지 기준의 PFN이 아니고 chunk의 첫 유닛을 기준으로 한다. 그리고 pcpu_chunk_populated() 함수를 통해 chunk에 해당 영역이 populate되었다는 정보를 비트맵 방식으로 기록한다.
- 코드 라인 31~32에서 빈 populated 페이지 수가 2개 미만이면 populate를 하기 위해 백그라운드에서 워크큐를 통해 pcpu_balance_workfn( )을 호출하게 하여 하나의 빈 chunk에 어토믹 할당이 가능하도록 populated free pages를 PCPU_EMPTY_POP_PAGES_LOW(2)~HIGH(4)까지 확보한다. 어토믹 연산을 위해 미리 populate된 페이지를 확보해둔다.
- 코드 라인 35~36에서 할당된 사이즈의 영역을 깨끗이 0으로 청소한다.
- 코드 라인 38에서 주어진 주소로 per-cpu 포인터 주소로의 변환을 하여 리턴한다. per-cpu 포인터 주소는 유닛 0에 해당하는 실제 데이터의 주소가 아니라 그 주소에서 delta를 뺀 주소를 가리킨다. 실제 사용 시에는 이 값에 해당 cpu가 저장하고 있는 TPIDRPRW 값을 더해 사용한다.
- TPIDRPRW에는 first chunk의 처음 설정 시 cpu에 해당하는 유닛 offset + delta 값이 보관되어 있으며, 이 값은 향후 바뀌지 않는다.
- delta 값은 first chunk를 처음 설정할 때 계산된 가장 낮은 노드(그룹)의 base offset에서 per-cpu 섹션의 시작 주소를 뺀 가상의 주소다.
- 실제 static 변수의 경우 per-cpu 섹션에 컴파일 타임에 만들어진 주소를 가지며, 동적 할당에서는 그 delta 값을 고려하여 미리 감소시킨 값을 가리킨다. 따라서 어떠한 경우에도 per-cpu 포인터 값을 액세스하면 안 된다. static per-cpu 데이터, 동적으로 할당되어 사용하는 per-cpu 데이터 상관없이 동일한 this_cpu_ptr( ) 등의 API 함수를 사용하게 하기 위해 고려되었다.
- 코드 라인 39~44에서 메모리 누수 감시를 위해 객체를 등록하고 성공했으므로 함수를 빠져나간다.
- 코드 라인 46~57에서 할당에 실패한 경우 이 루틴으로 진입한다. 어토믹 할당 요청을 받은 경우가 아니면 경고를 출력한다.
- 코드 라인 58~65에서 어토믹 할당 요청을 받은 경우 pcpu_schedule_balance_work( ) 루틴을 호출하여 워크큐에서 별도로 스케줄 할당을 받아 populated된 free 페이지의 할당을 준비한다.
chunk 내 필요 free 공간 검색
pcpu_find_block_fit()
mm/percpu.c
/** * pcpu_find_block_fit - finds the block index to start searching * @chunk: chunk of interest * @alloc_bits: size of request in allocation units * @align: alignment of area (max PAGE_SIZE bytes) * @pop_only: use populated regions only * * Given a chunk and an allocation spec, find the offset to begin searching * for a free region. This iterates over the bitmap metadata blocks to * find an offset that will be guaranteed to fit the requirements. It is * not quite first fit as if the allocation does not fit in the contig hint * of a block or chunk, it is skipped. This errs on the side of caution * to prevent excess iteration. Poor alignment can cause the allocator to * skip over blocks and chunks that have valid free areas. * * RETURNS: * The offset in the bitmap to begin searching. * -1 if no offset is found. */
static int pcpu_find_block_fit(struct pcpu_chunk *chunk, int alloc_bits,
size_t align, bool pop_only)
{
int bit_off, bits, next_off;
/*
* Check to see if the allocation can fit in the chunk's contig hint.
* This is an optimization to prevent scanning by assuming if it
* cannot fit in the global hint, there is memory pressure and creating
* a new chunk would happen soon.
*/
bit_off = ALIGN(chunk->contig_bits_start, align) -
chunk->contig_bits_start;
if (bit_off + alloc_bits > chunk->contig_bits)
return -1;
bit_off = chunk->first_bit;
bits = 0;
pcpu_for_each_fit_region(chunk, alloc_bits, align, bit_off, bits) {
if (!pop_only || pcpu_is_populated(chunk, bit_off, bits,
&next_off))
break;
bit_off = next_off;
bits = 0;
}
if (bit_off == pcpu_chunk_map_bits(chunk))
return -1;
return bit_off;
}
@chunk 내에서 적절한 빈 공간을 찾아 chunk 기준 bit_off 값을 반환한다. @pop_only가 1로 주어진 경우 populate 페이지 들에서만 검색한다.
- 코드 라인 12~15에서 최대 연속된 free 공간을 보고 @align 정렬 단위로 @alloc_bits 만큼 할당할 공간이 없으면 -1을 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 17~19에서 bit_off 위치부터 시작하여 bits 단위로 순회하며 align 조건이 만족하는 빈 공간을 찾아 bit_off를 구한다.
- 코드 라인 20~22에서 @pop_only가 0인 경우 처음 찾은 위치가 확정된다. 그렇지 않고 @pop_only가 1로 설정된 경우 @bit_off 부터 bits 만큼의 공간이 populate된 공간인지를 확인하여 확정한다. 만일 populate 공간이 아니면 next_off에 다음 populate 페이지의 시작 비트를 가리키는 값을 반환한다.
- 코드라인24~26에서 다음 populate 페이지의 시작 비트를 next_off로 가져왔으므로 이를 bit_off에 넣고 계속 루프를 반복한다.
- 코드 라인 28~31에서 할당이 실패한 경우 -1을 반환하고, 성공한 경우 bit_off를 반환한다.
pcpu_for_each_fit_region()
mm/percpu.c
#define pcpu_for_each_fit_region(chunk, alloc_bits, align, bit_off, bits) \
for (pcpu_next_fit_region((chunk), (alloc_bits), (align), &(bit_off), \
&(bits)); \
(bit_off) < pcpu_chunk_map_bits((chunk)); \
(bit_off) += (bits), \
pcpu_next_fit_region((chunk), (alloc_bits), (align), &(bit_off), \
&(bits)))
@chunk 내에서 입출력인자 @bit_off부터 시작하여 @align 단위로 @alloc_bits 만큼 free 공간이 확보 가능한 영역을 찾아 입출력 인자 @bit_off에 비트 오프셋 위치와, 출력 인자 @bits에 free 영역의 사이즈를 반환한다. 참고로 각 비트는 4바이트 단위의 할당 상태를 표시한다.
pcpu_next_fit_region()
mm/percpu.c
/** * pcpu_next_fit_region - finds fit areas for a given allocation request * @chunk: chunk of interest * @alloc_bits: size of allocation * @align: alignment of area (max PAGE_SIZE) * @bit_off: chunk offset * @bits: size of free area * * Finds the next free region that is viable for use with a given size and * alignment. This only returns if there is a valid area to be used for this * allocation. block->first_free is returned if the allocation request fits * within the block to see if the request can be fulfilled prior to the contig * hint. */
static void pcpu_next_fit_region(struct pcpu_chunk *chunk, int alloc_bits,
int align, int *bit_off, int *bits)
{
int i = pcpu_off_to_block_index(*bit_off);
int block_off = pcpu_off_to_block_off(*bit_off);
struct pcpu_block_md *block;
*bits = 0;
for (block = chunk->md_blocks + i; i < pcpu_chunk_nr_blocks(chunk);
block++, i++) {
/* handles contig area across blocks */
if (*bits) {
*bits += block->left_free;
if (*bits >= alloc_bits)
return;
if (block->left_free == PCPU_BITMAP_BLOCK_BITS)
continue;
}
/* check block->contig_hint */
*bits = ALIGN(block->contig_hint_start, align) -
block->contig_hint_start;
/*
* This uses the block offset to determine if this has been
* checked in the prior iteration.
*/
if (block->contig_hint &&
block->contig_hint_start >= block_off &&
block->contig_hint >= *bits + alloc_bits) {
*bits += alloc_bits + block->contig_hint_start -
block->first_free;
*bit_off = pcpu_block_off_to_off(i, block->first_free);
return;
}
/* reset to satisfy the second predicate above */
block_off = 0;
*bit_off = ALIGN(PCPU_BITMAP_BLOCK_BITS - block->right_free,
align);
*bits = PCPU_BITMAP_BLOCK_BITS - *bit_off;
*bit_off = pcpu_block_off_to_off(i, *bit_off);
if (*bits >= alloc_bits)
return;
}
/* no valid offsets were found - fail condition */
*bit_off = pcpu_chunk_map_bits(chunk);
}
@chunk 내에서 입출력 인자 @bit_off부터 시작하여 @align 단위로 @alloc_bits 만큼 free 공간이 확보 가능한 영역을 찾는다. 그런 후 입출력 인자 @bit_off에 찾은 free 영역의 시작 비트 오프셋 위치와, 출력 인자 @bits에 free 영역의 사이즈를 반환한다. 참고로 각 비트는 4바이트 단위의 할당 상태를 표시한다.
- 코드 라인 9~18에서 청크에서 pcpu 블럭(페이지) 수 만큼 순회하며 처음 호출되어 @bits가 0인 경우 가장 첫 free 공간에서 할당 가능하면 @bits를 갱신하여 함수를 빠져나오고, 그렇지 않고 free 공간의 중간 블럭인 경우 skip 한다.
- 코드 라인 21~34에서 free 공간에서 할당 가능하면 그 위치와 사이즈를 산출하여 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 36~43에서 가장 우측 free 공간에서 할당 가능한 경우 그 위치와 사이즈를 산출하여 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 47에서 더 이상 찾지 못한 경우 함수 밖에 있는 루프를 끝내기 위해 @bit_off에 마지막 값을 담는다.
할당한 영역을 비트맵에 표기
pcpu_alloc_area()
mm/percpu.c
/** * pcpu_alloc_area - allocates an area from a pcpu_chunk * @chunk: chunk of interest * @alloc_bits: size of request in allocation units * @align: alignment of area (max PAGE_SIZE) * @start: bit_off to start searching * * This function takes in a @start offset to begin searching to fit an * allocation of @alloc_bits with alignment @align. It needs to scan * the allocation map because if it fits within the block's contig hint, * @start will be block->first_free. This is an attempt to fill the * allocation prior to breaking the contig hint. The allocation and * boundary maps are updated accordingly if it confirms a valid * free area. * * RETURNS: * Allocated addr offset in @chunk on success. * -1 if no matching area is found. */
static int pcpu_alloc_area(struct pcpu_chunk *chunk, int alloc_bits,
size_t align, int start)
{
size_t align_mask = (align) ? (align - 1) : 0;
int bit_off, end, oslot;
lockdep_assert_held(&pcpu_lock);
oslot = pcpu_chunk_slot(chunk);
/*
* Search to find a fit.
*/
end = start + alloc_bits + PCPU_BITMAP_BLOCK_BITS;
bit_off = bitmap_find_next_zero_area(chunk->alloc_map, end, start,
alloc_bits, align_mask);
if (bit_off >= end)
return -1;
/* update alloc map */
bitmap_set(chunk->alloc_map, bit_off, alloc_bits);
/* update boundary map */
set_bit(bit_off, chunk->bound_map);
bitmap_clear(chunk->bound_map, bit_off + 1, alloc_bits - 1);
set_bit(bit_off + alloc_bits, chunk->bound_map);
chunk->free_bytes -= alloc_bits * PCPU_MIN_ALLOC_SIZE;
/* update first free bit */
if (bit_off == chunk->first_bit)
chunk->first_bit = find_next_zero_bit(
chunk->alloc_map,
pcpu_chunk_map_bits(chunk),
bit_off + alloc_bits);
pcpu_block_update_hint_alloc(chunk, bit_off, alloc_bits);
pcpu_chunk_relocate(chunk, oslot);
return bit_off * PCPU_MIN_ALLOC_SIZE;
}
per-cpu 할당 영역에 대한 비트맵, 블럭 메타데이터들 및 각종 관련 정보들을 갱신한다.
- 코드 라인 9에서 할당 영역 갱신으로 인해 슬롯 이동이 될 수 있으므로 현재 슬롯 번호를 알아온다.
- 코드 라인 14~18에서 범위내 @align 정렬 단위로 @alloc_bits 만큼의 free 영역을 찾는다. 적합한 free 영역이 없는 경우 -1을 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 21에서 할당 범위의 할당맵을 모두 1로 채운다.
- 코드 라인 24~26에서 할당 범위의 경계 맵을 모두 클리어하고 시작과 끝+1 비트만 1로 설정한다.
- 코드 라인 28에서 남은 free 바이트를 갱신한다.
- 코드 라인 31~35에서 만일 할당한 영역이 첫 번째 free 공간인 경우 첫 번째 free 공간 비트 위치를 갱신한다.
- 코드 라인 37에서 chunk내의 per-cpu 블럭 메타데이터들을 갱신한다.
- 코드 라인 39에서 슬롯의 이동이 필요한 경우 갱신한다.
- 코드 라인 41에서 할당이 성공한 경우이다. 할당된 영역의 비트 offset을 반환한다.
할당 페이지 범위 활성화
pcpu_populate_chunk()
mm/percpu-vm.c
/** * pcpu_populate_chunk - populate and map an area of a pcpu_chunk * @chunk: chunk of interest * @page_start: the start page * @page_end: the end page * For each cpu, populate and map pages [@page_start,@page_end) into * * For each cpu, populate and map pages [@page_start,@page_end) into * @chunk. * * CONTEXT: * pcpu_alloc_mutex, does GFP_KERNEL allocation. */
static int pcpu_populate_chunk(struct pcpu_chunk *chunk,
int page_start, int page_end, gfp_t gfp)
{
struct page **pages;
pages = pcpu_get_pages();
if (!pages)
return -ENOMEM;
if (pcpu_alloc_pages(chunk, pages, page_start, page_end, gfp))
return -ENOMEM;
if (pcpu_map_pages(chunk, pages, page_start, page_end)) {
pcpu_free_pages(chunk, pages, page_start, page_end);
return -ENOMEM;
}
pcpu_post_map_flush(chunk, page_start, page_end);
return 0;
}
chunk의 요청 페이지 범위에 대해 활성화(population)한다.
- 코드 라인 6~8에서 필요 page descriptor 만큼 할당을 받는다. 할당 실패시 -ENOMEM으로 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 10~11에서 필요 페이지 범위를 cpu 수 만큼 할당 받는다. 할당 실패시 -ENOMEM으로 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 13~16에서 할당받은 영역 페이지들을 vmalloc 공간에 매핑시킨다.
- 코드 라인 17에서 매핑이 완료되면 TLB 캐시를 flush 한다.
pcpu_get_pages()
mm/percpu-vm.c
/** * pcpu_get_pages - get temp pages array * @chunk: chunk of interest * * Returns pointer to array of pointers to struct page which can be indexed * with pcpu_page_idx(). Note that there is only one array and accesses * should be serialized by pcpu_alloc_mutex. * * RETURNS: * Pointer to temp pages array on success. */
static struct page **pcpu_get_pages(void)
{
static struct page **pages;
size_t pages_size = pcpu_nr_units * pcpu_unit_pages * sizeof(pages[0]);
lockdep_assert_held(&pcpu_alloc_mutex);
if (!pages)
pages = pcpu_mem_zalloc(pages_size, GFP_KERNEL);
return pages;
}
chunk 할당을 위해 전체 per-cpu 유닛에 필요한 page descriptor 사이즈 만큼 메모리 할당을 받아온다.
pcpu_map_pages()
mm/percpu-vm.c
/** * pcpu_map_pages - map pages into a pcpu_chunk * @chunk: chunk of interest * @pages: pages array containing pages to be mapped * @page_start: page index of the first page to map * @page_end: page index of the last page to map + 1 * * For each cpu, map pages [@page_start,@page_end) into @chunk. The * caller is responsible for calling pcpu_post_map_flush() after all * mappings are complete. * * This function is responsible for setting up whatever is necessary for * reverse lookup (addr -> chunk). */
static int pcpu_map_pages(struct pcpu_chunk *chunk,
struct page **pages, int page_start, int page_end)
{
unsigned int cpu, tcpu;
int i, err;
for_each_possible_cpu(cpu) {
err = __pcpu_map_pages(pcpu_chunk_addr(chunk, cpu, page_start),
&pages[pcpu_page_idx(cpu, page_start)],
page_end - page_start);
if (err < 0)
goto err;
for (i = page_start; i < page_end; i++)
pcpu_set_page_chunk(pages[pcpu_page_idx(cpu, i)],
chunk);
}
return 0;
err:
for_each_possible_cpu(tcpu) {
if (tcpu == cpu)
break;
__pcpu_unmap_pages(pcpu_chunk_addr(chunk, tcpu, page_start),
page_end - page_start);
}
pcpu_post_unmap_tlb_flush(chunk, page_start, page_end);
return err;
}
할당받은 영역 페이지들을 vmalloc 공간에 매핑시킨다
- 코드 라인 7~12에서 possible cpu 수 만큼 루프를 돌며 per-cpu chunk를 vmalloc 공간에 매핑한다.
- 코드 라인 14~16에서 각 페이지(page->index)들이 pcpu_chunk를 가리키도록 설정한다.
__pcpu_map_pages()
mm/percpu-vm.c
static int __pcpu_map_pages(unsigned long addr, struct page **pages,
int nr_pages)
{
return map_kernel_range_noflush(addr, nr_pages << PAGE_SHIFT,
PAGE_KERNEL, pages);
}
할당받은 영역 페이지들을 요청 vmalloc 가상 주소 공간에 매핑시킨다
map_kernel_range_noflush()
mm/vmalloc.c
/** * map_kernel_range_noflush - map kernel VM area with the specified pages * @addr: start of the VM area to map * @size: size of the VM area to map * @prot: page protection flags to use * @pages: pages to map * * Map PFN_UP(@size) pages at @addr. The VM area @addr and @size * specify should have been allocated using get_vm_area() and its * friends. * * NOTE: * This function does NOT do any cache flushing. The caller is * responsible for calling flush_cache_vmap() on to-be-mapped areas * before calling this function. * * RETURNS: * The number of pages mapped on success, -errno on failure. */
int map_kernel_range_noflush(unsigned long addr, unsigned long size,
pgprot_t prot, struct page **pages)
{
return vmap_page_range_noflush(addr, addr + size, prot, pages);
}
할당받은 영역 페이지들을 요청 vmalloc 가상 주소 공간에 vmap 매핑시킨다
범위의 활성화 여부
pcpu_is_populated()
mm/percpu.c
/** * pcpu_is_populated - determines if the region is populated * @chunk: chunk of interest * @bit_off: chunk offset * @bits: size of area * @next_off: return value for the next offset to start searching * * For atomic allocations, check if the backing pages are populated. * * RETURNS: * Bool if the backing pages are populated. * next_index is to skip over unpopulated blocks in pcpu_find_block_fit. */
static bool pcpu_is_populated(struct pcpu_chunk *chunk, int bit_off, int bits,
int *next_off)
{
int page_start, page_end, rs, re;
page_start = PFN_DOWN(bit_off * PCPU_MIN_ALLOC_SIZE);
page_end = PFN_UP((bit_off + bits) * PCPU_MIN_ALLOC_SIZE);
rs = page_start;
pcpu_next_unpop(chunk->populated, &rs, &re, page_end);
if (rs >= page_end)
return true;
*next_off = re * PAGE_SIZE / PCPU_MIN_ALLOC_SIZE;
return false;
}
@chunk에서 @bit_off부터 @bits 까지의 공간이 활성화(populate)된 상태인지 여부를 반환한다. 출력 인자 @next_off에는 다음 검색을 시작할 offset 위치가 담긴다.
pcpu_next_unpop()
mm/percpu.c
static void pcpu_next_unpop(unsigned long *bitmap, int *rs, int *re, int end)
{
*rs = find_next_zero_bit(bitmap, end, *rs);
*re = find_next_bit(bitmap, end, *rs + 1);
}
@end 까지의 per-cpu 페이지 중 활성화되지 않은 페이지의 시작 @rs과 끝 @re를 산출한다.
참고
- Per-cpu -1- (Basic) | 문c
- Per-cpu -2- (초기화) | 문c
- Per-cpu -3- (동적 할당) | 문c – 현재 글
- Per-cpu -4- (atomic operations) | 문c