<kernel v5.0>
page extension
memmap extension 또는 extended memap 이라고도 불린다. page 구조체를 변경하지 않고 page_ext라는 별도의 구조체를 만들어 page 확장을 하여 디버깅에 도움을 줄 수 있게 하였다. 이 기능은 2014년 12월 kernel v3.19-rc1에 LG 전자의 김준수님이 추가하였다.
다음과 같은 기능들이 준비되어 있다.
- page alloc 디버깅
- page poisoning 디버그
- page owner 트래킹
- idle page 트래킹
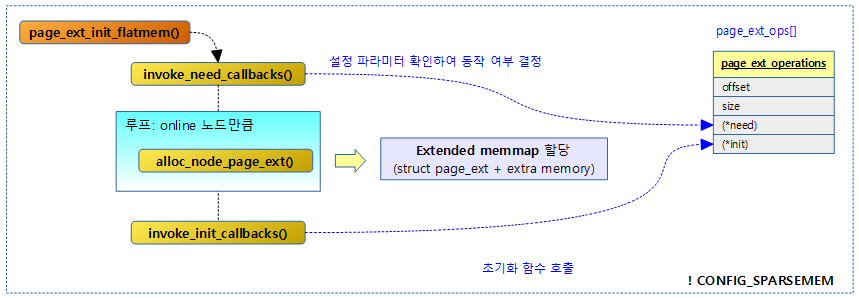
다음 그림은 sparse 메모리 모델이 아닌 경우 수행되는 page_ext_init_flatmem() 함수가 동작하여 확장 memmap을 생성하는 과정을 보여준다.
Flat & Discontiguous 메모리 모델에서의 page_ext 초기화
- 참고로 sparse 메모리 모델에서의 초기화 루틴은 page_ext_init() 함수에서 한다.
page_ext_init_flatmem()
mm/page_ext.c
void __init page_ext_init_flatmem(void)
{
int nid, fail;
if (!invoke_need_callbacks())
return;
for_each_online_node(nid) {
fail = alloc_node_page_ext(nid);
if (fail)
goto fail;
}
pr_info("allocated %ld bytes of page_ext\n", total_usage);
invoke_init_callbacks();
return;
fail:
pr_crit("allocation of page_ext failed.\n");
panic("Out of memory");
}
page_ext가 필요한 경우 각 노드에 page_ext를 할당 받고 초기화한다.
invoke_need_callbacks()
mm/page_ext.c
static bool __init invoke_need_callbacks(void)
{
int i;
int entries = ARRAY_SIZE(page_ext_ops);
bool need = false;
for (i = 0; i < entries; i++) {
if (page_ext_ops[i]->need && page_ext_ops[i]->need()) {
page_ext_ops[i]->offset = sizeof(struct page_ext) +
extra_mem;
extra_mem += page_ext_ops[i]->size;
need = true;
}
}
return need;
}
page_ext_ops 엔트리 수 만큼 루프를 돌며 엔트리에 등록된 need 함수를 수행시켜 엔트리 하나라도 초기화가 필요한 경우 true를 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 7~8에서 컴파일 타임에 결정된 page_ext_ops[] 배열 엔트리 수 만큼 순회하며 해당 오퍼레이션에 등록된 (*need) 후크 함수에서 초기화가 필요한 경우 true를 반환하여 조건을 만족시킨다.
- 코드 라인 9~10에서 해당 오퍼레이션의 offset에는 page_ext 구조체 + 해당 오퍼레이션이 사용할 extra 메모리에 대한 offset 바이트 수를 대입한다.
- CONFIG_PAGE_OWNER 커널 옵션을 사용하는 경우 extra 메모리로 page_owner 구조체 사이즈를 사용한다.
- 코드 라인 11에서 오퍼레이션에서 사용한 extra 메모리 사이즈 만큼 전역 변수 extra_mem에 더한다.
alloc_node_page_ext()
mm/page_ext.c
static int __init alloc_node_page_ext(int nid)
{
struct page_ext *base;
unsigned long table_size;
unsigned long nr_pages;
nr_pages = NODE_DATA(nid)->node_spanned_pages;
if (!nr_pages)
return 0;
/*
* Need extra space if node range is not aligned with
* MAX_ORDER_NR_PAGES. When page allocator's buddy algorithm
* checks buddy's status, range could be out of exact node range.
*/
if (!IS_ALIGNED(node_start_pfn(nid), MAX_ORDER_NR_PAGES) ||
!IS_ALIGNED(node_end_pfn(nid), MAX_ORDER_NR_PAGES))
nr_pages += MAX_ORDER_NR_PAGES;
table_size = get_entry_size() * nr_pages;
base = memblock_virt_alloc_try_nid_nopanic(
table_size, PAGE_SIZE, __pa(MAX_DMA_ADDRESS),
BOOTMEM_ALLOC_ACCESSIBLE, nid);
if (!base)
return -ENOMEM;
NODE_DATA(nid)->node_page_ext = base;
total_usage += table_size;
return 0;
}
지정된 노드에 MAX_ORDER_NR_PAGES 단위로 align된 존재하는 페이지 수 만큼의 page_ext 구조체 + extra 메모리 만큼을 memblock에 할당한다.
- 코드 라인 7~9에서 해당 노드가 관리하는 홀을 포함한 전체 페이지 수를 가져온다.
- 코드 라인 16~18에서 해당 노드의 시작과 끝 페이지가 최대 버디 오더 페이지 단위로 정렬되지 않은 경우 extra 공간을 더 정렬 단위만큼 추가한다.
- MAX_ORDER_NR_PAGES는 버디 시스템에서 최대 할당 가능한 오더 페이지 수 이다.
- 코드 라인 20~26에서 page_ext 용도로 메모리를 할당한다.
- memblock의 DMA 주소 ~ lowmem 범위에 가능하면 노드 공간에 page_ext 공간을 할당한다.
- 노드 주소 범위가 DMA 주소 ~ lowmem 범위에 포함되지 않는 경우에는 지정된 노드가 아니더라도 할당을 시도한다.
- 코드 라인 27에서 할당된 메모리는 노드 멤버 node_page_ext에 지정한다.
- 코드 라인 28에서 전역 사용량(바이트)에 할당 사이즈 만큼 추가한다.
invoke_init_callbacks()
mm/page_ext.c
static void __init invoke_init_callbacks(void)
{
int i;
int entries = ARRAY_SIZE(page_ext_ops);
for (i = 0; i < entries; i++) {
if (page_ext_ops[i]->init)
page_ext_ops[i]->init();
}
}
page_ext_ops 엔트리 수 만큼 루프를 돌며 초기화 핸들러 함수를 호출한다.
lookup_page_ext()
mm/page_ext.c
struct page_ext *lookup_page_ext(struct page *page)
{
unsigned long pfn = page_to_pfn(page);
unsigned long offset;
struct page_ext *base;
base = NODE_DATA(page_to_nid(page))->node_page_ext;
#ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_VM
/*
* The sanity checks the page allocator does upon freeing a
* page can reach here before the page_ext arrays are
* allocated when feeding a range of pages to the allocator
* for the first time during bootup or memory hotplug.
*/
if (unlikely(!base))
return NULL;
#endif
offset = pfn - round_down(node_start_pfn(page_to_nid(page)),
MAX_ORDER_NR_PAGES);
return base + offset;
}
page로 page_ext 정보츨 찾아 반환한다.
구조체
page_ext_operations 구조체
include/linux/page_ext.h
struct page_ext_operations {
size_t offset;
size_t size;
bool (*need)(void);
void (*init)(void);
};
- offset
- page_ext 뒤에 추가된 extra 메모리를 가리키는 offset 이다.
- size
- 해당 오퍼레이션에서 사용하는 extra 메모리 바이트 수
- CONFIG_PAGE_OWNER 커널 옵션을 사용하는 경우 page_owner 구조체 크기가 사용된다.
- need
- 필요 여부 조회 핸들러 함수 등록
- init
- 초기화 핸들러 함수 등록
page_ext_ops[] 전역 객체
mm/page_ext.c
/* * struct page extension * * This is the feature to manage memory for extended data per page. * * Until now, we must modify struct page itself to store extra data per page. * This requires rebuilding the kernel and it is really time consuming process. * And, sometimes, rebuild is impossible due to third party module dependency. * At last, enlarging struct page could cause un-wanted system behaviour change. * * This feature is intended to overcome above mentioned problems. This feature * allocates memory for extended data per page in certain place rather than * the struct page itself. This memory can be accessed by the accessor * functions provided by this code. During the boot process, it checks whether * allocation of huge chunk of memory is needed or not. If not, it avoids * allocating memory at all. With this advantage, we can include this feature * into the kernel in default and can avoid rebuild and solve related problems. * * To help these things to work well, there are two callbacks for clients. One * is the need callback which is mandatory if user wants to avoid useless * memory allocation at boot-time. The other is optional, init callback, which * is used to do proper initialization after memory is allocated. * * The need callback is used to decide whether extended memory allocation is * needed or not. Sometimes users want to deactivate some features in this * boot and extra memory would be unneccessary. In this case, to avoid * allocating huge chunk of memory, each clients represent their need of * extra memory through the need callback. If one of the need callbacks * returns true, it means that someone needs extra memory so that * page extension core should allocates memory for page extension. If * none of need callbacks return true, memory isn't needed at all in this boot * and page extension core can skip to allocate memory. As result, * none of memory is wasted. * * When need callback returns true, page_ext checks if there is a request for * extra memory through size in struct page_ext_operations. If it is non-zero, * extra space is allocated for each page_ext entry and offset is returned to * user through offset in struct page_ext_operations. * * The init callback is used to do proper initialization after page extension * is completely initialized. In sparse memory system, extra memory is * allocated some time later than memmap is allocated. In other words, lifetime * of memory for page extension isn't same with memmap for struct page. * Therefore, clients can't store extra data until page extension is * initialized, even if pages are allocated and used freely. This could * cause inadequate state of extra data per page, so, to prevent it, client * can utilize this callback to initialize the state of it correctly. */
static struct page_ext_operations *page_ext_ops[] = {
#ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_PAGEALLOC
&debug_guardpage_ops,
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_PAGE_OWNER
&page_owner_ops,
#endif
#if defined(CONFIG_IDLE_PAGE_TRACKING) && !defined(CONFIG_64BIT)
&page_idle_ops,
#endif
};
커널 옵션에 따라 몇 가지 기능의 핸들러 객체들이 등록되어 있다.
debug_guardpage_ops 전역 객체
mm/page_alloc.c
#ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_PAGEALLOC
struct page_ext_operations debug_guardpage_ops = {
.need = need_debug_guardpage,
.init = init_debug_guardpage,
};
#endif
가드 페이지 디버깅에 관련된 핸들러 함수들이 등록되어 있다.
page_owner_ops 전역 객체
mm/page_owner.c
struct page_ext_operations page_owner_ops = {
.size = sizeof(struct page_owner),
.need = need_page_owner,
.init = init_page_owner,
};
페이지 owner 트래킹에 관련된 핸들러 함수들이 등록되어 있다.
- 디버그용으로 CONFIG_PAGE_OWNER 커널 옵션이 동작하는 경우에만 사용된다.
page_idle_ops 전역 객체
mm/page_idle.c
#ifndef CONFIG_64BIT
struct page_ext_operations page_idle_ops = {
.need = need_page_idle,
};
#endif
idle 페이지 트래킹에 관련된 핸들러 함수들이 등록되어 있다.
- 이 오퍼레이션은 32비트 시스템에서만 사용되며, 64비트 시스템에서는 page_ext를 사용하는 이러한 오퍼레이션 없이 page 구조체만을 사용하여 동작한다.
참고
- 디버그 메모리 -1- (Page Alloc) | 문c
- 디버그 메모리 -2- (Page Poisoning) | 문c
- 디버그 메모리 -3- (Page Owner 추적) | 문c
- 디버그 메모리 -4- (Idle Page 추적) | 문c
- page_ext_init_flatmem() | 문c – 현재글
- page_ext_init() | 문c
- page owner: Tracking about who allocated each page | kernel.org
- Resurrect and use struct page extension for some debugging features | LWN.net
- Per-CPU Page Frame Cache (zone->pageset) | 문c
- Idle Page Tracking | Kernel.org