<kernel v5.0>
kmalloc 할당자
커널에서 주로 작은 사이즈의 연속된 물리 주소 공간을 할당 받아 사용한다. 물리적으로 연속된 공간이므로 dma 버퍼로도 사용 가능하다.
특징
커널에서 물리 및 가상 주소가 연속된 메모리의 할당이 필요한 경우 사용된다. kmalloc을 이용한 커널 메모리의 할당은 다음과 같은 특징이 있다.
- 미리 매핑된 커널 메모리를 사용하므로 별도의 매핑 작업없이 곧바로 사용할 수 있어 빠르다.
- 미리 준비된 kmalloc용 슬랩 캐시를 사용한다.
- 슬랩 캐시를 사용 시 물리적으로 연속된 메모리를 제공하므로 장점으로는 DMA 용으로 사용될 수 있다.
- 단점으로는 싱글 페이지를 사용하지 않고 order 단위의 페이지를 사용하므로 fragment 관리에 민감하다.
kmalloc 타입
커널에서 자주 사용되는 사이즈를 지정하여 슬랩 캐시를 미리 만들어 제공하는 형태이며, 사이즈별로 다음과 같이 3종류가 지원된다.
- kmalloc-<size>
- 일반적으로 사용되는 타입으로 메모리 회수 불가능하다.
- kmalloc-rcl-<size>
- shrinker를 제공하여 회수 가능한 타입에 사용되는 타입이다.
- __GFP_RECLAIMABLE 플래그를 사용할 때 이 타입을 사용한다.
- 참고: mm, slab/slub: introduce kmalloc-reclaimable caches (v4.20-rc1, 2018)
- dma-kmalloc-<size>
- 주소 제한이 있는 dma 존이 필요한 시스템에서만 사용되는 타입이다.
- __GFP_DMA 플래그를 사용하여 dma용 커널 메모리의 할당을 위해 ZONE_DMA 영역을 사용한다.
- 별도의 dma 존이 필요하지 않는 시스템에서는 dma를 위한 메모리 할당 시 일반 타입의 kmalloc을 사용한다.
kmalloc 사이즈
- 아키텍처의 L1 캐시 라인 크기부터 2의 배수단위 사이즈 까지 슬랩 캐시를 미리 준비하여 제공한다.
- Slub 캐시의 경우 2 페이지 사이즈까지 미리 준비하여 사용된다. 이 크기를 넘어가는 메모리를 요청하는 경우 kmalloc용 슬랩 캐시가 아니라 버디 시스템을 사용하는 페이지 할당자를 사용하여 제공한다.
- 아키텍처에 따라 96 또는 192 사이즈를 제공하는 시스템도 있다.
슬랩(Slub) 캐시를 사용하는 kmalloc에서 지원하는 사이즈는 다음과 같다. (ARM64의 경우 오렌지 색상으로 표기된 항목을 사용한다)
- kmalloc-8
- kmalloc-16
- kmalloc-32
- kmalloc-64
- kmalloc-96
- kmalloc-128
- kmalloc-192
- kmalloc-256
- kmalloc-512
- kmalloc-1k
- kmalloc-2k
- kmalloc-4k
- kmalloc-8k
다음은 다양한 kmalloc 타입을 보여준다. (커널/tools/vm/slabinfo.c를 컴파일하여 사용하는 유틸리티)
$ slabinfo kmalloc Name Objects Objsize Space Slabs/Part/Cpu O/S O %Fr %Ef Flg kmalloc-128 8081 128 1.0M 246/61/14 32 0 23 97 kmalloc-256 1232 256 315.3K 65/0/12 16 0 0 100 kmalloc-512 707 512 483.3K 50/28/9 16 1 47 74 kmalloc-1k 590 1024 638.9K 35/6/4 16 2 15 94 kmalloc-2k 176 2048 360.4K 9/0/2 16 3 0 100 kmalloc-4k 53 4096 229.3K 4/1/3 8 3 14 94 kmalloc-8k 32 8192 262.1K 7/0/1 4 3 0 100 kmalloc-rcl-128 448 128 57.3K 13/0/1 32 0 0 100 a
API
할당 및 해제 관련한 주요 API는 다음과 같다.
- kmalloc()
- kfree()
kmalloc()에서 사용하는 GFP 플래그
- GFP_KERNEL
- kernel용 메모리 할당이며 sleep될 수 있다.
- GFP_ATOMIC
- sleep되면 안될 때 사용되며 인터럽트 핸들러 등에서 사용한다.
- GFP_HIGHUSER
- 유저용 highmem(high memory)에 우선 페이지 할당을 한다.
- GFP_NOWAIT
- 메모리 할당을 하는 동안 메모리 부족 시 kswapd를 깨워 reclaim을 하도록 허용한다.
- __GFP_HIGH
- 높은 우선 순위에서 처리되도록 요청할 때 사용한다.
- __GFP_NOFAIL
- 실패를 허용하지 않고, 메모리 할당 요청에 대해 성공할 때까지 처리하도록 요청할 때 사용한다.
- __GFP_NORETRY
- 메모리 할당 요청에 대해 실패 시 재시도 하지 않는다.
- __GFP_NOWARN
- 메모리 할당이 실패할 때 어떠한 경고도 처리하지 않도록 한다.
- __GFP_RETRY_MAYFAIL
- 메모리 할당이 처음 실패하는 경우 재시도 가능하나 실패 가능하다.
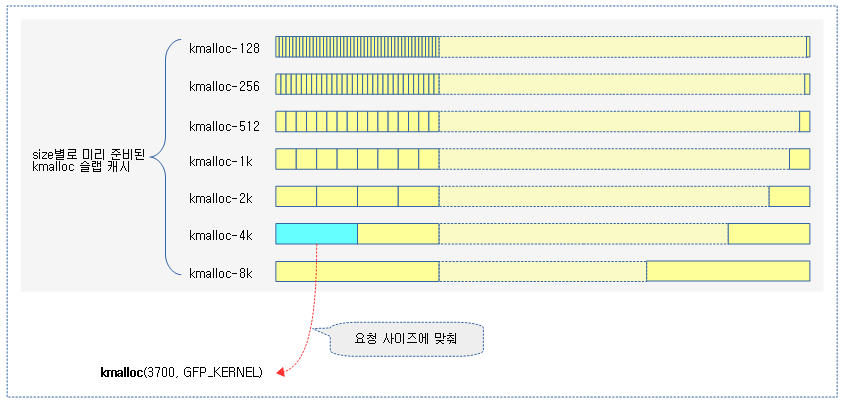
다음 그림은 kmalloc() 함수가 미리 준비된 kmalloc 슬랩 캐시 중 하나를 사용하여 object를 할당하는 모습을 보여준다.
Kmalloc 초기화
size_index[] 테이블
mm/slab_common.c”
/* * Conversion table for small slabs sizes / 8 to the index in the * kmalloc array. This is necessary for slabs < 192 since we have non power * of two cache sizes there. The size of larger slabs can be determined using * fls. */
static s8 size_index[24] = {
3, /* 8 */
4, /* 16 */
5, /* 24 */
5, /* 32 */
6, /* 40 */
6, /* 48 */
6, /* 56 */
6, /* 64 */
1, /* 72 */
1, /* 80 */
1, /* 88 */
1, /* 96 */
7, /* 104 */
7, /* 112 */
7, /* 120 */
7, /* 128 */
2, /* 136 */
2, /* 144 */
2, /* 152 */
2, /* 160 */
2, /* 168 */
2, /* 176 */
2, /* 184 */
2 /* 192 */
};
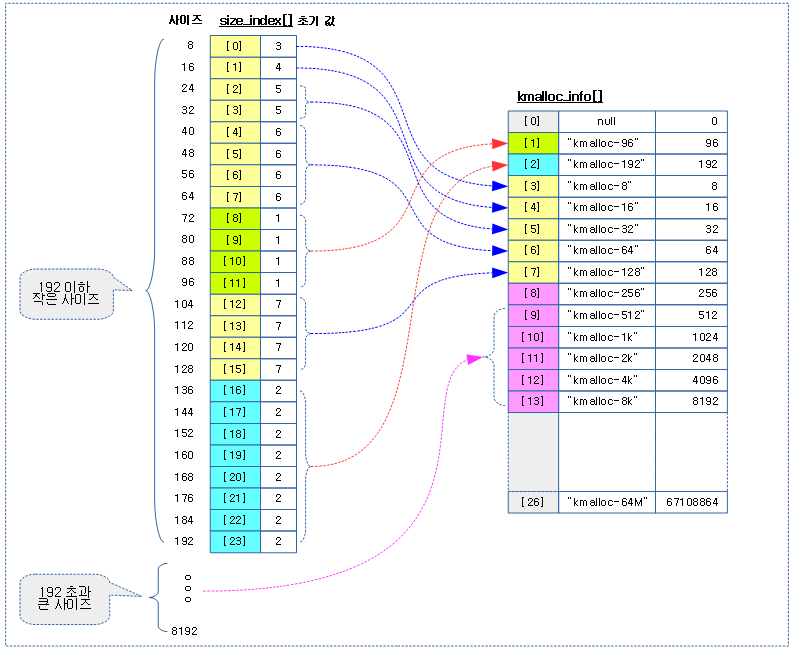
슬랩 object 크기가 192 바이트 이하일 때 사용할 kmalloc 슬랩 캐시를 선택하기 위한 테이블이다. 괄호 안의 인덱스 값은 사이즈를8로 나눈 값 이고, 엔트리 값과 이에 따른 kmalloc 슬랩 캐시명은 다음과 같다.
- 1 -> 72~96 사이즈를 사용하는 kmalloc-96
- 아키텍처에서 지원하는 캐시 라인이 64 이상인 경우 kmalloc-96 생성을 포기하고 kmalloc-128으로 대치된다
- 2 -> 136~192 사이즈를 사용하는kmalloc-192
- 아키텍처에서 지원하는 캐시 라인이 128 이상인 경우 kmalloc-192 생성을 포기하고 kmalloc-256으로 대치된다.
- 3 -> kmalloc-8
- 4 -> kmalloc-16
- 5 -> kmalloc-32
- 6 -> kmalloc-64
- 7 -> kmalloc-128
kmalloc_info[] 테이블
mm/slab_common.c
/* * kmalloc_info[] is to make slub_debug=,kmalloc-xx option work at boot time. * kmalloc_index() supports up to 2^26=64MB, so the final entry of the table is * kmalloc-67108864. */
const struct kmalloc_info_struct kmalloc_info[] __initconst = {
{NULL, 0}, {"kmalloc-96", 96},
{"kmalloc-192", 192}, {"kmalloc-8", 8},
{"kmalloc-16", 16}, {"kmalloc-32", 32},
{"kmalloc-64", 64}, {"kmalloc-128", 128},
{"kmalloc-256", 256}, {"kmalloc-512", 512},
{"kmalloc-1k", 1024}, {"kmalloc-2k", 2048},
{"kmalloc-4k", 4096}, {"kmalloc-8k", 8192},
{"kmalloc-16k", 16384}, {"kmalloc-32k", 32768},
{"kmalloc-64k", 65536}, {"kmalloc-128k", 131072},
{"kmalloc-256k", 262144}, {"kmalloc-512k", 524288},
{"kmalloc-1M", 1048576}, {"kmalloc-2M", 2097152},
{"kmalloc-4M", 4194304}, {"kmalloc-8M", 8388608},
{"kmalloc-16M", 16777216}, {"kmalloc-32M", 33554432},
{"kmalloc-64M", 67108864}
};
kmalloc_info 테이블은 인덱스 26까지에 해당하는 kmalloc 캐시의 이름과 사이즈 정보로 초기 구성되어 있다.
- 1번 kmalloc-96의경우 아키텍처의 캐시 라인이 64이상인 경우 운영되지 않는다.
- ARM64는 운영하지 않는다.
- 2번 kmalloc-192의경우 아키텍처의 캐시 라인이 128이상인 경우 운영되지 않는다.
- ARM64는 운영하지 않는다.
- 3~6번 kmalloc-8 ~ kmalloc-64의경우 캐시 라인의 크기 보다 작은 kmalloc은 운영되지 않는다.
- ARM64는 모두 운영하지 않는다.
- slub 캐시에서는 페이지 사이즈 2배 크기 만큼만 지원한다.
- 예) ARM64, 4K 페이지의 경우 kmalloc-128 ~ kmalloc-8k까지 지원한다.
아래 그림은 size에따라 size_index[] 테이블을 통해 적절한 kmalloc 슬랩 캐시를 선택하는 모습을 보여준다.
- size_index[] 테이블 값은 변경되기 전의 초기 상태이다.
kmalloc 캐시 인덱스 테이블 초기화
setup_kmalloc_cache_index_table()
mm/slab_common.c
/* * Patch up the size_index table if we have strange large alignment * requirements for the kmalloc array. This is only the case for * MIPS it seems. The standard arches will not generate any code here. * * Largest permitted alignment is 256 bytes due to the way we * handle the index determination for the smaller caches. * * Make sure that nothing crazy happens if someone starts tinkering * around with ARCH_KMALLOC_MINALIGN */
void __init setup_kmalloc_cache_index_table(void)
{
unsigned int i;
BUILD_BUG_ON(KMALLOC_MIN_SIZE > 256 ||
(KMALLOC_MIN_SIZE & (KMALLOC_MIN_SIZE - 1)));
for (i = 8; i < KMALLOC_MIN_SIZE; i += 8) {
unsigned int elem = size_index_elem(i);
if (elem >= ARRAY_SIZE(size_index))
break;
size_index[elem] = KMALLOC_SHIFT_LOW;
}
if (KMALLOC_MIN_SIZE >= 64) {
/*
* The 96 byte size cache is not used if the alignment
* is 64 byte.
*/
for (i = 64 + 8; i <= 96; i += 8)
size_index[size_index_elem(i)] = 7;
}
if (KMALLOC_MIN_SIZE >= 128) {
/*
* The 192 byte sized cache is not used if the alignment
* is 128 byte. Redirect kmalloc to use the 256 byte cache
* instead.
*/
for (i = 128 + 8; i <= 192; i += 8)
size_index[size_index_elem(i)] = 8;
}
}
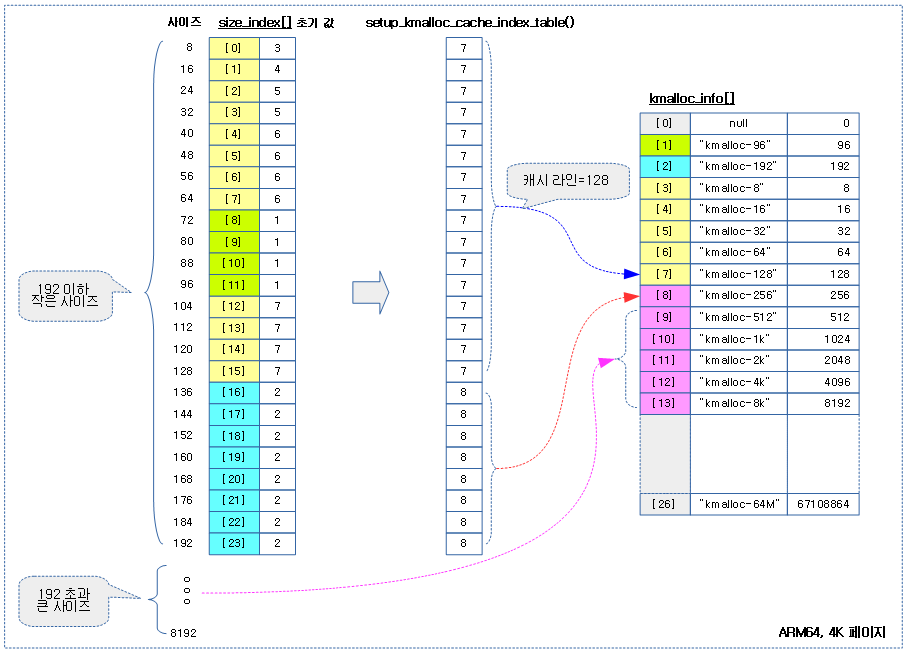
kmalloc 캐시용 size_index 테이블을 초기화한다
- 코드 라인8~14에서 KMALLOC_MIN_SIZE 사이즈 까지는 최저 사이즈 캐시를 통합하여 운영한다.
- ARM32 rpi2의 경우 최하 사이즈는 kmalloc-64이다.
- ARM32 rpi3의 경우 최하 사이즈는 kmalloc-128이다.
- ARM64 rpi4의 경우 최하 사이즈는 kmalloc-128이다.
- 코드 라인 16~24에서 KMALLOC_MIN_SIZE 사이즈가 64 이상인 경우 72~96까지의사이즈는 kmalloc-96을 만들지않고 kmalloc-128을사용하게 한다.
- ARM32 rpi2의 경우 72~96까지의 사이즈에 대해 kmalloc-128을 사용한다
- ARM32 rpi3의 경우 72~96까지의 사이즈에 대해 kmalloc-128을 사용한다
- ARM64 rpi4의 경우 72~96까지의 사이즈에 대해 kmalloc-128을 사용한다.
- 코드 라인 26~34에서 KMALLOC_MIN_SIZE 사이즈가 128 이상인 경우 140~192까지의사이즈는 kmalloc-192을만들지 않고 kmalloc-256을사용하게 한다.
- ARM32 rpi2의 경우 72~96까지의 사이즈에 대해 kmalloc-192를 지원한다.
- ARM32 rpi3의 경우 72~96까지의 사이즈에 대해 kmalloc-256을 사용한다
- ARM64 rpi4의 경우 72~96까지의 사이즈에 대해 kmalloc-256을 사용한다.
아래 그림은 setup_kmalloc_cache_index_table() 함수에 의해 조정된 size_index[] 테이블을 통해 적절한 kmalloc 슬랩 캐시를 선택하는 모습을 보여준다
kmalloc 캐시 초기화
create_kmalloc_caches() – (slab, slub)
mm/slab_common.c
/* * Create the kmalloc array. Some of the regular kmalloc arrays * may already have been created because they were needed to * enable allocations for slab creation. */
void __init create_kmalloc_caches(slab_flags_t flags)
{
int i, type;
for (type = KMALLOC_NORMAL; type <= KMALLOC_RECLAIM; type++) {
for (i = KMALLOC_SHIFT_LOW; i <= KMALLOC_SHIFT_HIGH; i++) {
if (!kmalloc_caches[type][i])
new_kmalloc_cache(i, type, flags);
/*
* Caches that are not of the two-to-the-power-of size.
* These have to be created immediately after the
* earlier power of two caches
*/
if (KMALLOC_MIN_SIZE <= 32 && i == 6 &&
!kmalloc_caches[type][1])
new_kmalloc_cache(1, type, flags);
if (KMALLOC_MIN_SIZE <= 64 && i == 7 &&
!kmalloc_caches[type][2])
new_kmalloc_cache(2, type, flags);
}
}
/* Kmalloc array is now usable */
slab_state = UP;
#ifdef CONFIG_ZONE_DMA
for (i = 0; i <= KMALLOC_SHIFT_HIGH; i++) {
struct kmem_cache *s = kmalloc_caches[KMALLOC_NORMAL][i];
if (s) {
unsigned int size = kmalloc_size(i);
const char *n = kmalloc_cache_name("dma-kmalloc", size);
BUG_ON(!n);
kmalloc_caches[KMALLOC_DMA][i] = create_kmalloc_cache(
n, size, SLAB_CACHE_DMA | flags, 0, 0);
}
}
#endif
}
kmalloc 슬랩 캐시를 타입 및 사이즈별로 미리 생성한다.
- 코드 라인 5~22에서 normal 타입과reclaim 타입두 가지 타입으로 슬랩이 지원하는 사이즈에 대해 순회하며 kmalloc 캐시를 생성한다.
- 코드 라인25에서 지금부터 kmalloc array 캐시가 사용될 수 있다.
- 코드 라인 28~39에서 슬랩이지원하는 사이즈에 대해 순회하며 dma 타입의 kmalloc 캐시를 생성한다.
new_kmalloc_cache()
mm/slab_common.c
static void __init
new_kmalloc_cache(int idx, int type, slab_flags_t flags)
{
const char *name;
if (type == KMALLOC_RECLAIM) {
flags |= SLAB_RECLAIM_ACCOUNT;
name = kmalloc_cache_name("kmalloc-rcl",
kmalloc_info[idx].size);
BUG_ON(!name);
} else {
name = kmalloc_info[idx].name;
}
kmalloc_caches[type][idx] = create_kmalloc_cache(name,
kmalloc_info[idx].size, flags, 0,
kmalloc_info[idx].size);
}
kmalloc_infi[@idx] 정보를사용하여@type에 대한 kmalloc 슬랩 캐시를 생성한다.
- 예) idx=8, type=KMALLOC_RECLAIM
- kmalloc-rcl-256
- 예) idx=10, type=KMALLOC_NORMAL
- kmalloc-1k
size_index_elem()
mm/slab_common.c
static inline int size_index_elem(size_t bytes)
{
return (bytes - 1) / 8;
}
인수 bytes에 대해 8바이트 단위로 사용되는 size_index[] 배열 엘레멘트 인덱스 값을 반환한다.
- 예) 0~7=0, 8~15=1, 16~23=2, …
kmalloc_size()
include/linux/slab.h
/* * Determine size used for the nth kmalloc cache. * return size or 0 if a kmalloc cache for that * size does not exist */
static __always_inline unsigned int kmalloc_size(unsigned int n)
{
#ifndef CONFIG_SLOB
if (n > 2)
return 1U << n;
if (n == 1 && KMALLOC_MIN_SIZE <= 32)
return 96;
if (n == 2 && KMALLOC_MIN_SIZE <= 64)
return 192;
#endif
return 0;
}
인수 n 값에 대응하는 사이즈를 반환한다.
- 예) rpi2: 0->0, 1->0, 2->192, 3->8, 4->16, 5->32, 6->64, 7->128, …
create_kmalloc_cache()
mm/slab_common.c
struct kmem_cache *__init create_kmalloc_cache(const char *name,
unsigned int size, slab_flags_t flags,
unsigned int useroffset, unsigned int usersize)
{
struct kmem_cache *s = kmem_cache_zalloc(kmem_cache, GFP_NOWAIT);
if (!s)
panic("Out of memory when creating slab %s\n", name);
create_boot_cache(s, name, size, flags, useroffset, usersize);
list_add(&s->list, &slab_caches);
memcg_link_cache(s);
s->refcount = 1;
return s;
}
인수로 주어진 @name, @size 및 @flags로 슬랩 캐시를 생성한다.
- 코드 라인 5~8에서 kmem_cache 캐시에서 슬랩 object를 할당 받아온다.
- 코드 라인 10에서 kmem_cache 캐시에서 사용하는 per cpu 캐시를 per-cpu 자료형으로 할당 받고, per 노드에서 사용할 kmem_cache_node 구조체는 kmem_cache_node 캐시에서 slub object를 할당받아 partial 리스트에 등록한다
- 코드 라인 11~14에서 전역 slab_caches 리스트에 생성한 캐시를 추가하고 memcg에도 추가한 후, 참조카운터에 1을 대입하고 생성한 슬랩 캐시를 반환한다.
mm/slab_common.c
struct kmem_cache * kmalloc_caches[NR_KMALLOC_TYPES][KMALLOC_SHIFT_HIGH + 1] __ro_after_init; EXPORT_SYMBOL(kmalloc_caches);
kmalloc 슬랩 캐시 리스트이다.
Kmalloc 할당자
커널에서 물리 및 가상 주소가 연속된 메모리의 할당이 필요한 경우 요청 사이즈에 따라 다음과 같은 메모리 할당자를 사용하여 할당한다.
- slub 할당자
- 2 페이지 이하 사이즈 요청 시 2의 배수로 미리 만들어 운영되는 kmalloc 슬랩 캐시를 사용하여 슬랩 object를 할당한다.
- 페이지 할당자
- 2 페이지를 초과하는 사이즈 요청 시 버디 시스템을 사용하는 페이지 할당자를 사용하여 order 단위의 페이지를 할당한다.
다음 그림은 kmalloc() 함수가 사이즈에 따라 호출되는 함수들을 보여준다. 할당 요청 사이즈가 클 때에는 페이지 할당자에 요구하고, 작을 때에는 미리 준비된 kmalloc 슬랩(slub) 캐시에 요청한다.
kmalloc()
include/mm/slab.h
/** * kmalloc - allocate memory * @size: how many bytes of memory are required. * @flags: the type of memory to allocate. * * kmalloc is the normal method of allocating memory * for objects smaller than page size in the kernel. * * The @flags argument may be one of the GFP flags defined at * include/linux/gfp.h and described at * :ref:`Documentation/core-api/mm-api.rst <mm-api-gfp-flags>` * * The recommended usage of the @flags is described at * :ref:`Documentation/core-api/memory-allocation.rst <memory-allocation>` * * Below is a brief outline of the most useful GFP flags * * %GFP_KERNEL * Allocate normal kernel ram. May sleep. * * %GFP_NOWAIT * Allocation will not sleep. * * %GFP_ATOMIC * Allocation will not sleep. May use emergency pools. * * %GFP_HIGHUSER * Allocate memory from high memory on behalf of user. * * Also it is possible to set different flags by OR'ing * in one or more of the following additional @flags: * * %__GFP_HIGH * This allocation has high priority and may use emergency pools. * * %__GFP_NOFAIL * Indicate that this allocation is in no way allowed to fail * (think twice before using). * * %__GFP_NORETRY * If memory is not immediately available, * then give up at once. * * %__GFP_NOWARN * If allocation fails, don't issue any warnings. * * %__GFP_RETRY_MAYFAIL * Try really hard to succeed the allocation but fail * eventually. */
static __always_inline void *kmalloc(size_t size, gfp_t flags)
{
if (__builtin_constant_p(size)) {
#ifndef CONFIG_SLOB
unsigned int index;
#endif
if (size > KMALLOC_MAX_CACHE_SIZE)
return kmalloc_large(size, flags);
#ifndef CONFIG_SLOB
index = kmalloc_index(size);
if (!index)
return ZERO_SIZE_PTR;
return kmem_cache_alloc_trace(
kmalloc_caches[kmalloc_type(flags)][index],
flags, size);
#endif
}
return __kmalloc(size, flags);
}
커널로부터 메모리 할당 요청에 대해 할당 요청 사이즈가 2 페이지(slub 기준)를 초과하는 경우 버디 시스템을 사용하는 페이지 할당자에 요청하고, 그렇지 않은 경우에는 kmalloc 슬랩 캐시를 사용하여 요청한다.
- 코드 라인 3~8에서 요청 사이즈가 상수이면서 KMALLOC_MAX_CACHE_SIZE(slub 기준 2 페이지)를 초과하는 경우 직접 버디 시스템을 사용하는 페이지 할당자로 요청한다.
- KMALLOC_MAX_CACHE_SIZE
- slub을 사용하는 경우 2 페이지 사이즈
- KMALLOC_MAX_CACHE_SIZE
- 코드 라인 10~17에서 요청 사이즈가 상수이면 사이즈 및 타입에 따른 kmalloc 슬랩 캐시를 선택하여 슬랩 object를 할당 받는다.
- kmalloc_index() 함수는 사이즈로 인덱스 값을 산출한다.
- 코드 라인 20에서 size에 변수를 사용한 경우 __kmalloc() 함수를 호출한다.
kmalloc_large()
include/linux/slab.h
static __always_inline void *kmalloc_large(size_t size, gfp_t flags)
{
unsigned int order = get_order(size);
return kmalloc_order_trace(size, flags, order);
}
size에 필요한 order를 결정한 후 버디 시스템을 사용하는 페이지 할당자로부터 페이지를 할당 받는다.
kmalloc_order_trace()
mm/slab_common.c
#ifdef CONFIG_TRACING
void *kmalloc_order_trace(size_t size, gfp_t flags, unsigned int order)
{
void *ret = kmalloc_order(size, flags, order);
trace_kmalloc(_RET_IP_, ret, size, PAGE_SIZE << order, flags);
return ret;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(kmalloc_order_trace);
#endif
버디 시스템을 사용하는 페이지 할당자로부터 order 만큼의 페이지를 할당 받는다.
kmalloc_order()
mm/slab_common.c
/* * To avoid unnecessary overhead, we pass through large allocation requests * directly to the page allocator. We use __GFP_COMP, because we will need to * know the allocation order to free the pages properly in kfree. */
void *kmalloc_order(size_t size, gfp_t flags, unsigned int order)
{
void *ret;
struct page *page;
flags |= __GFP_COMP;
page = alloc_pages(flags, order);
ret = page ? page_address(page) : NULL;
ret = kasan_kmalloc_large(ret, size, flags);
/* As ret might get tagged, call kmemleak hook after KASAN. */
kmemleak_alloc(ret, size, 1, flags);
return ret;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(kmalloc_order);
큰 페이지에 대한 할당 요청이므로 compound 페이지를 할당받기 위해 __GFP_COMP 플래그를 추가하고, 버디 시스템을 사용하는 페이지 할당자로부터 order 만큼의 페이지를 할당 받는다.
kmalloc_index()
include/linux/slab.h
#ifndef CONFIG_SLOB /* * Figure out which kmalloc slab an allocation of a certain size * belongs to. * 0 = zero alloc * 1 = 65 .. 96 bytes * 2 = 120 .. 192 bytes * n = 2^(n-1) .. 2^n -1 */
static __always_inline int kmalloc_index(size_t size)
{
if (!size)
return 0;
if (size <= KMALLOC_MIN_SIZE)
return KMALLOC_SHIFT_LOW;
if (KMALLOC_MIN_SIZE <= 32 && size > 64 && size <= 96)
return 1;
if (KMALLOC_MIN_SIZE <= 64 && size > 128 && size <= 192)
return 2;
if (size <= 8) return 3;
if (size <= 16) return 4;
if (size <= 32) return 5;
if (size <= 64) return 6;
if (size <= 128) return 7;
if (size <= 256) return 8;
if (size <= 512) return 9;
if (size <= 1024) return 10;
if (size <= 2 * 1024) return 11;
if (size <= 4 * 1024) return 12;
if (size <= 8 * 1024) return 13;
if (size <= 16 * 1024) return 14;
if (size <= 32 * 1024) return 15;
if (size <= 64 * 1024) return 16;
if (size <= 128 * 1024) return 17;
if (size <= 256 * 1024) return 18;
if (size <= 512 * 1024) return 19;
if (size <= 1024 * 1024) return 20;
if (size <= 2 * 1024 * 1024) return 21;
if (size <= 4 * 1024 * 1024) return 22;
if (size <= 8 * 1024 * 1024) return 23;
if (size <= 16 * 1024 * 1024) return 24;
if (size <= 32 * 1024 * 1024) return 25;
if (size <= 64 * 1024 * 1024) return 26;
BUG();
/* Will never be reached. Needed because the compiler may complain */
return -1;
}
#endif /* !CONFIG_SLOB */
0~64M 이하의 요청 사이즈에 따른 index를 0~23 까지의 수로 반환한다. 64M를 초과하는 경우 에러로 -1을 반환한다.
- 요청 사이즈에 따른 index 값
- 0 = 할당 없음 (zero alloc)
- 1 = 65 .. 96 bytes
- 2 = 120 .. 192 bytes
- n = 2^(n-1) .. 2^n -1
- 3 = 1 .. 8
- 4 = 9 .. 16
- 5 = 17 .. 32
- 6 = 33 .. 64
- …
- 26 = 32M-1 .. 64M
- 단, size가 1~KMALLOC_MIN_SIZE인 경우 KMALLOC_SHIFT_LOW를 반환한다.
- rpi2 예) KMALLOC_MIN_SIZE=64, KMALLOC_SHIFT_LOW=6
- arm64예) KMALLOC_MIN_SIZE=128, KMALLOC_SHIFT_LOW=7
kmem_cache_alloc_node_trace()
mm/slub.c
#ifdef CONFIG_TRACING
void *kmem_cache_alloc_node_trace(struct kmem_cache *s,
gfp_t gfpflags,
int node, size_t size)
{
void *ret = slab_alloc_node(s, gfpflags, node, _RET_IP_);
trace_kmalloc_node(_RET_IP_, ret,
size, s->size, gfpflags, node);
ret = kasan_kmalloc(s, ret, size, gfpflags);
return ret;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(kmem_cache_alloc_node_trace);
#endif
요청한 슬랩 캐시의 @node에서 슬랩 object를 할당 받는다.
__kmalloc()
mm/slub.c
void *__kmalloc(size_t size, gfp_t flags)
{
struct kmem_cache *s;
void *ret;
if (unlikely(size > KMALLOC_MAX_CACHE_SIZE))
return kmalloc_large(size, flags);
s = kmalloc_slab(size, flags);
if (unlikely(ZERO_OR_NULL_PTR(s)))
return s;
ret = slab_alloc(s, flags, _RET_IP_);
trace_kmalloc(_RET_IP_, ret, size, s->size, flags);
kasan_kmalloc(s, ret, size);
return ret;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(__kmalloc);
@size 값이 변수인 경우 호출되어 다음과 같이 처리한다.
- 코드 라인 6~7에서 size가 KMALLOC_MAX_CACHE_SIZE(slub의 경우 2 페이지)를 초과하는 경우 kmalloc_large() 함수를 통해 버디 시스템을 사용한 페이지 할당자로 부터 페이지를 할당 받는다.
- 코드 라인 9~12에서 size에 및 타입에 따른 적절한 kmalloc 슬랩 캐시를 구해온다.
- 코드 라인 14에서 구한 kmalloc 슬랩 캐시에서 슬랩 object를 할당 받는다.
kmalloc_slab()
mm/slab_common.c
/* * Find the kmem_cache structure that serves a given size of * allocation */
struct kmem_cache *kmalloc_slab(size_t size, gfp_t flags)
{
unsigned int index;
if (size <= 192) {
if (!size)
return ZERO_SIZE_PTR;
index = size_index[size_index_elem(size)];
} else {
if (WARN_ON_ONCE(size > KMALLOC_MAX_CACHE_SIZE))
return NULL;
index = fls(size - 1);
}
return kmalloc_caches[kmalloc_type(flags)][index];
}
@size 및 @flags로 구한 타입을 통해 해당 kmalloc 슬랩 캐시를 구해온다.
- 코드 라인 5~9에서 @size가 1 ~ 192인 경우 이미 만들어진 size_index[] 테이블을 활용하여 사이즈 값으로 인덱스를 산출한다.
- 코드 라인 10~14에서 @size가 193 ~ KMALLOC_MAX_SIZE(slub인 경우 2 페이지)인 경우 필요 비트 수를 산출하여 반환한다.
- 193 ~ 256 → 8
- 257 ~ 512 → 9
- 513 ~ 1024 → 10
- 1025 ~ 2048 → 11
- 2049 ~ 4096 → 12
- 4097 ~ 8192 → 13
- 코드 라인 16에서 @flags에서 타입을 추출하고, 산출한 인덱스로 얻은 kmallc 캐시를 반환한다.
size_index_elem()
mm/slab_common.c
static inline int size_index_elem(size_t bytes)
{
return (bytes - 1) / 8;
}
size_index[] 테이블은 인덱스 당 8바이트 범위를 사용한다. 따라서 요청 bytes-1을 8로 나눈 몫을 반환한다.
- 1 ~ 8 → 0
- 9 ~ 16 → 1
- 17 ~ 24 → 2
- 25 ~ 32 → 3
- 33 ~ 40 → 4
- 41 ~ 48 → 5
- …
참고
- Slab Memory Allocator -1- (구조) | 문c
- Kmalloc vs Vmalloc | 문c
- Kmalloc | 문c – 현재 글
- Vmalloc | 문c
- Vmap() | 문c