hotcpu_notifier()를 사용하여 등록하는 callback 함수들
- page_alloc_cpu_notify,
- percpu_counter_hotcpu_callback
- radix_tree_callback
- blk_mq_queue_reinit_notify
- pfault_cpu_notify
- smp_cpu_notify
- vgetcpu_cpu_notifier
- apbt_cpuhp_notify
- hpet_cpuhp_notify
- uv_scir_cpu_notify
- vfp_hotplug
- loongson3_cpu_callback
- octeon_cpu_callback
- buffer_cpu_notify
- cpu_callback
- memcg_cpu_hotplug_callback
- cpuset_cpu_inactive
- cpuset_cpu_active
- sched_domains_numa_masks_update
- hotplug_hrtick
- workqueue_cpu_down_callback
- console_cpu_notify
- profile_cpu_callback
- topology_cpu_callback
- cacheinfo_cpu_callback
- dev_cpu_callback
hotcpu notifier 등록
hotcpu_notifier()
include/linux/cpu.h
#define hotcpu_notifier(fn, pri) cpu_notifier(fn, pri)
cpu_notifier()
include/linux/cpu.h
/* Need to know about CPUs going up/down? */
#if defined(CONFIG_HOTPLUG_CPU) || !defined(MODULE)
#define cpu_notifier(fn, pri) { \
static struct notifier_block fn##_nb = \
{ .notifier_call = fn, .priority = pri }; \
register_cpu_notifier(&fn##_nb); \
}
#else /* #if defined(CONFIG_HOTPLUG_CPU) || !defined(MODULE) */
#define cpu_notifier(fn, pri) do { (void)(fn); } while (0)
#endif /* #else #if defined(CONFIG_HOTPLUG_CPU) || !defined(MODULE) */
신규 notifier_block 구조체 객체를 만들고 만들어진 객체를 cpu_chain에 추가하되 priority가 가장 높은 값이 선두에 위치한다.
- 예) hotcpu_notifer(page_alloc_cpu_notify, 0)
- static struct notifier_block page_alloc_cpu_notify_nb = { .notifier_call = page_alloc_cpu_notify, .priority = 0 };
- register_cpu_notifier(page_alloc_cpu_notify_nb);
register_cpu_notifer()
kernel/cpu.c
/* Need to know about CPUs going up/down? */
int __ref register_cpu_notifier(struct notifier_block *nb)
{
int ret;
cpu_maps_update_begin();
ret = raw_notifier_chain_register(&cpu_chain, nb);
cpu_maps_update_done();
return ret;
}
mutex lock으로 보호한 후 cpu chain에 신규 nb를 추가한다.
raw_notifier_chain_register()
kernel/notifier.c
/*
* Raw notifier chain routines. There is no protection;
* the caller must provide it. Use at your own risk!
*/
/**
* raw_notifier_chain_register - Add notifier to a raw notifier chain
* @nh: Pointer to head of the raw notifier chain
* @n: New entry in notifier chain
*
* Adds a notifier to a raw notifier chain.
* All locking must be provided by the caller.
*
* Currently always returns zero.
*/
int raw_notifier_chain_register(struct raw_notifier_head *nh,
struct notifier_block *n)
{
return notifier_chain_register(&nh->head, n);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(raw_notifier_chain_register);
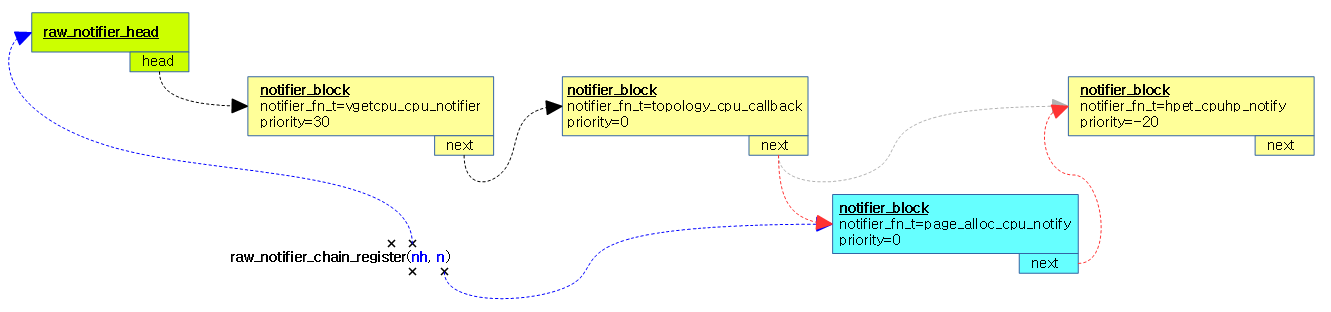
아래 그림과 같이 raw_notifier_head nh에 신규 notifier_block n을 추가하되 priority가 가장 높은 값이 선두에 위치한다. 동일 priority의 경우 나중에 추가한 블럭은 뒤로 추가된다.
notifier_chain_register()
kernel/notifier.c
/*
* Notifier chain core routines. The exported routines below
* are layered on top of these, with appropriate locking added.
*/
static int notifier_chain_register(struct notifier_block **nl,
struct notifier_block *n)
{
while ((*nl) != NULL) {
if (n->priority > (*nl)->priority)
break;
nl = &((*nl)->next);
}
n->next = *nl;
rcu_assign_pointer(*nl, n);
return 0;
}
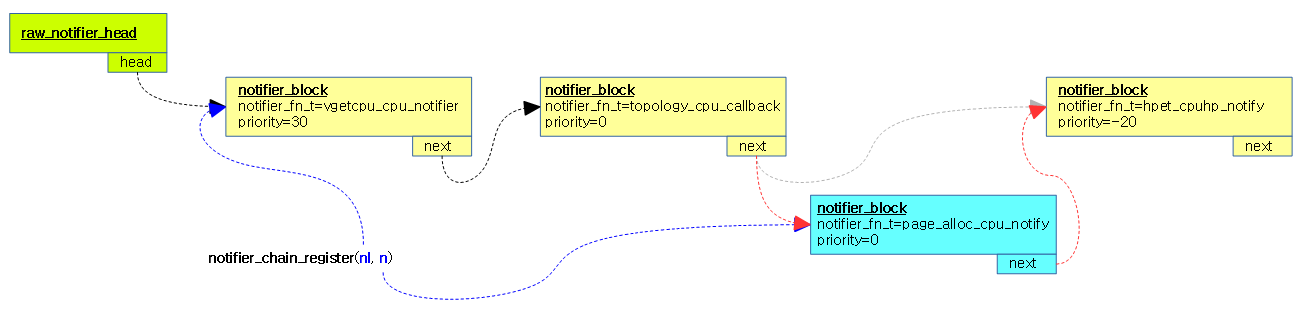
아래 그림과 같이 신규 n의 우선순위가 비교 블럭 nl의 우선순위보다 높은 경우 신규 n을 비교 블럭 nl 앞에 끼워넣는다.
호출(Notify)
호출 action
#define CPU_ONLINE 0x0002 /* CPU (unsigned)v is up */
#define CPU_UP_PREPARE 0x0003 /* CPU (unsigned)v coming up */
#define CPU_UP_CANCELED 0x0004 /* CPU (unsigned)v NOT coming up */
#define CPU_DOWN_PREPARE 0x0005 /* CPU (unsigned)v going down */
#define CPU_DOWN_FAILED 0x0006 /* CPU (unsigned)v NOT going down */
#define CPU_DEAD 0x0007 /* CPU (unsigned)v dead */
#define CPU_DYING 0x0008 /* CPU (unsigned)v not running any task,
* not handling interrupts, soon dead.
* Called on the dying cpu, interrupts
* are already disabled. Must not
* sleep, must not fail */
#define CPU_POST_DEAD 0x0009 /* CPU (unsigned)v dead, cpu_hotplug
* lock is dropped */
#define CPU_STARTING 0x000A /* CPU (unsigned)v soon running.
* Called on the new cpu, just before
* enabling interrupts. Must not sleep,
* must not fail */
cpu_notify()
kernel/cpu.c
static int cpu_notify(unsigned long val, void *v)
{
return __cpu_notify(val, v, -1, NULL);
}
- cpu action val과 data v로 cpu_chin에 등록되어 있는 모든 콜백함수를 호출한다.
__cpu_notify()
kernel/cpu.c
static int __cpu_notify(unsigned long val, void *v, int nr_to_call,
int *nr_calls)
{
int ret;
ret = __raw_notifier_call_chain(&cpu_chain, val, v, nr_to_call,
nr_calls);
return notifier_to_errno(ret);
}
cpu_chain에 등록된 콜백함수를 nr_to_call 수만큼 순서대로 호출하되 인수로 cpu action val과 데이터 v를 사용한다. 출력 인수 nr_calls에 호출된 수를 저장하고 에러 여부를 리턴한다.
__raw_notifier_call_chain()
kernel/notifier.c
/**
* __raw_notifier_call_chain - Call functions in a raw notifier chain
* @nh: Pointer to head of the raw notifier chain
* @val: Value passed unmodified to notifier function
* @v: Pointer passed unmodified to notifier function
* @nr_to_call: See comment for notifier_call_chain.
* @nr_calls: See comment for notifier_call_chain
*
* Calls each function in a notifier chain in turn. The functions
* run in an undefined context.
* All locking must be provided by the caller.
*
* If the return value of the notifier can be and'ed
* with %NOTIFY_STOP_MASK then raw_notifier_call_chain()
* will return immediately, with the return value of
* the notifier function which halted execution.
* Otherwise the return value is the return value
* of the last notifier function called.
*/
int __raw_notifier_call_chain(struct raw_notifier_head *nh,
unsigned long val, void *v,
int nr_to_call, int *nr_calls)
{
return notifier_call_chain(&nh->head, val, v, nr_to_call, nr_calls);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(__raw_notifier_call_chain);
nh가 가리키는 첫번째 콜백함수 부터 nr_to_call 수만큼 순서대로 호출하되 인수로 cpu action val과 데이터 v를 사용한다. 출력 인수 nr_calls에 호출된 수를 저장하고 에러 여부를 리턴한다.
notifier_call_chain()
kernel/notifier.c
/**
* notifier_call_chain - Informs the registered notifiers about an event.
* @nl: Pointer to head of the blocking notifier chain
* @val: Value passed unmodified to notifier function
* @v: Pointer passed unmodified to notifier function
* @nr_to_call: Number of notifier functions to be called. Don't care
* value of this parameter is -1.
* @nr_calls: Records the number of notifications sent. Don't care
* value of this field is NULL.
* @returns: notifier_call_chain returns the value returned by the
* last notifier function called.
*/
static int notifier_call_chain(struct notifier_block **nl,
unsigned long val, void *v,
int nr_to_call, int *nr_calls)
{
int ret = NOTIFY_DONE;
struct notifier_block *nb, *next_nb;
nb = rcu_dereference_raw(*nl);
while (nb && nr_to_call) {
next_nb = rcu_dereference_raw(nb->next);
#ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_NOTIFIERS
if (unlikely(!func_ptr_is_kernel_text(nb->notifier_call))) {
WARN(1, "Invalid notifier called!");
nb = next_nb;
continue;
}
#endif
ret = nb->notifier_call(nb, val, v);
if (nr_calls)
(*nr_calls)++;
if ((ret & NOTIFY_STOP_MASK) == NOTIFY_STOP_MASK)
break;
nb = next_nb;
nr_to_call--;
}
return ret;
}
NOKPROBE_SYMBOL(notifier_call_chain);
첫번째 콜백함수 nl 부터 nr_to_call 수만큼 순서대로 호출하되 인수로 cpu action val과 데이터 v를 사용한다. 출력 인수 nr_calls에 호출된 수를 저장하고 에러 발생 시 NOTIFY_STOP_MASK 비트를 포함하는 경우 루프를 탈출하고 에러 값을 리턴한다.
구조체
include/linux/notifier.h
/* * Notifier chains are of four types: * * Atomic notifier chains: Chain callbacks run in interrupt/atomic * context. Callouts are not allowed to block. * Blocking notifier chains: Chain callbacks run in process context. * Callouts are allowed to block. * Raw notifier chains: There are no restrictions on callbacks, * registration, or unregistration. All locking and protection * must be provided by the caller. * SRCU notifier chains: A variant of blocking notifier chains, with * the same restrictions. * * atomic_notifier_chain_register() may be called from an atomic context, * but blocking_notifier_chain_register() and srcu_notifier_chain_register() * must be called from a process context. Ditto for the corresponding * _unregister() routines. * * atomic_notifier_chain_unregister(), blocking_notifier_chain_unregister(), * and srcu_notifier_chain_unregister() _must not_ be called from within * the call chain. * * SRCU notifier chains are an alternative form of blocking notifier chains. * They use SRCU (Sleepable Read-Copy Update) instead of rw-semaphores for * protection of the chain links. This means there is _very_ low overhead * in srcu_notifier_call_chain(): no cache bounces and no memory barriers. * As compensation, srcu_notifier_chain_unregister() is rather expensive. * SRCU notifier chains should be used when the chain will be called very * often but notifier_blocks will seldom be removed. Also, SRCU notifier * chains are slightly more difficult to use because they require special * runtime initialization. */
notifier_fn_t 타입
typedef int (*notifier_fn_t)(struct notifier_block *nb,
unsigned long action, void *data);
notifier_block 구조체
struct notifier_block {
notifier_fn_t notifier_call;
struct notifier_block __rcu *next;
int priority;
};
atomic_notifier_head 구조체
struct atomic_notifier_head {
spinlock_t lock;
struct notifier_block __rcu *head;
};
blocking_notifier_head 구조체
struct blocking_notifier_head {
struct rw_semaphore rwsem;
struct notifier_block __rcu *head;
};
raw_notifier_head 구조체
struct raw_notifier_head {
struct notifier_block __rcu *head;
};
srcu_notifier_head 구조체
struct srcu_notifier_head {
struct mutex mutex;
struct srcu_struct srcu;
struct notifier_block __rcu *head;
};
전역 cpu_chain 구조체
static RAW_NOTIFIER_HEAD(cpu_chain);
- static raw_notifier_head cpu_chain = { .head = null }
/* srcu_notifier_heads cannot be initialized statically */
#define ATOMIC_NOTIFIER_HEAD(name) \
struct atomic_notifier_head name = \
ATOMIC_NOTIFIER_INIT(name)
#define BLOCKING_NOTIFIER_HEAD(name) \
struct blocking_notifier_head name = \
BLOCKING_NOTIFIER_INIT(name)
#define RAW_NOTIFIER_HEAD(name) \
struct raw_notifier_head name = \
RAW_NOTIFIER_INIT(name)
/* srcu_notifier_heads must be initialized and cleaned up dynamically */
extern void srcu_init_notifier_head(struct srcu_notifier_head *nh);
#define srcu_cleanup_notifier_head(name) \
cleanup_srcu_struct(&(name)->srcu);
#define ATOMIC_NOTIFIER_INIT(name) { \
.lock = __SPIN_LOCK_UNLOCKED(name.lock), \
.head = NULL }
#define BLOCKING_NOTIFIER_INIT(name) { \
.rwsem = __RWSEM_INITIALIZER((name).rwsem), \
.head = NULL }
#define RAW_NOTIFIER_INIT(name) { \
.head = NULL }