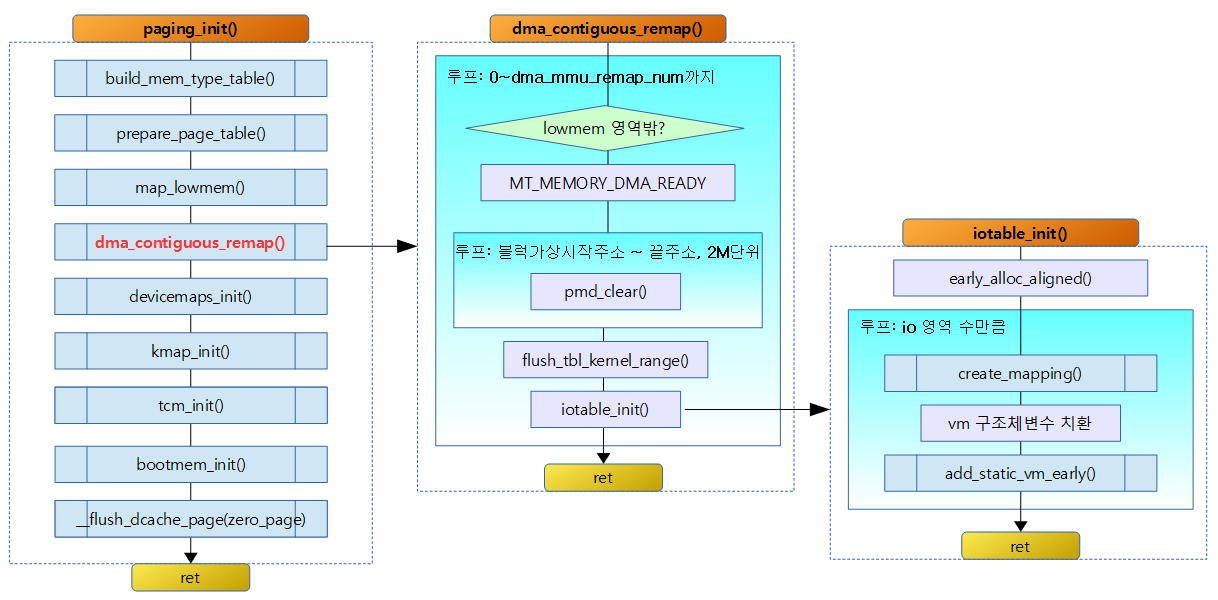
setup_arch() -> arm_memblock_init() -> dma_contiguous_reserve() 함수를 통해 reserve된 영역들은 CMA for DMA 용도의 메모리로 이 영역들을 순서대로 읽어 IO 매핑을 위해 다음과 같은 작업을 한다.
- DMA_READY 메모리 타입으로 페이지 테이블을 매핑할 준비를 한다. (실제 매핑은 정규 메모리 관리자가 설정된 후에 한다)
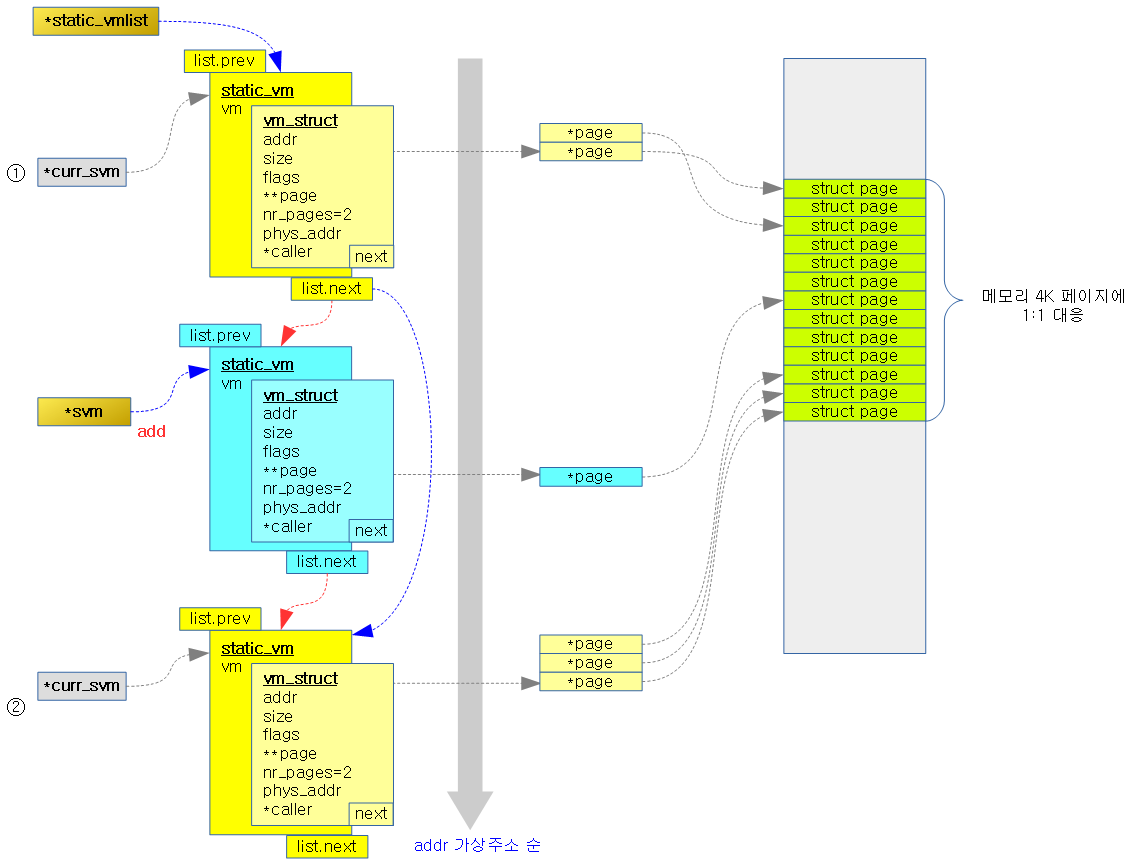
- IO 매핑 관리를 위해 static_vm 구조체 리스트인 static_vmlist에 static_vm 구조체를 추가한다. (vm->addr로 ascending 정렬)
- 내부에서는 또 하나의 vm_struct 구조체 리스트인 vmlist에 vm_struct 구조체를 추가한다. (addr로 ascending 정렬)
- early하게 추가된 이 리스트는 추후 mm_init() -> vmalloc_init()함수에 의해 다시 vmap_area 구조체로 변환되고 이 영역관리를 Red Black Tree 기법으로 관리하고 페이지 테이블에 매핑한다.
- 내부에서는 또 하나의 vm_struct 구조체 리스트인 vmlist에 vm_struct 구조체를 추가한다. (addr로 ascending 정렬)
dma_contiguous_remap()
arch/arm/mm/dma-mapping.c
void __init dma_contiguous_remap(void)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < dma_mmu_remap_num; i++) {
phys_addr_t start = dma_mmu_remap[i].base;
phys_addr_t end = start + dma_mmu_remap[i].size;
struct map_desc map;
unsigned long addr;
if (end > arm_lowmem_limit)
end = arm_lowmem_limit;
if (start >= end)
continue;
map.pfn = __phys_to_pfn(start);
map.virtual = __phys_to_virt(start);
map.length = end - start;
map.type = MT_MEMORY_DMA_READY;
/*
* Clear previous low-memory mapping to ensure that the
* TLB does not see any conflicting entries, then flush
* the TLB of the old entries before creating new mappings.
*
* This ensures that any speculatively loaded TLB entries
* (even though they may be rare) can not cause any problems,
* and ensures that this code is architecturally compliant.
*/
for (addr = __phys_to_virt(start); addr < __phys_to_virt(end);
addr += PMD_SIZE)
pmd_clear(pmd_off_k(addr));
flush_tlb_kernel_range(__phys_to_virt(start),
__phys_to_virt(end));
iotable_init(&map, 1);
}
}
dma_mmu_remap[] 배열에는 CMA for DMA 영역이 등록되어 있고 이 영역을 차례대로DMA_READY 메모리 타입 속성으로 페이지 매핑할 자료를 준비하고 iotable에 추가한다.
- for (i = 0; i < dma_mmu_remap_num; i++) {
- 리매핑이 필요한 수량 만큼 루프를 돈다.
- phys_addr_t start = dma_mmu_remap[i].base;
- 시작 물리 주소
- phys_addr_t end = start + dma_mmu_remap[i].size;
- 끝 물리 주소
- if (end > arm_lowmem_limit) end = arm_lowmem_limit;
- CMA for DMA 영역은 lowmem 영역 내에서만 매핑을 해야 하므로 끝 물리 주소가 lowmem 영역의 끝 주소인 arm_lowmem_limit를 초과하지 않게 조정한다.
- if (start >= end) continue;
- 시작 물리 주소가 lowmem 영역을 초과한 경우 무시하고 다음 리매핑 요청을 처리하기 위해 루프를 돈다.
- for (addr = __phys_to_virt(start); addr < __phys_to_virt(end); addr += PMD_SIZE) pmd_clear(pmd_off_k(addr));
- 가상 시작 주소부터 가상 끝 주소까지 pmd 엔트리를 삭제한다.
- flush_tlb_kernel_range(__phys_to_virt(start), __phys_to_virt(end));
- 영역 내의 1차, 2차 TLB 캐시 엔트리를 flush(삭제) 한다.
- iotable_init(&map, 1);
- 1개의 맵 영역을 iotable에 추가한다.
- map 영역들을 여러 개의 static_vm 구조체로 변환하고 이 관리 구조체 영역을 할당 받아 static_vmlist에 추가한다.
- 1개의 맵 영역을 iotable에 추가한다.
iotable_init()
arch/arm/mm/mmu.c
/*
* Create the architecture specific mappings
*/
void __init iotable_init(struct map_desc *io_desc, int nr)
{
struct map_desc *md;
struct vm_struct *vm;
struct static_vm *svm;
if (!nr)
return;
svm = early_alloc_aligned(sizeof(*svm) * nr, __alignof__(*svm));
for (md = io_desc; nr; md++, nr--) {
create_mapping(md);
vm = &svm->vm;
vm->addr = (void *)(md->virtual & PAGE_MASK);
vm->size = PAGE_ALIGN(md->length + (md->virtual & ~PAGE_MASK));
vm->phys_addr = __pfn_to_phys(md->pfn);
vm->flags = VM_IOREMAP | VM_ARM_STATIC_MAPPING;
vm->flags |= VM_ARM_MTYPE(md->type);
vm->caller = iotable_init;
add_static_vm_early(svm++);
}
}
요청 받은 맵 정보 배열 수 만큼 static_vm 구조체 배열로 reserve memblock에 할당 받는다. 그리고 요청 맵 영역들을 페이지 테이블에 매핑 구성하고 요청 맵 영역 각각을 관리하는 구조체 엔트리인 static_vm을 구성하고 그 엔트리들을 static_vmlist에 추가한다.
- svm = early_alloc_aligned(sizeof(*svm) * nr, __alignof__(*svm));
- nr개 만큼 static_vm 구조체 영역 크기를 reserve memblock으로 할당 받는다.
- align 단위는 static_vm 구조체 하나 크기만큼 이다.
- for (md = io_desc; nr; md++, nr–) {
- 요청 맵 영역 수(nr)만큼 루프를 돈다.
- create_mapping(md);
- 해당 영역을 페이지 테이블에 섹션 또는 4K 페이지로 매핑한다.
- static_vm 구조체에 영역에 대한 정보를 대입한다.
- flags = VM_IOREMAP | VM_ARM_STATIC_MAPPING | VM_ARM_MTYPE(md->type);
- IO 리매핑 속성, static 매핑 속성 및 메모리 타입을 플래그에 설정한다.
- VM_ARM_MTYPE()
- 지정된 메모리 타입을 좌측으로 20비트 쉬프트한 값
- flags = VM_IOREMAP | VM_ARM_STATIC_MAPPING | VM_ARM_MTYPE(md->type);
- add_static_vm_early(svm++);
- static_vmlist에 static_vm 구조체를 추가한다.
add_static_vm_early()
arch/arm/mm/ioremap.c
void __init add_static_vm_early(struct static_vm *svm)
{
struct static_vm *curr_svm;
struct vm_struct *vm;
void *vaddr;
vm = &svm->vm;
vm_area_add_early(vm);
vaddr = vm->addr;
list_for_each_entry(curr_svm, &static_vmlist, list) {
vm = &curr_svm->vm;
if (vm->addr > vaddr)
break;
}
list_add_tail(&svm->list, &curr_svm->list);
}
vm_struct 구조체 리스트인 vmlist에 vm을 추가하고 static_vm 구조체 리스트인static_vmlist에도 svm 엔트리를 추가한다.
- 2개의 리스트는 가상 주소가 작은 엔트리가 앞으로 순서대로 있다.
아래 그림은 static_vm 구조체 하나를 추가할 때의 모습을 나타낸다.
- static_vm 구조체 내부에 vm이라는 이름의 vm_struct 구조체가 있는데 그 멤버변수 addr(시작 가상 주소)가 가장 작은 경우 리스트의 선두에 있고 순서대로 정렬되어 있다.
vm_area_add_early()
mm/vmalloc.c
static struct vm_struct *vmlist __initdata;
/**
* vm_area_add_early - add vmap area early during boot
* @vm: vm_struct to add
*
* This function is used to add fixed kernel vm area to vmlist before
* vmalloc_init() is called. @vm->addr, @vm->size, and @vm->flags
* should contain proper values and the other fields should be zero.
*
* DO NOT USE THIS FUNCTION UNLESS YOU KNOW WHAT YOU'RE DOING.
*/
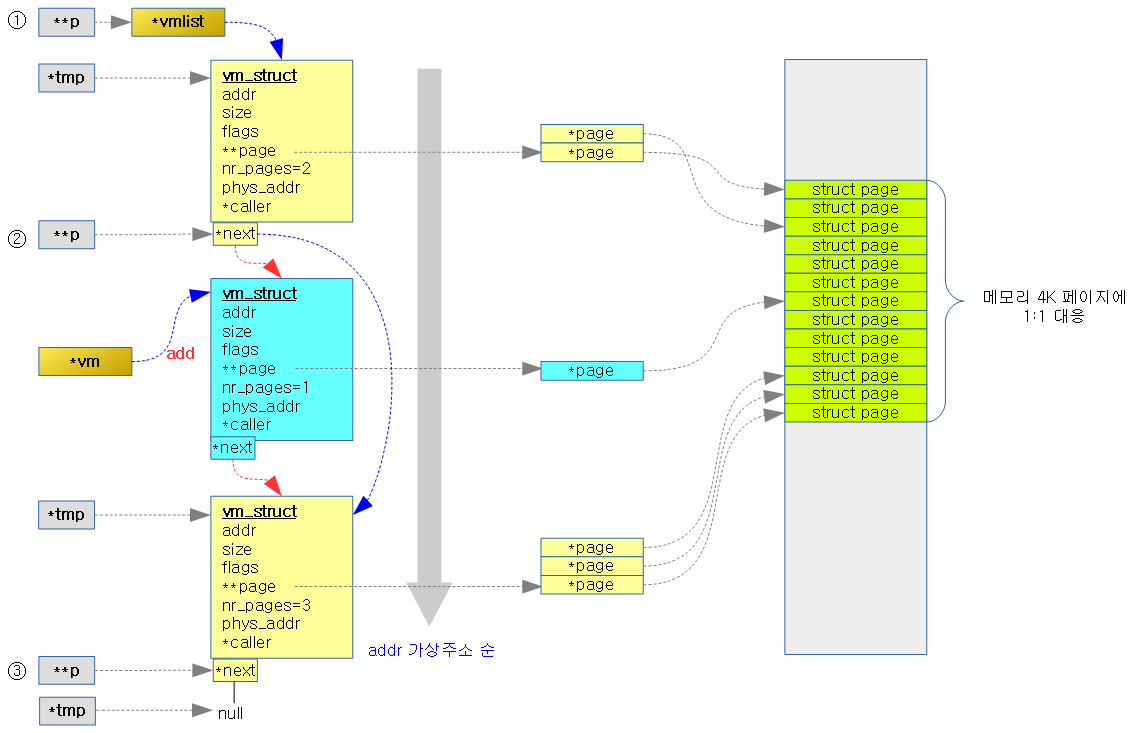
void __init vm_area_add_early(struct vm_struct *vm)
{
struct vm_struct *tmp, **p;
BUG_ON(vmap_initialized);
for (p = &vmlist; (tmp = *p) != NULL; p = &tmp->next) {
if (tmp->addr >= vm->addr) {
BUG_ON(tmp->addr < vm->addr + vm->size);
break;
} else
BUG_ON(tmp->addr + tmp->size > vm->addr);
}
vm->next = *p;
*p = vm;
}
- for (p = &vmlist; (tmp = *p) != NULL; p = &tmp->next) {
- vm_struct 더블 포인터 값인 p의 초기값으로 vmlist의 주소를 담고 *p가 null이 아닌 동안 루프를 돈다.
- 한 번 수행 시마다 p값을 현재 노드의 next 주소값으로 갱신한다.
- if (tmp->addr >= vm->addr) {
- 엔트리의 시작 가상 주소가 추가할 시작 가상 주소보다 크거나 같은 경우 그 엔트리 앞에 추가하기 위해 루프를 멈춘다.
- vm->next = *p; *p = vm
- 루프가 중단되지 않고 끝까지 수행되는 경우는 추가한 시작 가상 주소가 가장 큰 경우이므로 리스트의 마지막에 추가하기 위해 추가 노드의 next(vm->next)에 null(*p)을 대입하고 마지막 노드의 next(*p)에 추가 노드(vm)를 대입한다.
- 루프가 중간에 break 된 경우 현재 추가할 노드의 next(vm->next)에 현재 노드의 다음(*p) 주소를 대입하고 현재 노드의 next(*p)에 추가할 노드(vm)를 대입한다.
아래 그림은 vm_struct 하나를 추가할 때의 모습을 나타낸다.
- addr(시작 가상 주소)이 가장 작은 경우 리스트의 선두에 있고 순서대로 정렬되어 있다.
구조체 및 전역 변수
static_vm 구조체
arch/arm/mm/mm.h
struct static_vm {
struct vm_struct vm;
struct list_head list;
};
vm_struct 구조체
include/linux/vmalloc.h
struct vm_struct {
struct vm_struct *next;
void *addr;
unsigned long size;
unsigned long flags;
struct page **pages;
unsigned int nr_pages;
phys_addr_t phys_addr;
const void *caller;
};
- next
- 다음 vm_struct를 가리킨다.
- addr
- 영역의 시작 가상 주소
- size
- 영역의 크기
- flags
/* bits in flags of vmalloc's vm_struct below */ #define VM_IOREMAP 0x00000001 /* ioremap() and friends */ #define VM_ALLOC 0x00000002 /* vmalloc() */ #define VM_MAP 0x00000004 /* vmap()ed pages */ #define VM_USERMAP 0x00000008 /* suitable for remap_vmalloc_range */ #define VM_VPAGES 0x00000010 /* buffer for pages was vmalloc'ed */ #define VM_UNINITIALIZED 0x00000020 /* vm_struct is not fully initialized */ #define VM_NO_GUARD 0x00000040 /* don't add guard page */ #define VM_KASAN 0x00000080 /* has allocated kasan shadow memory */ /* bits [20..32] reserved for arch specific ioremap internals */
- pages
- 해당 영역에서 사용하고 있는 페이지를 가리키는 포인터 배열을 가리키는 이중 page 포인터이다.
- nr_pages
- 해당 영역에서 사용하고 있는 페이지 수
- phys_addr
- 영역의 시작 물리 주소
- caller
- 함수 포인터
전역 변수
arch/arm/mm/ioremap.c
LIST_HEAD(static_vmlist);
- static vm 엔트리들을 검색하고 관리하는 리스트이다.
mm/vmalloc.c
static struct vm_struct *vmlist __initdata;
- 이 리스트에 추가된 엔트리들은 커널이 설정되는 동안 early하게 추가되어 커널 정규 메모리 관리자가 정상적으로 동작할 때 vmalloc_init()에서 다시 allocation 된다.