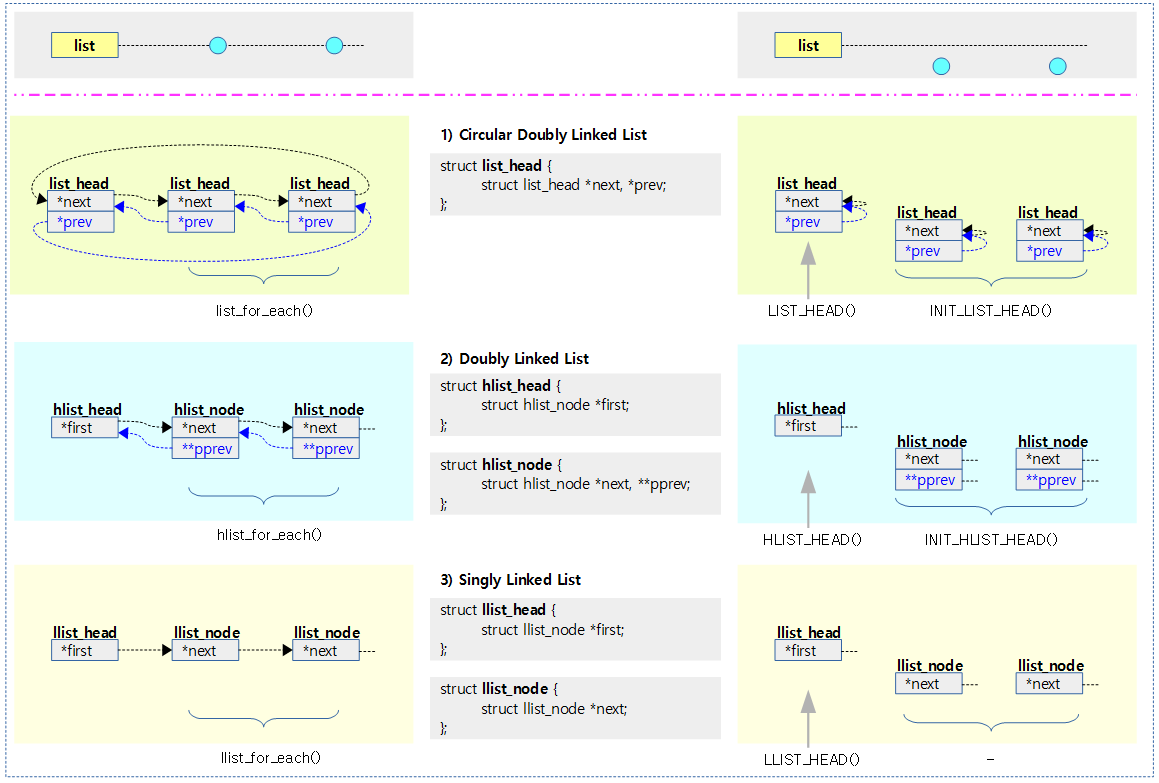
<kernel v5.4>
DMAEngine Subsystem
pci 및 pcie 디바이스들을 제외한 DMA를 사용하는 대부분의 디바이스들은 DMAEngine 서스시스템이 제공하는 API를 사용한다.
PCI/PCIe에서 DMA
호스트가 주도하는 DMA 시스템에서만 DMAEngine 서브시스템이 사용된다. 슬레이브 디바이스가 주도하는 pci/pcie 디바이스들은 DMAEngine 서스시스템을 사용하지 않고 각자 구현되어 사용중이다.
DMA 버퍼
dma 버퍼에 dma 전송 전후로 iommu 및 cache sync 유무에 따라 dma 매핑 API들을 같이 사용한다.
- dma 매핑
- iommu 사용 시 매핑/언매핑을 수행한다.
- dma 코히런트 메모리를 사용하지 않는 경우 매핑/언매핑 시 마다 invalidate 또는 clean & invalidate 한다.
- GFP_KERNEL 등으로 할당 받은 커널 메모리는 캐시를 사용하므로 이에 대한 sync 처리를 해야 한다.
DMA 활용
- 비동기 TX 전송용
- 메모리 to 메모리의 전송, XOR 및 cryptography 및 RAID 장치에서 사용되어 왔다.
- 슬레이브 전송용
- 그 후 발전되어 DMAEngine과 통합되어 슬레이브 디바이스와의 DMA를 위하여 사용되기 시작하였다.
- 심플한 슬레이브 DMA 컨트롤러들은 한 번에 요청한 바이트 수만큼 DMA를 수행한다.
- 조금 더 진보한 슬레이브 DMA 컨트롤러들은 전송시 widths(비트수)를 지정하고, 반복적인 전송을 지원하기 위해 버스트 사이즈를 지정할 수 있다.
- 더 많이 진보한 슬레이브 DMA 컨트롤러들은 scatter-gather 전송을 지원하여 연속적이지 않은 여러 곳의 버퍼 메모리를 지정하여 사용할 수 있게 하였다.
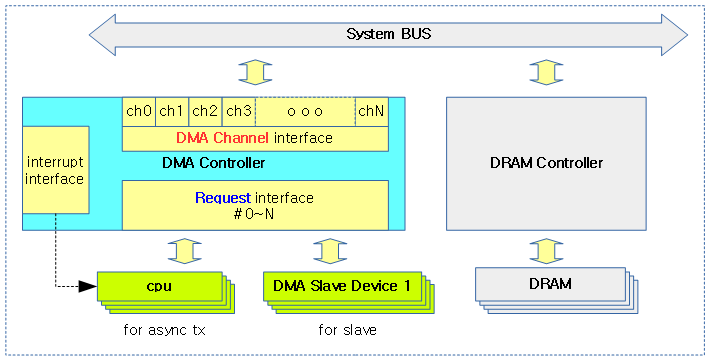
다음 그림은 메모리 <–> 메모리의 DMA 전송 방법과 슬레이브 디바이스 <–> 메모리의 DMA 전송 방법 차이를 보여준다.
- 메모리 <–> 메모리 DMA 요청을 위해 cpu가 async tx 방식의 DMA를 요청
- 슬레이브 디바이스 <–> 메모리 DMA 요청을 위해 slave 방식의 DMA를 요청

DMA 구성
다음 그림은 ARM 시스템의 AXI 버스에 연결된 DMA 컨트롤러가 연결된 모습을 보여준다. (amba pl330 dma 컨트롤러)
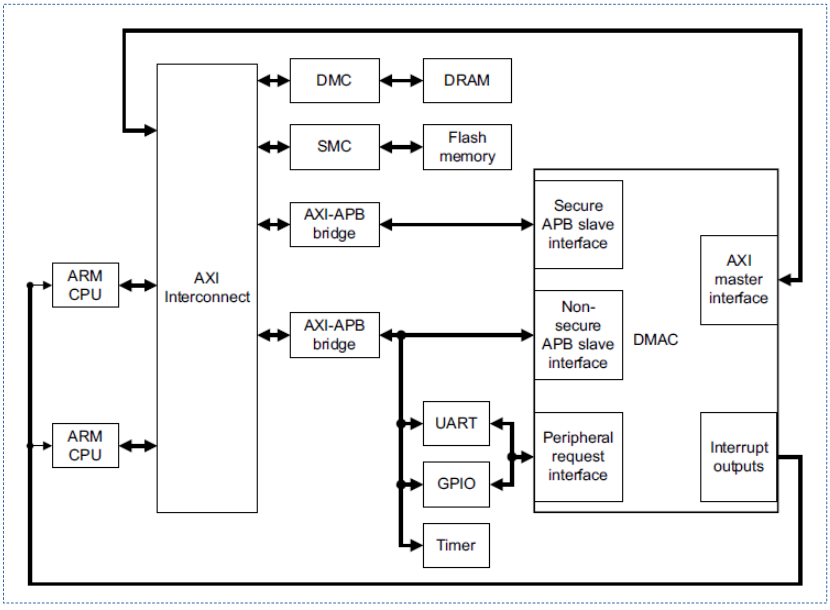
다음 그림은 위의 amba pl330 dma 컨트롤러를 확대하여 더 자세히 보여주고 있다.
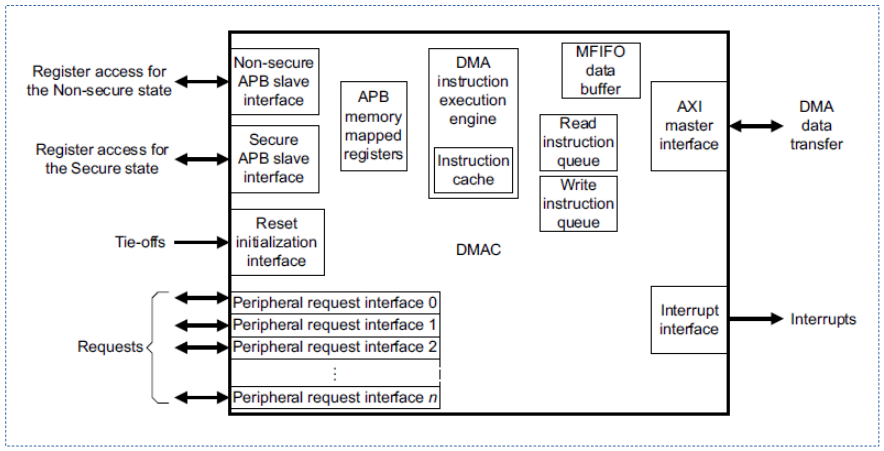
DMA 채널 및 request 인터페이스
여러 디바이스들이 DMA를 사용할 수 있도록 대부분의 DMA 컨트롤러들은 여러 개의 DMA를 동시 지원할 수 있도록 DMA 채널을 지원한다. 또한 여러 개의 슬레이브 디바이스들로 부터 DMA 요청을 받을 수 있도록 DMA 컨트롤러 H/W가 지원한다.
DMA MUX (DMA-Router)
DMA MUX 정보는 다음을 참고한다.
DMA 사이즈
DMAEngine을 통해 DMA 전송 요청하는 경우 디스크립터 단위로 요청된다. 이는 내부적으로 여러 개의 세그먼트가 포함될 수 있으며 각 세그먼트는 1개 이상의 burst 전송이 이루어진다.
- Descriptor > Segment > Burst

DMA 트랜스퍼 타입
- DMA_MEMCPY
- DMA_XOR
- 디바이스가 RAID5를 위해 메모리에서 XOR 연산을 수행한다.
- DMA_PQ
- 디바이스가 RAID6 P+Q 계산을 수행한다. (P=XOR, Q=Reed-Solomon 알고리즘)
- DMA_XOR_VAL
- 디바이스가 XOR를 사용한 메모리 버퍼 패리티 체크를 수행한다.
- DMA_PQ_VAL
- 디바이스가 RAID6 P+Q 계산을 사용한 메모리 버퍼 패리티 체크를 수행한다.
- DMA_MEMSET
- DMA_MEMSET_SG
- 메모리 to 메모리 memset scatter gather
- DMA_INTERRUPT
- 디바이스가 더미 전송을 통한 인터럽트를 생성한다.
- DMA_PRIVATE
- 슬레이브 전송만 지원하고, 비동기 tx 전송은 지원하지 않는다.
- 이 플래그를 설정하지 않는 경우 비동기 TX 사용 시 dma_request_channel() 함수를 거치지 않고 랜덤 채널을 사용한다.
- DMA_ASYNC_TX
- DMA_SLAVE
- 디바이스 to 메모리 및 메모리 to 디바이스 전송을 수행한다. (scatter-gather 포함)
- DMA_CYCLIC
- 디바이스가 사이클릭 전송 가능하다.
- 세그먼트(청크) 단위로 전송이 완료될 때마다 인터럽트로 보고된다.
- DMA_INTERLEAVE
- 메모리 to 메모리 인터리브(interleaved) 전송 방법을 사용한다.
Slave DMA Controller
기본적인 DMA 슬레이브 전송만을 지원하는 일반 dma 컨트롤러의 경우 다음과 같은 플래그가 주어진다. (예: pl330, bcm2835, stm32, …)
- DMA_SLAVE
- DMA_PRIVATE
- DMA_CYCLIC
- DMA_MEMCPY
RAID DMA Controller
예) raid 장치용 dma 컨트롤러의 경우 다음과 같은 플래그가 주어진다. (예: fsl-raideng, bcm-sba-raid, ioat, …)
- DMA_XOR
- DMA_PQ
- DMA_MEMCPY
주요 API
- dma_request_chan()
- dma_request_slave_channel()
- dma_request_slave_channel_reason()
- dmaengine_slave_config()
- dmaengine_prep_*()
- dmaengine_prep_slave_single()
- dmaengine_prep_slave_sg()
- dmaengine_prep_rio_sg()
- dmaengine_prep_dma_cyclic()
- dmaengine_prep_interleaved_dma()
- dmaengine_prep_dma_memset()
- dmaengine_prep_dma_memcpy()
- dmaengine_submit()
- dma_async_issue_pending()
DMA 엔진 – DMA 호스트 컨트롤러측
Device Operations
dma 호스트 컨트롤러 드라이버는 dma_device 구조체에 구현 관련 콜백 함수들을 연결한 후 dma_async_device_register() 함수를 사용하여 등록한다.
다음 그림은 arm사의 pl330 dma 컨트롤러를 사용한 드라이버이며, 구현된 오퍼레이션 함수를 모두 보여준다.
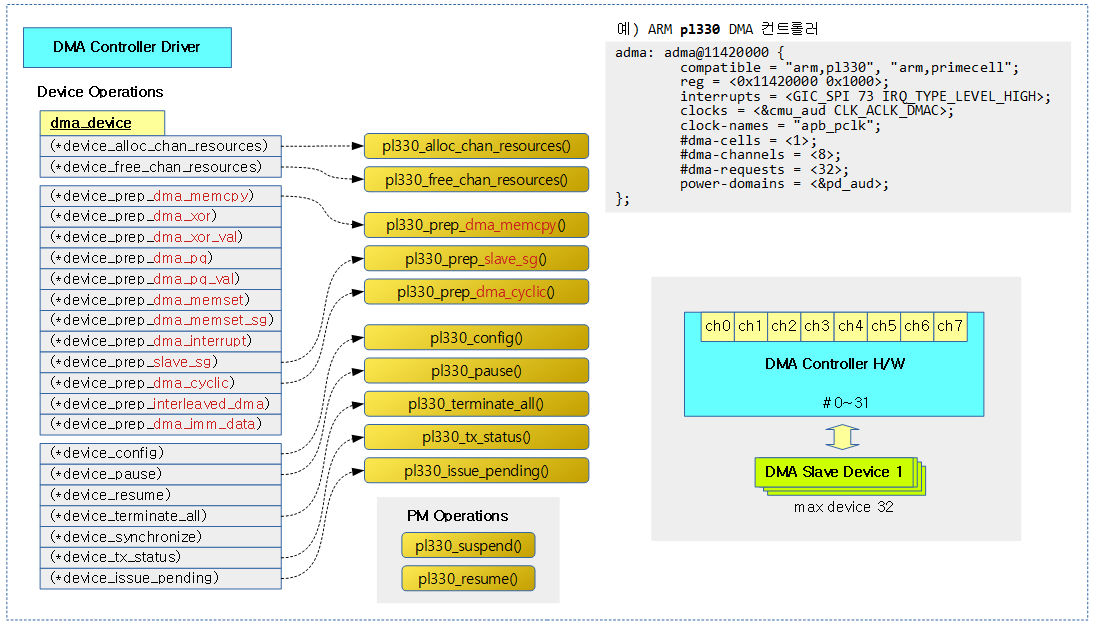
dma 호스트 컨트롤러 등록
dmaenginem_async_device_register()
drivers/dma/dmaengine.c
/**
* dmaenginem_async_device_register - registers DMA devices found
* @device: &dma_device
*
* The operation is managed and will be undone on driver detach.
*/
int dmaenginem_async_device_register(struct dma_device *device)
{
void *p;
int ret;
p = devres_alloc(dmam_device_release, sizeof(void *), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!p)
return -ENOMEM;
ret = dma_async_device_register(device);
if (!ret) {
*(struct dma_device **)p = device;
devres_add(device->dev, p);
} else {
devres_free(p);
}
return ret;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(dmaenginem_async_device_register);
dma 컨트롤러 디바이스를 등록한다. (managed 디바이스로 등록하므로 드라이버 모듈을 언로드하는 경우 자동으로 해제한다)
dma_async_device_register()
drivers/dma/dmaengine.c -1/3-
/**
* dma_async_device_register - registers DMA devices found
* @device: &dma_device
*/
int dma_async_device_register(struct dma_device *device)
{
int chancnt = 0, rc;
struct dma_chan* chan;
atomic_t *idr_ref;
if (!device)
return -ENODEV;
/* validate device routines */
if (!device->dev) {
pr_err("DMAdevice must have dev\n");
return -EIO;
}
if (dma_has_cap(DMA_MEMCPY, device->cap_mask) && !device->device_prep_dma_memcpy) {
dev_err(device->dev,
"Device claims capability %s, but op is not defined\n",
"DMA_MEMCPY");
return -EIO;
}
if (dma_has_cap(DMA_XOR, device->cap_mask) && !device->device_prep_dma_xor) {
dev_err(device->dev,
"Device claims capability %s, but op is not defined\n",
"DMA_XOR");
return -EIO;
}
if (dma_has_cap(DMA_XOR_VAL, device->cap_mask) && !device->device_prep_dma_xor_val) {
dev_err(device->dev,
"Device claims capability %s, but op is not defined\n",
"DMA_XOR_VAL");
return -EIO;
}
if (dma_has_cap(DMA_PQ, device->cap_mask) && !device->device_prep_dma_pq) {
dev_err(device->dev,
"Device claims capability %s, but op is not defined\n",
"DMA_PQ");
return -EIO;
}
if (dma_has_cap(DMA_PQ_VAL, device->cap_mask) && !device->device_prep_dma_pq_val) {
dev_err(device->dev,
"Device claims capability %s, but op is not defined\n",
"DMA_PQ_VAL");
return -EIO;
}
if (dma_has_cap(DMA_MEMSET, device->cap_mask) && !device->device_prep_dma_memset) {
dev_err(device->dev,
"Device claims capability %s, but op is not defined\n",
"DMA_MEMSET");
return -EIO;
}
if (dma_has_cap(DMA_INTERRUPT, device->cap_mask) && !device->device_prep_dma_interrupt) {
dev_err(device->dev,
"Device claims capability %s, but op is not defined\n",
"DMA_INTERRUPT");
return -EIO;
}
if (dma_has_cap(DMA_CYCLIC, device->cap_mask) && !device->device_prep_dma_cyclic) {
dev_err(device->dev,
"Device claims capability %s, but op is not defined\n",
"DMA_CYCLIC");
return -EIO;
}
if (dma_has_cap(DMA_INTERLEAVE, device->cap_mask) && !device->device_prep_interleaved_dma) {
dev_err(device->dev,
"Device claims capability %s, but op is not defined\n",
"DMA_INTERLEAVE");
return -EIO;
}
if (!device->device_tx_status) {
dev_err(device->dev, "Device tx_status is not defined\n");
return -EIO;
}
if (!device->device_issue_pending) {
dev_err(device->dev, "Device issue_pending is not defined\n");
return -EIO;
}
dma 컨트롤러 디바이스를 등록한다.
- 코드 라인 7~8에서 입력 인자로 디바이스가 null로 지정된 경우 -ENODEV 에러를 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 11~14에서 디바이스가 없는 경우 -EIO 에러를 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 16~77에서 dma 컨트롤러에 각 dma capacity에 해당하는 콜백 함수가 구현되어 있지 않은 경우 -EIO 에러를 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 80~89에서 dma 컨트롤러에 다음 기본 콜백 함수가 구현되어 있지 않은 경우 -EIO 에러를 반환한다.
- (*device_tx_status)
- (*device_issue_pending)
drivers/dma/dmaengine.c -2/3-
. /* note: this only matters in the
* CONFIG_ASYNC_TX_ENABLE_CHANNEL_SWITCH=n case
*/
if (device_has_all_tx_types(device))
dma_cap_set(DMA_ASYNC_TX, device->cap_mask);
idr_ref = kmalloc(sizeof(*idr_ref), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!idr_ref)
return -ENOMEM;
rc = get_dma_id(device);
if (rc != 0) {
kfree(idr_ref);
return rc;
}
atomic_set(idr_ref, 0);
/* represent channels in sysfs. Probably want devs too */
list_for_each_entry(chan, &device->channels, device_node) {
rc = -ENOMEM;
chan->local = alloc_percpu(typeof(*chan->local));
if (chan->local == NULL)
goto err_out;
chan->dev = kzalloc(sizeof(*chan->dev), GFP_KERNEL);
if (chan->dev == NULL) {
free_percpu(chan->local);
chan->local = NULL;
goto err_out;
}
chan->chan_id = chancnt++;
chan->dev->device.class = &dma_devclass;
chan->dev->device.parent = device->dev;
chan->dev->chan = chan;
chan->dev->idr_ref = idr_ref;
chan->dev->dev_id = device->dev_id;
atomic_inc(idr_ref);
dev_set_name(&chan->dev->device, "dma%dchan%d",
device->dev_id, chan->chan_id);
rc = device_register(&chan->dev->device);
if (rc) {
free_percpu(chan->local);
chan->local = NULL;
kfree(chan->dev);
atomic_dec(idr_ref);
goto err_out;
}
chan->client_count = 0;
}
if (!chancnt) {
dev_err(device->dev, "%s: device has no channels!\n", __func__);
rc = -ENODEV;
goto err_out;
}
device->chancnt = chancnt;
- 코드 라인 4~5에서 CONFIG_ASYNC_TX_ENABLE_CHANNEL_SWITCH=n으로 설정하여 async tx 채널이 설정되지 않은 경우 디바이스의 cap_mask에 DMA_ASYNC_TX 플래그를 추가한다.
- 코드 라인 7~16에서 디바이스에 대한 idr_ref를 할당받아 0으로 초기화한다. 또한 dma 컨트롤러의 id를 할당받아 device->dev_id에 지정한다.
- 코드 라인 19~56에서 dma 컨트롤러가 가진 채널을 순회하며 각 채널 디바이스를 초기화하고 디바이스로 등록한다.
- 코드 라인 58에서 dma 채널 수를 지정한다.
drivers/dma/dmaengine.c -3/3-
mutex_lock(&dma_list_mutex);
/* take references on public channels */
if (dmaengine_ref_count && !dma_has_cap(DMA_PRIVATE, device->cap_mask))
list_for_each_entry(chan, &device->channels, device_node) {
/* if clients are already waiting for channels we need
* to take references on their behalf
*/
if (dma_chan_get(chan) == -ENODEV) {
/* note we can only get here for the first
* channel as the remaining channels are
* guaranteed to get a reference
*/
rc = -ENODEV;
mutex_unlock(&dma_list_mutex);
goto err_out;
}
}
list_add_tail_rcu(&device->global_node, &dma_device_list);
if (dma_has_cap(DMA_PRIVATE, device->cap_mask))
device->privatecnt++; /* Always private */
dma_channel_rebalance();
mutex_unlock(&dma_list_mutex);
return 0;
err_out:
/* if we never registered a channel just release the idr */
if (atomic_read(idr_ref) == 0) {
ida_free(&dma_ida, device->dev_id);
kfree(idr_ref);
return rc;
}
list_for_each_entry(chan, &device->channels, device_node) {
if (chan->local == NULL)
continue;
mutex_lock(&dma_list_mutex);
chan->dev->chan = NULL;
mutex_unlock(&dma_list_mutex);
device_unregister(&chan->dev->device);
free_percpu(chan->local);
}
return rc;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(dma_async_device_register);
- 코드 라인 3~17에서 공유 dma 채널을 사용하고 있는 경우 dma 컨트롤러의 모든 채널을 순회하며 참조 카운터를 증가시킨다.
- 코드 라인 18에서 dma 컨트롤러 리스트 dma_device_list에 추가한다.
- 코드 라인 19~20에서 슬레이브 전송만 지원하고 async tx를 하지못하는 private dma 컨트롤러의 privatecnt를 1 증가시킨다.
- 코드 라인 21에서 dma tx 타입별로 채널을 재분배하는데 가능하면 로컬 노드에 포함된 dma 컨트롤러의 가장 적게 사용된 채널을 지정한다.
- 코드 라인 24에서 성공 값 0을 반환한다.
tx 타입별 채널 재분배
dma_channel_rebalance()
drivers/dma/dmaengine.c
/**
* dma_channel_rebalance - redistribute the available channels
*
* Optimize for cpu isolation (each cpu gets a dedicated channel for an
* operation type) in the SMP case, and operation isolation (avoid
* multi-tasking channels) in the non-SMP case. Must be called under
* dma_list_mutex.
*/
static void dma_channel_rebalance(void)
{
struct dma_chan *chan;
struct dma_device *device;
int cpu;
int cap;
/* undo the last distribution */
for_each_dma_cap_mask(cap, dma_cap_mask_all)
for_each_possible_cpu(cpu)
per_cpu_ptr(channel_table[cap], cpu)->chan = NULL;
list_for_each_entry(device, &dma_device_list, global_node) {
if (dma_has_cap(DMA_PRIVATE, device->cap_mask))
continue;
list_for_each_entry(chan, &device->channels, device_node)
chan->table_count = 0;
}
/* don't populate the channel_table if no clients are available */
if (!dmaengine_ref_count)
return;
/* redistribute available channels */
for_each_dma_cap_mask(cap, dma_cap_mask_all)
for_each_online_cpu(cpu) {
chan = min_chan(cap, cpu);
per_cpu_ptr(channel_table[cap], cpu)->chan = chan;
}
}
dma tx 타입별로 채널을 재분배하는데 가능하면 로컬 노드에 포함된 dma 컨트롤러의 가장 적게 사용된 채널을 지정한다.
- 코드 라인 9~11에서 모든 dma cap을 순회하고, 각 dma cap에 대한 possible cpu들을 순회하며 채널을 초기화한다.
- 코드 라인 13~18에서 dma 컨트롤러 리스트를 순회하며 DMA_PRIVATE cap을 가진 dma 컨트롤러는 skip 하고, 순회 중인 dma 컨트롤러의 모든 채널에 대해 table_count를 0으로 리셋한다.
- 코드 라인 21~22에서 dma 컨트롤러를 사용하는 사용자가 없는 경우 함수를 빠져나간다.
- 코드 라인 25~29에서 모든 dma cap을 순회하고, 각 dma cap에 대한 online cpu들을 순회하며 해당 cap에서 가장 사용이 적은 채널을 찾아 채널 테이블에 지정한다.
- channel_table[dma tx 타입]->chan에 가장 사용이 적은 컨트롤러의 채널을 지정한다.
min_chan()
drivers/dma/dmaengine.c
/**
* min_chan - returns the channel with min count and in the same numa-node as the cpu
* @cap: capability to match
* @cpu: cpu index which the channel should be close to
*
* If some channels are close to the given cpu, the one with the lowest
* reference count is returned. Otherwise, cpu is ignored and only the
* reference count is taken into account.
* Must be called under dma_list_mutex.
*/
static struct dma_chan *min_chan(enum dma_transaction_type cap, int cpu)
{
struct dma_device *device;
struct dma_chan *chan;
struct dma_chan *min = NULL;
struct dma_chan *localmin = NULL;
list_for_each_entry(device, &dma_device_list, global_node) {
if (!dma_has_cap(cap, device->cap_mask) ||
dma_has_cap(DMA_PRIVATE, device->cap_mask))
continue;
list_for_each_entry(chan, &device->channels, device_node) {
if (!chan->client_count)
continue;
if (!min || chan->table_count < min->table_count)
min = chan;
if (dma_chan_is_local(chan, cpu))
if (!localmin ||
chan->table_count < localmin->table_count)
localmin = chan;
}
}
chan = localmin ? localmin : min;
if (chan)
chan->table_count++;
return chan;
}
@cpu가 소속된 로컬 노드 dma 컨트롤러 중 @cap에 대한 가장 작은 채널을 찾아 반환한다. 단 로컬 디바이스가 없으면 전체 노드를 대상으로 한다.
- 코드 라인 8~11에서 모든 dma 컨트롤러를 순회하며 @cap이 없거나 DMA_PRIVATE cap의 경우 skip 한다.
- 코드 라인 12~14에서 순회 중인 dma 컨트롤러의 모든 채널을 순회하며 해당 채널에 연결된 클라이언트가 없는 경우 skip 한다.
- 코드 라인 15~16에서 순회 중인 채널 중 가장 작은 table_count 인 채널을 min 채널로 갱신한다.
- 코드 라인 18~21에서 @cpu가 포함된 노드에 소속된 디바이스이고 순회 중인 채널 중 가장 작은 table_count 인 채널을 localmin 채널로 갱신한다.
- 코드 라인 25~30에서 localmin이 지정된 경우 이를 반환한다. 그렇지 않은 경우 chan을 반환한다. 반환 전에 table_count를 증가킨다.
dma_chan_is_local()
drivers/dma/dmaengine.c
/**
* dma_chan_is_local - returns true if the channel is in the same numa-node as the cpu
*/
static bool dma_chan_is_local(struct dma_chan *chan, int cpu)
{
int node = dev_to_node(chan->device->dev);
return node == NUMA_NO_NODE ||
cpumask_test_cpu(cpu, cpumask_of_node(node));
}
로컬 노드에 소속된 디바이스인지 여부를 반환한다.
DMA 채널 획득
dma_get_slave_channel()
drivers/dma/dmaengine.c
/**
* dma_get_slave_channel - try to get specific channel exclusively
* @chan: target channel
*/
struct dma_chan *dma_get_slave_channel(struct dma_chan *chan)
{
int err = -EBUSY;
/* lock against __dma_request_channel */
mutex_lock(&dma_list_mutex);
if (chan->client_count == 0) {
struct dma_device *device = chan->device;
dma_cap_set(DMA_PRIVATE, device->cap_mask);
device->privatecnt++;
err = dma_chan_get(chan);
if (err) {
dev_dbg(chan->device->dev,
"%s: failed to get %s: (%d)\n",
__func__, dma_chan_name(chan), err);
chan = NULL;
if (--device->privatecnt == 0)
dma_cap_clear(DMA_PRIVATE, device->cap_mask);
}
} else
chan = NULL;
mutex_unlock(&dma_list_mutex);
return chan;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(dma_get_slave_channel);
요청한 dma 채널을 베타적으로 획득한다. 성공한 경우 요청한 dma 채널이 그대로 반화되며, 실패한 경우 null을 반환한다.
DMA 엔진 – 슬레이브 디바이스 유저 측
슬레이브측 DMA 사용 순서
크게 3 부분의 함수를 통해 dma api 호출 순서를 알아본다.
- probe 함수
- DMA 슬레이브 채널 할당
- dma_request_chan()
- or dma_request_slave_channel_reason()
- or dma_request_slave_channel()
- 슬레이브와 컨트롤러 관련 파라미터 설정
- DMA 전송 함수
- DMA 매핑 API (Option)
- 트랜잭션을 위한 트랜잭션 준비
- 트랜잭션 전송
- 이슈 펜딩 요청 및 콜백 통지 대기
- dma_async_issue_pending()
- DMA 인터럽트 핸들러
- DMA 언매핑 API (Option)
- dmaengine_terminate_all() – 타임아웃 처리
다음 그림은 dma 슬레이브 디바이스가 처음 인식되어 초기화될 때 dma 관련 명령이 처리되는 순서를 보여준다.
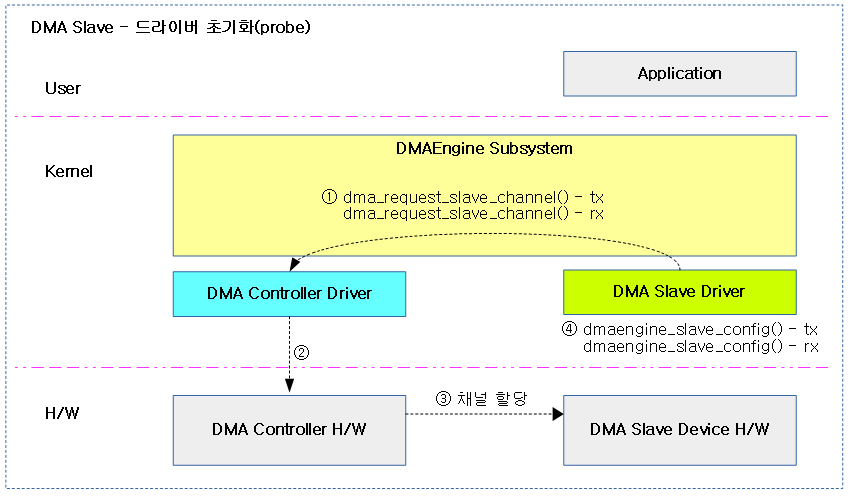
다음 그림은 dma 슬레이브 디바이스를 통해 전송을 시도 시 dma 관련 명령이 처리되는 순서를 보여준다.
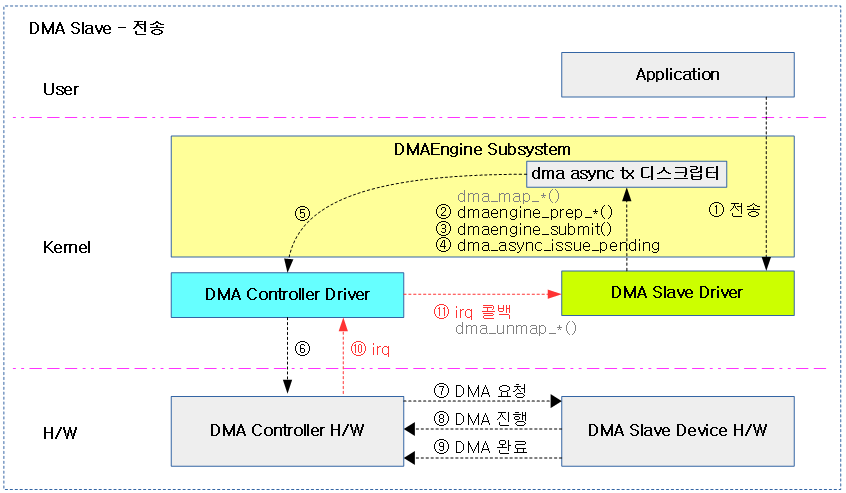
DMA 채널 할당 요청
dma 채널을 할당받아 사용해야 하는 dma 슬레이브 디바이스 유저들은 dma_request_chan() 함수를 통해 DT 또는 ACPI에서 정의한 dma 컨트롤러로부터 dma 채널을 할당받아온다.
- 예) master->dma_rx = dma_request_chan(user_slave_device->dev, “rx”);
dma_request_slave_channel()
drivers/dma/dmaengine.c
/**
* dma_request_slave_channel - try to allocate an exclusive slave channel
* @dev: pointer to client device structure
* @name: slave channel name
*
* Returns pointer to appropriate DMA channel on success or NULL.
*/
struct dma_chan *dma_request_slave_channel(struct device *dev,
const char *name)
{
struct dma_chan *ch = dma_request_chan(dev, name);
if (IS_ERR(ch))
return NULL;
return ch;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(dma_request_slave_channel);
슬레이브 채널을 할당 시도한다. 성공 시 dma 채널이 반환되고, 실패 시 에러가 반환된다.
dma_request_slave_channel_reason()
include/linux/dmaengine.h
#define dma_request_slave_channel_reason(dev, name) dma_request_chan(dev, name)
슬레이브 채널을 할당 시도한다. 성공 시 dma 채널이 반환되고, 실패 시 에러가 반환된다.
dma_request_chan()
drivers/dma/dmaengine.c
/**
* dma_request_chan - try to allocate an exclusive slave channel
* @dev: pointer to client device structure
* @name: slave channel name
*
* Returns pointer to appropriate DMA channel on success or an error pointer.
*/
struct dma_chan *dma_request_chan(struct device *dev, const char *name)
{
struct dma_device *d, *_d;
struct dma_chan *chan = NULL;
/* If device-tree is present get slave info from here */
if (dev->of_node)
chan = of_dma_request_slave_channel(dev->of_node, name);
/* If device was enumerated by ACPI get slave info from here */
if (has_acpi_companion(dev) && !chan)
chan = acpi_dma_request_slave_chan_by_name(dev, name);
if (chan) {
/* Valid channel found or requester needs to be deferred */
if (!IS_ERR(chan) || PTR_ERR(chan) == -EPROBE_DEFER)
return chan;
}
/* Try to find the channel via the DMA filter map(s) */
mutex_lock(&dma_list_mutex);
list_for_each_entry_safe(d, _d, &dma_device_list, global_node) {
dma_cap_mask_t mask;
const struct dma_slave_map *map = dma_filter_match(d, name, dev);
if (!map)
continue;
dma_cap_zero(mask);
dma_cap_set(DMA_SLAVE, mask);
chan = find_candidate(d, &mask, d->filter.fn, map->param);
if (!IS_ERR(chan))
break;
}
mutex_unlock(&dma_list_mutex);
return chan ? chan : ERR_PTR(-EPROBE_DEFER);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(dma_request_chan);
슬레이브 채널을 할당 시도한다. 성공 시 dma 채널이 반환되고, 실패 시 에러가 반환된다.
- 코드 라인 7~8에서 dma 슬레이브 디바이스가 디바이스 트리를 통해 등록된 경우 디바이스 트리를 통해 사용할 dma 컨트롤러의 dma 채널을 알아온다.
- 코드 라인 11~12에서 위에서 가져온 정보가 없으면서 ACPI 정보를 통해 등록된 경우 ACPI를 통해 사용할 dma 컨트롤러의 dma 채널을 알아온다.
- 코드 라인 14~18에서 dma 채널을 발견하였거나 -EPROBE_DEFER 에러인 경우 함수를 빠져나간다.
- 코드 라인 21~36에서 dma 채널을 발견하지 못한 경우 dma_list_mutex 락을 획득한 채로 dma filter를 사용하여 dma 채널을 알아온다.
- 코드 라인 38에서 성공한 경우 dma 채널을 반환하고, 실패한 경우 -EPROBE_DEFER 에러를 반환한다.
dma 슬레이브 설정
dmaengine_slave_config()
static inline int dmaengine_slave_config(struct dma_chan *chan,
struct dma_slave_config *config)
{
if (chan->device->device_config)
return chan->device->device_config(chan, config);
return -ENOSYS;
}
요청한 채널에 dma 슬레이브 설정을 한다.
DMA 전송 시작
dmaengine_submit()
include/linux/dmaengine.h
static inline dma_cookie_t dmaengine_submit(struct dma_async_tx_descriptor *desc)
{
return desc->tx_submit(desc);
}
준비한 비동기 전송용 디스크립터 내용으로 dma 요청한다.
펜딩된 남은 트랜잭션을 hw로 flush
dma_async_issue_pending()
include/linux/dmaengine.h
/**
* dma_async_issue_pending - flush pending transactions to HW
* @chan: target DMA channel
*
* This allows drivers to push copies to HW in batches,
* reducing MMIO writes where possible.
*/
static inline void dma_async_issue_pending(struct dma_chan *chan)
{
chan->device->device_issue_pending(chan);
}
dma 처리 중인 트랜잭션을 hw에 모두 전송하도록 요청한다.(flush)
dmaengine_terminate_all()
include/linux/dmaengine.h
/**
* dmaengine_terminate_all() - Terminate all active DMA transfers
* @chan: The channel for which to terminate the transfers
*
* This function is DEPRECATED use either dmaengine_terminate_sync() or
* dmaengine_terminate_async() instead.
*/
static inline int dmaengine_terminate_all(struct dma_chan *chan)
{
if (chan->device->device_terminate_all)
return chan->device->device_terminate_all(chan);
return -ENOSYS;
}
tdma 채널에서 동작중인 모든 dma 전송을 종료시킨다.
DMA 관련 디바이스 트리
ARM64 SoC에 내장된 DMA 컨트롤러들 (DT compatible 명)
- mediatek
- arm
- “arm,pl330”, “arm,primecell”
- juno, rockchip, exynos, broadcom(ns2,stingray),altera SoC에서 채택
- sprd
- qualcom
- freescale
- “fsl,imx8mn-sdma”, “fsl,imx8mq-sdma”
- “fsl,imx7d-dma-apbh”, “fsl,imx28-dma-apbh”
- “fsl,vf610-edma”
- renesas
- “renesas,usb-dmac”
- “renesas,dmac-r8a77965”
- “renesas,rcar-dmac”
- actions
- zte
- hisilicon
- “hisilicon,k3-dma-1.0”
- “hisilicon,hisi-pcm-asp-dma-1.0”
- allwinner
- “allwinner,sun8i-h3-dma”
- “allwinner,sun50i-h6-dma”
- “allwinner,sun50i-a64-dma”
- nvidia
- “nvidia,tegra194-adma”, “nvidia,tegra186-adma”
- broadcom(rpi)
예) 2개의 dma 컨트롤러 – DT
arch/arm64/boot/dts/rockchip/rk3399.dtsi
amba {
compatible = "simple-bus";
#address-cells = <2>;
#size-cells = <2>;
ranges;
dmac_bus: dma-controller@ff6d0000 {
compatible = "arm,pl330", "arm,primecell";
reg = <0x0 0xff6d0000 0x0 0x4000>;
interrupts = <GIC_SPI 5 IRQ_TYPE_LEVEL_HIGH 0>,
<GIC_SPI 6 IRQ_TYPE_LEVEL_HIGH 0>;
#dma-cells = <1>;
clocks = <&cru ACLK_DMAC0_PERILP>;
clock-names = "apb_pclk";
};
dmac_peri: dma-controller@ff6e0000 {
compatible = "arm,pl330", "arm,primecell";
reg = <0x0 0xff6e0000 0x0 0x4000>;
interrupts = <GIC_SPI 7 IRQ_TYPE_LEVEL_HIGH 0>,
<GIC_SPI 8 IRQ_TYPE_LEVEL_HIGH 0>;
#dma-cells = <1>;
clocks = <&cru ACLK_DMAC1_PERILP>;
clock-names = "apb_pclk";
};
};
- rk3399 SoC의 경우 arm사의 pl330 dma 컨트롤러 IP를 사용하고, 위의 디바이스 트리를 통해 2개의 dma 컨트롤러가 amba 버스 하위 플랫폼 디바이스로 등록된다.
- amba 노드의 “simple-bus”는 다음 하위 노드를 플랫폼 디바이스로 인식한다
예) 5개의 SPI 컨트롤러(2개의 dma 컨트롤러 사용) – DT
arch/arm64/boot/dts/rockchip/rk3399.dtsi
spi0: spi@ff1c0000 {
compatible = "rockchip,rk3399-spi", "rockchip,rk3066-spi";
interrupts = <GIC_SPI 68 IRQ_TYPE_LEVEL_HIGH 0>;
dmas = <&dmac_peri 10>, <&dmac_peri 11>;
dma-names = "tx", "rx";
...
};
spi1: spi@ff1d0000 {
compatible = "rockchip,rk3399-spi", "rockchip,rk3066-spi";
interrupts = <GIC_SPI 53 IRQ_TYPE_LEVEL_HIGH 0>;
dmas = <&dmac_peri 12>, <&dmac_peri 13>;
dma-names = "tx", "rx";
...
};
spi2: spi@ff1e0000 {
compatible = "rockchip,rk3399-spi", "rockchip,rk3066-spi";
interrupts = <GIC_SPI 52 IRQ_TYPE_LEVEL_HIGH 0>;
dmas = <&dmac_peri 14>, <&dmac_peri 15>;
dma-names = "tx", "rx";
...
};
spi4: spi@ff1f0000 {
compatible = "rockchip,rk3399-spi", "rockchip,rk3066-spi";
interrupts = <GIC_SPI 67 IRQ_TYPE_LEVEL_HIGH 0>;
dmas = <&dmac_peri 18>, <&dmac_peri 19>;
dma-names = "tx", "rx";
...
};
spi5: spi@ff200000 {
compatible = "rockchip,rk3399-spi", "rockchip,rk3066-spi";
interrupts = <GIC_SPI 132 IRQ_TYPE_LEVEL_HIGH 0>;
dmas = <&dmac_bus 8>, <&dmac_bus 9>;
dma-names = "tx", "rx";
};
- 다음 4개의 SPI 컨트롤러는 dmac_peri 컨트롤러를 사용한다.
- 10(tx), 11(rx)번 채널 및 SPI #68 인터럽트 사용
- 12(tx), 13(rx)번 채널 및 SPI #53 인터럽트 사용
- 14(tx), 15(rx)번 채널 및 SPI #52 인터럽트 사용
- 18(tx), 19(rx)번 채널 및 SPI #67 인터럽트 사용
- 다음 1개의 SPI 컨트롤러는 dmac_bus 컨트롤러를 사용한다.
- 8(tx), 9(rx)번 채널 및 SPI #132 인터럽트 사용
DMA 호스트 컨트롤러 관련 – DT
DMA 컨트롤러 등록
of_dma_controller_register()
drivers/dma/of-dma.c
/**
* of_dma_controller_register - Register a DMA controller to DT DMA helpers
* @np: device node of DMA controller
* @of_dma_xlate: translation function which converts a phandle
* arguments list into a dma_chan structure
* @data pointer to controller specific data to be used by
* translation function
*
* Returns 0 on success or appropriate errno value on error.
*
* Allocated memory should be freed with appropriate of_dma_controller_free()
* call.
*/
int of_dma_controller_register(struct device_node *np,
struct dma_chan *(*of_dma_xlate)
(struct of_phandle_args *, struct of_dma *),
void *data)
{
struct of_dma *ofdma;
if (!np || !of_dma_xlate) {
pr_err("%s: not enough information provided\n", __func__);
return -EINVAL;
}
ofdma = kzalloc(sizeof(*ofdma), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!ofdma)
return -ENOMEM;
ofdma->of_node = np;
ofdma->of_dma_xlate = of_dma_xlate;
ofdma->of_dma_data = data;
/* Now queue of_dma controller structure in list */
mutex_lock(&of_dma_lock);
list_add_tail(&ofdma->of_dma_controllers, &of_dma_list);
mutex_unlock(&of_dma_lock);
return 0;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(of_dma_controller_register);
디바이스 트리의 dma 노드에서 dma 컨트롤러를 정보를 읽어 등록한다. 성공 시 0을 반환한다.
- 두 번째 인자에 dma 채널을 결과로 반환하는 dma 변환(*of_dma_xlate) 콜백 함수가 지정된다.
DMA 변환 콜백 함수 (*of_dma_xlate)
of_dma_simple_xlate() – simple
drivers/dma/of-dma.c
/**
* of_dma_simple_xlate - Simple DMA engine translation function
* @dma_spec: pointer to DMA specifier as found in the device tree
* @of_dma: pointer to DMA controller data
*
* A simple translation function for devices that use a 32-bit value for the
* filter_param when calling the DMA engine dma_request_channel() function.
* Note that this translation function requires that #dma-cells is equal to 1
* and the argument of the dma specifier is the 32-bit filter_param. Returns
* pointer to appropriate dma channel on success or NULL on error.
*/
struct dma_chan *of_dma_simple_xlate(struct of_phandle_args *dma_spec,
struct of_dma *ofdma)
{
int count = dma_spec->args_count;
struct of_dma_filter_info *info = ofdma->of_dma_data;
if (!info || !info->filter_fn)
return NULL;
if (count != 1)
return NULL;
return __dma_request_channel(&info->dma_cap, info->filter_fn,
&dma_spec->args[0], dma_spec->np);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(of_dma_simple_xlate);
간단히 지정한 번호에 해당하는 dma 채널을 반환하는 dma 콜백함수이다.
- “dmas” 속성에서 phandle 값 뒤의 1개의 숫자를 그대로 채널로 해석하여 dma 채널을 알아온다.
- 예) dmas = <&dmac_bus 8>
- &dmac_bus alias 노드가 가리키는 dma 컨트롤러에서 8번에 해당하는 dma 채널을 알아온다.
of_dma_pl330_xlate() – for pl330
drivers/dma/pl330.c
static struct dma_chan *of_dma_pl330_xlate(struct of_phandle_args *dma_spec,
struct of_dma *ofdma)
{
int count = dma_spec->args_count;
struct pl330_dmac *pl330 = ofdma->of_dma_data;
unsigned int chan_id;
if (!pl330)
return NULL;
if (count != 1)
return NULL;
chan_id = dma_spec->args[0];
if (chan_id >= pl330->num_peripherals)
return NULL;
return dma_get_slave_channel(&pl330->peripherals[chan_id].chan);
}
pl330 dma 컨트롤러의 경우 요청한 번호에 해당하는 dma 채널을 반환하는 dma 콜백함수이다.
DMA 슬레이브 관련 – DT
슬레이브 채널 요청
of_dma_request_slave_channel()
drivers/dma/of-dma.c
/**
* of_dma_request_slave_channel - Get the DMA slave channel
* @np: device node to get DMA request from
* @name: name of desired channel
*
* Returns pointer to appropriate DMA channel on success or an error pointer.
*/
struct dma_chan *of_dma_request_slave_channel(struct device_node *np,
const char *name)
{
struct of_phandle_args dma_spec;
struct of_dma *ofdma;
struct dma_chan *chan;
int count, i, start;
int ret_no_channel = -ENODEV;
static atomic_t last_index;
if (!np || !name) {
pr_err("%s: not enough information provided\n", __func__);
return ERR_PTR(-ENODEV);
}
/* Silently fail if there is not even the "dmas" property */
if (!of_find_property(np, "dmas", NULL))
return ERR_PTR(-ENODEV);
count = of_property_count_strings(np, "dma-names");
if (count < 0) {
pr_err("%s: dma-names property of node '%pOF' missing or empty\n",
__func__, np);
return ERR_PTR(-ENODEV);
}
/*
* approximate an average distribution across multiple
* entries with the same name
*/
start = atomic_inc_return(&last_index);
for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {
if (of_dma_match_channel(np, name,
(i + start) % count,
&dma_spec))
continue;
mutex_lock(&of_dma_lock);
ofdma = of_dma_find_controller(&dma_spec);
if (ofdma) {
chan = ofdma->of_dma_xlate(&dma_spec, ofdma);
} else {
ret_no_channel = -EPROBE_DEFER;
chan = NULL;
}
mutex_unlock(&of_dma_lock);
of_node_put(dma_spec.np);
if (chan)
return chan;
}
return ERR_PTR(ret_no_channel);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(of_dma_request_slave_channel);
요청한 dma 채널을 사용하고자 하는 dma 슬레이브 디바이스 정보가 있는 @np 노드에서 @name에 해당하는 dma 채널을 알아온다. 실패한 경우 에러 값을 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 11~14에서 두 인자가 주어지지 않은 경우 에러 메시지를 출력하고 -ENODEV 에러 값을 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 17~18에서 dma 슬레이브 노드 내에 컨트롤러 및 채널 번호를 가리키는 “dmas” 속성을 발견할 수 없는 경우 -ENODEV 에러 값을 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 20~25에서 사용하고자 하는 dma 채널 이름을 의미하는 “dma-names” 속성 값에 포함된 문자열 수를 count에 담고, 속성을 발견할 수 없는 경으면 에러 메시지를 출력하고 -ENODEV 에러 값을 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 31에서 static 변수로 선언된 last_index를 증가시킨 값을 start에 알아온다.
- 코드 라인 32~36에서 count 만큼 순회하며 “dma-names” 속성에서 지정한 이름과 인자로 요청한 @name이 매치되지 않는 경우 skip 한다.
- 코드 라인 38~48에서 of_dma_lock을 획득한 채로 컨트롤러를 찾고, 컨트롤러에 지정된 dma 변환 콜백 함수 (*of_dma_xlate)를 호출하여 dma 채널을 알아온다.
- 코드 라인 50에서 phandle이 가리키는 dma 컨트롤러 노드의 참조 카운터를 1 감소시킨다.
- of_dma_match_channel() 함수에서 dma_spec.np 노드의 참조 카운터가 1 증가되었었다.
- 코드 라인 52~53에서 발견된 채널을 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 56에서 -ENODEV 또는 -EPROBE_DEFER 에러를 반환한다.
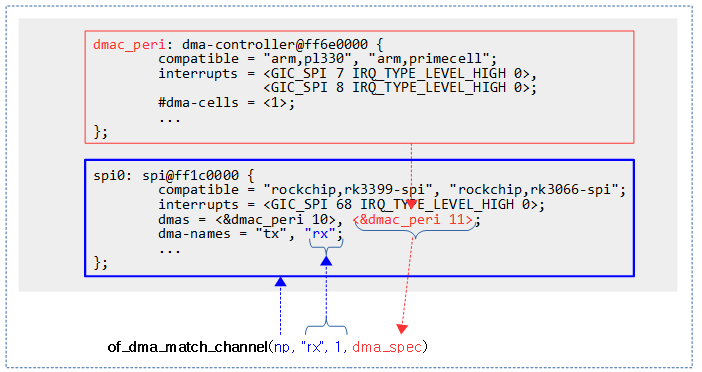
of_dma_match_channel()
drivers/dma/of-dma.c
/**
* of_dma_match_channel - Check if a DMA specifier matches name
* @np: device node to look for DMA channels
* @name: channel name to be matched
* @index: index of DMA specifier in list of DMA specifiers
* @dma_spec: pointer to DMA specifier as found in the device tree
*
* Check if the DMA specifier pointed to by the index in a list of DMA
* specifiers, matches the name provided. Returns 0 if the name matches and
* a valid pointer to the DMA specifier is found. Otherwise returns -ENODEV.
*/
static int of_dma_match_channel(struct device_node *np, const char *name,
int index, struct of_phandle_args *dma_spec)
{
const char *s;
if (of_property_read_string_index(np, "dma-names", index, &s))
return -ENODEV;
if (strcmp(name, s))
return -ENODEV;
if (of_parse_phandle_with_args(np, "dmas", "#dma-cells", index,
dma_spec))
return -ENODEV;
return 0;
}
디바이스 노드 @np에서 “dma-names” 속성의 @index 번째의 문자열과 @name이 일치하는 경우 “dmas” 속성의 @index 번째의 phandle 노드 및 속성 값을 읽어 출력 인자 @dma_spec에 알아온다. 성공 시 0을 반환하고, 싪패 시 -ENODEV 에러를 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 6~7에서 디바이스 노드 @np에서 “dma-names” 속성 값에서 @index 번째의 값을 읽어온다. 읽어올 수 없으면 -ENODEV 에러를 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 9~10에서 읽어온 값이 @name과 다른 경우 -ENODEV 에러를 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 12~14에서 “dmas 속성에서 @index 번째의 phandle 노드 및 속성 값을 읽어 출력 인자 @dma_spec에 알아온다. 만일 읽어 올 수 없으면 -ENODEV 에러를 반환한다.
- 코드 라인 16에서 성공 값 0을 반환한다.
다음 그림과 같이 “dma-names 속성의 1번 인덱스(0번 인덱스부터 시작)에 “rx”가 존재하는 경우 dmas 속성에서 1번 인덱스의 phandle을 통한 dmac_peri 노드와 뒤이어 이어지는 숫자 11을 #dma-cells 만큼 읽어 출력 인자 dma_spec에 알아온다.
of_dma_find_controller()
drivers/dma/of-dma.c
/**
* of_dma_find_controller - Get a DMA controller in DT DMA helpers list
* @dma_spec: pointer to DMA specifier as found in the device tree
*
* Finds a DMA controller with matching device node and number for dma cells
* in a list of registered DMA controllers. If a match is found a valid pointer
* to the DMA data stored is retuned. A NULL pointer is returned if no match is
* found.
*/
static struct of_dma *of_dma_find_controller(struct of_phandle_args *dma_spec)
{
struct of_dma *ofdma;
list_for_each_entry(ofdma, &of_dma_list, of_dma_controllers)
if (ofdma->of_node == dma_spec->np)
return ofdma;
pr_debug("%s: can't find DMA controller %pOF\n", __func__,
dma_spec->np);
return NULL;
}
dma 컨트롤러 리스트에 등록된 dma 컨트롤러들 중 @dma_spec가 가리키는 dma 컨트롤러 노드를 찾아 해당 of_dma를 찾아온다. 실패하는 경우 null을 반환한다.
구조체
dma_device 구조체
include/linux/dmaengine.h
/**
* struct dma_device - info on the entity supplying DMA services
* @chancnt: how many DMA channels are supported
* @privatecnt: how many DMA channels are requested by dma_request_channel
* @channels: the list of struct dma_chan
* @global_node: list_head for global dma_device_list
* @filter: information for device/slave to filter function/param mapping
* @cap_mask: one or more dma_capability flags
* @max_xor: maximum number of xor sources, 0 if no capability
* @max_pq: maximum number of PQ sources and PQ-continue capability
* @copy_align: alignment shift for memcpy operations
* @xor_align: alignment shift for xor operations
* @pq_align: alignment shift for pq operations
* @fill_align: alignment shift for memset operations
* @dev_id: unique device ID
* @dev: struct device reference for dma mapping api
* @src_addr_widths: bit mask of src addr widths the device supports
* Width is specified in bytes, e.g. for a device supporting
* a width of 4 the mask should have BIT(4) set.
* @dst_addr_widths: bit mask of dst addr widths the device supports
* @directions: bit mask of slave directions the device supports.
* Since the enum dma_transfer_direction is not defined as bit flag for
* each type, the dma controller should set BIT(<TYPE>) and same
* should be checked by controller as well
* @max_burst: max burst capability per-transfer
* @residue_granularity: granularity of the transfer residue reported
* by tx_status
* @device_alloc_chan_resources: allocate resources and return the
* number of allocated descriptors
* @device_free_chan_resources: release DMA channel's resources
* @device_prep_dma_memcpy: prepares a memcpy operation
* @device_prep_dma_xor: prepares a xor operation
* @device_prep_dma_xor_val: prepares a xor validation operation
* @device_prep_dma_pq: prepares a pq operation
* @device_prep_dma_pq_val: prepares a pqzero_sum operation
* @device_prep_dma_memset: prepares a memset operation
* @device_prep_dma_memset_sg: prepares a memset operation over a scatter list
* @device_prep_dma_interrupt: prepares an end of chain interrupt operation
* @device_prep_slave_sg: prepares a slave dma operation
* @device_prep_dma_cyclic: prepare a cyclic dma operation suitable for audio.
* The function takes a buffer of size buf_len. The callback function will
* be called after period_len bytes have been transferred.
* @device_prep_interleaved_dma: Transfer expression in a generic way.
* @device_prep_dma_imm_data: DMA's 8 byte immediate data to the dst address
* @device_config: Pushes a new configuration to a channel, return 0 or an error
* code
* @device_pause: Pauses any transfer happening on a channel. Returns
* 0 or an error code
* @device_resume: Resumes any transfer on a channel previously
* paused. Returns 0 or an error code
* @device_terminate_all: Aborts all transfers on a channel. Returns 0
* or an error code
* @device_synchronize: Synchronizes the termination of a transfers to the
* current context.
* @device_tx_status: poll for transaction completion, the optional
* txstate parameter can be supplied with a pointer to get a
* struct with auxiliary transfer status information, otherwise the call
* will just return a simple status code
* @device_issue_pending: push pending transactions to hardware
* @descriptor_reuse: a submitted transfer can be resubmitted after completion
*/
struct dma_device {
unsigned int chancnt;
unsigned int privatecnt;
struct list_head channels;
struct list_head global_node;
struct dma_filter filter;
dma_cap_mask_t cap_mask;
unsigned short max_xor;
unsigned short max_pq;
enum dmaengine_alignment copy_align;
enum dmaengine_alignment xor_align;
enum dmaengine_alignment pq_align;
enum dmaengine_alignment fill_align;
#define DMA_HAS_PQ_CONTINUE (1 << 15)
int dev_id;
struct device *dev;
u32 src_addr_widths;
u32 dst_addr_widths;
u32 directions;
u32 max_burst;
bool descriptor_reuse;
enum dma_residue_granularity residue_granularity;
int (*device_alloc_chan_resources)(struct dma_chan *chan);
void (*device_free_chan_resources)(struct dma_chan *chan);
struct dma_async_tx_descriptor *(*device_prep_dma_memcpy)(
struct dma_chan *chan, dma_addr_t dst, dma_addr_t src,
size_t len, unsigned long flags);
struct dma_async_tx_descriptor *(*device_prep_dma_xor)(
struct dma_chan *chan, dma_addr_t dst, dma_addr_t *src,
unsigned int src_cnt, size_t len, unsigned long flags);
struct dma_async_tx_descriptor *(*device_prep_dma_xor_val)(
struct dma_chan *chan, dma_addr_t *src, unsigned int src_cnt,
size_t len, enum sum_check_flags *result, unsigned long flags);
struct dma_async_tx_descriptor *(*device_prep_dma_pq)(
struct dma_chan *chan, dma_addr_t *dst, dma_addr_t *src,
unsigned int src_cnt, const unsigned char *scf,
size_t len, unsigned long flags);
struct dma_async_tx_descriptor *(*device_prep_dma_pq_val)(
struct dma_chan *chan, dma_addr_t *pq, dma_addr_t *src,
unsigned int src_cnt, const unsigned char *scf, size_t len,
enum sum_check_flags *pqres, unsigned long flags);
struct dma_async_tx_descriptor *(*device_prep_dma_memset)(
struct dma_chan *chan, dma_addr_t dest, int value, size_t len,
unsigned long flags);
struct dma_async_tx_descriptor *(*device_prep_dma_memset_sg)(
struct dma_chan *chan, struct scatterlist *sg,
unsigned int nents, int value, unsigned long flags);
struct dma_async_tx_descriptor *(*device_prep_dma_interrupt)(
struct dma_chan *chan, unsigned long flags);
struct dma_async_tx_descriptor *(*device_prep_slave_sg)(
struct dma_chan *chan, struct scatterlist *sgl,
unsigned int sg_len, enum dma_transfer_direction direction,
unsigned long flags, void *context);
struct dma_async_tx_descriptor *(*device_prep_dma_cyclic)(
struct dma_chan *chan, dma_addr_t buf_addr, size_t buf_len,
size_t period_len, enum dma_transfer_direction direction,
unsigned long flags);
struct dma_async_tx_descriptor *(*device_prep_interleaved_dma)(
struct dma_chan *chan, struct dma_interleaved_template *xt,
unsigned long flags);
struct dma_async_tx_descriptor *(*device_prep_dma_imm_data)(
struct dma_chan *chan, dma_addr_t dst, u64 data,
unsigned long flags);
int (*device_config)(struct dma_chan *chan,
struct dma_slave_config *config);
int (*device_pause)(struct dma_chan *chan);
int (*device_resume)(struct dma_chan *chan);
int (*device_terminate_all)(struct dma_chan *chan);
void (*device_synchronize)(struct dma_chan *chan);
enum dma_status (*device_tx_status)(struct dma_chan *chan,
dma_cookie_t cookie,
struct dma_tx_state *txstate);
void (*device_issue_pending)(struct dma_chan *chan);
};
dma 호스트 컨트롤러 정보 및 오퍼레이션이 포함된 구조체이다.
- chancnt
- privatecnt
- dma_request_channel() 함수로 요청된 dma 채널 수
- channels
- dma 채널들이 등록되는 리스트이다. (dma_chan 구조체들이 연결된다.)
- global_node
- dma 호스트 컨트롤러 글로벌 리스트에 연결될 때 사용되는 노드이다.
- filter
- cap_mask
- dma capability 플래그들이 표현된다.
- pl330 예)
- BIT(DMA_MEMCPY) |
- BIT(DMA_SLAVE) |
- BIT(DMA_CYCLIC) |
- BIT(DMA_PRIVATE)
- max_xor, max_pq
- xor, pq 소스의 최대 수 (지원되지 않는 경우 0)
- copy_align, xor_align, pq_align, fill_align
- memcpy, xor, pq, memset 오퍼레이션을 위한 정렬 바이트 수로 다음과 같이 지정할 수 있다.
- DMA_SLAVE_BUSWIDTH_UNDEFINED(0)
- DMAENGINE_ALIGN_1_BYTE(1)
- DMA_SLAVE_BUSWIDTH_2_BYTES(2)
- DMA_SLAVE_BUSWIDTH_3_BYTES(3)
- DMA_SLAVE_BUSWIDTH_4_BYTES(4)
- DMA_SLAVE_BUSWIDTH_8_BYTES(8)
- DMA_SLAVE_BUSWIDTH_16_BYTES(16)
- DMA_SLAVE_BUSWIDTH_32_BYTES(32)
- DMA_SLAVE_BUSWIDTH_64_BYTES(64)
- dev_id
- dev
- src_addr_widths
- 지원 가능한 소스 주소 폭들을 나타낸다.
- pl330 예) 0x117
- BIT(DMA_SLAVE_BUSWIDTH_UNDEFINED) |
- BIT(DMA_SLAVE_BUSWIDTH_1_BYTE) |
- BIT(DMA_SLAVE_BUSWIDTH_2_BYTES) |
- BIT(DMA_SLAVE_BUSWIDTH_4_BYTES) |
- BIT(DMA_SLAVE_BUSWIDTH_8_BYTES)
- dst_addr_widths
- directions
- 지원 가능한 dma 방향들의 비트들이다.
- DMA_MEM_TO_MEM(0)
- DMA_MEM_TO_DEV(1)
- DMA_DEV_TO_MEM(2)
- DMA_DEV_TO_DEV(3)
- DMA_TRANS_NONE(4)
- pl330 예) BIT(DMA_DEV_TO_MEM) | BIT(DMA_MEM_TO_DEV)
- max_burst
- 최대 버스트 가능한 전송 수
- pl330 예) 16 바이트
- 디바이스 트리에서 “arm,pl330-broken-no-flushp” 속성이 사용되는 경우 버스트 최대 바이트는 1바이트로 제한된다.
- pl330이 사용된 rockchip사의 일부 칩(rk3368)에서는 오류로 인해 1 바이트만 사용가능하다.
- descriptor_reuse
- 전송에 사용된 디스크립터를 전송 후에 자사용할 수 있는지 여부를 나타낸다.
- residue_granularity
- tx_status에 의해 보고된 전송 단위(단위 크기: 디스크립터 > 세그먼트 > 버스트)
- DMA_RESIDUE_GRANULARITY_DESCRIPTOR(0)
- 미지원하므로 디스크립터의 완료 여부만 알고, 즉 잔여(residue) 보고하지 않아 dma_tx_state.residue는 항상 0이다.
- DMA_RESIDUE_GRANULARITY_SEGMENT(1)
- 사이클릭 전송에서 매 피리어드의 완료 성공시마다 tx_status가 보고된다.
- scatter-gather 전송에서 세그먼트의 완료 시마다 tx_status가 보고된다.
- DMA_RESIDUE_GRANULARITY_BURST(2)
- 사이클릭 전송에서 버스트 전송의 완료 시에 tx_status가 보고된다.
- pl330 예) DMA_RESIDUE_GRANULARITY_BURST(2)가 사용된다.
- (*device_alloc_chan_resources)
- dma 채널 리소스를 할당하고 할당된 디스크립터의 수를 반환하는 콜백 함수를 구현하기 위해 사용된다.
- (*device_free_chan_resources)
- dma 채널 리소스를 반납하기 위해 해제하는 콜백 함수를 구현하기 위해 사용된다.
- (*device_prep_*)
- dma 전송 오퍼레이션을 위한 각각을 준비하는 콜백 함수를 구현하기 위해 사용된다.
- (*device_config)
- 채널에 대한 새로운 설정을 지정하는 콜백 함수를 구현하기 위해 사용된다.
- (*device_pause)
- 전송을 잠시 멈추기 위한 콜백 함수를 구현하기 위해 사용된다.
- (*device_resume)
- 잠시 멈춘 전송을 재계하기 위한 콜백 함수를 구현하기 위해 사용된다. (sleepable)
- (*device_terminate_all)
- 하나의 채널에서 모든 전송을 취소하기 위한 콜백 함수를 구현하기 위해 사용된다. (atomic)
- (*device_synchronize)
- 현재 dma 전송을 마치도록 대기하는 콜백 함수를 구현하기 위해 사용된다. (sleepable)
- (*device_tx_status)
- dma 트랜잭션 완료 상태를 알아보기 위해 사용하는 콜백 함수를 구현하기 위해 사용된다.
- (*device_issuepending)
dma_async_tx_descriptor 구조체
include/linux/dmaengine.h
/**
* struct dma_async_tx_descriptor - async transaction descriptor
* ---dma generic offload fields---
* @cookie: tracking cookie for this transaction, set to -EBUSY if
* this tx is sitting on a dependency list
* @flags: flags to augment operation preparation, control completion, and
* communicate status
* @phys: physical address of the descriptor
* @chan: target channel for this operation
* @tx_submit: accept the descriptor, assign ordered cookie and mark the
* descriptor pending. To be pushed on .issue_pending() call
* @callback: routine to call after this operation is complete
* @callback_param: general parameter to pass to the callback routine
* ---async_tx api specific fields---
* @next: at completion submit this descriptor
* @parent: pointer to the next level up in the dependency chain
* @lock: protect the parent and next pointers
*/
struct dma_async_tx_descriptor {
dma_cookie_t cookie;
enum dma_ctrl_flags flags; /* not a 'long' to pack with cookie */
dma_addr_t phys;
struct dma_chan *chan;
dma_cookie_t (*tx_submit)(struct dma_async_tx_descriptor *tx);
int (*desc_free)(struct dma_async_tx_descriptor *tx);
dma_async_tx_callback callback;
dma_async_tx_callback_result callback_result;
void *callback_param;
struct dmaengine_unmap_data *unmap;
#ifdef CONFIG_ASYNC_TX_ENABLE_CHANNEL_SWITCH
struct dma_async_tx_descriptor *next;
struct dma_async_tx_descriptor *parent;
spinlock_t lock;
#endif
};
dma 비동기 전송용 tx 디스크립터 구조체이다.
- cookie
- flags
- 오퍼레이션을 준비, 완료 제어 및 통신 상태에 대한 플래그
- phys
- *chan
- (*tx_submit)
- 디스크립터를 받아 전송할 콜백 함수가 지정된다.
- (*desc_free)
- 디스크립터 전송 후 해제할 콜백 함수가 지정된다.
- callback
- callback_result
- 오퍼레이션이 완료되면 호출된 콜백 함수이다.
- 이 함수가 구현된 경우 위의 callback 대신 이 콜백이 호출된다.
- *callback_param
- *unmap
- dmaengine_unmap_data 구조체 포인터를 가리킨다.
- *next
- *parent
- 디펜던시 체인 내의 부모 디스크립터를 가리킨다.
- lock
- parent 및 next 포인터를 보호하기 위한 락이다.
dma_slave_config 구조체
include/linux/dmaengine.h
/**
* struct dma_slave_config - dma slave channel runtime config
* @direction: whether the data shall go in or out on this slave
* channel, right now. DMA_MEM_TO_DEV and DMA_DEV_TO_MEM are
* legal values. DEPRECATED, drivers should use the direction argument
* to the device_prep_slave_sg and device_prep_dma_cyclic functions or
* the dir field in the dma_interleaved_template structure.
* @src_addr: this is the physical address where DMA slave data
* should be read (RX), if the source is memory this argument is
* ignored.
* @dst_addr: this is the physical address where DMA slave data
* should be written (TX), if the source is memory this argument
* is ignored.
* @src_addr_width: this is the width in bytes of the source (RX)
* register where DMA data shall be read. If the source
* is memory this may be ignored depending on architecture.
* Legal values: 1, 2, 3, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64.
* @dst_addr_width: same as src_addr_width but for destination
* target (TX) mutatis mutandis.
* @src_maxburst: the maximum number of words (note: words, as in
* units of the src_addr_width member, not bytes) that can be sent
* in one burst to the device. Typically something like half the
* FIFO depth on I/O peripherals so you don't overflow it. This
* may or may not be applicable on memory sources.
* @dst_maxburst: same as src_maxburst but for destination target
* mutatis mutandis.
* @src_port_window_size: The length of the register area in words the data need
* to be accessed on the device side. It is only used for devices which is using
* an area instead of a single register to receive the data. Typically the DMA
* loops in this area in order to transfer the data.
* @dst_port_window_size: same as src_port_window_size but for the destination
* port.
* @device_fc: Flow Controller Settings. Only valid for slave channels. Fill
* with 'true' if peripheral should be flow controller. Direction will be
* selected at Runtime.
* @slave_id: Slave requester id. Only valid for slave channels. The dma
* slave peripheral will have unique id as dma requester which need to be
* pass as slave config.
*
* This struct is passed in as configuration data to a DMA engine
* in order to set up a certain channel for DMA transport at runtime.
* The DMA device/engine has to provide support for an additional
* callback in the dma_device structure, device_config and this struct
* will then be passed in as an argument to the function.
*
* The rationale for adding configuration information to this struct is as
* follows: if it is likely that more than one DMA slave controllers in
* the world will support the configuration option, then make it generic.
* If not: if it is fixed so that it be sent in static from the platform
* data, then prefer to do that.
*/
struct dma_slave_config {
enum dma_transfer_direction direction;
phys_addr_t src_addr;
phys_addr_t dst_addr;
enum dma_slave_buswidth src_addr_width;
enum dma_slave_buswidth dst_addr_width;
u32 src_maxburst;
u32 dst_maxburst;
u32 src_port_window_size;
u32 dst_port_window_size;
bool device_fc;
unsigned int slave_id;
};
dma 슬레이브 전송용 설정이 담기는 구조체이다.
- direction
- 지원 가능한 dma 방향들의 비트들이다.
- DMA_MEM_TO_MEM(0)
- DMA_MEM_TO_DEV(1)
- DMA_DEV_TO_MEM(2)
- DMA_DEV_TO_DEV(3)
- DMA_TRANS_NONE(4)
- pl330 예) BIT(DMA_DEV_TO_MEM) | BIT(DMA_MEM_TO_DEV)
- src_addr
- dst_addr
- src_addr_width
- src_addr을 통해 한 번에 읽어올 데이터 폭을 지정한다.
- 예) DMA_SLAVE_BUSWIDTH_4_BYTES
- dst_addr_width
- dst_addr을 통해 한 번에 기록할 데이터 폭을 지정한다.
- src_maxburst
- dst_maxburst
- src_port_window_size
- dma 읽기할 영역 사이즈(바이트). 특정 영역내에서만 dma 가능한 장치에서만 사용된다.
- 예) 8
- dst_port_window_size
- dma 기록할 영역 사이즈(바이트). 특정 영역내에서만 dma 가능한 장치에서만 사용된다.
- device_fc
- flow 컨트롤이 필요한 슬레이브 장치가 true로 설정한다. 슬레이브 채널에서만 사용된다.
- slave_id
- 슬레이브 요청자 id로 슬레이브 채널에서만 사용된다.
dma_chan 구조체
include/linux/dmaengine.h
/**
* struct dma_chan - devices supply DMA channels, clients use them
* @device: ptr to the dma device who supplies this channel, always !%NULL
* @cookie: last cookie value returned to client
* @completed_cookie: last completed cookie for this channel
* @chan_id: channel ID for sysfs
* @dev: class device for sysfs
* @device_node: used to add this to the device chan list
* @local: per-cpu pointer to a struct dma_chan_percpu
* @client_count: how many clients are using this channel
* @table_count: number of appearances in the mem-to-mem allocation table
* @router: pointer to the DMA router structure
* @route_data: channel specific data for the router
* @private: private data for certain client-channel associations
*/
struct dma_chan {
struct dma_device *device;
dma_cookie_t cookie;
dma_cookie_t completed_cookie;
/* sysfs */
int chan_id;
struct dma_chan_dev *dev;
struct list_head device_node;
struct dma_chan_percpu __percpu *local;
int client_count;
int table_count;
/* DMA router */
struct dma_router *router;
void *route_data;
void *private;
};
dma 채널 정보가 구성된 구조체이다.
- device
- dma 컨트럴러를 가리킨다. (dma_device)
- cookie
- completed_cookie
- chan_id
- dev
- device_node
- *local
- dma_chan_percpu 구조체를 가리키는 per-cpu 포인터
- client_count
- 얼마나 많은 클라이언트가 이 채널을 사용중인지 나타내는 카운터
- table_count
- *router
- *route_data
- *private
- 특정 클라이언트 채널 연결에 대한 private 데이터
dma_ctrl_flags enum
include/linux/dmaengine.h
/**
* enum dma_ctrl_flags - DMA flags to augment operation preparation,
* control completion, and communicate status.
* @DMA_PREP_INTERRUPT - trigger an interrupt (callback) upon completion of
* this transaction
* @DMA_CTRL_ACK - if clear, the descriptor cannot be reused until the client
* acknowledges receipt, i.e. has has a chance to establish any dependency
* chains
* @DMA_PREP_PQ_DISABLE_P - prevent generation of P while generating Q
* @DMA_PREP_PQ_DISABLE_Q - prevent generation of Q while generating P
* @DMA_PREP_CONTINUE - indicate to a driver that it is reusing buffers as
* sources that were the result of a previous operation, in the case of a PQ
* operation it continues the calculation with new sources
* @DMA_PREP_FENCE - tell the driver that subsequent operations depend
* on the result of this operation
* @DMA_CTRL_REUSE: client can reuse the descriptor and submit again till
* cleared or freed
* @DMA_PREP_CMD: tell the driver that the data passed to DMA API is command
* data and the descriptor should be in different format from normal
* data descriptors.
*/
enum dma_ctrl_flags {
DMA_PREP_INTERRUPT = (1 << 0),
DMA_CTRL_ACK = (1 << 1),
DMA_PREP_PQ_DISABLE_P = (1 << 2),
DMA_PREP_PQ_DISABLE_Q = (1 << 3),
DMA_PREP_CONTINUE = (1 << 4),
DMA_PREP_FENCE = (1 << 5),
DMA_CTRL_REUSE = (1 << 6),
DMA_PREP_CMD = (1 << 7),
};
dma engine 및 dma 컨트롤러에게 전달되어지는 플래그들이다.
- DMA_PREP_INTERRUPT
- DMA_CTRL_ACK
- 이 플래그가 없는 경우 클라이언트가 수신을 확인하기 전까지 디스크립터를 재사용할 수 없다.
- 즉 디펜던시 체인을 설정할 기회가 있다.
- DMA_PREP_PQ_DISABLE_P
- Q를 생성하는 도중에 P의 생성을 금지한다. (거의 사용하지 않는다)
- DMA_PREP_PQ_DISABLE_Q
- P를 생성하는 도중에 Q의 생성을 금지한다. (ppc4xx, ioat에서 사용되고 있다)
- DMA_PREP_CONTINUE
- 기존 결과가 담긴 버퍼의 재사용을 허용한다. (fsl, bcm-sba에서 사용되고 있다)
- DMA_PREP_FENCE
- DMA_CTRL_REUSE
- 클라이언트가 디스크립터가 삭제되기 전까지 재사용을 가능하게 한다.
- DMA_PREP_CMD
- 일반 데이터가 아니라 명령 데이터를 드라이버에게 전달한다. (qualcom bam-dma에서 사용된다)
of_dma 구조체
include/linux/of_dma.h
struct of_dma {
struct list_head of_dma_controllers;
struct device_node *of_node;
struct dma_chan *(*of_dma_xlate)
(struct of_phandle_args *, struct of_dma *);
void *(*of_dma_route_allocate)
(struct of_phandle_args *, struct of_dma *);
struct dma_router *dma_router;
void *of_dma_data;
};
디바이스 트리에서 DMA 컨트롤러에 대한 노드 구성정보를 담고 있다.
- of_dma_controllers
- of_dma_list 전역 리스트에 이 노드가 추가될 때 사용된다.
- *of_node
- (*of_dma_xlate)
- 슬레이브 디바이스가 phandle로 지정하여 가리킬 때 관련 인자들을 파싱할 수 있는 콜백 함수가 지정된다.
- (*of_dma_route_allocate)
- dma mux 할당에서 사용되는 콜백 함수가 지정된다.
- *dma_router
- of_dma_data
- void 형태의 private 데이터가 저장된다.
- of_dma_filter_info 정보 등
참고