<kernel v5.0>
ALTERNATIVE() 매크로
아키텍처마다 인자 개수가 조금씩 다르게 구성되었고, 이 글에서는 ARM64를 기반으로 설명한다.
컴파일 타임에 실행할 명령(old-instruction)을 준비하고, 조건에 따라 기존 명령을 새 명령(new-instruction)으로 대체시켜 동작시키는 기법으로 조건 처리를 했어도 수행 성능에 영향이 가지 않게 하는 기법이다.
- ARM에서는 ALTERNATIVE 기능이 적용되지 않았다.
- ARM64의 경우 ARMv8.1 코드와 ARMv8.2 코드를 준비해두고 부트업시 cpu capabilities(features)를 확인하여 가능하면 성능이 더 좋은 ARMv8.2 코드로 replacement 하도록 사용한다.
대체(replacement)
- 대체하는 시점은 SMP 시스템에서 부트 cpu가 초기화를 완료한 후 secondary cpu가 초기화될 때 조건을 만족하는 ALTERNATIVE() 매크로의 replacement를 수행하게 한다.
- 모듈인 경우 모듈이 로드될 때 조건을 만족하는 경우 replacement를 수행하게 한다.
조건
- cpu에 지정한 기능(capabilities, features)이 있는 경우
- _ALTERNATIVE_CFG() 매크로를 사용하는 경우 커널 옵션을 추가로 조건으로 지정할 수 있다.
예) ALTERNATIVE(llsc, lse, ARM64_HAS_LSE_ATOMICS)
- ARMv8.1의 경우 llsc 명령을 사용하고, ARMv8.2의 경우 LSE atomic 명령을 사용할 수 있다. 이러한 경우 lse 명령을 사용하게 한다.
arch/arm64/include/asm/alternative.h
/* * Usage: asm(ALTERNATIVE(oldinstr, newinstr, feature)); * * Usage: asm(ALTERNATIVE(oldinstr, newinstr, feature, CONFIG_FOO)); * N.B. If CONFIG_FOO is specified, but not selected, the whole block * will be omitted, including oldinstr. */
#define ALTERNATIVE(oldinstr, newinstr, ...) \
_ALTERNATIVE_CFG(oldinstr, newinstr, __VA_ARGS__, 1)
SMP 시스템에서 처음 부트 cpu는 첫 번째 인자에 있는 old 명령을 사용하여 명령이 진행된다. 그러다가 다른 cpu들의 설정이 완료될 때 세 번째인자의 cpu capabilities가 동작하는 경우 해당 코드들이 두 번째 인자 명령으로 치환된다. 이를 통해 더 빠른 성능을 수행하게 한다.
- oldinstr
- 부트업 cpu 또는 조건을 만족시키지 못할 때 수행할 1개의 assembly 명령
- newinstr
- secondary cpu 들에서 조건을 만족시킬 때 대치될 1개의 assembly 명령
- 3번 째 인자 (feature)
- cpu 아키텍처가 지원하는 기능(capabilities)
#define _ALTERNATIVE_CFG(oldinstr, newinstr, feature, cfg, ...) \
__ALTERNATIVE_CFG(oldinstr, newinstr, feature, IS_ENABLED(cfg), 0)
- 4번 째 인자 (cfg)
- 커널에 enable되어야 할 옵션을 추가로 조건을 지정할 수 있다.
/* * alternative assembly primitive: * * If any of these .org directive fail, it means that insn1 and insn2 * don't have the same length. This used to be written as * * .if ((664b-663b) != (662b-661b)) * .error "Alternatives instruction length mismatch" * .endif * * but most assemblers die if insn1 or insn2 have a .inst. This should * be fixed in a binutils release posterior to 2.25.51.0.2 (anything * containing commit 4e4d08cf7399b606 or c1baaddf8861). * * Alternatives with callbacks do not generate replacement instructions. */
#define __ALTERNATIVE_CFG(oldinstr, newinstr, feature, cfg_enabled, cb) \
".if "__stringify(cfg_enabled)" == 1\n" \
"661:\n\t" \
oldinstr "\n" \
"662:\n" \
".pushsection .altinstructions,\"a\"\n" \
ALTINSTR_ENTRY(feature,cb) \
".popsection\n" \
" .if " __stringify(cb) " == 0\n" \
".pushsection .altinstr_replacement, \"a\"\n" \
"663:\n\t" \
newinstr "\n" \
"664:\n\t" \
".popsection\n\t" \
".org . - (664b-663b) + (662b-661b)\n\t" \
".org . - (662b-661b) + (664b-663b)\n" \
".else\n\t" \
"663:\n\t" \
"664:\n\t" \
".endif\n" \
".endif\n"
.altinstructions 섹션에 push한 newinstr 코드들은 secondary cpu를 부트업한 후 apply_alternatives_all() 함수에서 oldinstr 코드들을 모두 replace한다.
- start_kernel() -> kernel_init() -> kernel_init_freeable() -> smp_init() -> smp_cpus_done() -> apply_alternatives_all()
arch/arm64/include/asm/alternative.h
#define ALTINSTR_ENTRY(feature,cb) \
" .word 661b - .\n" /* label */ \
" .if " __stringify(cb) " == 0\n" \
" .word 663f - .\n" /* new instruction */ \
" .else\n" \
" .word " __stringify(cb) "- .\n" /* callback */ \
" .endif\n" \
" .hword " __stringify(feature) "\n" /* feature bit */ \
" .byte 662b-661b\n" /* source len */ \
" .byte 664f-663f\n"
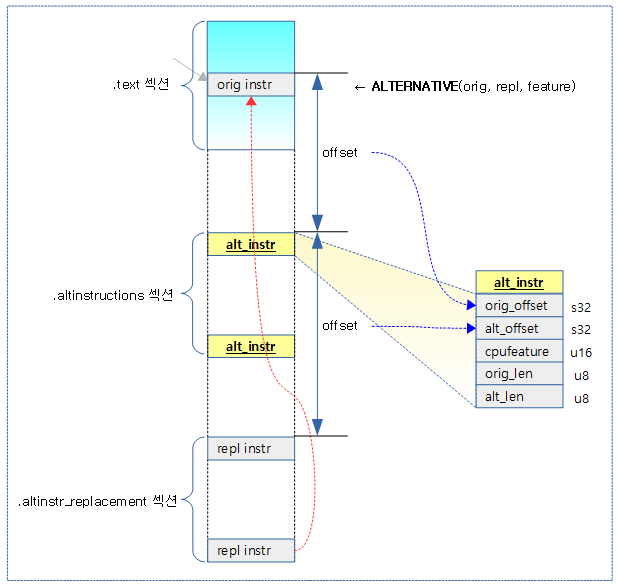
다음 그림은 ALTERNATIVE() 매크로가 저장하는 섹셕들과 alt_instr 구조체의 각 offset 값들에 대해 보여준다.
Cpu Capabilities(Features)
다음 항목들은 ALTERNATIVE() 매크로 함수에서 사용할 수 있는 cpu capabilities이다. cpu features라고도 불린다.
arch/arm64/include/asm/cpucaps.h
#define ARM64_WORKAROUND_CLEAN_CACHE 0 #define ARM64_WORKAROUND_DEVICE_LOAD_ACQUIRE 1 #define ARM64_WORKAROUND_845719 2 #define ARM64_HAS_SYSREG_GIC_CPUIF 3 #define ARM64_HAS_PAN 4 #define ARM64_HAS_LSE_ATOMICS 5 #define ARM64_WORKAROUND_CAVIUM_23154 6 #define ARM64_WORKAROUND_834220 7 #define ARM64_HAS_NO_HW_PREFETCH 8 #define ARM64_HAS_UAO 9 #define ARM64_ALT_PAN_NOT_UAO 10 #define ARM64_HAS_VIRT_HOST_EXTN 11 #define ARM64_WORKAROUND_CAVIUM_27456 12 #define ARM64_HAS_32BIT_EL0 13 #define ARM64_HARDEN_EL2_VECTORS 14 #define ARM64_HAS_CNP 15 #define ARM64_HAS_NO_FPSIMD 16 #define ARM64_WORKAROUND_REPEAT_TLBI 17 #define ARM64_WORKAROUND_QCOM_FALKOR_E1003 18 #define ARM64_WORKAROUND_858921 19 #define ARM64_WORKAROUND_CAVIUM_30115 20 #define ARM64_HAS_DCPOP 21 #define ARM64_SVE 22 #define ARM64_UNMAP_KERNEL_AT_EL0 23 #define ARM64_HARDEN_BRANCH_PREDICTOR 24 #define ARM64_HAS_RAS_EXTN 25 #define ARM64_WORKAROUND_843419 26 #define ARM64_HAS_CACHE_IDC 27 #define ARM64_HAS_CACHE_DIC 28 #define ARM64_HW_DBM 29 #define ARM64_SSBD 30 #define ARM64_MISMATCHED_CACHE_TYPE 31 #define ARM64_HAS_STAGE2_FWB 32 #define ARM64_HAS_CRC32 33 #define ARM64_SSBS 34 #define ARM64_WORKAROUND_1188873 35 #define ARM64_HAS_SB 36 #define ARM64_WORKAROUND_1165522 37 #define ARM64_HAS_ADDRESS_AUTH_ARCH 38 #define ARM64_HAS_ADDRESS_AUTH_IMP_DEF 39 #define ARM64_HAS_GENERIC_AUTH_ARCH 40 #define ARM64_HAS_GENERIC_AUTH_IMP_DEF 41 #define ARM64_NCAPS 42
시스템에 위의 cpu capabilities가 사용되는지 여부를 알아오기 위해 init_cpu_features() 함수가 여러 개의 ARM64 레지스터들을 읽어 cpu features를 파악한다. 그런 후 cpu_hwcap_keys[] 전역 배열에 capabilities 여부를 저장하고 성능을 위해 이를 static key로 제공한다.
- capabilities(features) detection에 대한 범위는 다음과 같이 다르다.
- SCOPE_LOCAL_CPU
- 시스템 내의 모든 cpu들에 대해 하나 cpu라도 기능이 들어가 있는 경우
- 부트 cpu를 제외한 나머지 cpu들이 seconary_start_kernel() -> check_local_cpu_capabilities() 함수를 통해 capabilities를 파악한다.
- SCOPE_SYSTEM
- 시스템 내의 모든 cpu들에 기능이 모두 들어가 있는 경우
- 부트 cpu를 제외한 cpu들에 대해 setup_system_capabilities() 함수를 통해 capabilities를 파악한다.
- SCOPE_BOOT_CPU
- 시스템 내의 부트 cpu에 기능이 들어가 있는 경우
- 부트 cpu만 setup_boot_cpu_capabilities()를 통해 capabilities를 파악한다.
- SCOPE_LOCAL_CPU
- 이에 대한 코드 해석은 방대한 데이터 시트의 설명을 필요로하여 생략한다.
코드 대체(replacement)
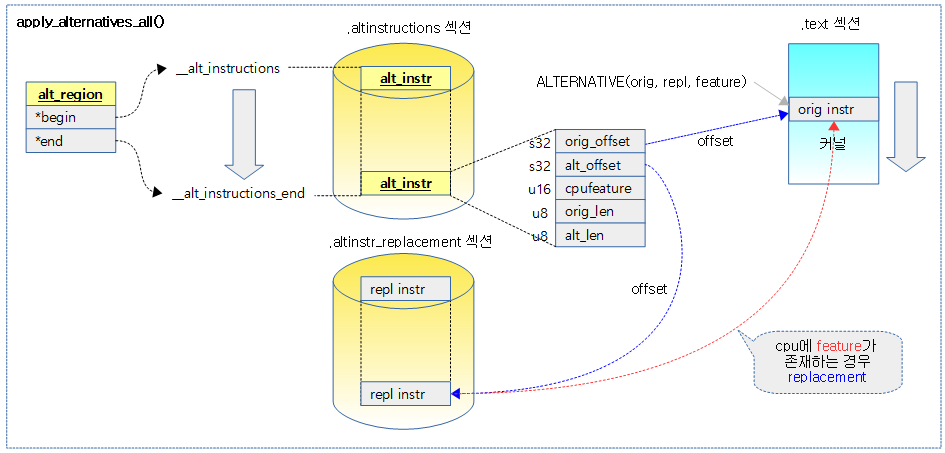
다음 그림은 부트업 마지막 과정에서 cpu에 capabilities(feature)가 지원하는 새 코드로 대체하는 과정을 보여준다.
apply_alternatives_all()
arch/arm64/kernel/alternative.c
void __init apply_alternatives_all(void)
{
/* better not try code patching on a live SMP system */
stop_machine(__apply_alternatives_multi_stop, NULL, cpu_online_mask);
}
모든 cpu를 멈춘 후 alternative 매크로를 사용한 명령들에 대해 조건을 만족시키면 대체 명령으로 replace한다.
__apply_alternatives_multi_stop()
arch/arm64/kernel/alternative.c
/* * We might be patching the stop_machine state machine, so implement a * really simple polling protocol here. */
static int __apply_alternatives_multi_stop(void *unused)
{
struct alt_region region = {
.begin = (struct alt_instr *)__alt_instructions,
.end = (struct alt_instr *)__alt_instructions_end,
};
/* We always have a CPU 0 at this point (__init) */
if (smp_processor_id()) {
while (!READ_ONCE(alternatives_applied))
cpu_relax();
isb();
} else {
BUG_ON(alternatives_applied);
__apply_alternatives(®ion, false);
/* Barriers provided by the cache flushing */
WRITE_ONCE(alternatives_applied, 1);
}
return 0;
}
alternative 매크로를 사용하여 .altinstructions 섹션에 위치한 명령들에 대해 조건을 만족시키면 대체 명령으로 replace한다.
- __alt_instructions ~ __alt_instructions_end는 .altinstructions 섹션을 포함한 범위 이다.
__apply_alternatives()
arch/arm64/kernel/alternative.c
static void __apply_alternatives(void *alt_region, bool is_module)
{
struct alt_instr *alt;
struct alt_region *region = alt_region;
__le32 *origptr, *updptr;
alternative_cb_t alt_cb;
for (alt = region->begin; alt < region->end; alt++) {
int nr_inst;
/* Use ARM64_CB_PATCH as an unconditional patch */
if (alt->cpufeature < ARM64_CB_PATCH &&
!cpus_have_cap(alt->cpufeature))
continue;
if (alt->cpufeature == ARM64_CB_PATCH)
BUG_ON(alt->alt_len != 0);
else
BUG_ON(alt->alt_len != alt->orig_len);
pr_info_once("patching kernel code\n");
origptr = ALT_ORIG_PTR(alt);
updptr = is_module ? origptr : lm_alias(origptr);
nr_inst = alt->orig_len / AARCH64_INSN_SIZE;
if (alt->cpufeature < ARM64_CB_PATCH)
alt_cb = patch_alternative;
else
alt_cb = ALT_REPL_PTR(alt);
alt_cb(alt, origptr, updptr, nr_inst);
if (!is_module) {
clean_dcache_range_nopatch((u64)origptr,
(u64)(origptr + nr_inst));
}
}
/*
* The core module code takes care of cache maintenance in
* flush_module_icache().
*/
if (!is_module) {
dsb(ish);
__flush_icache_all();
isb();
}
}
주어진 영역의 모든 alt_instr들에 대해 루프를 돌며 cpu feature가 있는 경우 replacement를 수행한다.
- 코드 라인 8~14에서 요청한 영역 범위를 루프를 돌며 alt->feature가 cpu가 지원하지 않는 기능이면 skip 한다.
- 코드 라인 16~21에서 길이 체크를 하고 커널 코드를 변경한다는 메시지 정보를 출력한다.
- 코드 라인 23~25에서 오리지널 명령 주소(dest), 변경할 명령 주소(alt)와 명령 개 수를 준비한다.
- 코드 라인 28~33에서 ARM64 표준 feature를 사용한 경우 patch_alternative() 함수를 사용하여 명령을 replace 하고, 그렇지 않은 경우 ALTERNATIVE_CB() 매크로를 통해 등록한 콜백 함수를 사용한다.
- kvm 사용 시 kvm_update_va_mask() 콜백 함수를 사용한다.
- 코드 라인 35~38에서 모듈에서 사용되지 않은 경우 replace한 영역에 대해 d-cache를 클린한다.
- 코드 라인 45에서 영역의 패치가 끝난 후 모듈에서 호출된 경우가 아니면 캐시 조작의 완료를 위해 dsb를 수행한다. 그런 후 명령 캐시와 명령 파이프를 모두 flush한다.
- 코드 replacement가 발생하면 관련 영역의 데이터 클린 및 명령 캐시 및 명령 파이프를 flush 해야 한다.
ALT_ORIG_PTR() & ALT_REPL_PTR()
arch/arm64/kernel/alternative.c
#define __ALT_PTR(a,f) ((void *)&(a)->f + (a)->f) #define ALT_ORIG_PTR(a) __ALT_PTR(a, orig_offset) #define ALT_REPL_PTR(a) __ALT_PTR(a, alt_offset)
- ALT_ORIG_PTR()
- original 명령이 위치한 주소를 가리킨다. (이 영역이 변경될 곳이다.)
- ALT_REPL_PTR()
- replace 명령이 위치한 주소를 가리킨다. (이 영역을 copy하여)
arch/arm64/include/asm/alternative.h
typedef void (*alternative_cb_t)(struct alt_instr *alt,
__le32 *origptr, __le32 *updptr, int nr_inst);
현재 아래 두 종류의 callback 함수를 사용한다.
- patch_alternative()
- ALTERNATIVE() 매크로 사용 시
- kvm_update_va_mask()
- ALTERNATIVE_CB() 매크로 사용 시
alt_instr 구조체
arch/arm64/include/asm/alternative.h
struct alt_instr {
s32 orig_offset; /* offset to original instruction */
s32 alt_offset; /* offset to replacement instruction */
u16 cpufeature; /* cpufeature bit set for replacement */
u8 orig_len; /* size of original instruction(s) */
u8 alt_len; /* size of new instruction(s), <= orig_len */
};
- orig_offset
- alt_instr 구조체 위치를 기준으로 original 명령들이 위치한 주소 offset이 담긴다. (이 영역이 변경될 곳이다.)
- alt_offset
- alt_instr 구조체 위치를 기준으로 alt 명령들이 위치한 주소 offset이 담긴다. (이 영역을 copy하여)
- cpufeature
- 이 cpu feature가 있으면 replace를 하려고 한다.
- orig_len
- 오리지널 명령들의 길이
- alt_len
- alt 명령들의 길이
정말 감사합니다 🙂 copy_from_user, copy_to_user 등을 분석하고 있었는데, 해당 글이 너무나도 도움이 되었습니다 🙂
실제 어디서 대체 되는지 몰라서 의미만 보고 이게 뭔가 했는데… 속이 뻥 뚫리는 것 같아요 ㅎ
기존의에 있으신 copy_from_user 관련 분석 글과 해당 글을 링크해 주시면 좋을 것 같은데 어떠신가요?
윤여름님 안녕하세요?
도움이 되었다니 저도 좋습니다.
copy_from_user() 글은 다음 목록에 링크되어 있습니다. (가장 마지막에요 ^^;)
2. start_kernel() – http://jake.dothome.co.kr/linux_kernel/linux_4/
copy_from_user()의 직접 링크는 다음과 같습니다.
copy_from_user() – http://jake.dothome.co.kr/copy_from_user/
감사합니다.