이 함수를 사용하는 해시명과 사용하는 구조체들은 다음과 같다.
- “PID”, pid_hash
- “TCP established”, inet_ehash_bucket
- “TCP bind”, inet_bind_hashbucket
- “UDP”, udp_hslot
- “UDP-Lite”, udp_hslot
- “futex”, futex_queues
- “Inode-cache”, hlish_head
- “Dentry cache” hlist_bl_head
- “Mount-cache”, hlish_head
- “Mountpoint-cache”, hlist_head
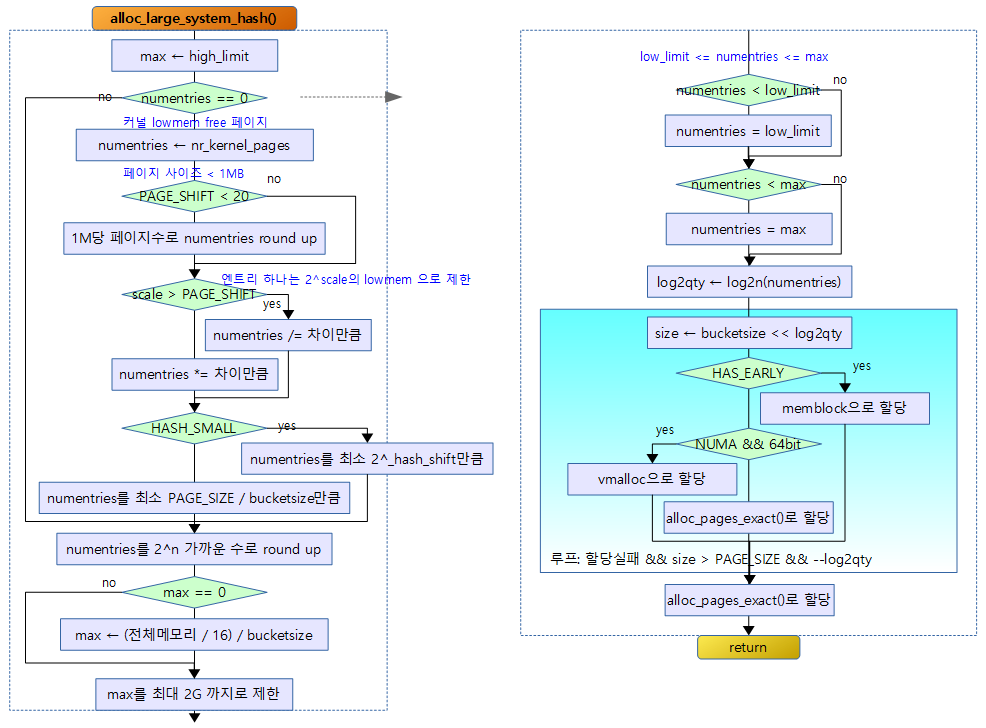
alloc_large_system_hash()
mm/page_alloc.c
/*
* allocate a large system hash table from bootmem
* - it is assumed that the hash table must contain an exact power-of-2
* quantity of entries
* - limit is the number of hash buckets, not the total allocation size
*/
void *__init alloc_large_system_hash(const char *tablename,
unsigned long bucketsize,
unsigned long numentries,
int scale,
int flags,
unsigned int *_hash_shift,
unsigned int *_hash_mask,
unsigned long low_limit,
unsigned long high_limit)
{
unsigned long long max = high_limit;
unsigned long log2qty, size;
void *table = NULL;
/* allow the kernel cmdline to have a say */
if (!numentries) {
/* round applicable memory size up to nearest megabyte */
numentries = nr_kernel_pages;
/* It isn't necessary when PAGE_SIZE >= 1MB */
if (PAGE_SHIFT < 20)
numentries = round_up(numentries, (1<<20)/PAGE_SIZE);
/* limit to 1 bucket per 2^scale bytes of low memory */
if (scale > PAGE_SHIFT)
numentries >>= (scale - PAGE_SHIFT);
else
numentries <<= (PAGE_SHIFT - scale);
/* Make sure we've got at least a 0-order allocation.. */
if (unlikely(flags & HASH_SMALL)) {
/* Makes no sense without HASH_EARLY */
WARN_ON(!(flags & HASH_EARLY));
if (!(numentries >> *_hash_shift)) {
numentries = 1UL << *_hash_shift;
BUG_ON(!numentries);
}
} else if (unlikely((numentries * bucketsize) < PAGE_SIZE))
numentries = PAGE_SIZE / bucketsize;
}
numentries = roundup_pow_of_two(numentries);
인수로 해시 엔트리 수가 0이 입력된 경우 커널 free 페이지 수를 사용하여 최대 수로 해시 엔트리 수를 산출하고 scale 값으로 조정하여 해시 엔트리 수를 결정하되 low ~ high limit 범위로 제한한다.
- if (!numentries) {
- 엔트리 수는 커널의 cmdline에서 커널 파라메터를 사용하여 설정될 수 있다.
- 예) thash_entries=, uhash_entries=, ihash_entries=, dhash_entries=, mhash_entries=, mphash_entries=
- 엔트리 수는 커널의 cmdline에서 커널 파라메터를 사용하여 설정될 수 있다.
- numentries = nr_kernel_pages;
- nr_kernel_pages
- 커널이 사용할 수 있는 free lowmem page 수
- setup_arch()->paging_init()->bootmem_init()->zone_sizes_init()->free_area_init_node()->free_area_init_core() 함수에서 설정된다.
- nr_kernel_pages
- if (PAGE_SHIFT < 20) numentries = round_up(numentries, (1<<20)/PAGE_SIZE);
- 페이지 프레임이 1M가 안되는 경우 엔트리 수를 1M/PAGE_SIZE로 round up 한다.
- if (scale > PAGE_SHIFT) numentries >>= (scale – PAGE_SHIFT);
- scale이 PAGE_SHIFT보다 큰 경우 엔트리 수를 n(scale – PAGE_SHIFT)으로 나눈다.
- 예) PID의 경우 scale=18 이므로 페이지 크기와 6 차이가 나므로 산출된 엔트리 수에서 2^6=64로 나눈다.
- numentries >>= (18 – 12)
- 예) PID의 경우 scale=18 이므로 페이지 크기와 6 차이가 나므로 산출된 엔트리 수에서 2^6=64로 나눈다.
- scale이 PAGE_SHIFT보다 큰 경우 엔트리 수를 n(scale – PAGE_SHIFT)으로 나눈다.
- else numentries <<= (PAGE_SHIFT – scale);
- 페이지 크기가 scale 크기보다 작은 경우 엔트리 수를 n(PAGE_SHIFT – scalke)으로 곱한다.
- if (unlikely(flags & HASH_SMALL)) {
- 작은 확률로 HASH_SMALL 플래그 옵션을 사용한 경우
- 이 옵션을 사용하는 해시
- PID 해시
- futex 해시의 경우 해시 사이즈가 256보다 작은 경우
- if (!(numentries >> *_hash_shift)) { numentries = 1UL << *_hash_shift; }
- 엔트리 수가 최소한 _hash_shift 표현 비트보다 크도록 조정한다.
- PID 해시 예) _hash_shift=4
- 해시 엔트리 수가 16보다 작은 경우 최소 16으로 조정된다.
- PID 해시 예) _hash_shift=4
- 엔트리 수가 최소한 _hash_shift 표현 비트보다 크도록 조정한다.
- } else if (unlikely((numentries * bucketsize) < PAGE_SIZE)) numentries = PAGE_SIZE / bucketsize;
- 작은 확률로 해시 엔트리 수 * 버킷사이즈가 페이지 보다 작은 경우 엔트리 수를 페이지당 버킷사이즈가 들어갈 수 있는 최대 수로 확대 조정한다.
- 한 페이지도 채우지 못하는 해시 엔트리의 경우 한 페이지를 채우는 수 만큼 확대 조정
- 작은 확률로 해시 엔트리 수 * 버킷사이즈가 페이지 보다 작은 경우 엔트리 수를 페이지당 버킷사이즈가 들어갈 수 있는 최대 수로 확대 조정한다.
- numentries = roundup_pow_of_two(numentries);
- 2^n에 가까운 값으로 round up 한다.
- 예) 4000
- -> 4096
- 예) 4000
- 2^n에 가까운 값으로 round up 한다.
/* limit allocation size to 1/16 total memory by default */
if (max == 0) {
max = ((unsigned long long)nr_all_pages << PAGE_SHIFT) >> 4;
do_div(max, bucketsize);
}
max = min(max, 0x80000000ULL);
if (numentries < low_limit)
numentries = low_limit;
if (numentries > max)
numentries = max;
log2qty = ilog2(numentries);
do {
size = bucketsize << log2qty;
if (flags & HASH_EARLY)
table = memblock_virt_alloc_nopanic(size, 0);
else if (hashdist)
table = __vmalloc(size, GFP_ATOMIC, PAGE_KERNEL);
else {
/*
* If bucketsize is not a power-of-two, we may free
* some pages at the end of hash table which
* alloc_pages_exact() automatically does
*/
if (get_order(size) < MAX_ORDER) {
table = alloc_pages_exact(size, GFP_ATOMIC);
kmemleak_alloc(table, size, 1, GFP_ATOMIC);
}
}
} while (!table && size > PAGE_SIZE && --log2qty);
if (!table)
panic("Failed to allocate %s hash table\n", tablename);
printk(KERN_INFO "%s hash table entries: %ld (order: %d, %lu bytes)\n",
tablename,
(1UL << log2qty),
ilog2(size) - PAGE_SHIFT,
size);
if (_hash_shift)
*_hash_shift = log2qty;
if (_hash_mask)
*_hash_mask = (1 << log2qty) - 1;
return table;
}
- if (max == 0) { max = ((unsigned long long)nr_all_pages << PAGE_SHIFT) >> 4; do_div(max, bucketsize); }
- 인수 high_limit이 지정되지 않은 경우 max(최대 할당 가능 바이트) 값을 산출하여 사용하는데 max를 최대 메모리의 1/16으로 설정 후 다시 max를 bucketsize로 나눈다.
- do_div(n, base)
- 64 bit n 값을 32 bit base로 나눈 몫을 n에 저장하고 나머지를 리턴한다.
- 실제 동작과 달리 코드는 무척 난해하므로 생략한다.
- 참고: arch/arm/include/asm/div64.h
- nr_all_pages
- 전체 메모리 페이지 수가 담긴 전역 변수이다.
- setup_arch()->paging_init()->bootmem_init()->zone_sizes_init()->free_area_init_node()->free_area_init_core() 함수에서 설정된다.
- max = min(max, 0x80000000ULL);
- max 값이 2G를 초과하지 않도록 한다.
- if (numentries < low_limit) numentries = low_limit;
- 계산된 해시 엔트리 수가 인수 low_limit 이상이 되게 조정한다.
- if (numentries > max) numentries = max;
- 계산된 해시 엔트리 수가 max 이하가 되게 조정한다.
- log2qty = ilog2(numentries);
- log2를 계산한다.
- 예) numentries=120
- 7
계산된 log2qty bit 수 만큼 메모리 할당을 시도하고 실패하면 반복하여 log2qty bit를 1씩 줄여서 시도한다. 메모리 할당은 다음 3가지 유형을 선택 사용한다.
- early 요청이 있는 경우 memblock에 할당한다.
- early 요청이 아니면서 NUMA 및 64비트 시스템인 경우 vmalloc에 할당한다.
- 그 외의 경우 alloc_pages_exact()를 사용하여 메모리를 할당한다.
- 내부에서 get_free_pages() 사용
- size = bucketsize << log2qty;
- 할당할 사이즈는 버킷사이즈를 log2qty 만큼 좌측으로 쉬프트한다.
- if (flags & HASH_EARLY) table = memblock_virt_alloc_nopanic(size, 0);
- early 요청이 있는 경우 memblock에 할당한다.
- else if (hashdist) table = __vmalloc(size, GFP_ATOMIC, PAGE_KERNEL);
- early 요청이 아니면서 NUMA 및 64비트 시스템인 경우 vmalloc에 할당한다.
- if (get_order(size) < MAX_ORDER) { table = alloc_pages_exact(size, GFP_ATOMIC); kmemleak_alloc(table, size, 1, GFP_ATOMIC); }
- size 처리 비트가 MAX_ORDER 보다 작은 경우에 한해 size 만큼의 메모리를 alloc_pages_exact()함수를 사용하여 할당한다.
- } while (!table && size > PAGE_SIZE && –log2qty);
- 메모리 할당이 실패한 경우 log2qty를 1씩 줄여 할당 공간을 반으로 줄여가며 재 시도한다.
- size가 PAGE_SIZE 이하가 되면 메모리 할당을 실패한 채로 루프를 빠져나온다.
- if (!table) panic(“Failed to allocate %s hash table\n”, tablename);
- 메모리 할당이 실패하면 panic() 코드를 수행한다.
- 해시 테이블 정보를 출력한다.
- rpi2 예)
- PID hash table entries: 4096 (order: 2, 16384 bytes)
- Dentry cache hash table entries: 131072 (order: 7, 524288 bytes)
- Inode-cache hash table entries: 65536 (order: 6, 262144 bytes)
- Mount-cache hash table entries: 2048 (order: 1, 8192 bytes)
- Mountpoint-cache hash table entries: 2048 (order: 1, 8192 bytes)
- TCP: Hash tables configured (established 8192 bind 8192)
- UDP hash table entries: 512 (order: 3, 49152 bytes)
- UDP-Lite hash table entries: 512 (order: 3, 49152 bytes)
- futex hash table entries: 1024 (order: 4, 65536 bytes)
- rpi2 예)
- if (_hash_shift) *_hash_shift = log2qty;
- _hash_shift가 지정된 경우 _hash_shift값을 업데이트 한다.
- if (_hash_mask) *_hash_mask = (1 << log2qty) – 1;
- _hash_mask가 지정된 경우 _hash_mask를 업데이트 한다.
참고
- pidhash_init() | 문c