<kernel v5.10>
set_task_stack_end_magic()
- start_kernel()이 커널 초기화 과정을 수행하는 동안 사용할 최초 커널 스택의 마지막에 magic value를 기록한다. 이후에 만들어지는 커널 스택은 메모리를 할당 받아 생성되어 사용되며 태스크가 종료되는 경우 메모리를 회수한다.
- 기록된 magic value(STACK_END_MAGIC: 0x57AC6E9D)를 통해 kernel stack overflow를 감지하는데 사용된다.
void set_task_stack_end_magic(struct task_struct *tsk)
{
unsigned long *stackend;
stackend = end_of_stack(tsk);
*stackend = STACK_END_MAGIC; /* for overflow detection */
}
- STACK_END_MAGIC=0x57AC_6E9D
end_of_stack()
CONFIG_THREAD_INFO_IN_TASK 사용 케이스 (ARM64 must)
include/linux/sched/task_stack.h
static inline unsigned long *end_of_stack(const struct task_struct *task)
{
return task->stack;
}
태스크에 해당하는 stack의 끝 주소를 반환한다. 스택의 마지막 위치에는 스택 마지막을 표시하는 매직 값이 위치한다.
ARM32 에서 CONFIG_THREAD_INFO_IN_TASK를 사용하지 않는 케이스
include/linux/sched/task_stack.h
/* * Return the address of the last usable long on the stack. * * When the stack grows down, this is just above the thread * info struct. Going any lower will corrupt the threadinfo. * * When the stack grows up, this is the highest address. * Beyond that position, we corrupt data on the next page. */
static inline unsigned long *end_of_stack(struct task_struct *p)
{
#ifdef CONFIG_STACK_GROWSUP
return (unsigned long *)((unsigned long)task_thread_info(p) + THREAD_SIZE) - 1;
#else
return (unsigned long *)(task_thread_info(p) + 1);
#endif
}
요청한 태스크에 해당하는 스택의 마지막 unsigned long 값을 반환한다. 스택의 마지막 위치에는 스택 마지막을 표시하는 매직 값이 위치한다.
- CONFIG_STACK_GROWSUP
- 스택이 상향으로 push되는 경우에 사용
- arm, arm64 default: 하향으로 스택이 push된다.
- task가 가지고 있는 kernel stack의 마지막 주소를 리턴한다.
- task는 kernel stack과 user stack를 각각 하나씩 가진다.
- kernel stack은 kernel이 자신의 코드를 수행할 때 사용하는 코드이다.
- 예를 들어, user application이 요청한 시스템 콜을 수행할 때 kernel stack이 사용될 수 있다.
- 참고: kernel stack
kernel stack 구조
- 아키텍처마다 커널 스택 크기가 다르다.
- arm32
- 8K (2 페이지)
- 1개 페이지로 돌아가려고 노력하고 있으므로, 나중에 변경될 수도 있다.
- arm64
- 16K (default)
- 64K (1페이지=64K 이면서 vmap stack 사용시)
- arm32
아래 그림은 커널 스택에서의 스택 보호용 매직 번호가 있는 위치를 보여준다.
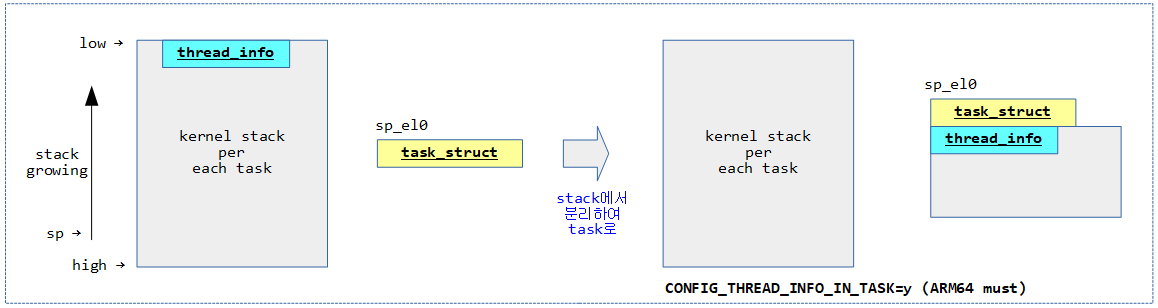
- arm64의 경우 thread_info가 스택에서 제거되어 task_struct의 안으로 들어가므로 매직 번호는 가장 하단에 위치하게 된다.
thread_union
include/linux/sched.h
union thread_union {
#ifndef CONFIG_ARCH_TASK_STRUCT_ON_STACK
struct task_struct task;
#endif
#ifndef CONFIG_THREAD_INFO_IN_TASK
struct thread_info thread_info;
#endif
unsigned long stack[THREAD_SIZE/sizeof(long)];
};
- CONFIG_ARCH_TASK_STRUCT_ON_STACK
- ia64 아키텍처만 이 커널 옵션을 사용한다.
- CONFIG_THREAD_INFO_IN_TASK
- 커널 v4.9-rc1에 추가된 기능으로 이 커널 옵션을 사용하는 경우 보안을 위해 스택의 아래에 존재하던 thread_info를 제거하여 task_struct의 첫 엔트리로 옮겼다. 이렇게 첫 부분에 옮겨 놓았으므로 task_struct 구조체도 thread_union의 thread_info를 통해 접근이 가능하다.
- arm은 사용하지 않는 옵션이지만 arm64의 경우는 적용되었다.
- 참고: sched/core: Allow putting thread_info into task_struct
task_struct 구조체 (처음 부분만)
include/linux/sched.h
struct task_struct {
#ifdef CONFIG_THREAD_INFO_IN_TASK
/*
* For reasons of header soup (see current_thread_info()), this
* must be the first element of task_struct.
*/
struct thread_info thread_info;
#endif
volatile long state;
/*
* This begins the randomizable portion of task_struct. Only
* scheduling-critical items should be added above here.
*/
randomized_struct_fields_start
void *stack;
...
}
CONFIG_THREAD_INFO_IN_TASK 커널 옵션을 사용한 경우 가장 처음에 스레드 정보가 위치함을 알 수 있다.
thread_info – ARM
arch/arm/include/asm/thread_info.h
struct thread_info {
unsigned long flags; /* low level flags */
int preempt_count; /* 0 => preemptable, <0 => bug */
mm_segment_t addr_limit; /* address limit */
struct task_struct *task; /* main task structure */
__u32 cpu; /* cpu */
__u32 cpu_domain; /* cpu domain */
#ifdef CONFIG_STACKPROTECTOR_PER_TASK
unsigned long stack_canary;
#endif
struct cpu_context_save cpu_context; /* cpu context */
__u32 syscall; /* syscall number */
__u8 used_cp[16]; /* thread used copro */
unsigned long tp_value[2]; /* TLS registers */
#ifdef CONFIG_CRUNCH
struct crunch_state crunchstate;
#endif
union fp_state fpstate __attribute__((aligned(8)));
union vfp_state vfpstate;
#ifdef CONFIG_ARM_THUMBEE
unsigned long thumbee_state; /* ThumbEE Handler Base register */
#endif
};
thread_info – ARM64
arch/arm64/include/asm/thread_info.h
struct thread_info {
unsigned long flags; /* low level flags */
mm_segment_t addr_limit; /* address limit */
#ifdef CONFIG_ARM64_SW_TTBR0_PAN
u64 ttbr0; /* saved TTBR0_EL1 */
#endif
union {
u64 preempt_count; /* 0 => preemptible, <0 => bug */
struct {
#ifdef CONFIG_CPU_BIG_ENDIAN
u32 need_resched;
u32 count;
#else
u32 count;
u32 need_resched;
#endif
} preempt;
};
};
task_thread_info()
include/linux/sched.h
#ifdef CONFIG_THREAD_INFO_IN_TASK
static inline struct thread_info *task_thread_info(struct task_struct *task)
{
return &task->thread_info;
}
#elif !defined(__HAVE_THREAD_FUNCTIONS)
# define task_thread_info(task) ((struct thread_info *)(task)->stack)
#endif
요청한 태스크에 해당하는 스레드 정보(thread_info 구조체)를 반환한다.
- CONFIG_THREAD_INFO_IN_TASK 커널 옵션을 사용한 여부와 관련하여
- 사용한 경우 task 디스크립터에 위치한 스레드 정보를 가져온다.
- 사용하지 않은 경우 스택에서 스레드 정보를 가져온다.
thread_union
include/linux/sched.h
union thread_union {
#ifndef CONFIG_ARCH_TASK_STRUCT_ON_STACK
struct task_struct task;
#endif
#ifndef CONFIG_THREAD_INFO_IN_TASK
struct thread_info thread_info;
#endif
unsigned long stack[THREAD_SIZE/sizeof(long)];
};
스택과 같은 주소를 공유하는 구조체들이다.
- CONFIG_ARCH_TASK_STRUCT_ON_STACK (default=n) 커널 옵션을 사용하지 않는 경우에 task_struct 구조체를 사용한다.
- Construct init thread stack in the linker script rather than by union (2018, v4.16-rc1)
- CONFIG_THREAD_INFO_IN_TASK (default=y) 커널 옵션을 사용하지 않는 경우에 thread_info 구조체를 사용한다. (ARM64는 사용하지 않는다)
- 참고: sched/core: Allow putting thread_info into task_struct (2016, v4.9-rc1)
- 스택은 THREAD_SIZE 크기 만큼 사용한다.
다음 그림은 CONFIG_THREAD_INFO_IN_TASK 커널 옵션 사용에 따른 변화를 보여준다.
- ARM64의 경우 이 커널 옵션은 항상 선택되어 thread_info가 스택에서 분리하여 태스크 디스크립터에 포함된다.
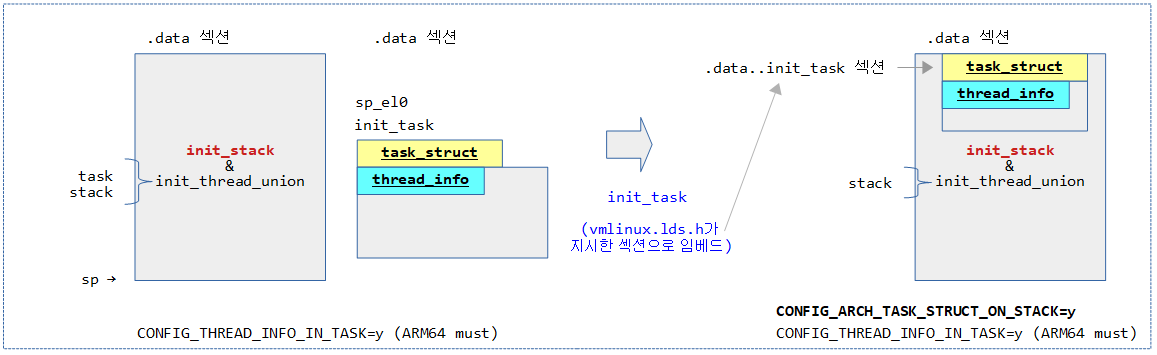
다음 그림은 CONFIG_ARCH_TASK_STRUCT_ON_STACK 커널 옵션 사용에 따른 변화를 보여준다.
- 이 커널 옵션을 사용하는 경우 vmlinux.lds.h가 지정하는 섹션을 통해 들어가다보면 init_task가 init_stack 내에 포함되는 것을 알 수 있다.
INIT_TASK_DATA()
include/asm-generic/vmlinux.lds.h
#define INIT_TASK_DATA(align) \
. = ALIGN(align); \
__start_init_task = .; \
init_thread_union = .; \
init_stack = .; \
KEEP(*(.data..init_task)) \
KEEP(*(.data..init_thread_info)) \
. = __start_init_task + THREAD_SIZE; \
__end_init_task = .;
init_stack을 만들때 __start_init_task, init_thread_union 심볼등도 같은 주소로 생성한다.
- init_task의 경우 CONFIG_ARCH_TASK_STRUCT_ON_STACK 커널 옵션을 사용하는 경우 아래의 __init_task_data 섹션 지시 매크로를 통해 .data..init_task 섹션에 포함시킨다.
- init_thread_info의 경우 CONFIG_THREAD_INFO_IN_TASK 커널 옵션을 사용지 않는 경우 .data..init_task 섹션에 포함시킨다. (ARM64의 경우 이 옵션을 사용하지 않으므로 해당 섹션 위치를 사용하지 않는다.)
__init_task_data
include/linux/init_task.h
/* Attach to the init_task data structure for proper alignment */
#ifdef CONFIG_ARCH_TASK_STRUCT_ON_STACK
#define __init_task_data __section(".data..init_task")
#else
#define __init_task_data /**/
#endif
init_task 생성 시 이 섹션 지시 매크로를 통해 .data..init_task 섹션에 포함시키도록 한다.
get_current()
arch/arm64/include/asm/current.h
/* * We don't use read_sysreg() as we want the compiler to cache the value where * possible. */
static __always_inline struct task_struct *get_current(void)
{
unsigned long sp_el0;
asm ("mrs %0, sp_el0" : "=r" (sp_el0));
return (struct task_struct *)sp_el0;
}
현재 태스크를 반환한다.
- 커널(el1)에서는 사용하지 않는 sp_el0 레지스터를 사용하여 태스크를 가리키도록 하여 사용하고 있다.
참고
- User stack vs Kernel stack | 문c
- Kernel Small Stacks | elinux.org
- 커널 최초의 스택은 어떻게 설정하나요? | 박문식