<kernel v5.10>
페이지 주소 해시 테이블
페이지 주소 해시 테이블은 다음과 같은 용도로 사용된다.
- 32비트 시스템에서 HIGHMEM 영역을 관리하기 위해 kmap(pkmap)용 hash table로 사용한다.
- 커널이 사용할 용도의 메모리 할당을 위해 사용하는 영역은 lowmem 영역이다. 그런데 커널이 메모리 부족 시 highmem 영역을 이용하는 경우 이를 매핑하여 사용하기도 하는데, 이의 관리를 위해 사용한다.
- 참고로 유저 사용 용도의 메모리 할당 역시 highmem을 우선 사용하지만 rmap 자료 구조를 사용하여 매핑된 사용자 주소 공간들을 알아올 수 있다.
- 이 hash table은 128개의 hash 엔트리를 사용하여 page 주소로 virtual 주소를 빠르게 변환하여 알아올 수 있다.
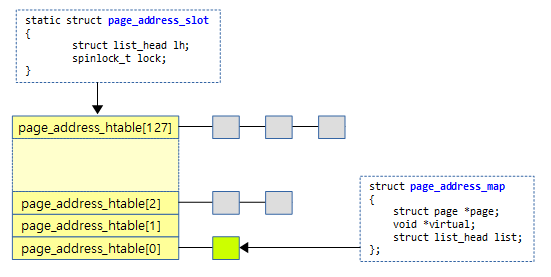
다음 그림은 page 주소에 해당하는 가상 주소를 검색하기 위해 사용되는 페이지 주소 해시 테이블이다.
- 해쉬 페이지 테이블은 128개의 배열 즉 128개의 해쉬 슬롯으로 이루어진다.
- 각 해쉬 페이지 테이블 엔트리는 page_address_map 엔트리를 여러 개 리스트에 등록할 수 있다.
page_address_init()
mm/highmem.c
void __init page_address_init(void)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < ARRAY_SIZE(page_address_htable); i++) {
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&page_address_htable[i].lh);
spin_lock_init(&page_address_htable[i].lock);
}
}
highmem을 사용하는 kmap의 빠른 페이지 검색을 위해 해시테이블을 초기화한다.
page_address_slot 구조체
mm/highmem.c
/* * Hash table bucket */
static struct page_address_slot {
struct list_head lh; /* List of page_address_maps */
spinlock_t lock; /* Protect this bucket's list */
} ____cacheline_aligned_in_smp page_address_htable[1<<PA_HASH_ORDER];
- PA_HASH_ORDER=7
- 해쉬 테이블의 크기를 128개로 설정한다.
- ____cacheline_aligned_in_smp
- 성능을 위하여 해당 아키텍처의 L1 d-cache line 크기로 정렬하여 사용한다.
- __attribute__((__aligned__(SMP_CACHE_BYTES)))
- SMP_CACHE_BYTES=6
- rpi2: ARMv7 L1 d-cache line = 64 bytes
- SMP_CACHE_BYTES=6
- lh
- page_address_map 구조체를 여러 개 등록 관리하기 위한 리스트 헤더로 사용한다.
- lock
- lh 연결 리스트를 보호하기 위한 spin lock 용도이다.
page_address_map 구조체
mm/highmem.c
/* * Describes one page->virtual association */
struct page_address_map {
struct page *page;
void *virtual;
struct list_head list;
};
- page
- 해당 page 구조체가 저장된 주소
- virtual
- 매핑된 virtual address
- list
- 이 페이지가 관리되고 있는 hash table의 위치
page_address_maps[] 전역 변수
mm/highmem.c
static struct page_address_map page_address_maps[LAST_PKMAP];
- 이 테이블은 HIGHMEM 영역에 대한 L2 table로 kmap(pkmap)이 유지 보수 한다.
- kmap(), kunmap() 함수를 사용하여 매핑 설정 및 해제된다.
- ARM에서 L2용도로 사용하는 엔트리는 512개이다.
- 매핑 영역의 크기는 총 2M 크기를 사용할 수 있다.
- 매핑 영역의 시작 위치는 PAGE_OFFSET – 2M 이다.
page_slot()
mm/highmem.c
static struct page_address_slot *page_slot(const struct page *page)
{
return &page_address_htable[hash_ptr(page, PA_HASH_ORDER)];
}
page 구조체 주소로 hash(slot) 값을 알아와 해쉬 테이블의 인덱스로 사용하여 해당 해쉬 테이블의 구조체 주소를 리턴한다.
- 예)
- page = 0x10000000 -> hash slot index = 8
hash_ptr()
include/linux/hash.h
static inline unsigned long hash_ptr(const void *ptr, unsigned int bits)
{
return hash_long((unsigned long)ptr, bits);
}
- 주소 값을 사용하여 hash(slot) 값을 알아온다.
- bits=7 인 경우 hash(slot) 값이 0~127의 값으로 리턴된다.
hash_long()
include/linux/hash.h
/* * The "GOLDEN_RATIO_PRIME" is used in ifs/btrfs/brtfs_inode.h and * fs/inode.c. It's not actually prime any more (the previous primes * were actively bad for hashing), but the name remains. */
#if BITS_PER_LONG == 32 #define GOLDEN_RATIO_PRIME GOLDEN_RATIO_32 #define hash_long(val, bits) hash_32(val, bits) #elif BITS_PER_LONG == 64 #define hash_long(val, bits) hash_64(val, bits) #define GOLDEN_RATIO_PRIME GOLDEN_RATIO_64 #else #error Wordsize not 32 or 64 #endif
- 32비트/64비트 아키텍처에 따라 hash_32() 함수 또는 hash_64() 함수를 호출한다.
GOLDEN_RATIO_32 & GOLDEN_RATIO_64
/* * This hash multiplies the input by a large odd number and takes the * high bits. Since multiplication propagates changes to the most * significant end only, it is essential that the high bits of the * product be used for the hash value. * * Chuck Lever verified the effectiveness of this technique: * http://www.citi.umich.edu/techreports/reports/citi-tr-00-1.pdf * * Although a random odd number will do, it turns out that the golden * ratio phi = (sqrt(5)-1)/2, or its negative, has particularly nice * properties. (See Knuth vol 3, section 6.4, exercise 9.) * * These are the negative, (1 - phi) = phi**2 = (3 - sqrt(5))/2, * which is very slightly easier to multiply by and makes no * difference to the hash distribution. */
#define GOLDEN_RATIO_32 0x61C88647 #define GOLDEN_RATIO_64 0x61C8864680B583EBull
hash_32()
static inline u32 hash_32(u32 val, unsigned int bits)
{
/* On some cpus multiply is faster, on others gcc will do shifts */
u32 hash = val * GOLDEN_RATIO_PRIME_32;
/* High bits are more random, so use them. */
return hash >> (32 - bits);
}
val * 0x9e370001UL 값을 구한 후 bits 만큼 우측 쉬프트한 값을 리턴한다.
- page_slot()에서 요청한 bits=7이므로 val * 0x9e370001UL 값을 구한 후 msb 7 bits를 우측으로 쉬프트한 후 리턴한다.
- 결국 hash(slot) 값은 0~127이 리턴된다.
- 예)
- val=0x0 -> hash slot index=0
- val=0x1 -> hash slot index=79
- val=0x2 -> hash slot index=30
- val=0x1000_0000 -> return=8
- val=0x2000_0000 -> return=16
hash_64_generic()
include/linux/hash.h
#ifndef HAVE_ARCH_HASH_64 #define hash_64 hash_64_generic #endif
static __always_inline u32 hash_64_generic(u64 val, unsigned int bits)
{
#if BITS_PER_LONG == 64
/* 64x64-bit multiply is efficient on all 64-bit processors */
return val * GOLDEN_RATIO_64 >> (64 - bits);
#else
/* Hash 64 bits using only 32x32-bit multiply. */
return hash_32((u32)val ^ __hash_32(val >> 32), bits);
#endif
}
참고
- Kmap(Pkmap) | 문c
- Fixmap | 문c