특징
- 부트업 프로세스(타임)에서 사용하는 물리 메모리 할당 및 조정자(A boot-time physical memory allocator and configurator)
- Bootmem 은 간단하다. 커널 부트업 프로세스의 early 파트를 진행하는 동안 low-레벨 메모리 할당자가 커널에 의해 사용된다.
- Bootmem은 초기에 MMU(페이징) 기능이 동작된 후부터 early boot process를 수행하는 동안 buddy 할당자가 동작하기 전까지 시스템에 필요한 메모리 할당을 담당하며 사용 후에는 buddy 할당으로 변환된다.
- Bootmem은 메모리의 사용 유무를 bitmap으로 표현한다.
- Bootmem은 각 아키텍처마다 메인 커널에서 점점 사용하지 않고 memblock만을 사용하여 운영하는 방법으로 전환 되어가고 있다.
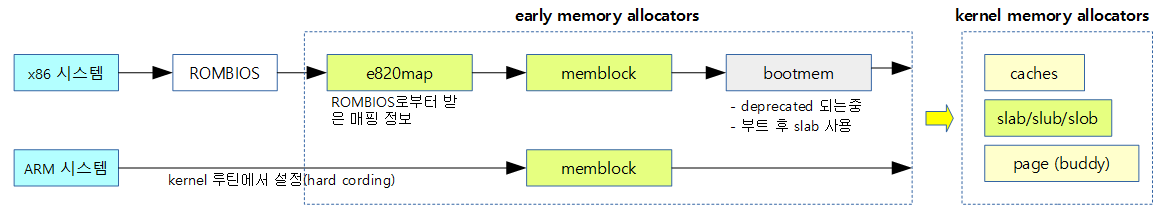
- x86 시스템의 메모리 할당 변천을 보면
- 1) very very early allocator (early brk model) [x86] – BIOS “e820″을 사용
- 2) very early allocator (early_res) -> (memblock) [some generic]
- kernel 2.6.35에서 early_res를 memblock으로 대체
- 3) early allocator (bootmem) [generic]
- 4) full buddy allocator
- ARM 커널 v3.14-rc1에서 arm_bootmem_init()이 삭제되고 CONFIG_NO_BOOTMEM 옵션을 추가하였다.
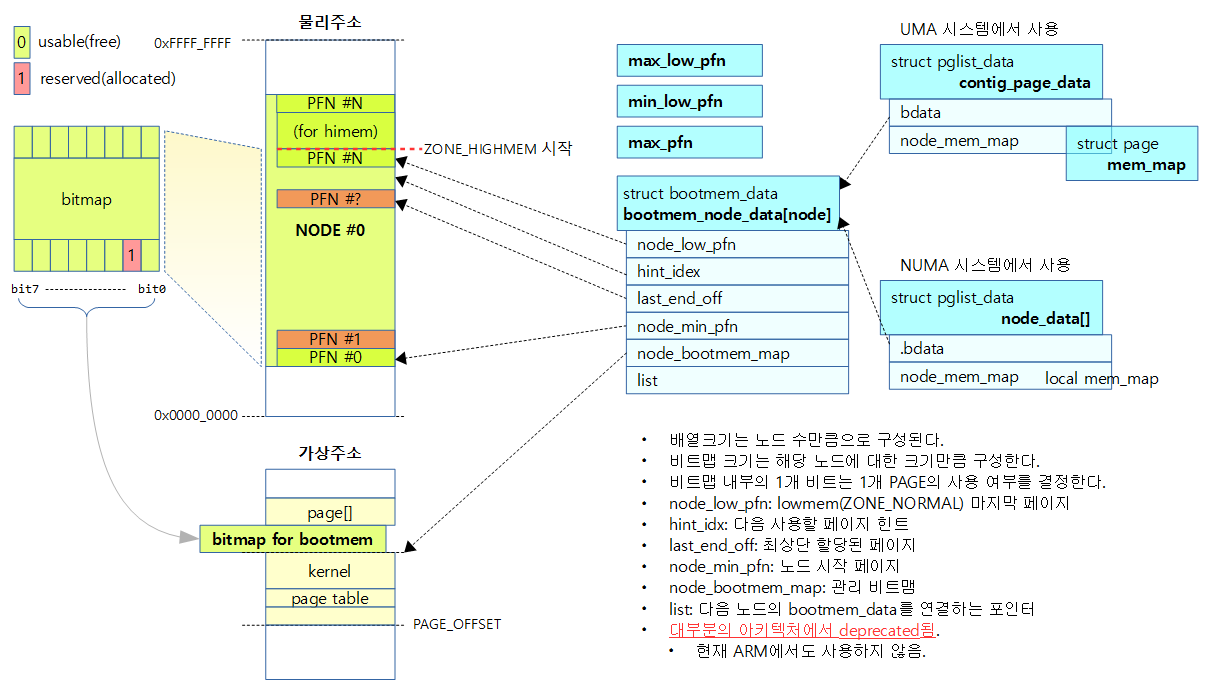
아래 그림은 bootmem이 비트맵으로 표현되는 방법을 보여준다.
구조체
struct bootmem_data
include/linux/bootmem.h
#ifndef CONFIG_NO_BOOTMEM
/*
* node_bootmem_map is a map pointer - the bits represent all physical
* memory pages (including holes) on the node.
*/
typedef struct bootmem_data {
unsigned long node_min_pfn;
unsigned long node_low_pfn;
void *node_bootmem_map;
unsigned long last_end_off;
unsigned long hint_idx;
struct list_head list;
} bootmem_data_t;
extern bootmem_data_t bootmem_node_data[];
#endif
struct pglist_data
include/linux/mmzone.h
/*
* The pg_data_t structure is used in machines with CONFIG_DISCONTIGMEM
* (mostly NUMA machines?) to denote a higher-level memory zone than the
* zone denotes.
*
* On NUMA machines, each NUMA node would have a pg_data_t to describe
* it's memory layout.
*
* Memory statistics and page replacement data structures are maintained on a
* per-zone basis.
*/
struct bootmem_data;
typedef struct pglist_data {
struct zone node_zones[MAX_NR_ZONES];
struct zonelist node_zonelists[MAX_ZONELISTS];
int nr_zones;
#ifdef CONFIG_FLAT_NODE_MEM_MAP /* means !SPARSEMEM */
struct page *node_mem_map;
#ifdef CONFIG_PAGE_EXTENSION
struct page_ext *node_page_ext;
#endif
#endif
#ifndef CONFIG_NO_BOOTMEM
struct bootmem_data *bdata;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_MEMORY_HOTPLUG
/*
* Must be held any time you expect node_start_pfn, node_present_pages
* or node_spanned_pages stay constant. Holding this will also
* guarantee that any pfn_valid() stays that way.
*
* pgdat_resize_lock() and pgdat_resize_unlock() are provided to
* manipulate node_size_lock without checking for CONFIG_MEMORY_HOTPLUG.
*
* Nests above zone->lock and zone->span_seqlock
*/
spinlock_t node_size_lock;
#endif
unsigned long node_start_pfn;
unsigned long node_present_pages; /* total number of physical pages */
unsigned long node_spanned_pages; /* total size of physical page
range, including holes */
int node_id;
wait_queue_head_t kswapd_wait;
wait_queue_head_t pfmemalloc_wait;
struct task_struct *kswapd; /* Protected by
mem_hotplug_begin/end() */
int kswapd_max_order;
enum zone_type classzone_idx;
#ifdef CONFIG_NUMA_BALANCING
/* Lock serializing the migrate rate limiting window */
spinlock_t numabalancing_migrate_lock;
/* Rate limiting time interval */
unsigned long numabalancing_migrate_next_window;
/* Number of pages migrated during the rate limiting time interval */
unsigned long numabalancing_migrate_nr_pages;
#endif
} pg_data_t;
contig_page_data 등
mm/bootmem.c
#ifndef CONFIG_NEED_MULTIPLE_NODES
struct pglist_data __refdata contig_page_data = {
.bdata = &bootmem_node_data[0]
};
EXPORT_SYMBOL(contig_page_data);
#endif
unsigned long max_low_pfn;
unsigned long min_low_pfn;
unsigned long max_pfn;
bootmem_data_t bootmem_node_data[MAX_NUMNODES] __initdata;
static struct list_head bdata_list __initdata = LIST_HEAD_INIT(bdata_list);
참고
- The NO_BOOTMEM patches | LWN.net
- mm: Use memblock interface instead of bootmem | LWN.net
- Understanding The Linux Virtual Memory Manager | Mel Gorman – 다운로드
- [Linux] bootmem 메모리 할당자 | F/OSS