<kernel v5.0>
Stack Overflow Protector
Stack Overflow 감지를 위해 커널은 다음과 같이 두 가지 방법을 지원한다.
- 스케줄 시마다 스택 종단의 매직값 체크
- 생성되는 태스크용 커널 스택마다 끝 부분에 매직 값을 기록하여 매 스케줄 시 유실 여부를 체크한다.
- 매 함수 호출시마다 스택 가드(canary) 설치 및 체크
- 함수의 호출 시마다 부트업 타임에 결정된 stack canary 값을 사용하여 스택에 가드를 설치하고, 함수가 종료되면 그 때 스택 가드의 유실 여부를 체크한다.
- 이 기능은 gcc의 도움을 받아 사용할 수 있다.
방법 1) 스케줄 시마다 스택 종단의 매직값 체크
STACK_END_MAGIC 값 설치
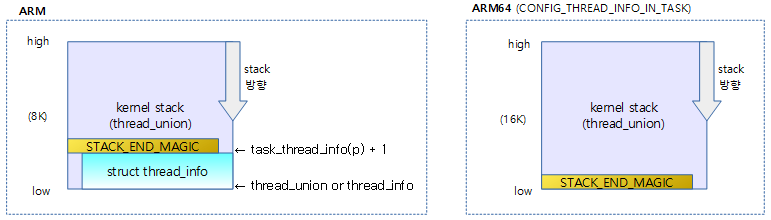
다음 그림과 같이 task를 fork할 때마다 태스크용 커널 스택이 만들어진다. 이 때 스택 overflow를 감지하기 위해 태스크용 커널 스택의 끝에 STACK_END_MAGIC 값을 설치한다.
set_task_stack_end_magic()
kernel/fork.c
void set_task_stack_end_magic(struct task_struct *tsk)
{
unsigned long *stackend;
stackend = end_of_stack(tsk);
*stackend = STACK_END_MAGIC; /* for overflow detection */
}
end_of_stack() – for ARM32
include/linux/sched/task_stack.h
/* * Return the address of the last usable long on the stack. * * When the stack grows down, this is just above the thread * info struct. Going any lower will corrupt the threadinfo. * * When the stack grows up, this is the highest address. * Beyond that position, we corrupt data on the next page. */
static inline unsigned long *end_of_stack(struct task_struct *p)
{
#ifdef CONFIG_STACK_GROWSUP
return (unsigned long *)((unsigned long)task_thread_info(p) + THREAD_SIZE) - 1;
#else
return (unsigned long *)(task_thread_info(p) + 1);
#endif
}
태스크용 커널 스택의 끝 위치를 반환한다. 스택 진행 방향에 따라 끝 위치가 달라지는데 ARM32와 ARM64의 경우 아래 방향으로 자라난다.
end_of_stack() – for ARM64
include/linux/sched/task_stack.h
#ifdef CONFIG_THREAD_INFO_IN_TASK
static inline unsigned long *end_of_stack(const struct task_struct *task)
{
return task->stack;
}
}
태스크용 커널 스택의 끝 위치를 반환한다.
- ARM64의 경우 태스크 구조체 내부에 thread_info 구조체를 포함시키도록 CONFIG_THREAD_INFO_IN_TASK 커널 옵션을 사용한다.
Stack Overflow 감지
스케줄 할때와 premption 포인트가 호출될 때마다 스택의 overflow 감지를 한다. 감지된 경우 panic 메시지를 출력한다.
schedule_debug()
kernel/sched/core.c
static inline void schedule_debug(struct task_struct *prev)
{
#ifdef CONFIG_SCHED_STACK_END_CHECK
if (task_stack_end_corrupted(prev))
panic("corrupted stack end detected inside scheduler\n");
#endif
(...생략...)
___might_sleep()
kernel/sched/core.c
void ___might_sleep(const char *file, int line, int preempt_offset)
{
(...생략...)
if (task_stack_end_corrupted(current))
printk(KERN_EMERG "Thread overran stack, or stack corrupted\n");
(...생략...)
task_stack_end_corrupted()
include/linux/sched/task_stack.h
#define task_stack_end_corrupted(task) \
(*(end_of_stack(task)) != STACK_END_MAGIC)
태스크의 커널 스택 마지막 위치에 STACK_END_MAGIC이 유실된지 여부를 반환한다.
2) 매 함수 호출시마다 스택 가드(canary) 설치 및 체크
stack 가드를 사용하기 전에 먼저 가드에 사용할 canary 값을 정해야 하는데 이 값은 부트업 타임에 결정한다.
stack canary 초기화
gcc가 지원하는 스택 프로텍터 기능에서 사용할 canary 값을 초기화한다.
- 함수의 진입시 stack에 canary 값을 기록하고 함수를 빠져나올 때 기록해 두었던 stack canary 값을 확인하여 stack 영역이 침범되었는지 확인할 수 있는 기능을 사용할 때 사용된다.
boot_init_stack_canary() – ARM32
arch/arm/include/asm/stackprotector.h
/* * Initialize the stackprotector canary value. * * NOTE: this must only be called from functions that never return, * and it must always be inlined. */
static __always_inline void boot_init_stack_canary(void)
{
unsigned long canary;
/* Try to get a semi random initial value. */
get_random_bytes(&canary, sizeof(canary));
canary ^= LINUX_VERSION_CODE;
current->stack_canary = canary;
#ifndef CONFIG_STACKPROTECTOR_PER_TASK
__stack_chk_guard = current->stack_canary;
#else
current_thread_info()->stack_canary = current->stack_canary;
#endif
}
stack overflow 검출을 위해 gcc가 지원하는 스택 프로텍터 기능에서 사용할 canary 값을 초기화한다.
- __always_inline:
- 100% inline화 할 수 있도록 컴파일러에 요청.
- current:
- 커널 스택의 마지막에 thread_info가 담기고 thread_info->task는 task_struct를 가리킨다. 즉 current->는 현재 task의 task_struct 구조체 정보를 가리킨다.
boot_init_stack_canary() – ARM64
arch/arm64/include/asm/stackprotector.h
/* * Initialize the stackprotector canary value. * * NOTE: this must only be called from functions that never return, * and it must always be inlined. */
static __always_inline void boot_init_stack_canary(void)
{
unsigned long canary;
/* Try to get a semi random initial value. */
get_random_bytes(&canary, sizeof(canary));
canary ^= LINUX_VERSION_CODE;
canary &= CANARY_MASK;
current->stack_canary = canary;
if (!IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_STACKPROTECTOR_PER_TASK))
__stack_chk_guard = current->stack_canary;
}
stack overflow 검출을 위해 gcc가 지원하는 스택 프로텍터 기능에서 사용할 canary 값을 초기화한다.
get_random_bytes()
drivers/char/random.c
void get_random_bytes(void *buf, int nbytes)
{
static void *previous;
warn_unseeded_randomness(&previous);
_get_random_bytes(buf, nbytes);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(get_random_bytes);
@buf에 @nbytes만큼 random 값을 만들어 온다.
_get_random_bytes()
drivers/char/random.c
/* * This function is the exported kernel interface. It returns some * number of good random numbers, suitable for key generation, seeding * TCP sequence numbers, etc. It does not rely on the hardware random * number generator. For random bytes direct from the hardware RNG * (when available), use get_random_bytes_arch(). In order to ensure * that the randomness provided by this function is okay, the function * wait_for_random_bytes() should be called and return 0 at least once * at any point prior. */
static void _get_random_bytes(void *buf, int nbytes)
{
__u8 tmp[CHACHA_BLOCK_SIZE] __aligned(4);
trace_get_random_bytes(nbytes, _RET_IP_);
while (nbytes >= CHACHA_BLOCK_SIZE) {
extract_crng(buf);
buf += CHACHA_BLOCK_SIZE;
nbytes -= CHACHA_BLOCK_SIZE;
}
if (nbytes > 0) {
extract_crng(tmp);
memcpy(buf, tmp, nbytes);
crng_backtrack_protect(tmp, nbytes);
} else
crng_backtrack_protect(tmp, CHACHA_BLOCK_SIZE);
memzero_explicit(tmp, sizeof(tmp));
}
@buf에 @nbytes만큼 random 값을 만들어 온다.
- 랜덤 값을 얻는 방법은 아키텍처 및 시스템마다 구현이 다르지만 특별한 방법을 사용하지 않는 경우 기본적으로 drivers/char/random.c를 사용한다.
스택 가드의 설치 및 체크
gcc에서 -fstack-protector-all 옵션을 사용할 때에만 동작하며 각 함수에서 canary 값을 기록하고 비교하는 루틴이 자동으로 추가된다.
- buffer를 overflow 시키는 공격 등을 통해 stack overflow를 시도 시 stack-smashing-detected 가 출력된 후 태스크가 중단된다.
- 보안 공격을 받아 변조된채 프로그램이 계속 진행되지 않도록 막을 수 있다.
참고
- “Strong” stack protection for GCC | LWN.net
- [gcc] SSP (stack-smashing protector) | F/OSS
- 스택침범(Stack Overflow)을 막는 스택보호 (Stack Protection) 컴파일 옵션 : -fstack-protector | Cloudrain
- 메모리 보호 기법 SSP(Stack Smashing Protector) | bbolmin
- TRACE_EVENT | 문c
- User stack vs Kernel stack | 문c