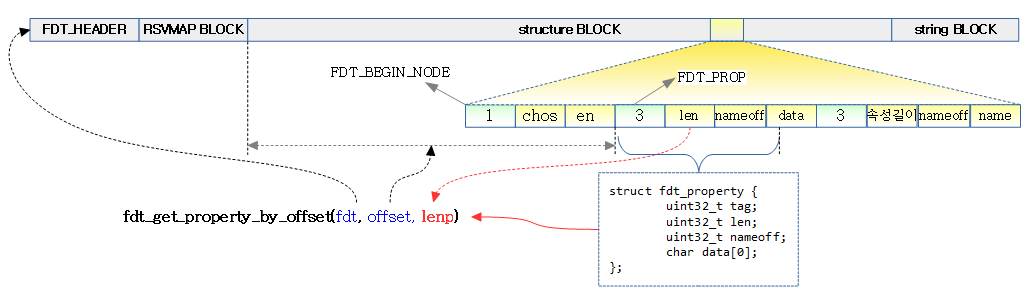
<kernel v5.0>
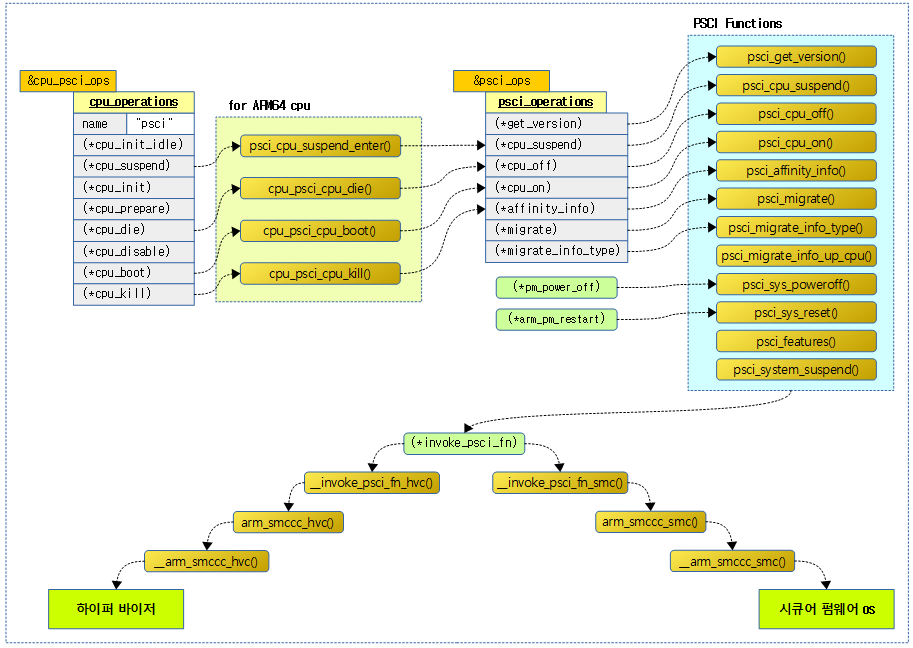
PSCI(Power State Coordination Interface)
절전 인터페이스로 psci가 선택되었을 때 사용 가능하다. psci 기능 호출 시 하이퍼 바이저 또는 시큐어 펌웨어(시큐어 모니터 또는 Trust Firmware)로 관련 요청을 전달하여 수행한다.
- 대부분 psci 방법을 사용하지만 일부는 spin-table 방식을 사용하고, 특정 회사의 경우 별도의 방법을 사용하기도 한다.
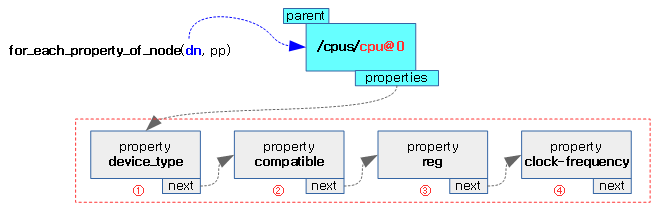
- cpu 노드의 enable-method 속성에서 지정한다.
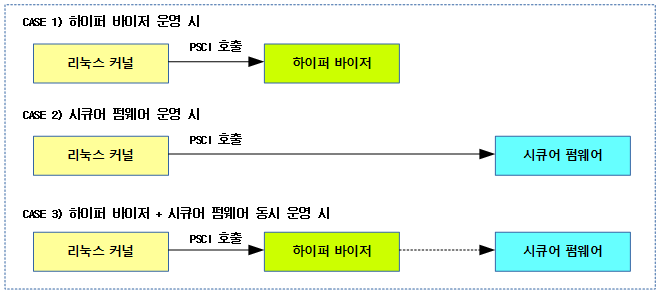
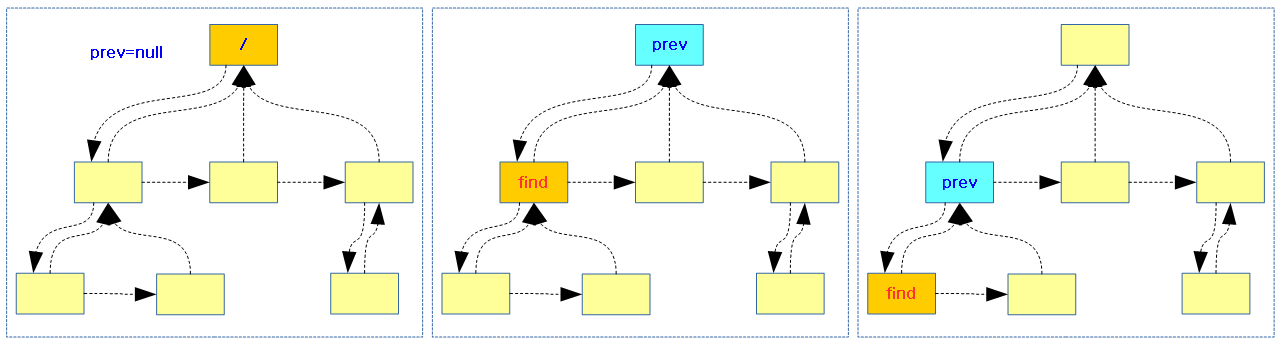
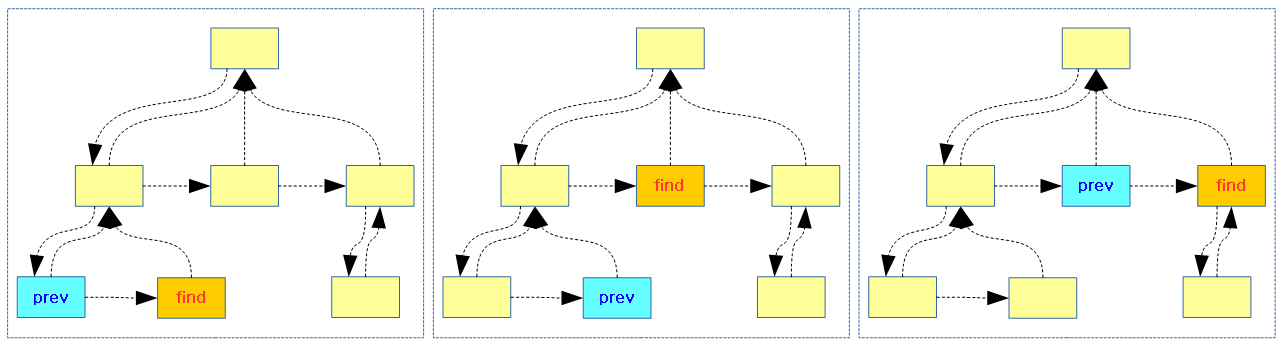
다음 그림은 리눅스 커널이 하이퍼 바이저 또는 시큐어 펌웨어로 psci 호출을 하는 모습을 3 가지 사례로 보여준다.
- 하이퍼 바이저와 시큐어 펌웨어가 동시에 동작하는 경우 커널은 하이퍼 바이저로 보낸다.
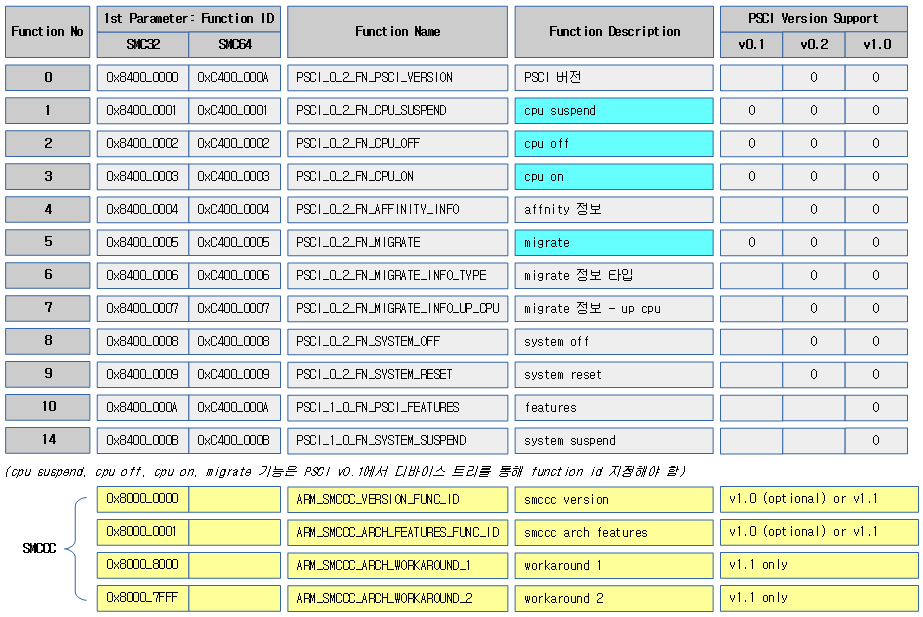
PSCI 기능들
다음은 PSCI 기능들이고 버전마다 지원되는 기능이 다르다.
- SMCCC에 관련한 기능도 4가지가 있다.
Function id
- PSCI v0.1
- 위의 기능들에 대해 펑션 id가 제각기 달라 디바이스 트리에서 id 값을 지정해주어야 한다.(implementation defined).
- PSCI v0.2
- 각 기능들에 대해 펑션 id가 고정되어 있다.
- PSCI v0.4
- PSCI v0.2에 두 개의 명령 features와 system suspend 기능을 추가하였다.
호출 후 결과 값들
/* PSCI return values (inclusive of all PSCI versions) */ #define PSCI_RET_SUCCESS 0 #define PSCI_RET_NOT_SUPPORTED -1 #define PSCI_RET_INVALID_PARAMS -2 #define PSCI_RET_DENIED -3 #define PSCI_RET_ALREADY_ON -4 #define PSCI_RET_ON_PENDING -5 #define PSCI_RET_INTERNAL_FAILURE -6 #define PSCI_RET_NOT_PRESENT -7 #define PSCI_RET_DISABLED -8 #define PSCI_RET_INVALID_ADDRESS -9
SMCCC(SMC Calling Convention)
SMC Calling Convention으로 커널이 시큐어 펌웨어 또는 하이퍼 바이저 콜 요청 시 사용할 SMC 및 HVC 호출 규약을 의미한다.
- SMCCC 버전은 1.0과 1.1이 사용되고 있다.
- 참고: arm64: Add SMCCC v1.1 support and CVE-2017-5715 | LWN.net
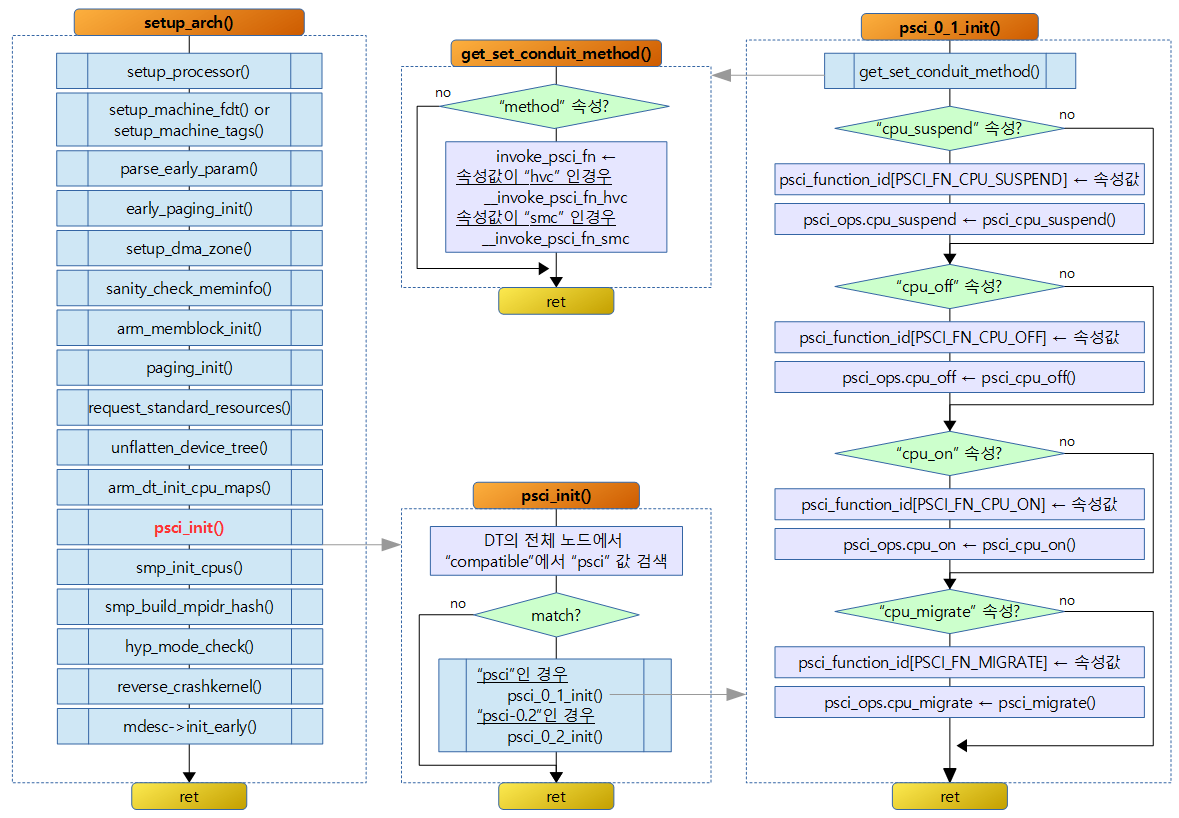
PSCI 초기화
SMP 아키텍처에서 PSCI 기능이 지원되는 경우 해당 초기화 함수를 동작시켜 각 기능에 해당하는 핸들러 함수를 연결해준다. 다음은 관련된 전역 변수이다.
- PSCI 동작 시 시큐어 모니터 콜을 호출할 때와 하이퍼 바이저 콜을 호출할 때 호출 함수를 지정한다.
- Secure Monitor Call
- 전역 invoke_psci_fn에 __invoke_psci_fn_smc()을 지정한다.
- Hyper Visor Call
- 전역 invoke_psci_fn에 __invoke_psci_fn_hvc() 함수를 가리키게 한다.
- Secure Monitor Call
- PSCI v0.1의 경우 기능 id를 지정하기 위해 디바이스 트리로부터 기능 별로 id를 읽어온다.
- 전역 psci_function_id[]에 device tree에서 읽은 속성 id 값이 기록된다.
- 전역 psci_ops의 각 핸들러 함수에 사용 가능한 PSCI 기능 함수를 가리키게 한다.
- psci v0.1에서는 디바이스 트리에서 지정한 함수만 핸들러 함수를 등록한다.
- psci v0.2 및 v1.0 에서는 전체 핸들러 함수를 등록한다.
psci_dt_init()
drivers/firmware/psci.c
int __init psci_dt_init(void)
{
struct device_node *np;
const struct of_device_id *matched_np;
psci_initcall_t init_fn;
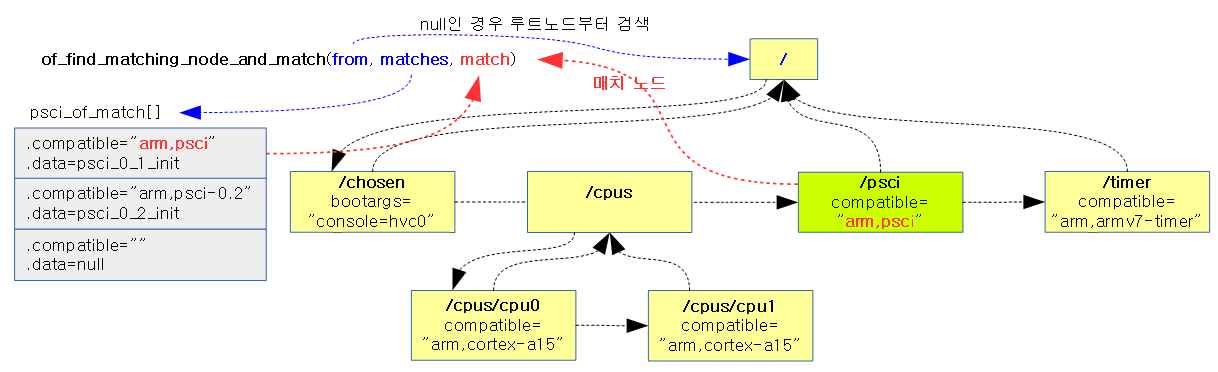
np = of_find_matching_node_and_match(NULL, psci_of_match, &matched_np);
if (!np || !of_device_is_available(np))
return -ENODEV;
init_fn = (psci_initcall_t)matched_np->data;
return init_fn(np);
}
PSCI 기능을 지원하기 위해 기능별로 시큐어 모니터 콜과 하이퍼 바이저 콜용 함수 준비한다.
- 코드 라인 7~9에서 device tree에서 psci_of_match[]에 있는 디바이스들 중 하나라도 일치되는 노드를 찾아 리턴하고 출력 인수 matched_up에 psci_of_match[]에 있는 of_device_id 구조체 엔트리 중 매치된 엔트리 포인터를 저장한다.
- 코드 라인 11~12에서 psci 버전에 해당하는 초기화 함수를 호출한다.
- psci_0_1_init() 또는 psci_0_2_init() 함수를 가리킨다.
psci_of_match
검색하고자 하는 디바이스 compatible 명과 초기화 함수가 담겨있다. psci v1.0의 경우 초기화 함수는 psci 0.2 초기화 함수를 그대로 사용한다.
drivers/firmware/psci.c
static const struct of_device_id psci_of_match[] __initconst = {
{ .compatible = "arm,psci", .data = psci_0_1_init},
{ .compatible = "arm,psci-0.2", .data = psci_0_2_init},
{ .compatible = "arm,psci-1.0", .data = psci_0_2_init},
{},
};
PSCI v0.1
아래 디바이스 트리는 psci v0.1을 사용하고, 이에 대응하는 초기화 함수는 psci_0_2_init() 이다.
arch/arm/boot/dts/xenvm-4.2.dts
*
* Based on ARM Ltd. Versatile Express CoreTile Express (single CPU)
* Cortex-A15 MPCore (V2P-CA15)
*
*/
/dts-v1/;
/ {
model = "XENVM-4.2";
compatible = "xen,xenvm-4.2", "xen,xenvm";
interrupt-parent = <&gic>;
#address-cells = <2>;
#size-cells = <2>;
chosen {
/* this field is going to be adjusted by the hypervisor */
bootargs = "console=hvc0 root=/dev/xvda";
};
cpus {
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
cpu@0 {
device_type = "cpu";
compatible = "arm,cortex-a15";
reg = <0>;
};
cpu@1 {
device_type = "cpu";
compatible = "arm,cortex-a15";
reg = <1>;
};
};
psci {
compatible = "arm,psci";
method = "hvc";
cpu_off = <1>;
cpu_on = <2>;
};
- psci 노드의 compatible이 “arm,psci” 디바이스를 사용한다고 되어 있다.
- “arm,psci”인 경우 초기화 함수는 psci_0_1_init() 함수이다.
다음 그림은 xennvm-4.2 시스템에서 hvc 방식의 PSCI 기능을 사용할 때의 모습을 보여준다.
psci_0_1_init()
drivers/firmware/psci.c
/* * PSCI < v0.2 get PSCI Function IDs via DT. */
static int psci_0_1_init(struct device_node *np)
{
u32 id;
int err;
err = get_set_conduit_method(np);
if (err)
goto out_put_node;
pr_info("Using PSCI v0.1 Function IDs from DT\n");
if (!of_property_read_u32(np, "cpu_suspend", &id)) {
psci_function_id[PSCI_FN_CPU_SUSPEND] = id;
psci_ops.cpu_suspend = psci_cpu_suspend;
}
if (!of_property_read_u32(np, "cpu_off", &id)) {
psci_function_id[PSCI_FN_CPU_OFF] = id;
psci_ops.cpu_off = psci_cpu_off;
}
if (!of_property_read_u32(np, "cpu_on", &id)) {
psci_function_id[PSCI_FN_CPU_ON] = id;
psci_ops.cpu_on = psci_cpu_on;
}
if (!of_property_read_u32(np, "migrate", &id)) {
psci_function_id[PSCI_FN_MIGRATE] = id;
psci_ops.migrate = psci_migrate;
}
out_put_node:
of_node_put(np);
return err;
}
psci v0.1용 호출 함수(svc 또는 hvc)와 기능들을 지정한다.
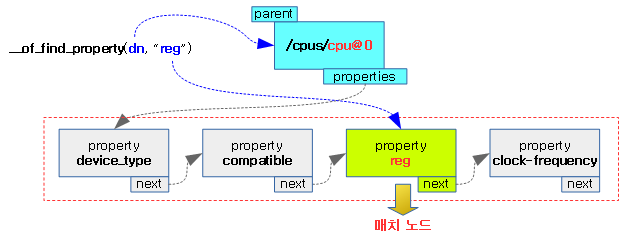
- 코드 라인 6~9에서 “method” 속성 값에 “hvc” 또는 “smc”가 지정되어야 한다.
- 코드 라인 13~31에서 아래 속성이 있는 경우 각각의 psci_function_id[]에 읽어들이 id 속성 값을 저장하고, psci_ops 구조체의 각각의 멤버변수에 해당 구동 함수를 연결한다.
- “cpu_suspend” 속성 -> psci_cpu_suspend()
- “cpu_off” 속성 -> psci_cpu_off()
- “cpu_on” 속성 -> psci_cpu_on()
- “cpu_migrate” 속성 -> psci_migrate()
다음 그림은 psci v0.1을 사용하는 경우의 호출 관계이다.
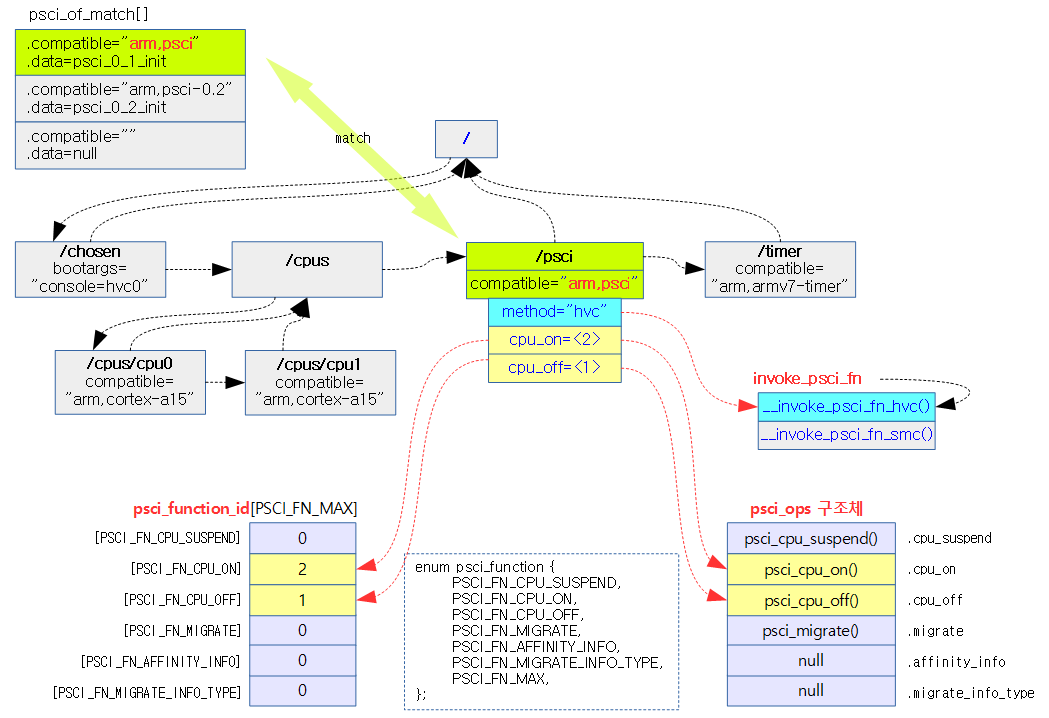
psci_function_id[] 배열
다음은 PSCI v0.1의 기능별로 고정되지 않은 펑션 id를 지정하는 psci_function_id[] 배열이다.
arch/arm/kernel/psci.c
enum psci_function {
PSCI_FN_CPU_SUSPEND,
PSCI_FN_CPU_ON,
PSCI_FN_CPU_OFF,
PSCI_FN_MIGRATE,
PSCI_FN_MAX,
};
static u32 psci_function_id[PSCI_FN_MAX];
get_set_conduit_method()
drivers/firmware/psci.c
static int get_set_conduit_method(struct device_node *np)
{
const char *method;
pr_info("probing for conduit method from DT.\n");
if (of_property_read_string(np, "method", &method)) {
pr_warn("missing \"method\" property\n");
return -ENXIO;
}
if (!strcmp("hvc", method)) {
set_conduit(PSCI_CONDUIT_HVC);
} else if (!strcmp("smc", method)) {
set_conduit(PSCI_CONDUIT_SMC);
} else {
pr_warn("invalid \"method\" property: %s\n", method);
return -EINVAL;
}
return 0;
}
psci 노드에 “method” 속성이 발견되면 “hvc” 및 “smc” 속성 값에 대해서는 전역 invoke_psci_fn에 각 함수를 연결시키고 그렇지 않은 경우 에러로 리턴한다.
- 코드 라인 7~10에서 노드에 “method” 속성이 없는 경우 경고 메시지를 출력하고 에러를 리턴한다.
- 코드 라인 12~13에서 속성 값이 “hvc”인 경우 hvc용 psci 호출 함수를 지정한다.
- 코드 라인 14~19에서 속성 값이 “smc”인 경우 smc용 psci 호출 함수를 지정한다. 그렇지 않은 경우 경고 메시지를 출력한다.
set_conduit()
drivers/firmware/psci.c
static void set_conduit(enum psci_conduit conduit)
{
switch (conduit) {
case PSCI_CONDUIT_HVC:
invoke_psci_fn = __invoke_psci_fn_hvc;
break;
case PSCI_CONDUIT_SMC:
invoke_psci_fn = __invoke_psci_fn_smc;
break;
default:
WARN(1, "Unexpected PSCI conduit %d\n", conduit);
}
psci_ops.conduit = conduit;
}
요청 @conduit에 따라 psci 호출 함수를 지정한다.
PSCI v0.2 이상 (include v1.0)
아래 broadcom 사의 northstar2 시스템에서 PSCI 1.0을 사용하고 이에 대응하는 초기화 함수는 psci_0_2_init() 이다.
arch/arm64/boot/dts/broadcom/northstar2/ns2.dtsi
psci {
compatible = "arm,psci-1.0";
method = "smc";
};
psci_0_2_init()
drivers/firmware/psci.c
/* * PSCI init function for PSCI versions >=0.2 * * Probe based on PSCI PSCI_VERSION function */
static int __init psci_0_2_init(struct device_node *np)
{
int err;
err = get_set_conduit_method(np);
if (err)
goto out_put_node;
/*
* Starting with v0.2, the PSCI specification introduced a call
* (PSCI_VERSION) that allows probing the firmware version, so
* that PSCI function IDs and version specific initialization
* can be carried out according to the specific version reported
* by firmware
*/
err = psci_probe();
out_put_node:
of_node_put(np);
return err;
}
psci v0.2 및 psci v1.0용 호출 함수(svc 또는 hvc)와 기능들을 지정한다.
- 코드 라인 5~8에서 “method” 속성 값에 “hvc” 또는 “smc”가 지정되어야 한다.
- 코드 라인 16에서 psci 버전 및 기능별로 고정된 호출 함수를 지정한다.
다음은 psci v1.0이 디텍트되어 사용됨을 보여주는 출력 로그이다.
[ 0.000000] psci: probing for conduit method from DT. [ 0.000000] psci: PSCIv1.0 detected in firmware. [ 0.000000] psci: Using standard PSCI v0.2 function IDs [ 0.000000] psci: MIGRATE_INFO_TYPE not supported.
psci_probe()
drivers/firmware/psci.c
/* * Probe function for PSCI firmware versions >= 0.2 */
static int __init psci_probe(void)
{
u32 ver = psci_get_version();
pr_info("PSCIv%d.%d detected in firmware.\n",
PSCI_VERSION_MAJOR(ver),
PSCI_VERSION_MINOR(ver));
if (PSCI_VERSION_MAJOR(ver) == 0 && PSCI_VERSION_MINOR(ver) < 2) {
pr_err("Conflicting PSCI version detected.\n");
return -EINVAL;
}
psci_0_2_set_functions();
psci_init_migrate();
if (PSCI_VERSION_MAJOR(ver) >= 1) {
psci_init_smccc();
psci_init_cpu_suspend();
psci_init_system_suspend();
}
return 0;
}
psci 버전 및 기능별로 고정된 호출 함수를 지정한다.
- 코드 라인 3~12에서 psci 버전을 알아와서 출력하고 psci v0.2 보다 낮은 경우 -EINVAL 에러로 함수를 빠져나간다.
- 코드 라인 14에서 psci v0.2를 위한 기능별로 호출 함수를 지정한다.
- 코드 라인 16에서 트러스트 펌웨어 OS가 cpu off 시 migration을 지원하는지 여부를 알아와 출력한다.
- 특정 cpu를 off 시 트러스트 펌웨어 OS가 동작하지 못하는 경우를 위해 동작 중인 cpu를 저장해두어야 한다.
- 코드 라인 18~22에서 psci v1.0 이상인 경우 smccc 버전을 알아오고, suspend 기능들을 준비한다.
- SMCCC 버전 기능이 지원되는 경우 SMCCC SMCC 버전을 알아와서 v1.1 여부를 기록한다.
psci_0_2_set_functions()
drivers/firmware/psci.c
static void __init psci_0_2_set_functions(void)
{
pr_info("Using standard PSCI v0.2 function IDs\n");
psci_ops.get_version = psci_get_version;
psci_function_id[PSCI_FN_CPU_SUSPEND] =
PSCI_FN_NATIVE(0_2, CPU_SUSPEND);
psci_ops.cpu_suspend = psci_cpu_suspend;
psci_function_id[PSCI_FN_CPU_OFF] = PSCI_0_2_FN_CPU_OFF;
psci_ops.cpu_off = psci_cpu_off;
psci_function_id[PSCI_FN_CPU_ON] = PSCI_FN_NATIVE(0_2, CPU_ON);
psci_ops.cpu_on = psci_cpu_on;
psci_function_id[PSCI_FN_MIGRATE] = PSCI_FN_NATIVE(0_2, MIGRATE);
psci_ops.migrate = psci_migrate;
psci_ops.affinity_info = psci_affinity_info;
psci_ops.migrate_info_type = psci_migrate_info_type;
arm_pm_restart = psci_sys_reset;
pm_power_off = psci_sys_poweroff;
}
psci v0.2를 위한 기능별로 호출 함수를 지정한다.
- psci v0.1 호환을 위해 cpu_suspend, cpu_off, cpu_on, migrate 등의 4 가지 기능의 경우 해당 기능 id 값을 지정한다.
- 각 기능에 대한 호출 함수를 psci_ops의 각 콜백 함수에 지정한다.
psci_init_migrate()
drivers/firmware/psci.c
/* * Detect the presence of a resident Trusted OS which may cause CPU_OFF to * return DENIED (which would be fatal). */
static void __init psci_init_migrate(void)
{
unsigned long cpuid;
int type, cpu = -1;
type = psci_ops.migrate_info_type();
if (type == PSCI_0_2_TOS_MP) {
pr_info("Trusted OS migration not required\n");
return;
}
if (type == PSCI_RET_NOT_SUPPORTED) {
pr_info("MIGRATE_INFO_TYPE not supported.\n");
return;
}
if (type != PSCI_0_2_TOS_UP_MIGRATE &&
type != PSCI_0_2_TOS_UP_NO_MIGRATE) {
pr_err("MIGRATE_INFO_TYPE returned unknown type (%d)\n", type);
return;
}
cpuid = psci_migrate_info_up_cpu();
if (cpuid & ~MPIDR_HWID_BITMASK) {
pr_warn("MIGRATE_INFO_UP_CPU reported invalid physical ID (0x%lx)\n",
cpuid);
return;
}
cpu = get_logical_index(cpuid);
resident_cpu = cpu >= 0 ? cpu : -1;
pr_info("Trusted OS resident on physical CPU 0x%lx\n", cpuid);
}
트러스트 펌웨어 OS가 cpu off 시 migration을 지원하는지 여부를 알아와 출력하고, 동작 중인 트러스트 펌웨어 OS의 cpu를 전역 변수 resident_cpu에 기억해둔다.
- 코드 라인 6에서 migrate info type 기능을 호출하여 type을 알아온다.
- 코드 라인 8~11에서 트러스트 펌웨어 OS가 mp를 지원하여 커널에서 migration 요청을 할 필요 없으므로 함수를 빠져나간다.
- 코드 라인 13~16에서 트러스트 펌웨어 OS가 migration을 지원하지 않으므로 에러 메시지를 출력하고 함수를 빠져나간다.
- 코드 라인 18~22에서 트러스트 펌웨어 OS가 알려지지 않은 타입을 반환한 경우 경고 메시지를 출력한다.
- 코드 라인 24~29에서트러스트 펌웨어 OS가 동작하는 물리 cpu 번호를 알아온다.
- 코드 라인 31~34에서 트러스트 펌웨어 OS가 동작하는 논리 cpu 번호를 알아내서 출력한다.
PSCI migrate 타입
커널에서 특정 cpu를 off하기 전에 트러스트 펌웨어 OS의 migration 지원 여부이다. 오렌지 색 항목은 cpu의 off가 가능하다.
- PSCI_0_2_TOS_UP_MIGRATE(0)
- 트러스트 펌웨어 OS가 하나의 코어에서 동작하지만 migration 요청을 지원한다.
- 해당 cpu를 off할 때 트러스트 펌웨어 OS도 해당 cpu에서 동작 중인 경우 cpu를 off하기 전에 migration을 요청해야 한다.
- PSCI_0_2_TOS_UP_NO_MIGRATE(1)
- 트러스트 펌웨어 OS가 하나의 특정 코어에 고정되어 동작하므로 migration 요청을 하면 안된다.
- PSCI_0_2_TOS_MP(2)
- 트러스트 펌웨어 OS가 멀티 코어 시스템에서 동작 가능하므로 migration을 할 필요가 없다.
- PSCI_RET_NOT_SUPPORTED(-1)
- 트러스트 펌웨어 OS가 migration 요청을 지원하지 않는다.
psci_init_smccc()
drivers/firmware/psci.c
static void __init psci_init_smccc(void)
{
u32 ver = ARM_SMCCC_VERSION_1_0;
int feature;
feature = psci_features(ARM_SMCCC_VERSION_FUNC_ID);
if (feature != PSCI_RET_NOT_SUPPORTED) {
u32 ret;
ret = invoke_psci_fn(ARM_SMCCC_VERSION_FUNC_ID, 0, 0, 0);
if (ret == ARM_SMCCC_VERSION_1_1) {
psci_ops.smccc_version = SMCCC_VERSION_1_1;
ver = ret;
}
}
/*
* Conveniently, the SMCCC and PSCI versions are encoded the
* same way. No, this isn't accidental.
*/
pr_info("SMC Calling Convention v%d.%d\n",
PSCI_VERSION_MAJOR(ver), PSCI_VERSION_MINOR(ver));
}
SMCCC 버전 기능이 지원되는 경우 SMCCC SMCC 버전을 알아와서 v1.1 여부를 기록한다.
- Cortex A57/A72인 경우 SMCCC 버전이 1.1이면 BP hardening workaround 처리를 위해 psci 호출을 수행해야 한다.
- 참고
psci_init_cpu_suspend()
drivers/firmware/psci.c
static void __init psci_init_cpu_suspend(void)
{
int feature = psci_features(psci_function_id[PSCI_FN_CPU_SUSPEND]);
if (feature != PSCI_RET_NOT_SUPPORTED)
psci_cpu_suspend_feature = feature;
}
cpu suspend 기능이 지원되는지 여부를 알아온다.
psci_init_system_suspend()
drivers/firmware/psci.c
static void __init psci_init_system_suspend(void)
{
int ret;
if (!IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_SUSPEND))
return;
ret = psci_features(PSCI_FN_NATIVE(1_0, SYSTEM_SUSPEND));
if (ret != PSCI_RET_NOT_SUPPORTED)
suspend_set_ops(&psci_suspend_ops);
}
system suspend 기능이 지원되는지 여부를 알아와서 절전 기능에 대한 ops를 psci 방식으로 연결한다.
suspend_set_ops()
kernel/power/suspend.c
/**
* suspend_set_ops - Set the global suspend method table.
* @ops: Suspend operations to use.
*/
void suspend_set_ops(const struct platform_suspend_ops *ops)
{
lock_system_sleep();
suspend_ops = ops;
if (valid_state(PM_SUSPEND_STANDBY)) {
mem_sleep_states[PM_SUSPEND_STANDBY] = mem_sleep_labels[PM_SUSPEND_STANDBY];
pm_states[PM_SUSPEND_STANDBY] = pm_labels[PM_SUSPEND_STANDBY];
if (mem_sleep_default == PM_SUSPEND_STANDBY)
mem_sleep_current = PM_SUSPEND_STANDBY;
}
if (valid_state(PM_SUSPEND_MEM)) {
mem_sleep_states[PM_SUSPEND_MEM] = mem_sleep_labels[PM_SUSPEND_MEM];
if (mem_sleep_default >= PM_SUSPEND_MEM)
mem_sleep_current = PM_SUSPEND_MEM;
}
unlock_system_sleep();
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(suspend_set_ops);
PSCI 기능 호출
psci_get_version()
drivers/firmware/psci.c
static u32 psci_get_version(void)
{
return invoke_psci_fn(PSCI_0_2_FN_PSCI_VERSION, 0, 0, 0);
}
psci 버전을 알아온다. 결과 값의 하위 16비트에 minor 버전이 담기고, 나머지에 major 버전이 담겨있다.
psci_cpu_suspend()
drivers/firmware/psci.c
static int psci_cpu_suspend(u32 state, unsigned long entry_point)
{
int err;
u32 fn;
fn = psci_function_id[PSCI_FN_CPU_SUSPEND];
err = invoke_psci_fn(fn, state, entry_point, 0);
return psci_to_linux_errno(err);
}
cpu를 절전 모드로 변경하기 위해 psci 호출을 수행한다.
psci_cpu_off()
drivers/firmware/psci.c
static int psci_cpu_off(u32 state)
{
int err;
u32 fn;
fn = psci_function_id[PSCI_FN_CPU_OFF];
err = invoke_psci_fn(fn, state, 0, 0);
return psci_to_linux_errno(err);
}
cpu를 off하기 위해 psci 호출을 수행한다.
psci_cpu_on()
drivers/firmware/psci.c
static int psci_cpu_on(unsigned long cpuid, unsigned long entry_point)
{
int err;
u32 fn;
fn = psci_function_id[PSCI_FN_CPU_ON];
err = invoke_psci_fn(fn, cpuid, entry_point, 0);
return psci_to_linux_errno(err);
}
cpu를 on하기 위해 psci 호출을 수행한다.
psci_affinity_info()
drivers/firmware/psci.c
static int psci_affinity_info(unsigned long target_affinity,
unsigned long lowest_affinity_level)
{
return invoke_psci_fn(PSCI_FN_NATIVE(0_2, AFFINITY_INFO),
target_affinity, lowest_affinity_level, 0);
}
cpu의 affinity 정보를 알아오기 위해 psci 호출을 수행한다.
psci_migrate()
drivers/firmware/psci.c
static int psci_migrate(unsigned long cpuid)
{
int err;
u32 fn;
fn = psci_function_id[PSCI_FN_MIGRATE];
err = invoke_psci_fn(fn, cpuid, 0, 0);
return psci_to_linux_errno(err);
}
시큐어 펌웨어를 다른 cpu로 migration하기 위해 psci 호출을 수행한다.
psci_migrate_info_type()
drivers/firmware/psci.c
static int psci_migrate_info_type(void)
{
return invoke_psci_fn(PSCI_0_2_FN_MIGRATE_INFO_TYPE, 0, 0, 0);
}
시큐어 펌웨어의 cpu migration 타입 정보를 알아오기 위해 psci 호출을 수행한다.
psci_migrate_info_up_cpu()
drivers/firmware/psci.c
static unsigned long psci_migrate_info_up_cpu(void)
{
return invoke_psci_fn(PSCI_FN_NATIVE(0_2, MIGRATE_INFO_UP_CPU),
0, 0, 0);
}
시큐어 펌웨어가 싱글 코어에서만 동작할 때 현재 동작 중인 물리 cpu 번호를 알아오기 위해 psci 호출을 수행한다.
psci_sys_poweroff()
drivers/firmware/psci.c
static void psci_sys_poweroff(void)
{
invoke_psci_fn(PSCI_0_2_FN_SYSTEM_OFF, 0, 0, 0);
}
시스템을 off 하기 위해 psci 호출을 수행한다.
psci_sys_reset()
drivers/firmware/psci.c
static void psci_sys_reset(enum reboot_mode reboot_mode, const char *cmd)
{
invoke_psci_fn(PSCI_0_2_FN_SYSTEM_RESET, 0, 0, 0);
}
시스템을 reset 하기 위해 psci 호출을 수행한다.
psci_features()
drivers/firmware/psci.c
static int __init psci_features(u32 psci_func_id)
{
return invoke_psci_fn(PSCI_1_0_FN_PSCI_FEATURES,
psci_func_id, 0, 0);
}
요청한 psci 기능이 지원되는지 여부를 알아온다.
psci_system_suspend()
drivers/firmware/psci.c
static int psci_system_suspend(unsigned long unused)
{
return invoke_psci_fn(PSCI_FN_NATIVE(1_0, SYSTEM_SUSPEND),
__pa_symbol(cpu_resume), 0, 0);
}
시스템을 suspend 하기 위해 psci 호출을 수행한다.
PSCI 호출 API
invoke_psci_fn()
typedef unsigned long (psci_fn)(unsigned long, unsigned long,
unsigned long, unsigned long);
static psci_fn *invoke_psci_fn;
위의 전역 펑션콜용 변수에는 hvc 및 smc 호출을 위한 함수가 지정된다.
- 첫 번째 인자에는 function id가 지정되고 나머지엔 3 개의 인자가 전달된다.
HVC 호출
__invoke_psci_fn_hvc()
drivers/firmware/psci.c
static unsigned long __invoke_psci_fn_hvc(unsigned long function_id,
unsigned long arg0, unsigned long arg1,
unsigned long arg2)
{
struct arm_smccc_res res;
arm_smccc_hvc(function_id, arg0, arg1, arg2, 0, 0, 0, 0, &res);
return res.a0;
}
smccc를 통해 하이퍼바이저를 위해 psci 기능을 호출하는데 8개의 인자를 전달할 때 나머지 4개는 0으로 채워 전달한다.
arm_smccc_hvc()
include/linux/arm-smccc.h
#define arm_smccc_hvc(...) __arm_smccc_hvc(__VA_ARGS__, NULL)
__arm_smccc_hvc()
include/linux/arm-smccc.h
/** * __arm_smccc_hvc() - make HVC calls * @a0-a7: arguments passed in registers 0 to 7 * @res: result values from registers 0 to 3 * @quirk: points to an arm_smccc_quirk, or NULL when no quirks are required. * * This function is used to make HVC calls following SMC Calling * Convention. The content of the supplied param are copied to registers 0 * to 7 prior to the HVC instruction. The return values are updated with * the content from register 0 to 3 on return from the HVC instruction. An * optional quirk structure provides vendor specific behavior. */
asmlinkage void __arm_smccc_hvc(unsigned long a0, unsigned long a1,
unsigned long a2, unsigned long a3, unsigned long a4,
unsigned long a5, unsigned long a6, unsigned long a7,
struct arm_smccc_res *res, struct arm_smccc_quirk *quirk);
arch/arm64/kernel/smccc-call.S
/* * void arm_smccc_hvc(unsigned long a0, unsigned long a1, unsigned long a2, * unsigned long a3, unsigned long a4, unsigned long a5, * unsigned long a6, unsigned long a7, struct arm_smccc_res *res, * struct arm_smccc_quirk *quirk) */
ENTRY(__arm_smccc_hvc)
SMCCC hvc
ENDPROC(__arm_smccc_hvc)
EXPORT_SYMBOL(__arm_smccc_hvc)
SMCCC 매크로
.macro SMCCC instr
.cfi_startproc
\instr #0
ldr x4, [sp]
stp x0, x1, [x4, #ARM_SMCCC_RES_X0_OFFS]
stp x2, x3, [x4, #ARM_SMCCC_RES_X2_OFFS]
ldr x4, [sp, #8]
cbz x4, 1f /* no quirk structure */
ldr x9, [x4, #ARM_SMCCC_QUIRK_ID_OFFS]
cmp x9, #ARM_SMCCC_QUIRK_QCOM_A6
b.ne 1f
str x6, [x4, ARM_SMCCC_QUIRK_STATE_OFFS]
1: ret
.cfi_endproc
.endm
SMC 호출
__invoke_psci_fn_smc()
drivers/firmware/psci.c
static unsigned long __invoke_psci_fn_smc(unsigned long function_id,
unsigned long arg0, unsigned long arg1,
unsigned long arg2)
{
struct arm_smccc_res res;
arm_smccc_smc(function_id, arg0, arg1, arg2, 0, 0, 0, 0, &res);
return res.a0;
}
smccc를 통해 시큐어 펌웨어를 위해 psci 기능을 호출하는데 8개의 인자를 전달할 때 나머지 4개는 0으로 채워 전달한다.
arm_smccc_smc()
include/linux/arm-smccc.h
#define arm_smccc_smc(...) __arm_smccc_smc(__VA_ARGS__, NULL)
__arm_smccc_smc()
include/linux/arm-smccc.h
/** * __arm_smccc_smc() - make SMC calls * @a0-a7: arguments passed in registers 0 to 7 * @res: result values from registers 0 to 3 * @quirk: points to an arm_smccc_quirk, or NULL when no quirks are required. * * This function is used to make SMC calls following SMC Calling Convention. * The content of the supplied param are copied to registers 0 to 7 prior * to the SMC instruction. The return values are updated with the content * from register 0 to 3 on return from the SMC instruction. An optional * quirk structure provides vendor specific behavior. */
asmlinkage void __arm_smccc_smc(unsigned long a0, unsigned long a1,
unsigned long a2, unsigned long a3, unsigned long a4,
unsigned long a5, unsigned long a6, unsigned long a7,
struct arm_smccc_res *res, struct arm_smccc_quirk *quirk);
arch/arm64/kernel/smccc-call.S
/* * void arm_smccc_smc(unsigned long a0, unsigned long a1, unsigned long a2, * unsigned long a3, unsigned long a4, unsigned long a5, * unsigned long a6, unsigned long a7, struct arm_smccc_res *res, * struct arm_smccc_quirk *quirk) */
ENTRY(__arm_smccc_smc)
SMCCC smc
ENDPROC(__arm_smccc_smc)
EXPORT_SYMBOL(__arm_smccc_smc)
참고
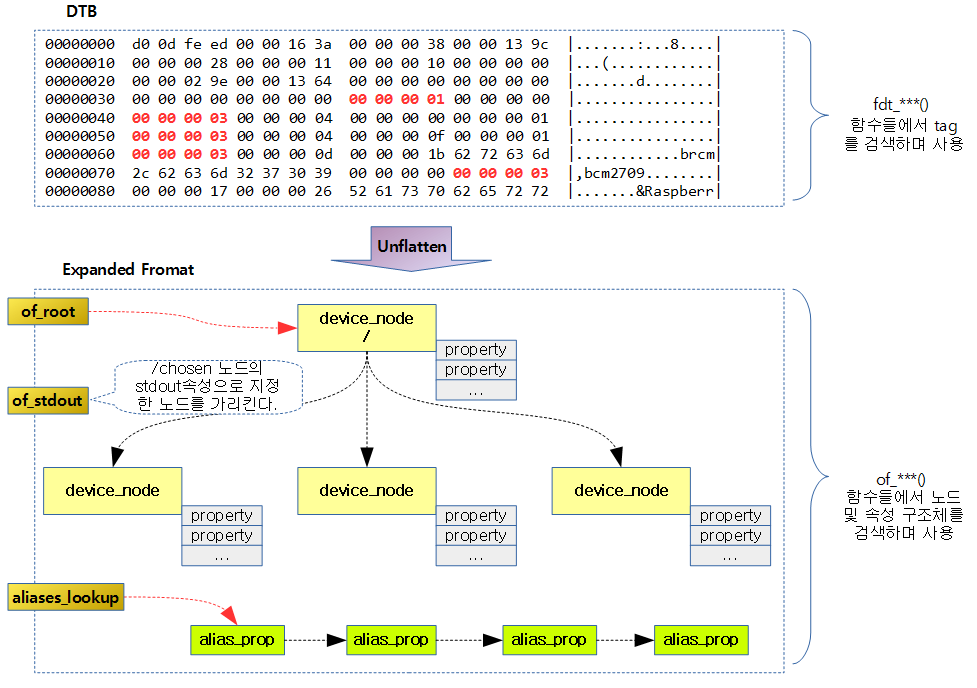
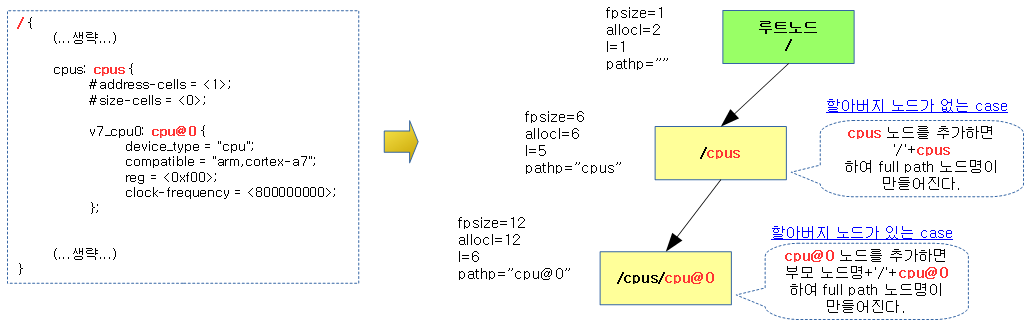
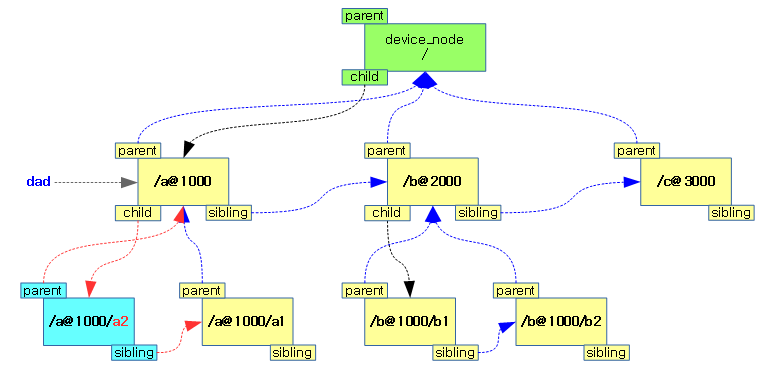
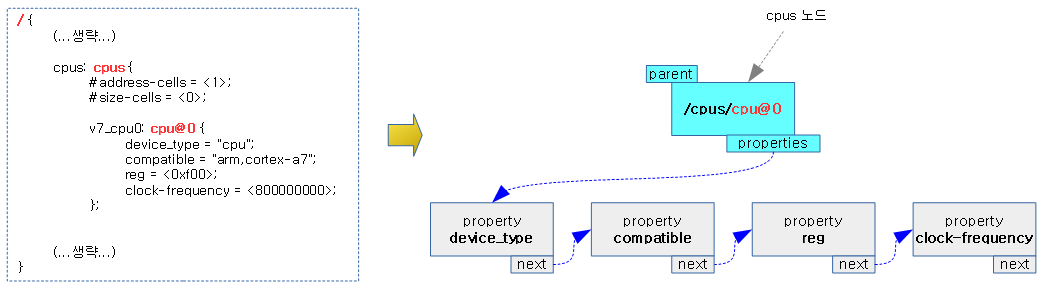
- DTB (of API) | 문c
- POWER STATE COORDINATION INTERFACE (PSCI) | arm – 다운로드
- Firmware interfaces for mitigating cache speculation vulnerabilities System Software on Arm Developer (2018) | arm – 다운로드 pdf
- SMC CALLING CONVENTION System Software on ARM® Platforms (2016) | arm – 다운로드 pdf
- Power State Coordination Interface (PSCI) | kernel.org