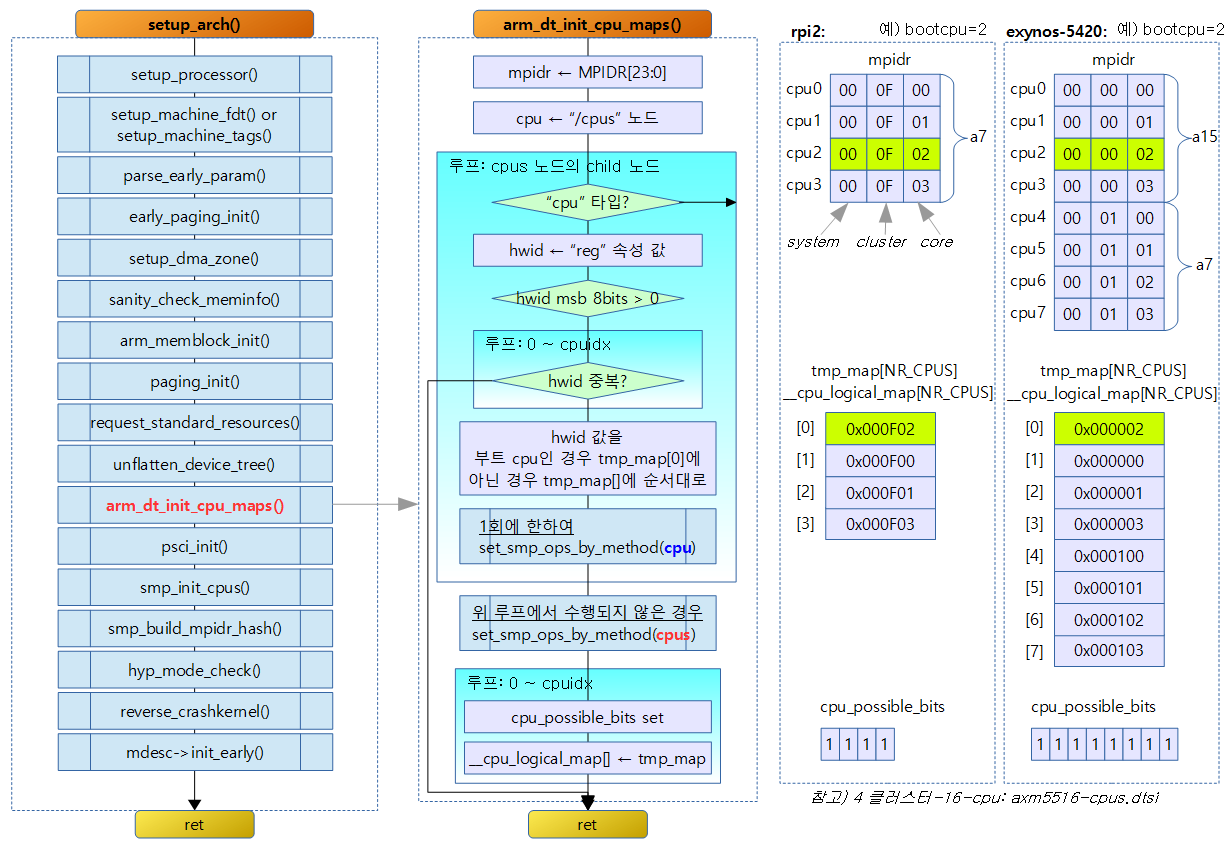
smp_setup_processor_id()에서 로지컬 cpu id 배열을 구성하였었는데 이 함수에서 다시 DTB와 비교하여 재 구성하고 특정 SMP 아키텍처의 SMP 핸들러가 준비되어 있는 경우 전역 smp_ops를 설정 한다.
- “/cpu” 노드에서 읽은 reg 속성 값 순서대로 로지컬 맵을 구성하되 예외로 현재 부팅된 물리 cpu id는 로지컬 cpu id 0으로 구성한다.
arm_dt_init_cpu_maps()
arch/arm/kernel/devtree.c
/*
* arm_dt_init_cpu_maps - Function retrieves cpu nodes from the device tree
* and builds the cpu logical map array containing MPIDR values related to
* logical cpus
*
* Updates the cpu possible mask with the number of parsed cpu nodes
*/
void __init arm_dt_init_cpu_maps(void)
{
/*
* Temp logical map is initialized with UINT_MAX values that are
* considered invalid logical map entries since the logical map must
* contain a list of MPIDR[23:0] values where MPIDR[31:24] must
* read as 0.
*/
struct device_node *cpu, *cpus;
int found_method = 0;
u32 i, j, cpuidx = 1;
u32 mpidr = is_smp() ? read_cpuid_mpidr() & MPIDR_HWID_BITMASK : 0;
u32 tmp_map[NR_CPUS] = { [0 ... NR_CPUS-1] = MPIDR_INVALID };
bool bootcpu_valid = false;
cpus = of_find_node_by_path("/cpus");
if (!cpus)
return;
for_each_child_of_node(cpus, cpu) {
u32 hwid;
if (of_node_cmp(cpu->type, "cpu"))
continue;
pr_debug(" * %s...\n", cpu->full_name);
/*
* A device tree containing CPU nodes with missing "reg"
* properties is considered invalid to build the
* cpu_logical_map.
*/
if (of_property_read_u32(cpu, "reg", &hwid)) {
pr_debug(" * %s missing reg property\n",
cpu->full_name);
return;
}
/*
* 8 MSBs must be set to 0 in the DT since the reg property
* defines the MPIDR[23:0].
*/
if (hwid & ~MPIDR_HWID_BITMASK)
return;
/*
* Duplicate MPIDRs are a recipe for disaster.
* Scan all initialized entries and check for
* duplicates. If any is found just bail out.
* temp values were initialized to UINT_MAX
* to avoid matching valid MPIDR[23:0] values.
*/
for (j = 0; j < cpuidx; j++)
if (WARN(tmp_map[j] == hwid, "Duplicate /cpu reg "
"properties in the DT\n"))
return;
/*
* Build a stashed array of MPIDR values. Numbering scheme
* requires that if detected the boot CPU must be assigned
* logical id 0. Other CPUs get sequential indexes starting
* from 1. If a CPU node with a reg property matching the
* boot CPU MPIDR is detected, this is recorded so that the
* logical map built from DT is validated and can be used
* to override the map created in smp_setup_processor_id().
*/
if (hwid == mpidr) {
i = 0;
bootcpu_valid = true;
} else {
i = cpuidx++;
}
if (WARN(cpuidx > nr_cpu_ids, "DT /cpu %u nodes greater than "
"max cores %u, capping them\n",
cpuidx, nr_cpu_ids)) {
cpuidx = nr_cpu_ids;
break;
}
tmp_map[i] = hwid;
if (!found_method)
found_method = set_smp_ops_by_method(cpu);
}
/*
* Fallback to an enable-method in the cpus node if nothing found in
* a cpu node.
*/
if (!found_method)
set_smp_ops_by_method(cpus);
if (!bootcpu_valid) {
pr_warn("DT missing boot CPU MPIDR[23:0], fall back to default cpu_logical_map\n");
return;
}
/*
* Since the boot CPU node contains proper data, and all nodes have
* a reg property, the DT CPU list can be considered valid and the
* logical map created in smp_setup_processor_id() can be overridden
*/
for (i = 0; i < cpuidx; i++) {
set_cpu_possible(i, true);
cpu_logical_map(i) = tmp_map[i];
pr_debug("cpu logical map 0x%x\n", cpu_logical_map(i));
}
}
- u32 mpidr = is_smp() ? read_cpuid_mpidr() & MPIDR_HWID_BITMASK : 0;
- mpidr에 cpu 물리 id를 읽어온다.
- SMP의 경우 MPIDR의 lsb 24bits를 읽어오고 UP의 경우 0으로 한다.
- MPIDR_HWID_BITMASK=0xFFFFFF
- mpidr에 cpu 물리 id를 읽어온다.
- u32 tmp_map[NR_CPUS] = { [0 … NR_CPUS-1] = MPIDR_INVALID };
- 임시 tmp_map[]의 각 값을 MPIDR_INVALID(0xff00_0000)로 초기화한다.
- cpus = of_find_node_by_path(“/cpus”);
- “/cpus” 노드를 찾아 발견되지 않으면 함수를 빠져나간다.
- for_each_child_of_node(cpus, cpu) {
- “/cpus” 노드의 서브 노드들로 루프를 돈다.
- if (of_node_cmp(cpu->type, “cpu”)) continue;
- 노드 타입이 “cpu”가 아닌 경우 skip
- if (of_property_read_u32(cpu, “reg”, &hwid)) {
- “reg” 속성이 없는 경우 디버그 메시지를 출력하고 함수를 빠져나간다.
- if (hwid & ~MPIDR_HWID_BITMASK) return;
- hwid의 msb 8bits가 값이 있는 경우 함수를 빠져나간다.
- for (j = 0; j < cpuidx; j++) if (WARN(tmp_map[j] == hwid, “Duplicate /cpu reg properties in the DT\n”)) return;
- “/cpu” 노드의 reg 속성 값이 중복된 경우 에러 메시지를 출력하고 함수를 빠져나간다.
- if (hwid == mpidr) { i = 0; bootcpu_valid = true;
- DTB에서 읽은 hwid와 MPIDR[bit23:0] 값을 비교하여 같은 경우 현재 부팅되어 진행중인 물리 cpu인 경우 i=0, bootcpu_valid=true로 대입한다.
- } else { i = cpuidx++; }
- 매치되지 않으면 cpuidx를 1 증가시킨다.
- if (WARN(cpuidx > nr_cpu_ids, “DT /cpu %u nodes greater than max cores %u, capping them\n”, cpuidx, nr_cpu_ids)) { cpuidx = nr_cpu_ids; break; }
- cpuidx가 nr_cpu_ids를 초과한 경우 에러 메시지를 출력하고 cpuidx = nr_cpu_ids로 변경하고 루프를 빠져나간다.
- tmp_map[i] = hwid;
- tmp_map[i]에 물리 cpu id를 대입한다.
- if (!found_method) found_method = set_smp_ops_by_method(cpu);
- 처음 이곳을 수행할 때만 현재 cpu 노드에 대해 set_smp_ops_by_method()를 수행한다.
- rpi2의 경우 smp_ops를 사용하지 않는다.
- if (!found_method) set_smp_ops_by_method(cpus);
- found_method가 false인 경우 set_smp_ops_by_method() 함수를 “/cpus” 노드에 대해 수행한다.
- if (!bootcpu_valid) {
- bootcpu를 DTB에서 발견하지 못한 경우 에러 메시지를 출력하고 함수를 빠져나간다.
- for (i = 0; i < cpuidx; i++) {
- cpuidx 만큼 루프를 돈다.
- set_cpu_possible(i, true);
- i 논리 cpu 번호에 대해 possible 비트를 true로 설정한다.
- cpu_logical_map(i) = tmp_map[i];
- i 논리 cpu 번호에 물리 cpu id를 저장한다.
- __cpu_logical_map[]
- i 논리 cpu 번호에 물리 cpu id를 저장한다.
set_smp_ops_by_method()
arch/arm/kernel/devtree.c
static int __init set_smp_ops_by_method(struct device_node *node)
{
const char *method;
struct of_cpu_method *m = __cpu_method_of_table;
if (of_property_read_string(node, "enable-method", &method))
return 0;
for (; m->method; m++)
if (!strcmp(m->method, method)) {
smp_set_ops(m->ops);
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
특정 SMP 아키텍처가 ops 핸들러가 구성된 경우 전역 변수 smp_ops가 이를 가리키게 한다.
- struct of_cpu_method *m = __cpu_method_of_table;
- 전역 __cpu_method_of_table은 특정 SMP 아키텍처에서 CPU_METHOD_DECLARE() 함수를 사용하여 추가될 수 있다.
- if (of_property_read_string(node, “enable-method”, &method)) return 0;
- 현재 노드의 “enable-method” 속성이 발견되지 않으면 함수를 빠져나간다.
- for (; m->method; m++)
- __cpu_method_of_table의 시작부터 끝까지
- 테이블의 마지막은 m->method가 null이다.
- __cpu_method_of_table의 시작부터 끝까지
- if (!strcmp(m->method, method)) { smp_set_ops(m->ops); return 1; }
- 테이블에 있는 method 문자열과 “enable-method” 속성 값이 같은 경우 ops 설정을 위해 smp_set_ops() 함수를 호출하여 전역 변수 smp_ops를 설정하고 결과 값이 1인채로 리턴한다.
arch/arm/boot/dts/hip01-ca9x2.dts
/* First 8KB reserved for secondary core boot */
/memreserve/ 0x80000000 0x00002000;
#include "hip01.dtsi"
/ {
model = "Hisilicon HIP01 Development Board";
compatible = "hisilicon,hip01-ca9x2", "hisilicon,hip01";
cpus {
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
enable-method = "hisilicon,hip01-smp";
cpu@0 {
device_type = "cpu";
compatible = "arm,cortex-a9";
reg = <0>;
};
cpu@1 {
device_type = "cpu";
compatible = "arm,cortex-a9";
reg = <1>;
};
};
- “/cpus” 노드의 enable-method 속성 값에 대응하는 디바이스 소스는 다음을 참고한다.
- enable-arch/arm/mach-hisi/platsmp.c
smp_set_ops()
arch/arm/kernel/smp.c
static struct smp_operations smp_ops;
void __init smp_set_ops(struct smp_operations *ops)
{
if (ops)
smp_ops = *ops;
};
- 전역 smp_ops에 인수로 주어진 ops를 대입한다.
CPU_METHOD_OF_DECLARE()
arch/arm/include/asm/smp.h
#define CPU_METHOD_OF_DECLARE(name, _method, _ops) \
static const struct of_cpu_method __cpu_method_of_table_##name \
__used __section(__cpu_method_of_table) \
= { .method = _method, .ops = _ops }
- 위 매크로는 rpi에서 사용하지 않으므로 아래 화일에서 선언된 소스로 추적을 해본다.
arch/arm/mach-hisi/platsmp.c
CPU_METHOD_OF_DECLARE(hip01_smp, "hisilicon,hip01-smp", &hip01_smp_ops);
- 다음 문장과 같이 구조체 데이터가 만들어진다.
- static const struct of_cpu_method __cpu_method_of_table_hip01_smp __used __section(__cpu_method_of_table) = { .method = “hisilicon,hip01-smp”, .ops = &hip01_smp_ops )
arch/arm/mach-hisi/platsmp.c
struct smp_operations hip01_smp_ops __initdata = {
.smp_prepare_cpus = hisi_common_smp_prepare_cpus,
.smp_boot_secondary = hip01_boot_secondary,
};
- hip01_smp 시스템의 ops는 두 개의 함수가 연결되어 있음을 알 수 있다.
CPU_METHOD_OF_TABLES()
include/asm-generic/vmlinux.lds.h
#define CPU_METHOD_OF_TABLES() OF_TABLE(CONFIG_SMP, cpu_method)
- CONFIG_SMP=y로 설정된 경우 각각의 호출되는 매크로를 통해 따라가 본다.
- “#defind CONFIG_SMP 1″이 include/generated/autoconf.h 화일에 자동 생성되어 있다.
#define OF_TABLE(cfg, name) __OF_TABLE(config_enabled(cfg), name)
- __OF_TABLE(config_enabled(1), cpu_method)
#define __OF_TABLE(cfg, name) ___OF_TABLE(cfg, name)
- ___OF_TABLE(1, cpu_method)
#define ___OF_TABLE(cfg, name) _OF_TABLE_##cfg(name)
- _OF_TABLE_1(cpu_method)
#define _OF_TABLE_0(name)
#define _OF_TABLE_1(name) \
. = ALIGN(8); \
VMLINUX_SYMBOL(__##name##_of_table) = .; \
*(__##name##_of_table) \
*(__##name##_of_table_end)
- OF_TABLE_0(cpu_method)의 경우 아무런 동작을 하지 않는다.
- OF_TABLE_1(cpu_method)의 경우 다음과 같은 문장을 만들어낸다.
- . = ALIGN(8) \
- __cpu_method_of_table = .; \
- *(__cpu_method_of_table) \
- *(__cpu_method_of_table_end)
/* init and exit section handling */
#define INIT_DATA \
*(.init.data) \
MEM_DISCARD(init.data) \
KERNEL_CTORS() \
MCOUNT_REC() \
*(.init.rodata) \
FTRACE_EVENTS() \
TRACE_SYSCALLS() \
KPROBE_BLACKLIST() \
MEM_DISCARD(init.rodata) \
CLK_OF_TABLES() \
RESERVEDMEM_OF_TABLES() \
CLKSRC_OF_TABLES() \
IOMMU_OF_TABLES() \
CPU_METHOD_OF_TABLES() \
KERNEL_DTB() \
IRQCHIP_OF_MATCH_TABLE() \
EARLYCON_OF_TABLES()
- 위 INIT_DATA의 16번째 줄에 CPU_METHOD_OF_TABLES()가 포함되어 있다.
- __cpu_method_of_table이 위치한다.
static const struct of_cpu_method __cpu_method_of_table_sentinel
__used __section(__cpu_method_of_table_end);
위의 빈 구조체 하나가 __cpu_method_of_table_end 테이블의 마지막에 들어간다.
- 전체 검색 시 멤버 변수 method가 null인 경우 테이블의 마지막임을 알린다.
config_enabled()
include/linux/kconfig.h
/* * Getting something that works in C and CPP for an arg that may or may * not be defined is tricky. Here, if we have "#define CONFIG_BOOGER 1" * we match on the placeholder define, insert the "0," for arg1 and generate * the triplet (0, 1, 0). Then the last step cherry picks the 2nd arg (a one). * When CONFIG_BOOGER is not defined, we generate a (... 1, 0) pair, and when * the last step cherry picks the 2nd arg, we get a zero. */ #define __ARG_PLACEHOLDER_1 0, #define config_enabled(cfg) _config_enabled(cfg) #define _config_enabled(value) __config_enabled(__ARG_PLACEHOLDER_##value) #define __config_enabled(arg1_or_junk) ___config_enabled(arg1_or_junk 1, 0) #define ___config_enabled(__ignored, val, ...) val
- 이 매크로는 커널 옵션 설정에 따라 1과 0으로 만들어진다.
- CONFIG_SMP=y 또는 CONFIG_SMP=m -> 1
- CONFIG_SMP= -> 0
- config_enabled(CONFIG_SMP)를 하는 경우 다음의 순서를 따른 후에 결과가 1이만들어진다.
-
- _config_enabled(1)
- __config_enabled(__ARG_PLACEHOLDER_1)
- ___config_enabled(0, 1, 0)
- 1
구조체
smp_operations 구조체
arch/arm/include/asm/smp.h
struct smp_operations {
#ifdef CONFIG_SMP
/*
* Setup the set of possible CPUs (via set_cpu_possible)
*/
void (*smp_init_cpus)(void);
/*
* Initialize cpu_possible map, and enable coherency
*/
void (*smp_prepare_cpus)(unsigned int max_cpus);
/*
* Perform platform specific initialisation of the specified CPU.
*/
void (*smp_secondary_init)(unsigned int cpu);
/*
* Boot a secondary CPU, and assign it the specified idle task.
* This also gives us the initial stack to use for this CPU.
*/
int (*smp_boot_secondary)(unsigned int cpu, struct task_struct *idle);
#ifdef CONFIG_HOTPLUG_CPU
int (*cpu_kill)(unsigned int cpu);
void (*cpu_die)(unsigned int cpu);
int (*cpu_disable)(unsigned int cpu);
#endif
#endif
};
- 특정 SMP 아키텍처는 별도로 위의 구조체를 사용하여 핸들러 함수들을 지정할 수 있다.
of_cpu_method 구조체
arch/arm/include/asm/smp.h
struct of_cpu_method {
const char *method;
struct smp_operations *ops;
};
- method
- “/cpus” 노드의 enable-method 속성 값
- 예) “hisilicon,hip01-smp”;
- “/cpus” 노드의 enable-method 속성 값
- ops
- 해당 SMP 머신의 각 핸들러가 속해있는 smp_operations 구조체를 가리킨다.